If you think that dentists never tire of repeating the importance of preventive examinations and timely treatment of caries and gum inflammation just for the sake of advertising their profession, you are mistaken. Inattention to the health of your own teeth and vain fears of dental treatment can ultimately lead to complications, the treatment of which will be both difficult and expensive. A striking example of such a complication is dental granuloma - a pathological formation that occurs in the root part of the tooth.
In the early stages of its development, granuloma does not show itself with any noticeable symptoms, but as the tumor grows and becomes inflamed, severe pain in the tooth may appear, which cannot be relieved with tablets from the pharmacy. It is possible to remove a granuloma and save a diseased tooth only in dentistry and there is no need to delay contacting a doctor, because an untreated granuloma can lead to the development of serious complications, including osteomyelitis, general infections of the body and even cancer.
In this article we will tell you:
- What causes dental granuloma?
- Symptoms of dental granuloma;
- How is dental granuloma treated?
Also in the article you will find information on the prevention of dental granuloma and prices for treatment/removal of dental granuloma in Moscow.
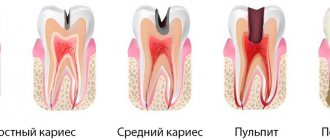
Tooth granuloma
Granuloma on the root of a tooth - what is it and why does it appear? Granuloma is an inflammatory formation that affects part of the root. It is the initial stage of a granular cyst and differs from it only in its smaller size. The disease is characterized by the formation of a purulent sac of granular tissue. The sac is surrounded by a fibrous capsule that connects to the apex of the tooth root.
The appearance of a granuloma under a tooth indicates that an inflammatory process is underway. Before installing dentures, it must be eliminated, otherwise the granuloma will grow under the crown.
The formation of a focus of inflammation in the jaw bone is the body’s defensive reaction to the attack of pathogenic microbes. A dense connective capsule is formed around the lesion, isolating it from the healthy bone. But this protection does not last forever, so granuloma is often compared to a time bomb.
Classification
All cysts that occur in the human oral cavity can be divided into the following types:
- root;
- residual;
- follicular;
- teething;
- primordial;
- lateral periodontal;
- calcifying odontogenic.
Let's talk about each of them in more detail.
Root
It is a consequence of granuloma that appears due to periapical inflammation and necrosis. Located in the area of the apical part of the root. The boundaries of such a structure are easily determined. Its size can be from 2 mm to 3 cm. But even with a large diameter, root formation does not lead to a change in bone volume or displacement of the incisor. Only if a secondary inflammatory process is involved, the disease makes itself known through pain and swelling.
When identifying a disease, you need to understand what led to its appearance and take measures to eliminate the provoking factors. Usually the problem can be resolved with endodontic therapy.
Residual
It is also called residual. Appears after removal right in the place where the roots of the torn out unit were previously located. X-ray diagnostics helps determine the presence of a residual structure.
Follicular
It is formed from the tissues of the follicular sac that covers the rudiments. Easily visible in the photo. Often leads to serious damage to premolars and molars.
As a rule, follicular formations quickly increase in size and can spread to adjacent teeth, changing their location and angle of inclination. Traditionally, their treatment involves surgical curettage.
Teething
Appears during the period of eruption of permanent units. Covers the emerging rudiment. May contain blood. Visually resembles edema, swelling. Has a bluish tint.
Sometimes it ruptures spontaneously, spontaneously. Then the person simply notices that the “ball” has disappeared, the liquid has flowed out of it. In rare cases, surgery may have to be performed. During this procedure, the blood sac is opened, and the structures that interfere with further eruption of the molar are excised.
Primordial
Formed on the basis of the tooth germ. Most often diagnosed in the area of the posterior units. This type of formation is prone to recurrence. To cure the primordial structure, it is necessary to curettage the altered tissues.
Lateral periodontal
Rarely encountered in dental practice. It has modest dimensions. Clearly visible on X-ray images. This cavity is called a lateral cavity, since it is fixed to the side of the tooth root.
The tumor can only be removed by curettage. The material obtained during the operation is necessarily sent for histological analysis to ensure that the disease present in the person is benign.
