Teeth hurt when you have a cold or runny nose: what to do if your jaw hurts
Toothache during a cold is quite common.
Moreover, those teeth that were previously completely healthy can suffer. Discomfort may also be observed in the gums, and the condition is accompanied by fever, cough and runny nose.
Why do teeth hurt when you have a cold? Most often, pain is explained by pressure generated in the maxillary sinuses.
Why do teeth hurt when you have a cold?
In addition to high sinus pressure, the causes of pain in the teeth and gums may be due to the following factors:
What to do to eliminate pain
If the cause of the pain is known, it is easier to find treatment methods.
The very first thing to do in case of severe pain is to take an analgesic. If the sensations do not disappear even after eliminating the cold, the patient should consult a dentist.
Tooth pain can develop due to inflammation of the trigeminal nerve. In such a situation, the following methods will help the patient:
- heating with electrophoresis;
- ultrasound and laser therapy;
- magnetic therapy;
- taking painkillers.
Traditional methods of treatment are often used for dental treatment.
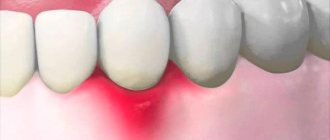
Rinsing the mouth with soda solution. This measure will relieve inflammation from the gums and eliminate pain.
Typically, the basis of such drops is valerian and camphor. Both of these substances have a calming effect.
Lozenges of mint tablets will also help eliminate discomfort in the mouth during a cold. You need to put several pieces on your tongue at once, so the effect will come much faster.
A hot decoction of sage helps with toothache. The liquid is taken into the mouth and held for several minutes, then spat out.
Propolis is an effective remedy for toothache. This substance will not only eliminate pain, but will also prevent a purulent abscess.
It is impossible to get rid of acute pain using traditional medicine. Here a doctor will come to the patient’s aid, but usually the symptom disappears immediately after the cold is eliminated, that is, the cause of the discomfort in the teeth and gums.
As for colds, the video in this article will show you what to do at the first sign of a cold.
- Ears hurt when you have a cold: how to treat complications at home
- Headache due to sinusitis: what to do if you have a headache
- What to do with the flu if you get sick during an epidemic
I don’t know how it is with a cold, but when sinusitis worsens in spring and autumn, my teeth constantly hurt. To stay awake all night and suffer from terrible pain, just take a walk in the fresh air before bed.
Prevention methods
Doctors have several recommendations on how to prevent the manifestation of the disease, which causes pain in the nose and head. They include the following activities:
- support for general immunity, including proper nutrition, sufficient vitamins, regular physical activity;
- tests for suspected allergies to identify the irritant and stop contact with it;
- timely diagnosis to identify sinusitis, neoplasms and other dangerous diseases that may progress over time.
The Clinical Brain Institute specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of all types of headaches, including those associated with nasal diseases. To receive recommendations for treatment and prevention, all you need to do is make an appointment and undergo a full examination. Our center is equipped with modern tools for diagnostics and treatment procedures, and our doctors are experienced specialists in a narrow and broad profile.
Teeth hurt when you have a cold or runny nose: what to do if your jaw hurts
Toothache during a cold is quite common.
Moreover, those teeth that were previously completely healthy can suffer. Discomfort may also be observed in the gums, and the condition is accompanied by fever, cough and runny nose.
Why do teeth hurt when you have a cold? Most often, pain is explained by pressure generated in the maxillary sinuses.
Why do teeth hurt when you have a cold?
In addition to high sinus pressure, the causes of pain in the teeth and gums may be due to the following factors:
What to do to eliminate pain
If the cause of the pain is known, it is easier to find treatment methods.
The very first thing to do in case of severe pain is to take an analgesic. If the sensations do not disappear even after eliminating the cold, the patient should consult a dentist.
Tooth pain can develop due to inflammation of the trigeminal nerve. In such a situation, the following methods will help the patient:
- heating with electrophoresis;
- ultrasound and laser therapy;
- magnetic therapy;
- taking painkillers.
Traditional methods of treatment are often used for dental treatment.
Rinsing the mouth with soda solution. This measure will relieve inflammation from the gums and eliminate pain.
Typically, the basis of such drops is valerian and camphor. Both of these substances have a calming effect.
Lozenges of mint tablets will also help eliminate discomfort in the mouth during a cold. You need to put several pieces on your tongue at once, so the effect will come much faster.
