What to do if your tooth hurts
Medicines
Folk remedies
Causes
If children have toothache
Toothache can occur unexpectedly and take you by surprise in the most inopportune place. Let's look at how to relieve pain before going to the dentist in this article.
What not to do if you have a toothache
The goal of first aid for dental pain is to alleviate suffering and create tolerable conditions for the patient before going to the dentist. And it is advisable to do this without serious health complications for the sake of five-minute relief. Therefore, it is worth knowing first of all what not to do.
Do not apply heat. If you suffer from acute toothache, it is not recommended to heat either the tooth itself or the cheek. Severe toothache indicates the presence of an inflammatory or infectious process. By applying warm compresses or using other heating methods, you stimulate blood flow to the pathological area. Instead of one diseased tooth, you can get a complication affecting the entire dentition.
If a tooth hurts, it is much more effective to replace warm compresses with briefly applied ice;
Use medications carefully. You cannot blindly believe everything that is written on the Internet. Severe toothache can be effectively relieved or alleviated only in a dental office. All other methods give only an insignificant short-term effect; you should not expect a miraculous cure from them. Do not inject painkillers into the gums yourself, and do not use medications not intended for this purpose to relieve toothache. For example, an aspirin tablet applied to a disturbing tooth can cause severe burns to the mucous membrane, but will not bring relief;
Bed rest is not for you. If you are taken by surprise by an acute toothache, it is better to resist it on your feet or while sitting. The half-sitting position is the very compromise that will allow you to more comfortably endure an unpleasant and exhausting situation and will not cause even more harm to the aching tooth. The fact is that when a person is in a horizontal position, the blood flow to the diseased tooth increases. Increased pressure is created around the already irritated nerve endings and severe toothache becomes simply unbearable. If an acute toothache catches you at night, place the pillows higher, lean back on them and try to take a nap in this position;
Hot rinses and folk remedies. Most ways to relieve tooth pain are based on traditional methods of treatment and pain relief. And the vast majority of recipes advise using hot rinses. You can't do this! But if you use these same herbal decoctions warm, the effect can be very positive, in extreme cases, harmless.
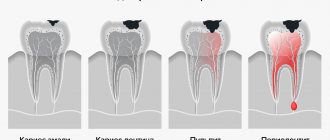
Tooth structure
The tooth consists of two parts. 1 - The top part of the tooth - the crown, which is visible in the mouth and 2 - the root of the tooth, which extends into the jaw bone to support the tooth in the desired position.
Teeth also consist of:
- enamel - hard outer coating
- dentin - the softer material that supports the enamel and forms the majority of the tooth
- pulp is the soft tissue in the center of the tooth, consisting of nerves, blood vessels and lymphatic vessels.
The root canal system contains the pulp of the tooth and extends from the crown of the tooth to the end of the root, its apex. One tooth can have more than one root canal.
What to do if your tooth hurts
First aid for a toothache begins with identifying the causes of the discomfort and eliminating irritating factors. Toothache can be caused by various irritants:
- Hot or cold food and drinks;
- Cold air;
- Sweet, sour, salty foods and drinks;
- Pressure drop;
- Head position;
- By pressure or other influence;
- Food getting into the carious cavity;
- Other mechanical effects on the tooth.
As soon as it becomes clear why the tooth hurts at a particular moment, it is necessary to stop the irritating influence. After this, consult a doctor for help. If the appointment is postponed for a long time, then it is worth taking painkillers.
What is characteristic of inflammation of the root tissues of the tooth?
There are acute, chronic forms and exacerbation of the chronic course of periodontitis. The acute form is characterized by the following symptoms: aching, sharp and at times unbearable pain of a constant nature, localization of pain in the area of the diseased dental crown. If dental care is not provided against the background of such manifestations, the pain begins to increase, pulsate and feel like an abscess. This clearly illustrates the flow of initial inflammation into the purulent phase.
