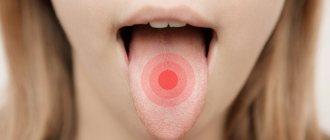
Pain under the tongue can serve as one of the main symptoms of a whole range of problems, from banal mechanical injuries to a number of pathologies of the oral cavity, nervous system or internal organs. Depending on the cause and location of the pain, it can have a different nature and intensity.
If you or your loved one has pain under the tongue, there is no need to panic or self-medicate - this can only lead to aggravation of the situation. Contact a dentist at a dental clinic, he will conduct a diagnosis, determine the exact cause of the discomfort and prescribe an adequate treatment regimen to effectively eliminate the pain.
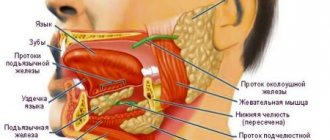
What is in the sublingual area
The tissues located on the lower jaw under the tongue are called the floor of the mouth. Due to the complexity of the structure, as well as the natural functionality of this area, a person often experiences problems accompanied by pain.
Structure of the sublingual region:
- Hyoid muscles - have an elastic structure and are responsible for the motor function of the area;
- Hyoid bone - has an anatomical shape in the form of a horseshoe, located in the muscle layer. It is the only bone in the human body that has no connections with other bones of the body;
- Nerve endings are elements of the peripheral nervous system, responsible for the sensitivity of the sublingual area to various physical, mechanical and thermal stimuli;
- Salivary glands - responsible for the production of saliva, which is involved in the process of wetting the mucous membranes of the oral cavity and the digestion process;
- Blood vessels - provide nutrition to the tissues of the sublingual area;
- Frenules are connecting folds in the sublingual area, responsible for connecting the sublingual tissues with the tongue.
Each of the above elements ensures the natural functionality of the dentofacial apparatus and participates in all physiological processes of the oral cavity.
What is dystonia?
Dystonia of the tongue muscles causes involuntary movements of the tongue and uncontrolled mobility of structures adjacent to the tongue, which can lead to problems with chewing food and articulating sounds. As experts note, this may result in weight loss and loss of the ability to speak. In particularly severe cases, for example, when a patient may suddenly choke on food, tongue dystonia can provoke the development of more serious health problems.
According to observations, musicians who play wind instruments are more susceptible to spasms of the mouth muscles.
Causes of pain under the tongue
Modern medicine knows dozens of different reasons that can cause unpleasant and painful sensations under the tongue in an adult, teenager and child: from a banal mechanical injury to the frenulum, leading to tissue damage, to allergic reactions causing swelling. At the same time, there is a list of the most common causes observed in most patients.
The main causes of pain under the tongue:
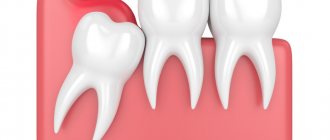
- Mechanical injuries to the frenulum and muscle tissue are the most common cause of sublingual pain. As a rule, it is observed in people with a short frenulum. It is injured due to stretching, as well as in the event of mechanical trauma to tissues, for example, during eating, hygienic brushing of teeth, etc.;
- Dental pathologies of the oral cavity – stomatitis, dental problems (caries, periodontitis, periodontitis), gumboil, etc.;
- Infectious inflammation of the oral cavity - pain often manifests itself with sore throat. During this period, it is painful for a person to eat, swallow water and saliva, stick out his tongue or simply chew;
- Cellulitis or abscess of the floor of the mouth is a significant accumulation of pus in a small area of the floor of the mouth. Causes “bursting” of internal tissues, putting pressure on peripheral nerves - this provokes pain and tactile discomfort;
- An allergic reaction can be the body’s response to various irritants. Causes swelling of the soft tissues of the oral cavity, accompanied by discomfort or pain in the sublingual area;
- Asymmetry of the hyoid bone - an anatomical disorder in the growth of the hyoid bone, can provoke excessive or nonspecific pressure on the peripheral nerves, causing pain;
- Neuralgia is a general disease of the nervous system that manifests itself in its various parts. It is often a consequence of nervous shock and is accompanied by a feeling of painful numbness in the oral cavity;
- Diseases of internal organs and body systems - some areas of the tongue may reflect (irradiate) pathologies of internal organs, which is accompanied by painful sensations in the sublingual area;
Note! Most of the above problems that provoke the development of pain in the sublingual area can be caused by bacterial infections (streptococci), fungi (candidiasis), and herpes.