A hot decoction of sage helps with toothache. The liquid is taken into the mouth and held for several minutes, then spat out.
Propolis is an effective remedy for toothache. This substance will not only eliminate pain, but will also prevent a purulent abscess.
It is impossible to get rid of acute pain using traditional medicine. Here a doctor will come to the patient’s aid, but usually the symptom disappears immediately after the cold is eliminated, that is, the cause of the discomfort in the teeth and gums.
As for colds, the video in this article will show you what to do at the first sign of a cold.
- Ears hurt when you have a cold: how to treat complications at home
- Headache due to sinusitis: what to do if you have a headache
- What to do with the flu if you get sick during an epidemic
I don’t know how it is with a cold, but when sinusitis worsens in spring and autumn, my teeth constantly hurt. To stay awake all night and suffer from terrible pain, just take a walk in the fresh air before bed.
Symptoms of acute sinusitis
- Unilateral or bilateral pain over the cheek area that extends to the upper jaw, can also affect the upper row of teeth, the teeth of the upper jaw may ache constantly
- feeling of pressure on the eye
- local redness of the skin of the nose, cheeks and eyelids
- headache, mainly in the temporal and occipital region of the head
- hyposmia (decreased sense of smell)
- nasal congestion
- discharge of mucus or pus from the nose
- hearing loss
- temperature is about 37, with acute inflammation above 37
- General weakness, weakness
The diagnosis is made based on the patient's complaints. Your doctor will perform a thorough examination to look for inflammatory changes that are causing your symptoms. Imaging tests, such as a cranial x-ray or CT scan, may be added to the examination for a more accurate diagnosis (this test visualizes the sinus cavities very well, so it is the preferred method). They evaluate the extent of damage to the sinus cavities, which is useful for proper treatment. In addition, laboratory tests may be performed, such as nasal cytology, sinus biopsies, and tests for immunodeficiency diseases that may accompany acute sinusitis.
The settlement of Krasny Yar has developed healthcare and wonderful resort places to live, the rural settlement of Novy Buyan - but sometimes even there people get sinusitis and their teeth hurt, the village of Svetloye Pole are there any problems in this settlement with dentistry and treatment of the upper teeth as a preventive measure for sinusitis, the village of Staraya Binaradka among the pine trees - you can only catch a cold while hunting. Running around with a gun through the winter forest - what could be better! The main thing is, without colds and sinusitis, you should take care of your nose.
Treatment of acute sinusitis
It is necessary to make a differential diagnosis between a viral and bacterial infection. A viral infection is expected to last between 7 and 10 days, whereas a bacterial infection is expected to last for a longer period. This is extremely important because infections caused by viruses cannot be treated with antibiotics, nor do they work in antiviral therapy. In addition, prescribing antibiotics for a viral infection carries the risk of developing antibiotic resistance. Antibiotic prescriptions can vary significantly between regions. This is due to the circulation of different strains of microorganisms in different parts of the country and the corresponding recommendations for regional health units after monitoring. Because of this, the drugs listed below are for informational purposes only and in no case for self-medication; it is quite possible that in your region they will do nothing but harm. Moreover, modern standards require different courses and different combinations, tested by practice and scientifically recommended. Antibiotic treatment is prescribed if complaints persist for more than 10 days. A 14-day course of antibiotics is given using one of the following antibiotics suitable for the treatment of acute sinusitis (first-line antibiotics):
- Amoxicillin
- Clarithromycin
- Azithromycin
Second-line antibiotics should be considered for the following conditions: Presence of microbial communities (associations) with a high frequency of resistant microorganisms (See Biofilms).
- Persistence of symptoms after antibiotic treatment.
- Lack of general improvement in the patient within 48-72 hours from the start of antibiotic treatment
The most common second-line antibiotics are:
- Amoxicillin with clavulanic acid
- Second or third generation cephalosporins
- Macrolides
- Clindamycin
It should be noted that the gold standard of treatment is preliminary culture and determination of the sensitivity of microflora to antibiotic therapy; based on the culture data, the doctor chooses a treatment strategy. Let’s say that treatment for acute and chronic sinusitis can differ significantly, since as the process becomes chronic, the spectrum of flora shifts to the gram-negative side.
