For a long time, dental granuloma develops asymptomatically! There is a feeling of an overgrown tooth, slight pain when pressed. At the initial stage, there are no visual changes; inflammation in the apex is discovered by chance during an X-ray or computed tomography scan prescribed when visiting a doctor for other dental diseases. The question begins to worry, what is a granuloma?
Dental granuloma can be detected when a dense nodule of 5-8 mm appears at the base of the tooth, nearby tissues become red and swollen, acute pain begins to bother you, or in a photograph of the tooth before prosthetics. Because of the fear of opening the gums, many people put off visiting a doctor and are treated with rinsing decoctions.
| A nodular root formation is a source of infection; without treatment, inflammation spreads to the tooth socket, periosteum, subcutaneous tissue of the face, and lymph nodes. The periodontal tissue dissolves, in severe cases the tooth becomes loose and falls out. |
What is granuloma, its causes
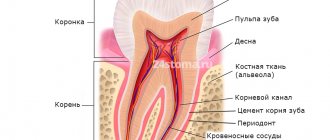
Dental granuloma is a focal proliferation of cells of the connective tissue that fixes the tooth. Externally, it appears in the form of a rounded nodule (up to 10 mm), usually localized at the root apex. A nodular neoplasm is formed as a result of prolonged inflammation in the pulp or periodontal tissues.
Granulation in the tooth, as a protective reaction, is triggered in response to infection and suppuration. A capsule is formed around the source of inflammation, isolating bacteria and dying cells. An infectious and inflammatory process occurs inside the nodule. The tissue that replaces the dead cells grows, and granulosa formation increases. The formation of a granuloma on the root of a tooth is provoked by an infection that has penetrated into the periodontium (periodontal tissue), which is preceded by:
- untreated caries and pulpitis, periodontitis;
- cracks, fractures;
- non-compliance with canal filling techniques;
- tooth extraction, which leaves an infected root tip.
The nodular neoplasm goes undetected for months and proceeds without pain! Exacerbation of dental granuloma is provoked by reasons not related to dental diseases - hypothermia, viral infections, physical overexertion. Granuloma of the tooth under the crown occurs due to secondary caries, insufficient oral hygiene after prosthetics. The infection progresses and enters the periodontium when the root bottom is perforated, carious tissue and pulp are incompletely removed, or the filling is not properly adhered to. When the edge of the crown moves away from the gum, bacterial plaque accumulates in the gap, the stump is destroyed, and inflammation develops in the soft tissues. Granuloma of the tooth after treatment of pulpitis develops when the canals are poorly cleaned and not tightly sealed.
Complications of granuloma
If granuloma treatment is ignored, the following complications may occur:
flux inflammation in the periosteal tissues; osteomyelitis is an inflammatory process in the jaw; cyst inflammatory neoplasm.
Since granuloma is a source of infection, complications can affect other body systems. So, the disease can be provoked by:
sepsis blood poisoning; sinusitis, inflammation of the maxillary sinuses; infectious myocarditis inflammation of the heart muscle; pyelonephritis is a kidney disease.
Treatment at the Family Dentist clinic
We have a good reputation in Minsk, consultations are conducted by dental therapists with 16 years of experience , specializing in the treatment of dental canals. They trust us; more than 80% of patients brought family members and friends to the clinic. Every second patient has been with us for more than 6 years. We do radiovisiography on site in the office, working with four hands together with an assistant to reduce the time of unpleasant manipulations. The effectiveness of dental granuloma treatment is ensured by premium class equipment. Even with serious damage to the crown and root, we strive to preserve the dental unit.
Treatment
Do not hesitate to treat granuloma. If you detect the slightest unpleasant symptoms, you should immediately consult a dentist. If you ignore the symptoms, the patient risks facing serious complications.
Treatment includes medical and surgical methods.
Therapeutic methods
Elimination of granuloma by therapeutic means is possible if it is detected in an unadvanced form during a consultation with a dentist. After confirming the diagnosis, the doctor performs endodontic treatment of the tooth. Timely treatment can stop the spread of infection and save the tooth.
Surgical methods
If the granuloma is large and drug therapy does not have the desired effect, then the doctor is forced to resort to surgery. First, the specialist cuts the gum to remove accumulated pus. This reduces the risk of infection entering the blood and surrounding tissues. After which drainage is installed in the tooth for 3 days. In order to relieve inflammation, antibiotics may be prescribed. The tooth is preserved in case of minor damage or is removed if it is impossible to heal due to severe damage.
Conservative therapy
Tooth granuloma grows for a long time without pain or visual signs. Patients turn to the dentist when the tumor increases in size, swelling and redness of the gums are clearly visible, or is discovered by chance in an image taken before prosthetics. But not all doctors undertake the treatment of dental granuloma and offer resection (removal) of the root apex.
In our clinic, a tooth can be removed from the source of inflammation without surgical intervention ; the cost of treating one root canal starts from 100 rubles. The doctor treats or re-treats the canals, disinfects them, and fills them with calcium hydroxide. The alkaline preparation kills bacterial flora and stimulates the formation of bone tissue. In difficult cases, we change the medicine several times.
The success of treatment can be assessed after 6-9 months using a control x-ray. If the granuloma in the tooth is eliminated, a permanent filling is installed and the coronal part is restored with composite material. If more than 50% of the dental tissue is destroyed, prosthetics with an inlay or crown are performed. We prescribe an additional antibiotic for dental granuloma to reduce the intensity of inflammation and prevent complications. In case of purulent inflammation, we install drainage and excise the nodular formation with the apex of the root.