The acute form of periodontitis can last from several days to two weeks; it is divided into two stages:
- The intoxication phase is debilitating, aching and incessant pain, a feeling of heaviness around the affected tooth, sharply increasing pain when trying to bite with this tooth.
- Exudative stage - inflammation is characterized by unbearable pain that does not subside without the use of analgesics. Painful “shooting” is caused not only by an attempt to bite with this tooth, but even by light pressure on it with the tongue. In this case, there may be a feeling that the unhealthy tooth is “moving”, because it actually acquires unusual mobility. During the exudative period, the periodontal soft tissues become swollen and the lymph nodes enlarge.
In the presence of a purulent focus, there is increased sensitivity to hot/cold foods and when chewing solid food. The pain also spreads to the teeth located nearby, purulent bumps appear on the gums, and swelling of the oral tissues is noticeable. The pulsation and burning sensation in the gums intensifies, and there is a putrid smell from the mouth. The purulent form is very insidious and can cause decreased performance, increased body temperature, lethargy and weakness.
Chronic inflammation of the tooth root is difficult to diagnose due to vague symptoms and similarity with some types of pulpitis. However, experts pay attention to the following markers of the disease:
- The patient experiences inconvenience and discomfort when biting the affected tooth or pressing on it, but there may not be debilitating and constant pain.
- Periodic feeling of slight bloating and heaviness in the periodontal area.
- The appearance of fistulas.
- Putrid taste and odor in the mouth.
- Change in color of tooth enamel (not to be confused with stains from caries).
- Enlarged and painful lymph nodes.
- When there is pressure on the gum, there is an unpleasant, painful sensation.
During the diagnosis, the dentist discovers a deep cavity, probing which with a probe causes severe pain. The final diagnosis is established based on the results of an x-ray examination. If the inflammatory process has become chronic, then its exacerbations occur from time to time, and the patient copes with them on painkillers. And, often, this is why it is so difficult to determine the chronic form of periodontitis.
Medicines for toothache
There are many painkillers in pharmacies that are quite effective in helping when a tooth hurts. However, when choosing medications without a prescription and doctor’s recommendations, it is worth remembering that each medicine has a number of contraindications and side effects, so you need to carefully read the instructions, and, if possible, check with pharmacists and pharmacists for information.
The following medications are used to relieve toothache:
| Analgin; | Indomethacin; | Piroxicam; |
| Denebol; | Ketanov; | Solpadeine; |
| Diclofenac; | Ketoprofen; | Tempalgin. |
| Ibuprofen; | Naproxen; |
For local anesthesia and gum disease, Kalgel, Dentinox, Cholisal, Kamistad and Mundizal are suitable. You can also use herbal rinses. They have a calming and antiseptic effect.
Why are rinses dangerous?
After removal within 1-2 minutes, a blood clot forms in the hole - this is a reliable biological protection of the wound, preventing bacteria from entering it and causing an inflammatory process. It is under no circumstances recommended to destroy, move or wash out this clot. However, during the rinsing process, patients often wash away the protective clot, leaving the socket “dry”. Dry socket is the main cause of alveolitis.
Today, dental surgeons are more inclined to believe that rinsing not only will not help the wound heal faster, but also increases the risk of secondary infection.
Folk remedies for toothache relief
The most popular folk remedies are also based on rinsing the mouth with a decoction of various herbs, as well as applying various non-heating compresses to the sore tooth.
The most effective rinses are:
| Sage; |
| Oregano; |
| Oak bark; |
| Chamomile decoction; |
| Calendula; |
| A solution of soda, salt and iodine. |
Pain in the teeth is well relieved by compresses or acupressure on the sore tooth. To do this, use tampons or cotton pads soaked in a medicinal solution or containing a medicinal substance. This may serve as:
- Propolis;
- Essential oils;
- Alcohol or strong alcohol;
- Garlic or onion-garlic mixture with salt.
Do not forget about the simplest and surest way to temporarily numb the tooth that is bothering you. Just take an ice cube out of the freezer and apply it briefly to the sore area. The cold freezes and stops all processes, so the pain will subside for a while. Do not apply cold for a long time, as it can chill the nerve endings.