As for the general treatment of acute sinusitis, the following medications are used to relieve symptoms. Some of the ones used:
- nasal decongestants
- antihistamines
- antipyretics
- antitussive drugs such as fluimucil
- topical corticosteroids
The rural settlement of Bolshaya Kamenka, Krasnoyarsk region, if you have a stuffy nose and a high temperature, can you take a steam bath in the village of Bolshaya Rakovka, how to cure sinusitis, what are the symptoms and complications after the flu and corona, the village of Kommunarsky, I got sick with the virus, now I only feel purulent odors and yellow crusts in my nose. My head hurts in the morning, what should I do?
Toothache due to cold #8212; Why does my jaw hurt so bad and my temples ache?
Compared to it, other symptoms of ARVI become unnoticeable factors. The patient is constantly looking for ways and methods to get rid of toothache. Let’s figure out why when you have a cold, your teeth often hurt, your jaw ache, and your gums ache, and we’ll also find out what you can do at home to relieve pain and improve the general condition of the body.
Where to look for the roots of the problem?
Typically, toothache during a cold is a collateral deviation in the functioning of the body and is not something special.
But the reasons may be completely different, which few people think about:
- Insufficient oral hygiene . The patient, due to weakness, fever and chills, gets out of bed only when absolutely necessary. People stop paying attention to such necessities as rinsing the mouth after eating and brushing their teeth. In this condition the teeth
When there is a river of snot and a fever, there is no time for oral hygiene#8230;
In this case, the situation can be corrected without outside help. It is necessary, no matter what, to carry out oral hygiene procedures.
You also need to control the amount of aggressive substances entering the body and gradually destroying healthy teeth. Food should not contain sour, cold, hot, spicy or too sweet ingredients.
How can this be unpleasant and dangerous?
If the respiratory process is accompanied by painful aching sensations in the gums and teeth, this may indicate the emergence of health-hazardous conditions. They may be:
To identify the exact cause, you need to seek help from specialists. In such cases, you cannot self-medicate at home. This can lead to serious consequences. Sinusitis, for example, can progress to a stage where surgical intervention is indispensable.
How does it feel?
It is known that patients with a cold infection may experience both mild and acute pain in the teeth, jaw and gums.
Why do teeth hurt when you have a cold?
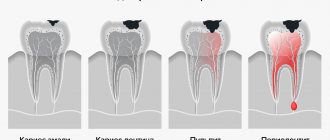
The causes of toothache are divided into 2 groups: caused by a cold, due to an exacerbation of a chronic disease or its manifestation due to a weakened immune system.
Teeth hurt when you have a cold due to:
- increased pressure on dentin due to the accumulation of mucous secretions and poor circulation in the respiratory tract - the tooth root begins to ache, and when opening the mouth, there is pain in the chin;
- an increase in the volume of the thyroid gland - a dull pain covers the jaw, after 30-40 minutes it intensifies in the frontal area, slight numbness of the jaw;
- tonsillitis (inflammation covers all the nerve endings of the teeth) - swelling of the gums, suppuration in the dentin, unstable pain. Changes in temperature in the oral cavity cause severe twitching pain, which is replaced by an unbearable dull pain;
- rhinitis, caused by a cold, is an inflammatory process that covers the bridge of the nose, the frontal bone, and after 2-3 days the pain covers the jaw.
Causes of toothache due to decreased immunity caused by a cold:
- Exacerbation of chronic herpes, periodically manifested stomatitis: aching in the jaws begins when the temperature rises to 38.5-40 degrees. Necessarily bad breath, with a sore throat - ear inflammation. flu - teeth and stomach start to hurt at the same time.
- Immune diseases of bone tissue: pain begins near the ears, itching in the auricles and middle ear. After a few hours, there is a crunching sound when opening the mouth, severe pain radiates into the eyes, and when biting, it shoots into the head.
- Autoimmune: burning gums, pain affects the entire oral cavity.
- Gastrointestinal tract: unpleasant odor, mucus on the gums, constant boring mild pain.
- Periodic nervousness: strong, stable, circles before the eyes may be accompanied by fainting. There is an increase in blood pressure, intracranial pressure rises at night or in bright light. Teeth ache when exposed to irritating sounds.
Reference! If the enamel is not damaged, regardless of the etiology of the disease, teeth never react to sour, sweet, or changes in temperature. With rhinitis, a headache precedes a toothache.
First aid: what to do if your teeth hurt
Rinse your mouth with soda solution. If the pain is concentrated in one area, apply honey and alcohol to the gum (for 2 tablespoons of hot honey, 1 teaspoon of alcohol). Do not hold for more than 30 seconds. Rinse your mouth with chamomile decoction: 1.5 tsp per 200 ml of boiling water. daisies. Boil for 2-3 minutes. Strain and let cool.