Which doctor should I contact?
If you have the slightest discomfort or pain in the space under the speech organ, you should visit a therapist. Consultation with an allergist may be required. Most often, dentists deal with problems of the floor of the mouth. It is important to regularly visit the hygienist. Professional oral cleaning prevents many dental and soft tissue problems.
In case of frenulum injuries, rinsing with romazulan, chlorophyllipt, and stomatophyte is prescribed. The disease requires repeated rinsing: in the morning, after meals, in the evening. The affected area is treated with antiseptic drugs and agents to relieve the inflammatory process. If the salivary glands are affected, therapy should be started before an abscess appears. Medicines are injected into the pathological gland, antibiotics, drugs for salivation, and a course of physiotherapy are prescribed.
When an abscess forms, the patient needs a surgeon to clean out the gland cavity. As a preventive measure, dentists recommend proper oral care. It is necessary to take care of the gum tissue, prevent the accumulation of pathogenic microbes, treat caries in a timely manner, and clean the oral cavity twice a day. You need to visit the dentist once every six months. Patients with a shortened frenulum and asymmetry of its structure need to be careful to avoid injury.
Symptomatic features of pain under the tongue
Pain in the sublingual area can have various symptomatic manifestations. First of all, they are accompanied by different types of pain (sharp, aching, throbbing), as well as constancy or frequency.
If you consult a doctor, it is very important to correctly characterize the pain - this will allow the specialist to narrow down the range of symptoms for differential diagnosis. For example, you may have pain in the frenulum under your tongue or pain under your tongue on the right/left.
One of the characteristic manifestations of stomatitis or candidiasis is a white pimple under the tongue. Its presence may indicate the development of a fungal or bacterial process. If such a symptom is detected, treatment will include antifungal and antibacterial therapy with the prescription of antibiotics or special antiseptic rinses. The presence of pimples of a different color may indicate the presence of a wide range of problems, the identification of which requires a thorough diagnosis of the oral cavity or the entire body.
Prevention of inflammation of the floor of the mouth
To prevent diseases of the sublingual area, dentists give recommendations on proper oral care:
- take care of your gums;
- avoid the accumulation of bacterial plaque;
- visit the dentist 2 times a year;
- prevent the occurrence of caries;
- brush your teeth 2 times a day.
But if the patient has congenital or acquired anomalies in the development of the floor of the oral cavity, such as a shortened frenulum or structural asymmetry, then you will have to be more careful to prevent injury. Some abnormalities can be treated. Come to an appointment at Family Dentistry and experienced specialists will tell you how to get rid of defects, tumors and inflammations.
Features of diagnosis and treatment of pain under the tongue
Treatment of pain in the sublingual area should be carried out after a high-quality diagnosis to determine the root cause of the problem. Sometimes, pain in the frenulum under the tongue or in the surrounding tissues is treated by therapists or allergists, but in most cases this is done by dentists, because about 90% of all cases of treatment are associated with a dental problem.
Diagnosis of pain under the tongue is carried out in several stages:
- Initial appointment - the doctor collects anamnesis, finds out information about the nature and location of pain, and also examines the patient’s oral cavity;
- A complete diagnostic examination is carried out in the absence of characteristic symptoms of common dental diseases. It is possible to use hardware techniques (X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.);
- Differential diagnosis – a specialist differentiates the underlying pathology from similar diseases;
- Making a diagnosis and prescribing treatment - based on the data of the initial examination and diagnosis, the doctor establishes an accurate diagnosis and prescribes an adequate treatment regimen.
Note! The method of treatment and the choice of drugs to eliminate pain in the sublingual area directly depend on the root cause of the symptoms. For example, if your frenulum hurts due to a mechanical injury, antiseptic and anti-inflammatory solutions for mouth rinsing will be prescribed, including: chlorophyllipt, hexoral, stomatophyte, alcohol tincture of calamus, stomatidine or others. If the pain is associated with the development of bacteria or fungi, antibacterial, antifungal and anti-inflammatory therapy is prescribed.
