If you ask people “which doctor scares them the most?”, the majority will answer dentist. This fear in adults, as a rule, comes from childhood, when dental treatment was a very unpleasant procedure. Memories of a white coat, the specific smell and sound of a drill evoke fear. Over time, everything has changed a lot, dental treatment has moved far forward, and modern anesthetics have made the treatment procedure as painless and comfortable as possible for the patient.
Is it painful to treat caries?
One of the most frequently asked questions when going to the dentist is whether it hurts to treat caries. Sitting down in a chair, we warn the doctor that we have a low pain threshold and, in general, we are simply afraid. The doctor will definitely select a drug that will make the treatment comfortable and painless, even in the most difficult cases.
Today, caries can be cured absolutely painlessly.
Content:
- Where can you cure caries painlessly?
- Types of anesthesia in dentistry
- When not to use local anesthesia
- Anesthesia and sedation in dentistry
- Anesthetics used in dentistry 5.1. Medicines based on aticaine 5.2. Painkillers containing mepivacaine
Is it painful to treat teeth?
This question worries almost any person planning to undergo dental treatment. In fact, the problem of pain relief in dentistry has always been very acute. Almost all medical procedures performed by a specialist cause severe discomfort. Knowing this, people are afraid to treat caries, pulpitis and other oral diseases. But refusal to seek medical help in a timely manner invariably entails another problem - the progression of the existing pathology. After all, dental diseases do not go away on their own. Over time, they become more pronounced and are less responsive to therapy.
Therefore, it is important to prevent the patient from having a negative experience associated with the lack of adequate pain relief. For this purpose, more and more effective anesthetics are being developed every year. Using them in their work, dentists can offer their clients the most comfortable and completely painless dental treatment.
Without anesthesia
In rare cases, doctors have to carry out treatment without anesthesia. This usually happens when there is an allergy to anesthetics. If the patient is intolerant to drugs, the doctor may suggest treatment with laser or chemical reagents. General anesthesia is also an option.
As a rule, the majority of people prefer to undergo treatment under local anesthesia. But there are brave souls who have a high pain threshold or even prefer to do without an injection.
If we are talking about superficial caries, when the tooth tissue is not yet damaged, then this is understandable. But with medium and deep caries, such pain is almost impossible to endure without anesthesia. And it’s not necessary - the latest generation of anesthetics do not cause allergic reactions, they can be used even when treating children and pregnant women.
There is no point in being a hero when treating teeth - without anesthesia it will hurt. And talking about savings also makes no sense.
Psychological aspect
To prevent children from being afraid of dentists, clinics use distracting maneuvers. While waiting and even during treatment, children can be shown their favorite cartoons. You can read a fairy tale, play games. Some clinics even have special rooms where boys and girls can relax and forget about the fear of an unfamiliar doctor.
The staff in children's clinics dress in bright clothes, and you can see smile masks on their faces. Each office has a thoughtful interior that resembles not a hospital, but a gaming center. The best clinics employ a psychologist who helps the child overcome his fear of dental treatment. The rest of the staff also takes courses in communicating with children.
A child’s teeth can be treated without general anesthesia, but it is better to use this safe method today. The main thing is to make it clear to the child from a very early age that the dentist is not a terrible doctor, but a friend of teeth from childhood.
Author: Zhukov M.A.
On the front teeth
The main feature of caries on the front teeth is that it develops very quickly. Due to the high load, the enamel quickly becomes thinner, causing tissue destruction to occur at a rapid pace. In advanced cases, severe pain begins, especially while eating. It is also necessary to talk about the aesthetic aspect - caries on the front teeth instantly attracts attention.
It is not painful to treat caries on the front teeth under local anesthesia. Perhaps the doctor will slightly increase the dosage of the drug to completely eliminate sensitivity.
Important. If you notice a spot or initial caries on your front teeth, we recommend that you immediately contact your dentist. If you wait, you risk losing a tooth in the most visible place. And this means additional costs for prosthetics.
Specifics of dental treatment in the smile area
The front teeth are included in the so-called smile zone and therefore, when treating them, the aesthetics of the final result of the treatment process is fundamental. To restore an anterior tooth, the dentist must have experience in selecting shades of light-curing composites, recreating the natural shape of the tooth, and all the natural irregularities of its surface.