If you have aching jaws, heat the salt. Wrap with a linen towel several times. Place under your cheek. Change position every 5-7 minutes.
If the enamel is damaged, rinse with boiled, settled water or add 1 tbsp per 200 ml. l. aloe juice Strictly prohibited: salt, soda, acetic and citric acid. Rinse only as directed by a doctor.
For immune and autoimmune diseases, you can use medications as prescribed by your doctor. Folk remedies aggravate the course of the disease and favor the crumbling of bone tissue. For autoimmune diseases, rowan, pomegranate and carrot juice are strictly prohibited. The pain goes away, immunity increases, but the disease worsens. Teeth may begin to fall out.
After cancer, rinse with water and beet juice in a ratio of 1:1. If there is a putrid smell - 1 tbsp per 200 g of mixture. l. garlic juice or 200 ml of boiling water, 1 tbsp. l. chamomile, calendula and valerian. Boil in a water bath for 3 minutes. Do not use the decoction for more than 12 hours.
In case of suppuration, rinse your mouth with boiled water before using rinse solutions. Herbs and alcohol thicken the pus. It remains in the tissues.
For bone tissue diseases, use non-concentrated decoctions, do not use alcohol tinctures, or decoctions containing herbs that have a drying effect. An infusion of chamomile is desirable.
How to treat toothache
If your teeth begin to react painfully to a cold, consult a doctor as soon as possible! Perhaps a toothache combined with a cold poses the threat of a more serious illness!
To begin treatment for the disease as soon as possible, consult a therapist. If you start with the dentist, you will spend several days redirecting for additional tests, or highly specialized treatment will be prescribed, without taking into account the cause and consequences of the cold. Only the therapist has the opportunity to refer patients to all laboratory and instrumental examinations carried out in this clinic.
If negative sensations do not go away during treatment, you should contact your dentist and get tested for tumor markers. Aches in the jaws can be the result of inflammation of the soft tissues of the cervical spine, displacement of a vertebra, compression of muscles or nerves, or suppuration near them. Also, periodic inflammation of the middle ear provokes pinched nerve endings - shooting pain from the head to the tooth.
Before you start treating toothache during a cold, you should take into account that during a cold, microelements are washed out of the bone tissue, and tooth enamel becomes more fragile.
Medicines
Medications act faster than traditional medicine, but have a lot of side effects, often cause allergies, reduce immunity - accelerating the development of colds and increasing the risk of complications.
Causes
The TMJ connects the lower jaw and the temporal bone of the skull. This is a very mobile joint, actively moving during speech, chewing, swallowing, and if its normal functioning is difficult, then the person’s quality of life suffers significantly. The tissues surrounding the joint have many nerve endings, and even minor disturbances in the functioning of the TMJ lead to discomfort, pain and deterioration in the general condition of a person. A complete clinical and instrumental examination will allow us to find out the exact cause of the pain and differentiate the pathology from other problems in the maxillofacial area.
Prevention
Prevention consists of preventing colds and preserving the integrity of tooth enamel:
- Do not brush your teeth with toothpastes containing sodium lauryl sulfate - fluoride compounds, which are part of tooth enamel, are destroyed.
- In winter, try to eat fresh vegetables and fruits grown in a greenhouse, preferably with organic fertilizers.
- Do not alternate hot and cold foods.
- Harden the body with a gradual decrease in temperature.
- Visit the dentist at least 2 times a year.
Why do teeth hurt and gums become inflamed during colds, flu and ARVI, how to treat the oral cavity?
Many patients are faced with the fact that during the flu or ARVI, not only their throat and head hurt, but also their teeth, gums or cheekbones (see also: what to do if your cheekbone hurts when chewing near your ear?). Why does this symptom occur? Most often, discomfort is caused by pressure arising in the maxillary sinuses, as well as the active proliferation of bacteria in the mouth. If your teeth hurt due to a cold, they usually do not need to be treated - the discomfort will go away after recovery. However, sometimes pain in the teeth and gums can be a complication of a serious disease that cannot be treated at home.
What can hurt your nose?
The most common cause of nasal pain is inflammatory reactions . They occur in response to the penetration of pathogenic microflora or mechanical damage. Inflammation can begin in any area, but often spreads to adjacent areas and affects several structures simultaneously. It often begins on the mucous membrane, as this is where the immune system's initial fight against viruses and bacteria occurs. Then the process can spread to the skin and subcutaneous tissue, cartilage tissue, blood vessels and nerves, paranasal sinuses, and nasopharynx.