Calcifying odontogenic
Another rare type of cyst. Observed in the lower part of the supporting surface of the jaw. Well visualized on x-rays. There is cloudy contents inside. Its color depends on the degree of calcification.
Immediately after diagnosis, surgical curettage is performed.
Symptoms
Even having an idea of what dental granuloma is, its symptoms are not so easy to determine. The fact is that the disease may not manifest itself for a long time. The tooth under which the formation is located may not outwardly stand out in the dentition. The gums may also look quite healthy.
In some cases, the disease is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- swelling of facial tissues;
- swelling of the gums;
- slight increase in temperature;
- the occurrence of flux;
- acute pain in the area where the granuloma has formed;
- slight discharge of pus between the tooth and gum;
- pain in the eyes, migraine, dizziness;
- On palpation there is acute pain.
Good to know. Granuloma often makes itself known if a person has had a cold, flu, pneumonia and other diseases that lead to a decrease in immunity.
Prevention
There is no unique prevention for granuloma. Basically, the dentist recommends the same measures as for the prevention of other dental diseases. You should adhere to the rules of oral hygiene, brush your teeth morning and evening. It is imperative to promptly treat diseases of the teeth and gums - such as caries, pulpitis, periostitis and others. It is necessary to visit the dentist regularly, preferably twice a year. All this will help prevent the occurrence of lesions, and if they occur, diagnose the disease in a timely manner.
Causes of granuloma
What causes dental granuloma? Among the main factors provoking the formation of a focus of inflammation, the following should be highlighted:
- treatment of pulpitis was carried out poorly (for example, tissues affected by caries were not completely removed);
- the dentist filled the root canals in violation of the rules of asepsis and antisepsis;
- the tooth was injured directly due to damage to the maxillofacial area, unsuitable orthodontic design or for other reasons.
Complications
Untimely treatment of apical granuloma leads to the following consequences:
- Transformation of a granuloma into a cyst, the treatment of which is more difficult. The cyst can degenerate into a malignant neoplasm.
- Tooth loss. This leads to aesthetic discomfort, disruption of chewing and speech functions, and necessitates prosthetics.
- Due to the spread of infection through the bloodstream, there is a high risk of infectious myocarditis, an inflammatory lesion of the heart muscle.
- The development of pyelonephritis is an inflammation of the kidneys, which is also caused by the spread of infection from the focus at the apex of the tooth root.
- The threat of odontogenic sinusitis - inflammation of the maxillary sinuses due to infection from the root of the tooth.
- The development of osteomyelitis – purulent-necrotic inflammation of the jaw bone.
- The appearance of odontogenic subcutaneous granuloma is a change in the subcutaneous fat layer under the influence of microorganisms that have penetrated from the source of inflammation. As the disease progresses, fistulas appear on the skin of the buccal and submandibular areas, from which bloody-purulent discharge is observed for a long time, sometimes for several months.
How is dental granuloma diagnosed?
Diagnosis at an early stage is almost impossible. Even a dentist with extensive experience will not always be able to visually determine the occurrence of a granuloma under a tooth; this will require additional research. Most often, a neoplasm is discovered completely by accident during radiovisiography, which was prescribed for a completely different purpose.
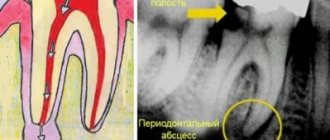
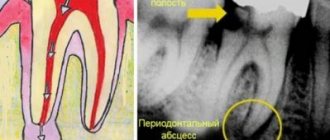
To confirm the diagnosis, the patient is prescribed radiography. Using this study, it is possible to differentiate dental granuloma from other diseases. In the picture, the source of inflammation and its location will be clearly visible. Based on the results of the study, the most suitable treatment method is prescribed.
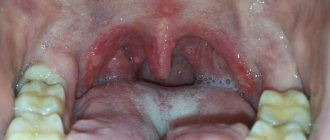
In the photo you can see what granuloma of the gums and teeth is and what it looks like.
It is important to know. Unfortunately, it is not always possible to save a tooth under which a cyst has formed. If the tooth is already partially destroyed or has a vertical crack, it must be removed.
Diagnostics
Often, tooth root granuloma is diagnosed completely by accident during treatment at the dentist. It happens that a doctor orders an X-ray examination for a completely different reason, but as a result, a disease is detected in the image.