If the tooth located in the smile area is healthy, but there are aesthetic defects, the use of veneers may be a treatment option. Veneers are miniature plates-onlays that are glued to the surface of the teeth and ideally mask defects such as curvature of teeth, unsightly shape, darkening of the enamel, and interdental spaces. If a tooth is destroyed by more than fifty percent, restoration with a crown is indicated. A pin that is used by some specialists for severe tooth destruction
Installation is not recommended. A large filling will not withstand the load that is inevitable during chewing processes and will fall out or break off, along with part of the tooth. If the root part is affected when the filling is broken, the tooth will have to be removed. In the area of the front teeth, prosthetics made from durable and aesthetic materials are recommended: ceramics, porcelain, zirconium.
Cervical caries
The majority of patients believe that the treatment of cervical caries is particularly painful. In principle, this is how it is - the cervical zone is characterized by increased sensitivity. Without anesthesia, it will undoubtedly hurt.
Cervical caries can not only be “in plain sight”, but also spread deeper. Therefore, the question of carrying out treatment without anesthesia is not even raised.
How to avoid getting sick
You need to regularly monitor the condition of your teeth, not only from the outside, but also from the inside. It is no coincidence that doctors advise cleaning them 2 times a day - this is required to prevent infections. But don’t forget about following your diet; you need to eat enough:
- hard vegetables and fruits (apples, carrots, cucumbers, beets, etc.);
- greens (parsley, lettuce, dill, celery);
- berries (currants, grapes, strawberries, cranberries);
- nuts (almonds, cedar, cashews);
- dairy products (cheese, cottage cheese, natural yogurt without additives);
- citrus fruits (grapefruit, lime, orange);
- seafood (fish, shrimp);
- eggs (chicken, quail);
- honey;
- water and tea without dyes (green and black).
Do not forget about the correct cleaning technique: you need to brush each unit from the gum to the cutting edge so that the dirt does not remain in the crevices and does not oxidize. It is convenient to use dental floss for this.
Average caries
With average caries, not only the enamel is destroyed, but the dentin is also affected. The disease at this stage is practically asymptomatic; sensitivity may occur when biting.
Treatment of average caries takes place with anesthesia, which allows the patient not to experience discomfort and feel absolutely comfortable.
Deep caries
Deep caries is characterized by extensive damage to the hard tissues of the tooth. Painful sensations occur during eating and under the influence of temperatures - the tooth reacts to hot and cold. The carious cavity is separated from the pulp by a thin layer of dentin, which explains the increased sensitivity of the tooth to irritants.
Deep caries cannot be treated without pain relief. The use of anesthetics ensures a comfortable state for the patient during treatment with a complete absence of pain.
Where can you cure caries painlessly?
Regardless of what teeth need to be treated, you need to pay special attention to finding an experienced specialist. At the same time, it is very important that he conducts the appointment in a well-equipped dental center.
These requirements are fully met by the Line of Smile clinic. We employ doctors with extensive experience. They have access to the most effective and safe painkillers, so when you contact us, you don’t need to think about whether it’s possible to treat your teeth without pain. We guarantee each of our clients comfortable service conditions.
Why do teeth hurt with caries?
Mostly, painful sensations appear already at the stage of deep caries. In this case, the pulp (nervous tissue of the tooth) is separated from the oral cavity by only a thin layer of dentin and reacts to irritants. Pain appears when brushing teeth, when food gets into a carious cavity, as well as from spicy, sweet, and salty foods.
Under the influence of irritants in the pulp, blood flow increases, which leads to excess pressure on the nerve fibers. The pain goes away quite quickly, immediately after the irritant is removed.
Important. Without treatment, deep caries turns into pulpitis. The inflammatory process affects the nerve fibers, the pain gradually becomes unbearable - constant or throbbing, sharp or dull, localized or spreading.
