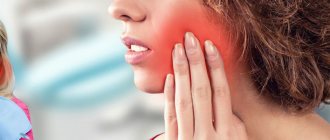
What is toothache like?
The symptoms of toothache, although difficult to confuse with anything else, can manifest themselves in completely different ways in terms of intensity, duration and location.
There are the following types of toothache in medicine:
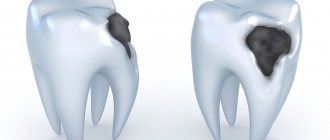
- Short-term sharp toothache while eating sweet food: serves as a signal of early stage caries, as well as erosion. You can eliminate the pain by simply rinsing your mouth. But this does not mean that you should calm down on this - because if left untreated, the pain will return, and the disease will continue to develop. A timely visit to a doctor will completely eliminate toothache due to caries and preserve healthy tooth tissue.
- Passing toothache, often after exposure to low/high temperatures: appears with medium and deep caries - when the nerve is at a close distance from the bottom of the carious cavity, which increases its susceptibility. If you put off visiting a doctor with such a toothache, inflammation of the nerve may become a natural result.
- Toothache from cold or during brushing: characteristic of increased tooth sensitivity, the presence of wedge-shaped defects, exposure of the neck of the tooth, pathological abrasion, and erosion. All these pathologies lead to thinning of the enamel and exposure of dentin, which contains the processes of nerve cells, resulting in pain. You can relieve pain with special toothpastes for sensitive teeth.
- Prolonged aching toothache is also under the influence of different temperatures: it can be caused by inflammation of the nerve. If the tooth reacts to cold, then this is serous inflammation, if it is hot, then the inflammation is purulent. In both cases, you need to contact a dental clinic as soon as possible, otherwise this may lead to complete loss of the tooth.
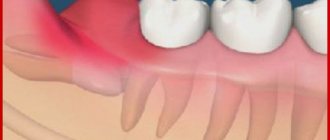
- Constant, acute toothache, throbbing in one tooth: in most cases, this is a sign of the development of periodontitis. With such a toothache, the gums swell and the tooth may become loose.
- Toothache when pressed, accompanied by a feeling of fullness: can be caused by chronic periodontitis, which has worsened due to stress or a cold. In this case, a granuloma or cyst forms on the root of the tooth, which can only be diagnosed using special equipment. Therefore, in this case, you should under no circumstances delay visiting a dentist, because if you ignore this toothache, gumboil or abscess will not take long to appear.
- Acute toothache at night in the entire jaw: signals diffuse pulpitis or exacerbation of chronic pulpitis - both are acute inflammation of the dental nerve. Often such toothache radiates to the ear and temple. You need to see a doctor urgently!
Therapy and rehabilitation
Treatment of the disease is carried out by two methods - conservative and surgical. The choice of method depends on the form of the disease, its severity, and the course of the disease. In the early stages of development of the pathological process, conservative treatment is possible by prescribing a complex of drugs:
- broad spectrum antibiotics
- anti-inflammatory;
- painkillers;
- antipyretic.
IMPORTANT! Conservative treatment requires careful compliance with all doctor’s instructions until the process is completely eliminated. Otherwise, there is a risk of the disease becoming chronic.
Purulent periostitis is treated by wide opening of the purulent sac with dissection of the periosteum to the bone. At the same time, the issue of treating the tooth that caused the inflammatory process is being resolved. Most often, such a tooth is removed. After removing the pus, medications are prescribed, including antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and painkillers. Additionally, physical therapy may be prescribed: UHF, microwaves. The patient is recommended to frequently rinse the mouth with a solution of baking soda or sage tincture.
Simple periostitis requires complete rest of the injured area and treatment with physiotherapeutic procedures. All other types are reduced to treating the underlying disease or eliminating the focus of fibrous tissue growth.
IMPORTANT! Under no circumstances should you treat flux yourself. It is especially not recommended to pierce a purulent sac: there is a high risk of infection in neighboring tissues.
To speed up the treatment and recovery processes, you can resort to traditional medicine methods.
Causes of toothache
Let us examine in more detail the reasons that provoke the appearance of various types of toothache in adults and children:
- Caries
- Exposure of dentin at the neck of the tooth
- Chips and cracks of traumatic origin
- Pulp inflammation
- Periodontitis
- Fluoride and calcium deficiency
- Wedge-shaped defect in the area of the tooth neck
- Abscess or purulent inflammation on the tooth root
- Angina and myocardial infarction
- Respiratory diseases
- Pathology of the temporomandibular joint
- Nervous system diseases
- Malignant formations in the maxillofacial area
- Severe stress
You may also experience toothache when wisdom teeth erupt; in this case, you need to consult a doctor to understand whether the tooth is developing correctly and whether there is enough space for it. In addition, one of the causes of toothache is inflammation due to poor treatment of caries and pulpitis. You may also experience toothache under the crown due to incorrect installation. Therefore, it is very important to take a responsible approach to choosing a clinic and a doctor.
If a patient has a toothache after dental treatment, then this is a normal reaction of the tooth to the intervention of a specialist. It goes away within 1-3 days. Toothache after tooth extraction is also a natural consequence of injury to surrounding tissues.
What is dangerous about severe inflammation of tooth tissue?