Inflammation of a wisdom tooth
The location of this tooth in the oral cavity is sometimes difficult to reach for a doctor and is therefore considered the most difficult to treat. The wisdom tooth begins to erupt closer to the age of eighteen, which is why it received the name “comes with wisdom.” When it erupts, painful discomfort is felt, the reason is the absence of milk teeth in this place previously, so the incisor, growing, cuts through the gum. Swelling of the cheek and inflammation of the gums begins, which covers the area of the wisdom tooth; various symptoms may also appear, the lymph nodes become inflamed, swallowing becomes difficult, and the temperature rises.
A slight swelling can be considered normal, and the cause of the inflammatory process can be several factors:
- The wisdom tooth is looking for a place to come out, but not finding it creates inflammation in the gum and nerve;
- When the gums come out, there is not enough free space for normal growth, it begins to put pressure on the teeth in the neighborhood, which causes inflammation;
- The location of the growth of wisdom teeth depends on the structure of the oral cavity; if the shape is irregular, inflammation often occurs and cysts form.
To determine the presence of an inflammatory process in a wisdom tooth, you will need an x-ray; there are characteristic signs of inflammation:
- Sensation of unpleasant taste;
- Swelling of the gums around the tooth;
- The resulting pus spreads in the oral cavity, forming a pungent odor;
- When a wisdom tooth grows, the pain radiates to the temple or ear.
In this case, consulting a doctor is mandatory. If proper treatment is not started on time, it can lead to severe pain and many complications, the formation of purulent abscesses and phlegmons, which are subsequently resolved surgically.
Today, more and more dentists are of the opinion that the wisdom tooth does not need to be treated, but should simply be removed, because it's more trouble than it's worth. The complexity of treating its roots is determined by its location, and the doctor will make a decision in each individual case: to treat or remove a wisdom tooth.
Acute toothache
It appears very unexpectedly and is rapidly gaining strength. Pain in the teeth can be so severe that a person may lose consciousness for a while.
Severe toothache can occur when eating, while talking, while drinking a cup of coffee, when clenching your jaw, turning or tilting your head, climbing stairs, and even just while breathing. During each of these actions, the sensitive tooth will encounter irritants and react with severe pain:
- For hot food or water;
- To cold air;
- To change pressure and increase blood circulation.
In this case, toothache can be short-term, occur only in the presence of irritating factors and subside after their removal, incessant, or it can appear and disappear.
In any case, toothache is a reason to immediately consult a doctor. Without delay and expectation of serious complications.
For what reasons can a tooth root become inflamed?
Despite the availability of many effective methods of therapeutic treatment of inflammation under the tooth root, it is often necessary to resort to the use of surgical treatment methods. This is indicated in the following cases:
- Root canal obstruction was detected
- there is a pin or stump tab that cannot be removed without damaging the root
- there are many cysts - perihilar or growing into the maxillary sinus
- there is a perforation (perforation) of the wall of the tooth root or its cavity
- The use of conservative methods of treating root inflammation does not help
Important:
Most often, periodontitis refers to inflammation in the area of the apex of the tooth root (apical, periapical periodontitis). The cause of tooth root inflammation is untimely treatment of caries and pulpitis. Another type of disease, marginal periodontitis, is classified as periodontology; in this case, the lesion spreads to the gums in the cervical part of the tooth.
Muffled pain in teeth
This is a toothache that a person is used to putting up with and has adapted to live with. It is not as severe as an acute toothache, but it is unpleasant and poisons life. It can be permanent or periodic, occur with a certain pattern, in response to known stimuli, or on its own.
The cause of muted pain is various diseases of the oral cavity. Even the first sensations of pain are a reason to consult a doctor. Most serious illnesses begin with a completely tolerable pain reaction. But if you don’t visit the dentist in time, you can get pulpitis instead of regular caries, and instead of bleeding gums, you can lose a tooth. To prevent this from happening, you don’t have to endure it when your tooth hurts; you need to immediately make an appointment with a doctor.