Methods and timing of modern treatment of dental diseases
Dental treatment in modern dental clinics is a whole series of special measures to stop the development of the inflammatory process, restore all useful functions, as well as the aesthetics of the dental unit. Most often, patients turn to dentists for the treatment of dental caries, which occurs in people of all ages and in a variety of forms - from the spot stage to deep caries, when the destruction of a unit has reached almost to the root. If caries was not cured on time or its treatment was carried out in violation of the rules, complications such as pulpitis and periodontitis arise. Treatment of these dental diseases is more complex; it is carried out in stages and involves at least 2-3 visits to a specialist’s office. The timing of dental treatment always depends on the complexity of the clinical case. For example, treatment of caries in the spot stage takes place in one visit
dentist, implantation and prosthetics are divided into several stages and the treatment period is maximum - from several months to a year. Do you want dental treatment to always proceed quickly and with a minimum of discomfort? Then attend regular preventive examinations at the dentist, because it has long been known that the best dental treatment is prevention!
Stages of caries
The causes of caries include hereditary factors, the quantity and quality of saliva, and disturbances in protein and mineral metabolism in dental tissues. Oral hygiene plays an important role, as does excessive consumption of sweets. Another factor contributing to the occurrence of caries is a lack of calcium and phosphorus in the diet. Teeth can rapidly deteriorate during pregnancy or after suffering from infectious diseases.
Caries develops gradually. Over time, without treatment, a carious cavity appears in place of an almost invisible spot, which at a certain point begins to increase, affecting an increasing amount of dentin.
Experts distinguish four stages of caries development - carious spot, superficial caries, medium caries, deep caries.
Caries in the spot stage
Initial stage of caries. Characterized by the appearance of spots on the enamel. In the demineralized area, damage to the enamel structure is observed. As a rule, patients cannot detect it themselves.
The spot may be white or pigmented. If a brown or black stain is easy to notice, then a coated stain can only be diagnosed using an aqueous solution of methylene blue.
Important. With timely treatment, remineralization therapy can be carried out and tissue can be restored. This is why experts recommend visiting the dentist once every six months - in order to take timely measures and prevent caries from developing.
The carious spot is treated with solutions of sodium fluoride and calcium fluoride. The patient is prescribed vitamins, calcium and phosphorus supplements, and brushing teeth with fluoridated toothpaste is recommended. Your doctor may also recommend a special diet that includes foods high in calcium and certain proteins.
Diagnostics
Only a dentist can correctly determine the nature and stage of development of the disease.
Therefore, you should not neglect going to the doctor at least once a year. Now clinics use various examination methods:
- Vital coloring. A solution of 1% methylene blue is mixed with 0.5% red and applied to the tooth surface, after which the lesion acquires a different color. This is a very economical option, but not the most effective: the depth of distribution cannot be determined.
- Fluorescent radiation testing. If a carious process begins in any area, it will not glow.
- Electroodontometry. When exposed to electric current, the condition of the pulp is determined. This method is absolutely safe for all ages.
Superficial caries
Affects only enamel with damage to the structure and the impossibility of restoration. At this stage, it is already possible for the damaged tooth to react to cold or hot.
Caries affects only the upper part of the tooth, without affecting the dentin. At this stage, treatment is already required. The dentist removes damaged tissue using a drill and installs a filling.
Since caries has not yet affected the tooth tissue, treatment can be carried out without anesthesia. But if you have a low pain threshold or are simply overcome by fear of the drill, you still need to perform local anesthesia.
Endodontic dental treatment: when and how is it carried out?
Endodontic dental treatment is used in practice if caries has destroyed the tooth and the inflammatory process has moved into the canals of the dental unit. When carrying out endodontic dental treatment, a specialist treats the canals: cleans the cavities from damaged tissue, rinses them with an antiseptic solution, and applies medicine. Typically, after these procedures, a temporary filling is placed on the tooth, and the patient is sent home to return to the dentist's office in a few days.
At the second visit, an x-ray of the diseased tooth is taken to evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment. If the inflammation has been stopped, the canals are treated with an antiseptic again, and then their space is filled with gutta-percha. The tooth treatment ends with the final restoration of the crown using a composite filling material.
Endodontic treatment must be carried out with high quality and using specialized modern tools: files that allow the canals to be expanded as needed, a microscope that allows the doctor to see the condition of the tissues and canals, an apex locator that shows the length of the tooth canals.
If root canal treatment is carried out incorrectly, errors are made in its technology - there are risks of serious complications that can lead to the loss of a dental unit.