We always warn that the result depends not only on our qualifications and experience, but also on the patience of the patient. After going through the canals, you need to prepare for several visits to the dentist to apply the paste, and do not miss appointments.
Symptoms
The asymptomatic occurrence of granuloma does not allow it to be detected at an early stage. In turn, diagnosing the disease at a later stage is dangerous due to suppuration and the release of infected fluid into the body. Among the obvious symptoms of the pathology are acute pain when pressed and swelling of the gums. Quite often, pus can be released from the gums under pressure.
Against the background of granuloma, flux may occur, which is accompanied by fever, headache and general weakness. Tooth pain intensifies when chewing food. When the disease passes into the chronic stage, the granuloma can transform into a jaw cyst.
Treatment of granuloma - the story of our patient
| The patient came to the appointment with complaints of the destruction of the 47th tooth and pain in the lower jaw on the right, which intensified when biting. A diagnostic radiograph taken after the examination revealed a granuloma in the area of the distal root. |
| On the first visit, after mechanical and medicinal treatment, the canals were temporarily filled with calcium hydroxide paste. The medicine has a bactericidal effect and stimulates the restoration of bone tissue. We took a control x-ray to make sure that there were no voids left in the root canals. |
Due to the presence of purulent discharge, anti-inflammatory therapy and antibiotics were prescribed. After the filling, the patient was bothered by pain when biting, which went away within a day.
| At the second appointment two weeks later, the patient did not complain of pain. The paste was removed, the canals were filled with gutta-percha pins (permanent filling), and a third control photograph was taken. To make sure that the inflammatory process has stopped, it was recommended to return for the next examination with a control x-ray in 6 months. |
What is the difference between a cyst and a granuloma and how do these formations manifest themselves?
A cyst is a cavity. It has a shell and an infected liquid containing microbial toxins.
Cysts can grow up to several centimeters and even lead to a jaw fracture, as they almost completely destroy bone tissue.
Cysts are often asymptomatic and less responsive to treatment.
Granuloma is scar tissue that replaces bone. Its size is much smaller than the cyst and it begins to bother you earlier.
Early diagnosis allows granulomas to be treated more successfully than cysts.
Outside of exacerbation, the granuloma and cyst may not bother you or may cause minor discomfort when biting on a tooth.
Since these are chronic foci of infection, sooner or later an exacerbation of the inflammatory process occurs.
An exacerbation can occur during cooling, exposure to other infectious diseases, stress, etc.
During exacerbation, granuloma and cyst can manifest themselves clearly:
- intense pain when biting and from hot foods
- swelling and tenderness of the gums in the area of the causative tooth
- feeling of a “grown” tooth
- pus formation with the possible appearance of a fistulous tract
- temperature and significant deterioration in general health
- in the absence of timely treatment, inflammation can spread to the soft tissues of the head and neck
As a rule, granuloma and cyst are discovered accidentally on an x-ray during the treatment of other teeth or preparation for prosthetics.
Our doctors are always ready to help and cure granuloma.
| Pankratieva Alesya Georgievna. Practicing dentist of the first qualification category. More than 15 years in the profession. Founder of the Family Dentist clinic, Member of the Belarusian Dental Association. View profile | Bobkova Irina Leonidovna. Practicing dentist of the highest qualification category. More than 20 years in the profession. Assistant professor. Co-author of a patent for a method of treating periodontitis. View profile |
Feedback from our patient:
Thank you very much for your attentive attitude towards patients. Quality services. I have been discussing at the Family Dentist for a long time and the doctors always have a good mood and a smile on their face. I will recommend your dentistry to my friends and acquaintances.
With respect, Gameza N.A.
| Do not leave the source of infection untreated - sign up for the Family Dentist clinic. The sooner you start treatment, the cheaper and easier it will be. | Call to make an appointment +375 29 604-61-61 |
Diagnostic methods
A dental therapist can identify dental root granuloma. During the initial examination, the doctor discovers:
- severe swelling of the gums,
- bone protrusion,
- pain when pressed,
- hyperemia of soft tissues.
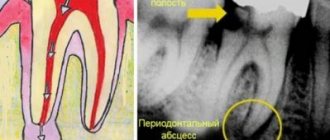
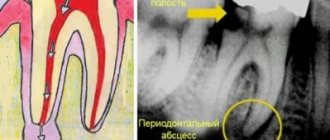
To confirm the suspected diagnosis, the patient must undergo radiography. In the photograph, the granuloma appears as a darkened area near the apex of the tooth root. This diagnostic method allows you to detect the disease at the first stage, when there are no pronounced symptoms.
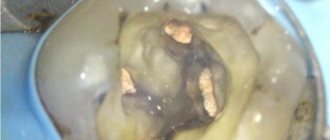
What does a dental granuloma look like?
The photos and x-rays that we post below will help you see what a dental granuloma looks like.
Main symptoms
For a long time, the disease may not manifest itself at all, but at some point swelling of the gums will occur and acute unbearable pain will appear. Only an experienced dentist can detect the presence of a granuloma using an X-ray examination.
The main signs of granuloma include:
- Explicit or mild pain when chewing;
- Swelling of the gums;
- Darkening of tooth enamel;
- Sometimes, in the acute phase, increased body temperature.
Basically, the listed symptoms appear quite late, when the disease has already progressed far. Therefore, in most cases, the dentist notices a granuloma by chance after an X-ray of the teeth, prescribed for completely different purposes.