Sometimes the pain that occurs after recently treated pulpitis is a natural phenomenon, but it may also be that the cause of the pain is mistakes made by the dentist. Statistics are not on the side of dentists: according to it, in approximately 60% of cases, treatment of pulpitis is carried out with gross violations, leading to not the most pleasant consequences.
To avoid problems in the future, after treatment it is necessary to take an x-ray: from the image it will be possible to immediately determine whether the doctor filled the root canals properly. But, again, according to statistics, in more than half of the cases, doctors, seeing the shortcomings of their own work, do nothing, and the absolute majority of patients do not know how to read x-rays. Why does this happen? Firstly , treating pulpitis is a troublesome and lengthy task, and secondly , errors will not manifest themselves immediately, but only towards the end of the treatment guarantee, when the patient will no longer have the right to make claims.
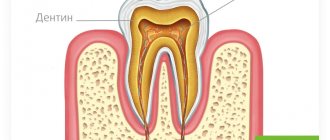
Tooth hurts after pulpitis treatment due to injured tissue near the root
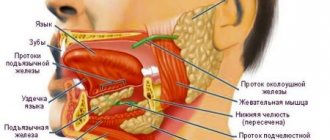
The first stage of treatment for pulpitis is the removal of the inflamed pulp, after which the canals are sealed so that subsequently the inflammatory process does not begin to develop in them again. During the procedure, minor tissue trauma occurs, which simply cannot be avoided.
Pain may occur due to:
- separation of a bundle of nerves located near the upper part of the root, which often occurs when removing pulp;
- mechanical treatment of the canals with special tools (very often the tool can extend beyond the canal, causing injury to the tissues located near the apex of the tooth root);
- penetration of antiseptic agents used to flush the canals outside of them, which can cause irritation.
In all of the above cases, pain is a natural reaction of the body. After proper treatment, pain will stop within a maximum of 3 days.
Prevention of pulpitis
Treatment of tooth pulpitis is a rather complex and unpleasant process. To prevent the development of the disease, it is better to perform prevention and prevent the occurrence of this disease. Prevention of pulpitis includes: → Timely treatment of caries is the most important prevention of pulpitis; → Systematic visits to the dentist; → In case of injury in the jaw area, it is necessary to undergo diagnostics, since pulpitis often occurs precisely due to various types of injuries to the oral cavity; → Proper nutrition. It is necessary to limit the consumption of soda, sweets, etc. → Proper dental hygiene. Mandatory daily teeth brushing. → It is recommended to have your teeth professionally cleaned at a dental clinic every six months.
Based on all of the above, we can conclude that the prevention of pulpitis does not involve any difficulties, but consists of following basic steps. By performing prevention, you will significantly reduce the chances of becoming acquainted with a disease such as pulpitis and the pain that occurs with the development of this pathology.
Return to list of services
A tooth hurts due to a poorly filled canal
A feeling of pain and swelling of the gums are the first signs that the tooth treatment was performed poorly. However, there are situations when the inflammatory process develops slowly, and it is possible to understand that something is wrong with the tooth only by taking a picture.
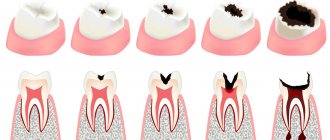
As mentioned above, filling canals is a common procedure, often performed with errors: if they are not corrected, then after some time inflammation and, consequently, pain will begin.
There are the following options for unsatisfactory filling:
- The canal was not sealed to the entire length of the root. The pulp becomes inflamed due to microorganisms that have entered it. After its removal and thorough treatment of the canal with drugs, some part of the microflora still remains. When the canal is not filled along its entire length or the filling material is not compacted tightly, the infection multiplies and affects the tissue surrounding the tooth. Eventually, a sac filled with pus appears at the apex of the root. If the doctor has not completely filled the canal, then the tooth must be re-treated (the sooner this is done, the greater the chances of saving it). Usually, a complete unfilling of the canal and its re-sealing is required. When the canal is unsealed only in the area of the upper part of the root, the doctor can perform a resection, which allows the canal not to be unsealed.
- Exit of filling material beyond the root apex. One of the causes of pain is the removal of the material used for filling beyond the upper part of the root. There is no universal method for eliminating the deficiency: a preliminary examination by a doctor is required. If little material has been removed, the pain will subside over time (in some cases you will have to wait up to 2 months). In this case, the patient is given a choice: either tolerate a slight reduction in pain, or agree to re-treat the tooth. If a lot of material has been removed, surgical intervention will be required: the doctor will make a small hole in the bone through which he can remove excess material (a simple operation takes about half an hour).