Types, signs and symptoms of periodontitis
According to the Russian classification, there are several forms of inflammatory processes developing in the periodontium.
- Spicy.
- Chronic.
- Separately, it is customary to highlight exacerbations of chronic inflammation of the tooth root.
Signs and symptoms of acute periodontitis
The main symptom of this form of the disease is sharp, aching, sometimes unbearable pain. In this case, the pain is clearly localized in the area of the diseased tooth and is permanent. If the patient did not receive dental care on time, the pain quickly intensifies, becomes tearing and pulsating, which in most cases indicates that the primary inflammation has turned purulent.
The period during which an acute form of tooth root inflammation can last is from several days to 2 weeks. In this case, two successive stages are distinguished.
- 1st (phase of periodontal intoxication). Severe, persistent aching pain is the main sign indicating the beginning of the development of the inflammatory process. Often the patient feels heaviness in the area of the affected tooth and complains of a dull pain, which sharply intensifies when trying to bite.
- 2nd (exudative). In this phase, inflammation of the tooth root is characterized by very strong pain that does not subside without the use of analgesics for almost a minute. Unbearable pain is now caused not only by biting, but even by a slight touch of the tip of the tongue to the affected tooth. Most patients complain of the feeling that the diseased tooth is “pushing out”, which to some extent corresponds to reality, since it acquires increased mobility. In the exudative stage, the adjacent soft tissues may swell and the lymph nodes may become inflamed.
Chronic inflammation of the tooth root
Diagnosing the chronic form in a timely manner is difficult for two reasons. First, many patients do not have the signs and symptoms characteristic of acute apical periodontitis, and complaints may be misleading. Secondly, the clinical picture of chronic periodontal inflammation is in many ways similar to other diseases, for example, some complex types of pulpitis.
The following signs and symptoms may indicate the development of chronic tooth root inflammation.
- There is usually no constant or prolonged pain, but severe discomfort is often felt when pressing and biting on the affected tooth.
- A weak, intermittent feeling of heaviness and fullness, intensifying from time to time.
- Bad breath.
- Change in tooth color (not to be confused with carious stains).
- The occurrence of fistulas.
- Enlargement of regional lymph nodes, their pain.
- Unpleasant sensations when pressing on the gums.
During a diagnostic examination, the dentist usually identifies a deep cavity, the probing of which causes severe pain in the patient. The diagnosis is made based on the X-ray obtained.
Possible causes of toothache
Caries at different stages can cause pain in the teeth. As a result of poor oral hygiene, tartar forms on the teeth, and as a result, caries develops. Gradually, the tooth enamel will be destroyed, and the internal sensitive tissues of the tooth will begin to be affected. In the first stages of caries development, the tooth may react painfully to hot and cold. When the nerve is already inflamed, toothache may occur as a result of food or water coming into contact with it. Self-medication will not help here: the cause of pain can only be eliminated in a doctor’s office;
abscess or gumboil. Purulent deposits form directly in the gums. In this case, the pain in the teeth is quite sharp and throbbing. There is severe swelling in the oral cavity; in particularly severe cases, the entire cheek may become swollen;
Pulpitis is a logical continuation of advanced caries, which causes severe pain in the teeth. When a tooth hurts due to pulpitis, unexpected severe attacks can be experienced at any time of the day or night, with irradiation into the ear or temple;
Mechanical damage . Tooth trauma, chipped enamel, damage to the crown of the tooth - all this will inevitably lead to pain. If the enamel is damaged, but the nerve remains intact, then pain may not occur immediately, but if you do not consult a doctor in a timely manner, an inflammatory process of the pulp may begin;
Various gum diseases - periodontitis, periodontitis, exposure of the necks of teeth. All these diseases often begin with bleeding gums and have very serious consequences, including tooth loss. Therefore, they definitely require treatment at the dentist’s office.