If measures are not taken in time, the inflammatory process can lead to:
- to the formation of granulomas, cysts, abscesses;
- pulp death;
- loosening of teeth;
- removal or loss of teeth;
- spread of infection to the jaw bone (flux);
- development of general diseases, including myocardial infarction.
It is very important to start treating tooth inflammation on time, and even better, to prevent it. Many clinics provide services for the treatment of dental inflammation. It is worth choosing one that has gained a lot of experience, has its own diagnostic base, and provides guarantees for the doctor’s work.
What to do if you have a toothache?
The answer to the question: “What is better for toothache?” - can be only one. This is a visit to the dental clinic. However, the time and place do not always allow this to be done without delay. In this case, you can try to relieve the pain yourself. Here are some first aid options for toothache:
- If discomfort occurs when eating food, brushing your teeth or rinsing with warm water/soda solution will help against toothache and swelling of the gums. You can also use a decoction of chamomile, mint, oregano, St. John's wort and sage.
- Refrain from chewing food with a sore tooth.
- For some time, severe toothache can be pacified by applying a piece of ice to the sore tooth.
- Acupressure of the hands in the area where the bones of the index and thumb touch will help reduce the intensity of pain. Nerves pass through this zone, and massage helps to “deceive” them, switching attention to another stream of information.
Important!
Often, with the most severe toothache in an adult, it is recommended to apply honey or cotton wool soaked in strong alcohol to the tooth so that under their influence the nerve stops sending pain impulses to the brain. But can such a compress eliminate toothache? Depends on the specific clinical case. Sometimes this is really a solution, and sometimes this method can provoke even more severe inflammation.
Before and after dental treatment at the Ilatan Clinic. Works by Zarivny S.S.
If you have an acute toothache, where should you go urgently?
At home, you can reduce or stop pain for a while, but there are situations when severe toothache in an adult or child is unbearable and is accompanied by swelling or fever. In this case, you need to immediately contact the clinic, if necessary, 24 hours a day. This way, you have a much better chance of getting enough sleep, because caries can be removed in a few minutes, but you can suffer with a tooth at home for many hours. But where to go with acute toothache at night? If it is not possible to contact the dentist on duty, seek emergency help for toothache in an ambulance. Specialists will administer a pain-relieving injection, which will help you wait until your visit to the dentist.
Treatment of toothache
When a toothache occurs, it is very important not to get carried away with self-medication, since in fact this is not a treatment at all, but only a temporary solution to a problem, the development of which can lead to serious consequences. Only a specialist can diagnose the cause of inflammation and prescribe adequate treatment for toothache. It is possible that to determine the source of pain, an x-ray or examination using a radiovisiograph or 3D tomograph will first be required.
It is extremely important to establish as early as possible whether the pain is a consequence of diseases in the oral cavity, or whether it is the result of other pathologies. For example, one of the common causes of toothache is psychosomatics. Then you will need to continue treatment with a specialist of the appropriate profile.
Prevention
Flux is easier to prevent than to treat. Prevention methods are simple and known to almost everyone. They consist of timely treatment of carious teeth, timely removal of the gum hood from wisdom teeth, the correct choice of toothbrush and toothpaste, and timely replacement of oral hygiene products. It is recommended that you visit your dentist at least twice a year and have your teeth professionally deep cleaned to remove plaque at least once a year.
IMPORTANT! Don’t forget about strengthening your immune system and giving up bad habits.
Dental flux is an unpleasant disease that requires treatment by specialists at an early stage of development. Self-medication in case of periostitis is unacceptable. With a favorable course and initial stage of development, conservative treatment is possible, but most often they resort to the surgical method.
Will painkillers help?
If a very severe toothache does not go away, and massage and other non-drug methods do not help, you will have to take painkillers. There are 4 groups of drugs that are used against toothache:
Based on ibuprofen, ketoprofen, nimesulide and ketorolac:
considered one of the best for eliminating acute toothache in the jaw, they are considered non-steroidal drugs. However, these are still not completely harmless substances, since they put a strain on the kidneys and liver.
Based on paracetamol:
do not relieve inflammation, but block pain impulses sent to the brain. That is, the tooth hurts, but the person feels the pain less intensely.
Based on analgin and aspirin:
can slightly reduce pain due to the anti-inflammatory effect. However, aspirin reduces blood clotting, so you should not drink it to reduce pain after tooth extraction.
Antibiotics:
have antimicrobial properties, but are unable to quickly relieve pain. They allow you to reduce inflammation during toothache only after a long course, and after that the pain will return. Therefore, you should take antibiotics only if you have been without access to places where you go for toothache for a long time, and there is nothing other than antibiotics in your first aid kit.
It is important to understand that none of these drugs will get rid of the cause of toothache - after taking them, the intensity of the discomfort will only decrease temporarily. Many, well aware of this, continue to ignore the problem, switching to regular medication. Under no circumstances should you do this, since you will not only not eliminate the problem, but you will acquire a lot of new ones - painkillers have many limitations and negatively affect other human organs.
Symptoms of tooth inflammation
Inflammation is the body's response to bacterial attack. Tissues begin to produce immune cells, signaling the hematopoietic organs that more white blood cells are needed. As a result, the vessels dilate, and the place where the microbes have penetrated swells and turns red. Nerve endings connect the pain syndrome so that we react as quickly as possible.