- Leaving a broken part of a medical instrument in the canal. When processing the canal, the instruments used by the doctor may break off. There may be several reasons for this: careless actions of the dentist; curved channels. Sometimes it is possible to get a fragment out, but if a piece of the instrument remains in the upper third of the root, it becomes very difficult to remove it. The broken part does not allow filling the entire length of the canal. There is a risk of infection multiplying, which can provoke the development of an inflammatory process in the tissues surrounding the tooth.
- Root perforation. Perforation is a small hole that appears in the root either due to natural causes (excessive curvature of the canals, but this happens rarely), or due to the actions of a doctor. Today, perforation is a very intractable problem in dentistry. Most often, perforation occurs when a pin is installed, when it is not fixed in the canal, but is brought out through its wall directly into the bone. If the canal is very curved or difficult to navigate, then working in it requires great precision from the doctor. But even extreme accuracy does not guarantee that mistakes will be avoided. Often, high-quality treatment of curved canals becomes a difficult task for an experienced doctor.
Perforation can be corrected, but it is difficult to do. To properly close the hole, expensive materials like Pro Root MTA are used. Sometimes filling with this material can be done from the inside of the tooth, sometimes surgical access to the area where the perforation has occurred is required. If the doctor is to blame for its appearance, then the hospital must correct the shortcomings at its own expense.
Recovery period
Once treatment for pulpitis is completed, the patient will need some more time to fully recover - from one week to a month. During this period, physical therapy is indicated, for example laser therapy using a helium-neon apparatus. This is necessary to speed up the healing process and consolidate the therapeutic effect.
Since pulpitis is an inflammatory disease, after treatment in the clinic it is necessary to take a course of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs at home, such as: Ibuprofen, Ketanov, Naproxen-Acri. However, it should be remembered that all anti-inflammatory and painkillers have their contraindications, so the choice of a specific medication must be agreed with your doctor.
How is canal filling performed?
High-quality filling is the key to the absence of complications in the future. Before filling, the canals must be prepared: widen them slightly and ensure patency along the entire length.
Preparation consists of the following steps:
- elimination of tissues on which carious formations have appeared (removal of healthy tissue is allowed in order to gain access to the orifices);
- complete removal of the pulp;
- correct determination of the channel length (they are different in length);
- high-quality mechanical processing (includes expanding the diameter of the channel along the entire length);
- filling with gutta-percha.
The quality of the filling depends on:
- Correct determination of the channel length. In case of a dentist’s mistake, the canal may be either underfilled, which subsequently leads to the formation of cysts, or overfilled when the material extends beyond the boundaries of the root (consequences - pain, inflammation).
- High quality machining. The purpose of the procedure is to widen the canal so that it can be filled with filling material to its full length. Treatment can be carried out either using hand instruments, which the doctor rotates in the canal with his fingers, or using an endodontic tip (rotating in the canal, they remove a thin layer from the walls, gradually expanding it). This option is the most preferable, since the quality of processing increases and safety increases (the tip cannot break off due to automatic control of the load level).
- The chosen filling method and the doctor’s competence.
The patient can understand without the help of a doctor how well the canal was filled. To do this, you need to carefully look at the x-ray:
- The filling material will appear as a rich white color. This color should fill the channel throughout its entire length;
- in a properly sealed canal there should be no voids or gaps.
What not to do?
If, after treatment, a tooth hurts when pressed or without mechanical action, you should under no circumstances resort to folk remedies such as heating, hot compresses, heating pads - if there is an inflammatory process, this can greatly worsen the condition. In case of allergic reactions, heat will also increase swelling.
It is also not recommended to use folk remedies for rinsing, which can cause a burn to the mucous membrane - iodine, tinctures of alcohol or vodka, liquids with the juice of “scorching” plants, etc. Even if there is no gum damage, such measures can worsen the situation.
It is also not worth taking various painkillers uncontrollably - firstly, you need to see a doctor in any case, and the effect of analgesics will not allow you to fully evaluate the clinical picture. Secondly, it can be dangerous to health.
It is important to visit a doctor at the first opportunity and perform all the necessary procedures to eliminate unpleasant consequences and improve the condition.