What salt should you use for rinsing?
The simplest salt is suitable for the procedure, which is stored in a cabinet in any kitchen. To rinse with salt for gum inflammation and toothache, you can use table, sea or iodized salt. But you need to give up powder with flavorings and bath salts. Dyes and other chemical components have an adverse effect on the mucous membrane.
By the way, if toothache or inflammation of the gums caught you on vacation at sea, you should not look for the nearest manufactured goods in southern countries. Simply rinse your mouth with sea water containing healing salt. The main thing is to collect water not near the shore, but away from the swimming area, in an area where it does not stagnate.
How to rinse your mouth correctly?
For the saline solution to work effectively, it is important to rinse your mouth correctly:
- Make sure the rinse solution is warm, but not hot or cold. In no case should you burn the already inflamed mucous membrane, and cold water, on the contrary, will increase the pain. By the way, if cold water helps relieve toothache, this indicates purulent inflammation of the nerve.
- Before rinsing, brush your teeth thoroughly: it is important to remove all food particles.
- The rinsing procedure should last at least 5 minutes, but the solution should be changed every 30 seconds.
- When rinsing with salt for a toothache, you should tilt the solution more towards the diseased tooth.
- You should rinse your mouth as often as possible, preferably once an hour.
- After rinsing, no matter how hard it is, you should not rinse your mouth with clean water. Try to be patient for at least 5 minutes.
Recipes for saline solutions and their uses
Here are the most effective recipes used for gum inflammation and toothache.
Simple saline solution
How to cook:
Take a glass of warm water (temperature about 30 °C), add 2 teaspoons of salt and stir well.
How to use
: Rinse your mouth according to the diagram below.
Salt and soda
Rinsing with soda and salt is effective for both gum inflammation and toothache. The mixture is also suitable for patients with acute reactions to salty foods. The tandem of salt and soda will be effective both in the presence of tartar and periodontitis.
How to cook:
Mix 1 teaspoon of baking soda and 1 teaspoon of salt in a glass of warm water.
How to use:
Rinse after brushing your teeth using the above method. Also, some dentists recommend using the solution after tooth extraction. In this case, you need to rinse your mouth very carefully so as not to injure the formed hole.
Salt + soda + iodine
You can add 2-3 drops of iodine to the solutions described above - it will enhance their disinfectant effect.
How to cook:
Mix 1 teaspoon of salt, 1 teaspoon of soda and 2-3 drops of iodine in a glass of water. The latter will enhance the disinfecting properties of the mixture.
How to use:
Rinse according to the indicated method every 2 hours.
Sea salt
How to cook:
For a glass of warm water, take 1 level teaspoon of sea salt.
How to use:
Rinse your mouth once an hour according to the above scheme. By the way, sea saline solution can be used not only for toothache and gum inflammation, but also as a preventive measure for various dental diseases. In addition, sea salt will give your teeth whiteness and strengthen the enamel.
Some people also use salt as toothpaste, first grinding it to a powdery state.
Salt + vodka
How to cook:
In a glass of warm water you need to add 2-3 tablespoons of vodka and 1 teaspoon of salt.
How to use:
It is worth using the vodka solution very carefully so as not to burn the oral mucosa. Rinsing is acceptable 2-3 times a day.
Salt with herbs
Saline solutions, if desired and necessary, can be supplemented with herbal decoctions. Simply put, the warm water in the glass should be replaced with a healing decoction. Which one? Choose the most pleasant and useful herbs for your situation.
- Chamomile and sage
. To prepare the solution, mix 1 part chamomile, 3 parts mullein and 2 parts sage and pour boiling water over the mixture. The mixture should sit to room temperature. Then you need to add 2 teaspoons of salt and rinse the tooth. - Oak bark.