Average caries
At the third stage, caries already affects the tooth tissue – dentin. A small carious cavity forms, the tooth begins to bother and hurt. It reacts to cold air entering when talking or breathing, to leftover food, to cold and hot.
The manipulation is carried out under anesthesia, as the patient may experience quite strong pain. Depending on the degree of tissue damage, the dentist selects the necessary treatment. In most cases, the carious cavity is prepared, infected tissue is removed, and filling is performed.
Indications and contraindications for the use of local anesthesia
Any dental intervention that causes pain must be accompanied by “freezing” of the required area of the oral cavity. There is a list of diseases for the treatment of which it is necessary to administer anesthetic drugs:
- Complex caries;
- Removal of a tooth or its roots;
- Periodontitis;
- Inflammatory processes in the dental system;
- During prosthetics.
Before drawing up a treatment plan and choosing medications, the doctor must interview the patient and find out from him the presence of contraindications in order to exclude the possibility of complications.
- Allergy to drugs used;
- Heart diseases;
- Diabetes;
- Problems with the endocrine system.
Pain relief during treatment
For local anesthesia, drugs based on articaine and mepivacaine are used. Articaine-type drugs are more effective than novocaine - 5-6 times, lidocaine - 1.5-2 times.
Most anesthetics contain, in addition to the main active ingredient, vasoconstrictor components - adrenaline or epinephrine, which reduce the leaching of the anesthetic, which in turn leads to an increase in the duration of the effect in time and the strength of anesthesia.
Articaine anesthetics include:
Ultracaine
French drug, available in 1.7 ml carpules in three forms:
- Ultracaine DS forte
– containing 1:100,000 epinephrine. A highly effective anesthetic for operations and treatment of pulpy teeth. Not recommended for patients with thyroid diseases and cardiovascular pathologies. - Ultracaine DS
- with an epinephrine concentration of 1:200,000. Ideal for pain relief in pregnant and lactating women and patients with compensated cardiovascular diseases. - Ultracaine D
– without adrenaline/epinephrine. Used when there is a high risk of allergic manifestations. Can be used by patients with bronchial asthma, cardiovascular pathologies, and thyroid diseases.
The drug can be used starting from the age of four.
Septanest (France)
They are produced in two forms with an adrenaline content of 1:100,000 and 1:200,000. Unlike Ultracaine and Ubistezin, the anesthetic contains preservatives that have a strong allergenic effect.
The drug Scandonest is produced based on mepivacaine. The anesthetic does not contain preservatives or vasoconstrictors. Recommended for anesthesia for pregnant and lactating women suffering from cardiovascular diseases, bronchial asthma and thyroid diseases.
Important. When visiting a dentist, be sure to tell the doctor if you have allergies or chronic diseases. This will help the doctor choose the right anesthetic for you.
Will it hurt when I get an injection in the gum?
To administer the anesthetic, special carpule syringes with a very thin needle are used, which minimizes discomfort during the injection. The drug is administered quite slowly, over 40-45 seconds.
In most clinics, before the injection, so-called topical anesthesia is performed using a special anesthetic gel or septic tank. In this case, the specific area of the mucous membrane to which the composition was applied is anesthetized. In this case, the needle entry will be painless.
Anesthesia in dentistry - don't be afraid!
For most patients, a visit to the dentist is stressful. Every second patient is afraid to have their teeth treated, afraid of pain.
Many people still remember when anesthesia was used mainly for tooth extraction. They remember the notorious “be patient” - instead of pain relief and painful sensations during dental treatment, even with an anesthetic injection. This is explained by the fact that previously local anesthesia took effect 15 minutes after the injection, and according to the regulations, the doctor had to spend approximately this time on one patient.
Today, the treatment of dental diseases has become completely different - painless and more and more comfortable. And anesthesia plays an important role in this.
What should anesthesia be like in dentistry?
You can hear from patients at an appointment: “Give a good injection - one that doesn’t hurt.”
But pain medications vary significantly: some may not be suitable for you, others will cause swelling or an allergic reaction.
The dentist selects an anesthetic drug for the patient INDIVIDUALLY
, depending on the goals and methods of dental treatment and the condition of his body.
The method of pain relief must be effective, reasonable and safe for the patient.