Brief conclusions
The main consequences of poor treatment of pulpitis are as follows:
- flux, formation of cysts in cases where the canals are not completely filled, periodontitis;
- prolonged pain and neuralgia during repeated canal filling.
One of the most unpleasant consequences for the patient is tooth extraction. It cannot be avoided if:
- the doctor during the treatment broke the root or caused a perforation, which was not eliminated as soon as possible;
- A periodontal abscess formed at the root apex, and the patient delayed its treatment.
Symptoms of pulpitis
In modern dentistry, it is customary to distinguish between acute and chronic pulpitis. Each of these periods of the disease is characterized by certain symptoms. Below we will analyze the characteristic symptoms for each type of pulpitis.
The acute period of the disease is characterized by the following clinical manifestations
→ Acute pain. The pain may radiate to the side of the head on which the affected tooth is located; → Increased pain in the evening and at night; → Attack-like pain. The pain may subside or occur suddenly; → Severe sensitivity to thermal, mechanical and chemical stimuli. Even after eliminating the irritant (a stuck piece of food, hot tea, etc.), the pain does not subside, and often only intensifies; → Lack of appetite; → Sleep disturbance; → Sometimes there may be an increase in body temperature.
If proper treatment was not carried out at the acute stage, then the pathology becomes chronic.
Chronic pulpitis often does not have such pronounced symptoms that appear during the period of acute pulpitis. Nevertheless, several clinical manifestations characteristic of it can be identified.
→ The appearance of pain when the tooth comes into contact with hot food or drinks and the pain subsides when it comes into contact with cold ones; → The appearance of bad breath;
Diagnostics
Looking at the photo of purulent pulpitis, you can see the presence of a deep carious cavity with softened dentin, emitting a putrid odor. The color of dentin can be light in acute forms of the disease, and dark in chronic ones. On the mucous membrane around the diseased tooth you can see a whitish coating and (sometimes) swelling of the transitional fold.
During probing and percussion, a pronounced pain reaction is observed. When you press on the layer that separates the tooth cavity, pus is released and a throbbing pain appears, which subsides as the pus drains. All these signs are identified by a dentist during a visual examination. In addition, radiography and electroodontodiagnostics are prescribed to diagnose the disease.
Differential diagnosis of acute purulent pulpitis requires that this disease be distinguished from:
- diffuse pulpitis in the acute phase - with it there is no pus and pain symptoms are not so intense;
- focal pulpitis - characterized by the absence of purulent discharge and weaker pain;
- purulent periodontitis - characterized by sharp “shooting” pain in the affected tooth at the slightest pressure on it;
- trigeminal neuralgia - there is no feeling of discomfort during thermal exposure, but pain occurs when touching certain points on the face.
Clinical researches
Clinical studies have proven that regular use of professional toothpaste ASEPTA REMINERALIZATION improved the condition of the enamel by 64% and reduced tooth sensitivity by 66% after just 4 weeks.
Sources:
- Report on the determination/confirmation of the preventive properties of personal oral hygiene products “ASEPTA PLUS” Remineralization doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
- Clinical and laboratory assessment of the influence of domestic therapeutic and prophylactic toothpaste based on plant extracts on the condition of the oral cavity in patients with simple marginal gingivitis. Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Elovikova T.M.1, Candidate of Chemical Sciences, Associate Professor Ermishina E.Yu. 2, Doctor of Technical Sciences Associate Professor Belokonova N.A. 2 Department of Therapeutic Dentistry USMU1, Department of General Chemistry USMU2
- Clinical experience in using the Asepta series of products Fuchs Elena Ivanovna Assistant of the Department of Therapeutic and Pediatric Dentistry State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education Ryazan State Medical University named after Academician I.P. Pavlova of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation (GBOU VPO RyazSMU Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia)
Reviews about our doctors
I would like to express my gratitude to the dentist Elena Nikolaevna Kiseleva and her assistant Svetlana - they are real specialists and at the same time sensitive, not burnt out by years of practice.
Thanks to them, I have been coming back here for many years. Thanks to the management for such doctors! Read full review Svetlana Nikolaevna
13.08.2021
I am very grateful to Evgeniy Borisovich Antiukhin for removing my three eights. Especially considering that the lower tooth was not the simplest (it was located in an embrace with a nerve). The removal took place in 2 stages, one tooth under local anesthesia, two under general anesthesia. I had no idea that wisdom teeth could be... Read full review
Sofia
28.12.2020