When making a diagnosis, the doctor may note such signs as protrusion of the bone opposite the apex of the roots, the presence of a painful bulge on the gum opposite the granuloma.
X-ray examination is decisive in making a diagnosis. The image reveals a zone of rarefaction of bone tissue, which is very clearly defined and usually has a rounded shape.
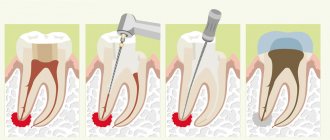
Treatment options for granuloma
Treatment of the tumor consists of eliminating the source of infection and preventing relapse. Therapeutic and surgical techniques are used.
Therapeutic method
It will bring results only if the disease is detected at an early stage. The patient is prescribed antibiotics and sulfonamide medications. Timely treatment will help eliminate the infection and save the damaged tooth.
Non-surgical method
It appeared relatively recently, the essence of the method is as follows: the affected tooth canal is expanded and a substance is introduced into it that destroys the infection.
Surgical method
It is used if the granuloma has grown greatly and the use of drug therapy will be ineffective. During the operation, the dentist cuts the gum to allow pus to come out. Then a drainage is installed in the tooth, which the patient must endure for three days. Also during this period, drug therapy is carried out. After three days, another operation is performed, during which purulent sacs, tumors, or a tooth root with a cyst are removed. Then the doctor makes a decision about the fate of the tooth: it is either left or removed.
Removal is necessary in the following cases:
- the tooth is so damaged that it can no longer be restored;
- root canals cannot be treated;
- the cause of inflammation was problems in the periodontal pocket;
- the patient is undergoing a prosthetic procedure;
- cracks have formed in the area of the tooth or its root;
- There are multiple perforations of the tooth.
In other cases, doctors try to save the tooth.
Physiotherapeutic methods
In some clinical cases, when the granuloma is small and the inflammatory process is not acute, treatment is possible using the following methods.
Electrophoresis
This procedure involves introducing iodine-based medications into the infected canals using current pulses, designed to kill bacteria and also promote the resorption of the formation. True, physiotherapy requires patience and a lot of free time, because it will take about 10–20 procedures performed daily or every other day to get rid of the pathology.
Depophoresis
Another physiotherapeutic method is depophoresis. The principle of introducing medication into the root canals here is similar to that of electrophoresis. Copper/calcium hydroxide is used only as the main drug. Depophoresis can only be performed on teeth that lack pulp. The number of procedures is usually three, with a break of a week between them.
This method does not require complex surgical procedures.
Destruction of granuloma with laser
The method is more expensive, but fast and effective. Suitable even for curved root canals. Before this, the specialist cleans the canals and sterilizes them. Penetrating through the root, the doctor treats the granuloma with a laser, and it resolves. The laser has a powerful disinfecting effect, does not injure surrounding tissues, on the contrary, promotes their rapid healing, stops bleeding, because cauterizes blood vessels. Doctors who practice this type of innovative equipment claim that relapses of the disease are excluded.
The laser has a powerful disinfecting effect
Contraindications to the use of laser: oncology, cracks and fractures at the root.
Expert advice and recommendations
Having figured out what kind of disease this is - dental granuloma, you can protect yourself from it. To do this you need to follow a few simple rules:
- undergo preventive examinations every 6 months;
- contact your dentist in a timely manner if any unpleasant symptoms from the dental system occur;
- treat caries at an early stage;
- carry out hygiene procedures regularly;
- change the brush monthly.
Dentists at the Saint-Dent Clinic in Moscow will offer patients a modern and comprehensive approach to the diagnosis and treatment of dental granuloma. Only the most effective treatment methods and high-quality materials are used. You can find out the cost of services here PRICES. The contact section is located here CONTACTS.
What will happen if left untreated?
Ignoring the symptoms of the disease leads to dangerous consequences for health. Thus, the patient may encounter:
- destruction of roots, their strong loosening;
- jaw fracture;
- tumor formation;
- purulent abscess;
- periostat;
- osteomyelitis.
The disease can cause the development of sepsis. This is a very serious condition in which the infection enters the blood and quickly spreads throughout the body.