Basic methods of pain relief in dentistry
1. Application anesthesia -
non-invasive, non-injection method, i.e. this is NOT an injection! A special anesthetic gel or spray is applied to the gum in the area of the diseased tooth.
Application anesthesia
very relevant in adult patients with severe dental phobia and in pediatric dentistry, since it is difficult to give an injection to a child. Such anesthesia is used before the main one so that the patient does not feel the injection itself, or for light procedures - professional hygiene, enamel grinding, etc.
2. Infiltration anesthesia
creates a “depot” of anesthetic in the area of the diseased tooth, from where it will be absorbed and give an analgesic effect.
Infiltration anesthesia is especially effective in the upper jaw, and in the lower jaw - only in the area of the front teeth.
3. Conduction anesthesia.
The essence of conduction anesthesia is to block certain nerves.
Conduction anesthesia is recommended when complex complex surgical intervention is required, when working with several teeth, in the area of inflammation, when it is necessary to remove pulp, or open an abscess.
4. Ultrasound anesthesia.
Ultrasound helps to accurately determine the location of the anesthetic injection - literally down to the millimeter, adjust the place where to insert the needle so that the injected anesthetic gets as close to the nerve as possible. This will ensure the most effective and safe anesthesia of the desired area.
5.
Intraseptal (intraseptal) and intraligamentary ( intraligamentous/and intraperiodontal) anesthesia.
These methods require special personnel skills and special equipment. The anesthetic is injected into the bone septum between the teeth or into the periodontal space. Used when other methods of pain relief are ineffective.
Treatment under anesthesia
Anesthesia in dentistry is used less frequently than local anesthesia, and is not an everyday solution, but rather an exceptional necessity when dental treatment under any other anesthesia is impossible.
Yes, the drugs used for general anesthesia are safe for the patient’s health and have minimal contraindications, but general anesthesia affects the WHOLE BODY, while local anesthesia affects only the necessary areas.
General anesthesia is indicated for:
- severe dental phobia - an insurmountable fear of treatment;
- general diseases that cause inappropriate behavior of the patient, for example, epilepsy;
- complex surgical interventions requiring very long work by the surgeon;
- allergic intolerance to all modern local anesthetics.
General anesthesia can only be used in a clinic specially equipped for this, which either has its own team of anesthesiologists, or it provides for the deployment of a visiting team, with all the necessary equipment for resuscitation.
You need to understand that it is not the anesthesia itself that is dangerous, it is the clinic’s lack of medical equipment that is dangerous, and the administration of anesthesia by unqualified medical personnel is dangerous.
The main advantage of general anesthesia for dental treatment is the reduction of treatment time. During one visit, the doctor has the opportunity to remove or treat several teeth at once.
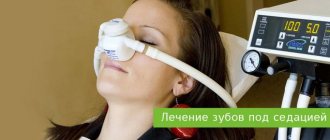
What is sedation in dentistry?
As an alternative to general anesthesia, sedation is used in combination with local anesthesia.
.
Sedation
- this is the introduction of sedatives that immerse the patient in a light superficial sleep, helping to relax and calm down during dental treatment. Sedation is used in the treatment of both adults and children.
There are three ways to administer sedation drugs:
- inhalation
- during the entire treatment the patient inhales a soothing gas (a mixture of oxygen and nitrous oxide) through a mask; - intravenous
- injection of a drug suitable for a particular patient; - oral
- the medicine is usually dissolved in a glass of water or juice.
Sedation is not anesthesia; it is part of a complex with local anesthesia.
Indications:
- age up to three years;
- individual intolerance to drugs;
- respiratory diseases;
- neuromuscular diseases, epilepsy.
The use of nitrous oxide is contraindicated if:
- intracranial hypertension, i.e. increased pressure in the cranial cavity;
- hyperexcitability syndrome.
What is carpule anesthesia?
As a rule, modern dental clinics use carpule anesthesia
.
The anesthetic is contained in disposable carpules
- a kind of cartridges with an anesthetic solution that are inserted into syringes with disposable needles.
Advantages:
- precise dosage of anesthetic, which makes it easier to control the dose of anesthesia;
- sterility - the solution inside the capsule is sealed in compliance with aseptic standards, contact of the medicine with air is excluded, a disposable needle is used.
What drugs are used for anesthesia at the dentist?