Pain due to inflammation of the salivary glands
In cases where a person feels pain on both sides of the tongue, the cause may be inflammation of the sublingual salivary gland. It arises as a result of:
- Complications of another disease (inflammation of the tonsils, acute respiratory viral infections, anemia, vitamin deficiency, dental diseases);
- Insufficient hygiene;
- Obstruction of salivary flow caused by stones or pathogens.
The main symptoms indicating inflammation of the salivary gland:
- Dry mouth – it always seems like there is not enough saliva;
- Pain that is observed not only under the tongue, but also in the ear area;
- Redness of the mucous membrane, thickening or swelling under the tongue;
- Putrid taste.
If you observe such signs in yourself, you should immediately go to the dentist and undergo a course of therapy. Otherwise, an abscess may develop or the disease may become chronic.
If you have a problem similar to that described in this article, be sure to contact our specialists. Don't diagnose yourself!
Why you should call us now:
- We will answer all your questions in 3 minutes
- Free consultation
- The average work experience of doctors is 12 years
- Convenient location of clinics
Single contact phone number: +7
Make an appointment
Diagnostics
The disease must be differentiated from traumatic and inflammatory lesions of the mucous membrane, neuralgia, and clinical manifestations of osteochondrosis.
Glossalgia is supported by the absence of changes in the language, the diffuseness of the pain syndrome, as well as a reaction that does not correspond to the intensity of the stimulus. It should be noted that neuralgia has a specific localization, corresponding to the area of innervation of a particular nerve. With glossalgia, sensations can be diffuse or migrate.
In case of injury, the pain is constant and localized. The consequences of damage are visible on the mucous membrane; the patient’s sensations and the picture visible upon examination coincide. With glossalgia there is no such pattern. Damages in this pathology are present, but they are secondary in nature and do not correspond to the localization of pain.
Symptoms of glossitis
- increased salivation;
- swelling and redness;
- pain and burning when eating;
- plaque on the tongue in the form of spots;
- bad breath;
- papillomas or warts on the tongue;
- speech disorder;
- foreign body sensation.
Prevention of glossitis - high-quality oral hygiene and no bad habits. It is important to undergo timely preventive examinations and also eat well. All these factors actively contribute to the development of the disease and bring a number of problems.
Causes of the disease
There are many types of pain in the tongue area. Most of them are inflammatory or traumatic in nature. Glossalgia is a functional disorder. This means that there is no damage of any kind in this case, and the painful sensations are reflexive in nature.
Glossalgia often manifests itself in combination with other disorders of the autonomic nervous system. Without proper treatment, the pain becomes chronic.
Many diseases can serve as a trigger for the development of glossalgia:
- endocrine disorders;
- mental disorders;
- CNS pathology;
- diseases of the digestive system;
- damage to peripheral nerves;
- encephalitis;
- stroke;
- neurosyphilis.
Symptoms usually appear in the presence of triggers, such as stress.
The tongue has pain receptors. When various injuries occur, they are irritated, an electrical impulse is formed, which is transmitted along nerve fibers to the corresponding parts of the brain. This process creates pain. In the case of glossalgia, there is no effect on pain receptors. False sensations arise due to incorrect perception of signals by the nervous system. Pain is usually a warning signal about problems in a particular organ, but in this situation the brain receives a false signal.
Pain Relief Methods
Before suppressing pain localized under the tongue, it is important to establish the cause of this symptom.
If the frenulum ruptures, it is necessary to apply a disinfectant composition to the injury site and seek medical help.
Inflammation of the sublingual salivary gland is treated with the following medications:
- antiseptic;
- antibacterial;
- anti-inflammatory;
- painkillers.
If foci of suppuration are detected, the cavity is additionally drained.
Normalization of nutrition plays an important role in eliminating pain under the tongue. It is recommended to give preference to soft, pureed dishes at room temperature. Active saliva production speeds up the healing process. To do this, acidic foods such as sauerkraut or citrus fruits are introduced into the diet.
Why can our articles be trusted?
We make health information clear, accessible and relevant.
- All articles are checked by practicing doctors.
- We take scientific literature and the latest research as a basis.
- We publish detailed articles that answer all questions.
Pain under the tongue is a symptom, not a separate disease. It occurs when an organ is injured or against the background of various pathologies. It is possible to suppress pain only if the factor that provoked it is eliminated.