1 tablespoon of oak bark should be poured with boiling water and kept in a water bath for 20 minutes, and then, after removing from the heat, leave for 40 minutes. The resulting cooled broth is decorated with 2 tablespoons of salt, then the crystals are stirred and used for rinsing. - Seed and strawberry
. For this decoction you should take 1 part of string, raspberry leaves, strawberries, and 2 parts of mint. Pour boiling water over the mixture of herbs and let it brew to room temperature, then strain and add 1 teaspoon of salt. You should rinse the tooth with the solution 9-10 times a day. - Plantain, chamomile and rose petals.
This aromatic mixture should be poured with boiling water and allowed to brew, then add salt and rinse the tooth. The solution will relieve pain, soothe and disinfect the oral cavity.
Herbal infusions are one of the most effective salt supplements. However, in order to prepare the right decoctions, you should follow several rules:
- Prepare the decoction only in enamel or glass containers.
- Adjust the heat to low.
- Use the cooled liquid immediately.
Does salt help gums?
Saline solutions are an excellent remedy not only for strengthening and whitening teeth, but also for sensitive and bleeding gums. Table, sea, and iodized salt are also suitable for preparing salt potions. Use rinses daily, 2 times a day, and within a week you will notice that your gums have become healthier.
However, you also need to rinse your gums with salt correctly:
- Brush your teeth thoroughly with the paste.
- Then remove any remaining food from the interdental spaces using dental floss.
- Rinse your mouth for 30 seconds and repeat the procedure several times.
Salt rinses for gum inflammation
If, while brushing your teeth, you begin to notice blood on the brush, this clearly signals inflammation of the gums and requires an early visit to the dentist.
Salt rinses for gum inflammation can be an excellent aid. Together with herbal decoctions, this white powder can relieve pain, inflammation and swelling of tissues and significantly simplify the patient’s life.
Here are the most popular recipes for salt compositions used for gum inflammation, in addition to the standard ones given earlier:
- Banana paste
. To prepare, several banana skins should be ground into powder. Add 1-2 tablespoons of olive oil and 2-3 tablespoons of pre-crushed sea salt to the resulting composition. You can lubricate the affected areas with the paste, in a couple of days the gums will become strong and healthy - Thyme, oak bark, sage, chamomile
can also be mixed with table salt and soda. You should rinse your mouth with the resulting mixture 1-2 times a day.
Is it possible to rinse your gums with baking soda, without salt?
Of course you can. Baking soda is found in almost every kitchen, as is salt. But, unlike salt, soda only cleans, disinfects and deodorizes teeth and gums without causing unnecessary irritation.
To prepare a soda solution:
- Mix 1 teaspoon of baking soda with a little water. The mixture should become similar in consistency to toothpaste.
- Apply the mixture to your teeth and gums and thoroughly brush your teeth with it in the usual way (with a brush).
- After washing off the composition, you will be surprised at how clean and polished your teeth become, how fresh your breath becomes, and how the soda managed to neutralize the increased acidity of the oral cavity.
Rinsing gums with baking soda
A very simple and at the same time useful procedure is rinsing the gums with soda. After all, baking soda is found in almost every kitchen. To rinse your gums, dilute one teaspoon of baking soda in a glass of boiled and cooled water. A solution of soda can be used for gum inflammation.
When should you not rinse your gums with salt?
You should not rinse your teeth and gums with salt if you suffer from severe tissue inflammation. In such cases, the solution can only worsen the situation. If you are experiencing unbearable pain and suspect serious tissue inflammation, replace the saline solution with one of the following:
- Aloe juice will perfectly eliminate inflammation. To rinse, you need to take freshly squeezed juice and dilute it in half a glass of water. You need to rinse your mouth three times a day.
- Golden mustache also perfectly strengthens sore gums. To prepare the solution, you need to grind a leaf of the plant, and then pour a glass of boiling water over it. The mixture should sit for 30 minutes and rinse your mouth after brushing your teeth every morning.
- Sage is one of the most effective remedies for bleeding gums, which prevents the spread of inflammation. To prepare the solution, you need to infuse 1 tablespoon of sage in 300 ml of boiled water. The composition can be used for rinsing, compresses, and oral baths.