Do you know the names of drugs used for anesthesia? Most likely, you remember Novocaine
or
lidocaine
.
By the way, novocaine is now not used in dental treatment. Many new and much safer drugs have appeared that are more effective: ultracaine, ubistezin, septonest, scandonest
.
Their analgesic effect is 5-6 times stronger.
When is anesthesia used in pediatric dentistry?
Pain relief for children is just as necessary as for adults.
It is a pure myth that children have no nerves in their baby teeth, so they cannot get sick! Considering that a child’s body is more vulnerable to all influences, selecting the correct and safe anesthesia for a child is even more responsible for the dentist.
Features of pain relief for dental treatment in elderly people
In elderly people, the use of anesthesia should be carried out taking into account the possibility of developing respiratory failure and complications from the cardiovascular system. A thorough preliminary medical history is required, including consultations with attending general practitioners.
Main contraindications to local anesthesia in dentistry
- Allergy, individual intolerance to pain-relieving components and excipients of the drug.
- Bronchial asthma, tachycardia, unstable angina, refractory arrhythmia.
- Mental abnormalities and disorders in the patient.
- Recent heart attack, stroke, heart surgery, coronary bypass surgery.
- Reduced blood clotting, including those caused by the use of anticoagulants.
- Diseases affecting the endocrine system - thyrotoxicosis, diabetes mellitus and others
- The use of antidepressants and adrenergic blockers.
- Severe liver and kidney failure.
It is not recommended to do anesthesia, and, in general, to treat teeth, on an empty stomach, when you feel unwell, in acute conditions and exacerbation of diseases.
If an allergy is suspected, the patient must undergo appropriate allergy tests.
If intolerance to all drugs for local anesthesia is detected, the patient is recommended to undergo general anesthesia.
What are the features of anesthesia in dentistry for pregnant women?
The main obstacle to dental treatment for pregnant women is anesthesia. Conventional painkillers are not suitable for them, since vasoconstrictors are usually added to the anesthetic solution. But the dentist is one of the very necessary doctors during pregnancy.
In our clinic, specialists provide pain relief using application, infiltration and conduction anesthesia.
When administering drugs by injection, we use carpule syringes.
For administration to patients, we use only certified anesthetic drugs from leading global manufacturers. We always select an anesthetic individually, so we always have a fairly wide range of anesthetics for adults.
Taking a thorough history before treatment is very important.
If there is a suspicion of a possible allergic reaction to anesthesia or the presence of any contraindications, the patient will be referred for further examination and allergy tests.
When to see a doctor, symptoms
Don’t delay going to the dentist if you suddenly experience even minor pain. The very fact of pain indicates that caries has begun to develop, which in some cases affects the tooth almost instantly.
When to go to the doctor:
- pain when biting;
- pain from temperature and chemical irritants;
- pain from exposure to cold air.
Without a doubt, the best option is to visit your dentist once every six months in order to take timely measures to prevent the development of caries.
Pregnancy period
Is it painful to treat a disease without pain relief during pregnancy? The question is very complex. It all depends on the stage of the disease and the patient’s pain threshold. Any stress during this period can negatively affect the condition of the expectant mother, but the disease cannot be left untreated, since it can affect the fetus. Therefore, the best solution is to sanitize the oral cavity before pregnancy. But, if it so happens that the disease began during pregnancy, you should immediately seek help from your attending dentist, and in no case put it off until later. In conclusion, we can say that caries treatment is not a simple and not always pleasant process. And in order to avoid pain during the treatment of this disease, you need to take timely care of the health of your teeth, attend preventive examinations every six months and have your mouth cleaned in the dental office. These measures will allow you to avoid the development of carious formations or identify them at an early stage. At Innovative Dentistry on Marata-31, preventive examinations for our patients are carried out absolutely free!
Complications
Teeth do not heal on their own. In any case, you will have to see a doctor, but it is better to do this as soon as possible. If it so happens that for some reason you have delayed this process, be prepared for the fact that caries will turn into pulpitis or periodontitis.
The pain in such cases becomes unbearable - throbbing, pulling, almost incessant. At a certain point, the patient will not even be able to tell which tooth hurts, since the pain can take over the entire jaw and radiate to the eye, ear, and temple.