Pain in the jaw due to ARVI
Inflammation of the trigeminal nerve
Toothache during a cold can be a consequence of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve (see also: what to do if the dental nerve has caught a cold?). This disease develops due to a viral infection and inflammation in the jaw joint. The infection that penetrates the nerve and plexus of blood vessels quickly spreads and sometimes makes the whole face hurt.
The patient feels that his jaw is aching and his teeth hurt on the side where the inflammation develops (we recommend reading: which doctor to see and what to do if your jaw hurts?). The disease is accompanied by slightly noticeable swelling of the face, and when trying to yawn or swallow food, the person feels severe discomfort.
What to do to reduce pain? It is worth remembering that you cannot self-medicate. Using a heating pad at home is strictly prohibited - improper heating of soft tissues can aggravate the inflammatory process and pain. In addition, discomfort in the cheekbones and teeth can be caused by otitis media or inflammation of the articular sac of the lower jaw, and not the nerve. In these cases, diagnosis and treatment is carried out by an ENT specialist, not a neurologist.
If there is an inflammatory process in the trigeminal nerve, the specialist will prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics. One of the commonly used drugs for this diagnosis is Carbamazepine. Physiotherapy is also used for treatment: electrophoresis, ultrasound and magnetic therapy.
There are several methods to reduce dental discomfort due to inflammation of the trigeminal nerve:
- use dental drops purchased at a pharmacy;
- suck mints;
- chew a piece of propolis or apply it to the gum;
- Take a little hot sage decoction into your mouth and hold it on the side where the tooth aches.
What if it’s sinusitis?
In some cases, a cold or flu can cause a serious complication in the form of sinusitis. The maxillary sinuses are located next to the upper jaw, and many people have teeth quite close to them. Due to the development of the disease and the concentration of fluid with pus in the sinuses, pressure on the bone increases, causing pain in the oral cavity. Sometimes sinusitis provokes pain in the temples, cheekbones, the pain spreads to the entire upper jaw and intensifies when the head is tilted.
Severe inflammation in the maxillary sinuses can lead to the formation of bags of pus on the gums or an abscess and cyst on the root of the tooth. Then the patient will need treatment aimed at eliminating the underlying disease and the complications caused by it. As a rule, the patient is prescribed antibiotics and physiotherapy, and then he is sent to the dentist for further treatment.
For extremely advanced sinusitis, a specialist uses a puncture. The sinus is pierced, after which the accumulated fluid, which is a source of infection, is washed out of it. A complete cure will require from 3 to 10 procedures.
To ease breathing, vasoconstrictor drops are used for 5–7 days, as well as drugs that thin the mucus in the nose. Sinupret, a product based on natural ingredients, is often used in therapy.
The relationship between nose and head pain
The nose is one of the sections of the respiratory system. It consists of several departments interconnected. If diseases occur on the visible part of the nose, they are easy to diagnose. However, nasal pain can be caused by damage to the internal parts that are located inside the skull. To understand why the nose hurts and radiates to the head, it is worth familiarizing yourself with its structure.
- The outer nose is the visible part. Its shape is formed by cartilage and several bones, as well as facial muscles. This is the first section into which the inhaled air penetrates, so it is initially purified from small particles and microorganisms.
- The nasal cavity is an expansion formed by bones and cartilage. Its posterior part narrows and passes into the nasopharynx.
- Paranasal sinuses (paranasal sinuses) are additional cavities that are located on opposite sides of the nasal cavity. There are anterior and posterior sinuses.
All parts of the nose are covered with mucous membrane. It is continuous, contains nerves and vessels, and connects to the epithelial layer of the oropharynx. The nasal mucosa has a distinctive feature - it contains olfactory receptors, with the help of which the nervous system is able to distinguish odors. In addition, it is the first barrier against viruses and bacteria that enter the body with inhaled air and can cause infectious diseases of the respiratory system.
Diseases that cause nasal congestion and discomfort reduce the supply of oxygen to the lower respiratory system. This causes insufficient nutrition of tissues, especially brain cells. Most colds are accompanied by a headache, which occurs due to respiratory failure. In addition, colds are accompanied by swelling of the mucous membrane, inflammatory processes, and increased formation of exudate.