- Oak bark perfectly relieves inflammation of the oral mucosa. To prepare the solution, boil 2 tablespoons of oak bark in half a liter of water, then let the mixture brew and use for rinsing.
- Chamomile flowers are an excellent remedy for gingivitis. To prepare the solution, you need to infuse one spoon of flowers for half an hour, and then cool the solution. The mouth should be rinsed systematically until complete healing.
Instead of a solution of salt and soda, you can also use essential oils to treat gum inflammation. The most popular are:
- Black cumin oil. Perfectly disinfects, relieves pain, eliminates bleeding. It is recommended to rub 1-2 drops of oil into the surface of the gums or make oral baths.
- Tea tree oil is an excellent natural antiseptic that eliminates pathogenic bacteria and relieves bleeding and discomfort. To prepare the solution, you need to dilute 2-3 drops of oil in a glass of water and rinse your gums after each meal.
- Sea buckthorn oil quickly heals inflamed tissues and relieves pain. The oil can be used for mouth baths, applications, rubbing, or simply hold a tablespoon of oil in your mouth for 2-3 minutes.
An effective and, most importantly, safe alternative to natural remedies is Asepta Active mouth rinse, used for gingivitis, periodontitis, stomatitis and toothache. The product has a pronounced antibacterial effect, prevents inflammation and bleeding of the gums, prevents the formation of plaque and freshens breath.
Tooth pain in children
An adult can still endure toothache. But when a child has a toothache, it is no less painful for a parent, since it can be very difficult to help in such a situation. Pain in the teeth, or more precisely in the gums, begins in the first year of life, when the baby begins to teethe. In this case, there is no need to urgently run to the dentist for help. A scheduled visit to a specialist as part of a scheduled medical examination is sufficient.
Special teething toys with a cooling effect, toothpastes and silicone brushes for babies, as well as local painkillers will help relieve your baby’s toothache during this period. The most popular and safest for the health of children are Kalgel and Cholisal.
If the problem is not teething, and the baby is worried about something else, for example, problems with the gums or oral mucosa, this is a reason to urgently consult a doctor. Even at such an early age, a dentist can diagnose candida or gingivitis. Proper oral hygiene and timely local treatment will help quickly solve the problem.
Your baby may experience toothache when baby teeth emerge. The very first serious disease is bottle caries. An incorrect diet and prolonged use of a bottle can lead to complete loss of the front baby teeth, so regular visits to the dentist are mandatory from an early age.
After bottle caries, the most common caries of baby teeth can develop. It is very difficult to treat such teeth, since fillings do not adhere well to small teeth. It is much easier and more effective to prevent the development of the disease. Today, pediatric dentistry offers many ways to preserve baby teeth.
Treatment of inflammatory processes of tooth roots
Let’s make a reservation right away: treatment is possible only in a highly qualified dental clinic. The pathology is serious, and therefore requires an accurate diagnosis and thoughtful treatment, which can be either conservative or surgical.
With the conservative method, the following is carried out:
- X-ray diagnostics.
- If there are old fillings, they are removed to give access to the dental canals.
- Mechanical cleaning of canal cavities and removal of nerve endings.
- Expansion and antiseptic treatment of canals (for tissue disinfection).
- Treatment by placing a medicinal mixture into the cavity and then installing a temporary filling.
Then, at a subsequent visit to the dentist, the temporary filling is removed; if the inflammation has stopped, a permanent filling is performed. In particularly difficult cases, two visits for a complete cure will not be enough, and up to several weeks or even months of therapy will be required. Upon completion of all treatment measures, a control x-ray is taken. During the healing period, antibiotics and other antibacterial drugs may be prescribed.
If the dentist sees that conservative methods of therapy will not bring the desired result or the procedures already performed have not produced a positive effect, surgical intervention is indicated. Surgical treatment of acute and chronic periodontitis involves removing the upper or slightly larger part of the root, and sometimes completely eliminating the tooth and the inflamed root.