Tonsillitis in children and adults is quite common. A person can get chronic tonsillitis several times a year.
The tonsils are located at the back of the throat on both sides. They serve as a kind of filter, trapping microbes that can enter the respiratory tract and cause an inflammatory process. The tonsils produce antibodies to fight bacteria, but sometimes the tonsils can also become infected. When infected by bacteria or viruses, the tonsils become enlarged and inflamed. Tonsillitis begins.
Depending on the causes, tonsillitis can be viral or bacterial. Tonsillitis can be acute or chronic, depending on the course of the disease. Sore throat is an acute form of tonsillitis. The disease can be caused not only by bacteria or a virus, but also by hypothermia, physical exertion or low immunity. With insufficient treatment, acute tonsillitis can develop into a chronic form.
In severe forms of chronic tonsillitis, a child may experience complications in the form of rheumatism, damage to the valvular apparatus of the heart, leading to heart disease and the development of heart failure. If the disease is not treated promptly and correctly, it will lead to kidney disease. Other complications of tonsillitis include acute inflammation of the ear and sinuses. Exacerbation of tonsillitis during pregnancy can cause complications on a woman’s body and also negatively affect the development of the baby.
Causes of tonsillitis
The cause of bacterial tonsillitis is the bacteria hemolytic streptococcus group A. The disease can begin due to various herpes viruses, influenza, other types of streptococci, mycoplasmas, and chlamydia. Chronic tonsillitis occurs after suffering from tonsillitis, scarlet fever, measles and other infectious diseases.
Tonsillitis is transmitted from a sick person by airborne droplets and from an infectious carrier. The disease develops against the background of reduced immunity, hypothermia, heavy workload, stress, malnutrition, and others. Tonsillitis can often occur during pregnancy, as the woman’s body’s defense mechanisms are weakened. If you start the process of sore throat or treat it incorrectly, it develops into acute tonsillitis.
Local causes of tonsillitis include conditions in which nasal breathing is impaired. The disease can begin due to a deviated nasal septum, the formation of adenoids or nasal polyps. The chronic form of tonsillitis often occurs against the background of purulent sinusitis and dental caries. Unfavorable climatic conditions, environmental pollution and hazardous production can trigger the development of chronic tonsillitis.
Read more about tonsils
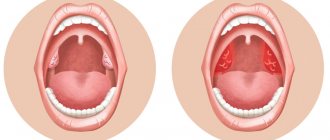
It must be said that the palatine tonsils are the largest lymphoid formations of the entire pharyngeal ring, and they play, perhaps, the leading role in the disposal of bacterial and viral infections that enter the pharynx by airborne droplets.
Due to their size, the palatine tonsils are the first to stand in the way of microbes that enter the oral cavity from the external environment, and protect the body from infection by viruses, bacteria, spirochetes, protozoa and other microorganisms.
The palatine tonsils have depressions - lacunae, which in turn are exit holes for deep and sharply convoluted canals - crypts, which are located in the thickness of the palatine tonsil, leading to its root. The number of lacunae and crypts can vary from 1 to 14, but on average, in each amygdala there are from 4 to 7 lacunae. The diameter of the lacunae can also vary, depending on gender, age, individual characteristics of the patient, as well as the duration and severity of the disease and the presence of scar changes in the tonsils themselves.
It is believed that the wider the exit hole - the lacuna - the higher the likelihood of the palatine tonsil to self-cleanse. This statement is true. Accordingly, the smaller the diameter of the lacuna, the more pronounced and severe the tonsillitis. Moreover, if the tonsil produces a large amount of caseous-necrotic detritus (plugs), the severity of the course also noticeably increases.
Normally, on the mucous membrane of the palatine tonsils, as well as in the thickness of the palatine tonsils, in the lacunae and crypts, there is a growth of non-pathogenic and conditionally pathogenic microflora, in normal (permissible) concentrations. If there are more microorganisms (for example, due to intensive growth, or the addition of other pathogenic microflora from the outside), the palatine tonsil immediately destroys and utilizes the dangerous infection and normalizes a dangerous condition for the body. At the same time, the macroorganism, that is, the person, does not notice this in any way.
The tissues of the palatine tonsils produce the following main protective substances: lymphocytes, interferon and gamma globulin.
The palatine tonsils act as a serious infectious and inflammatory barrier and are an important component in creating not only local, but also general immunity in the human body. Therefore, when it comes to removing the palatine tonsils, you first need to think ten times, weigh the pros and cons, and only after that make a decision about removing the tonsils.
Symptoms of tonsillitis
An infectious disease that causes inflammation of the tonsils is tonsillitis. The main signs of the disease are an increase in temperature, possibly up to 40 C, after a recent cold. Patients complain of dry throat mucosa, severe cough (to the point of vomiting), loss of strength, and migraine. Eating becomes unbearable for the patient due to severe pain when swallowing. There is also a change in the size of the lymph nodes. The disease occurs in several forms (chronic and acute).
Symptoms of tonsillitis appear acutely at the initial stage of the disease. The temperature rises quickly, headache, chills and fever, weakness, acute pain in the throat, which gets worse when swallowing and talking. Severe muscle and joint pain may occur. The acute form of tonsillitis in children is most often accompanied by such unpleasant symptoms as nausea, abdominal pain and vomiting, and enlarged lymph nodes.
The disease can last from five days to a week. If no complications arise, the patient recovers and recovers. The lymph nodes may be enlarged for another ten or twelve days.
In the chronic form of tonsillitis in children, the following symptoms are observed:
- slight increase in temperature in the evening;
- weakness and increased sweating;
- unpleasant taste and odor in the mouth;
- sore throat when talking, swallowing and eating;
- burning sensation in the tonsils;
- feeling of a lump in the throat;
- With a strong cough, purulent crumbs are released.
In complex forms of chronic tonsillitis, a child may experience unpleasant sensations in the form of:
- lack of air, suffocation;
- pain in the heart area;
- pain in joints and muscles;
- discharge in the form of liquid pus in the lacunae of the tonsils;
- increased heart rate and shortness of breath.
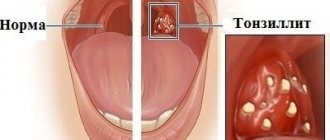
A pronounced sign of tonsillitis is enlargement of the tonsils, which can be seen during a routine examination of the throat. The acute form of tonsillitis manifests itself as a bright red color of the tonsils, while in the chronic form the tonsils are dark red. Depending on the development of the disease, white plaque, film, pustules and ulcers may accumulate on the tonsils.
Danger
Tonsillitis is not a disease that can be fatal, but it can cause serious complications. Thus, patients are often diagnosed with:
- peritonsillar abscess;
- formation of ulcers on the tonsils;
- acute rheumatic fever 1-4 weeks after recovery;
- joint inflammation;
- the occurrence of acquired valvular heart defects;
- kidney diseases;
- chronic pharyngitis;
- tonsillar sepsis (infection through the bloodstream spreads throughout the body).
Exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis
Factors contributing to the exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis: chronic fatigue, frequent nerves and stress, lack of sleep, lack of rest, a large number of “harmful enterprises” near the house, a large amount of radiation, heavy smoke, toxic materials in furniture and chemicals. A large amount of proteins and carbohydrates in food, less than two liters of fluid drunk per day, dirty water with impurities, working in a dusty or gassy place.
With an exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis, the lymphoid tissue becomes rough, and scars form on the lacunae. In these places, purulent foci appear that contain pus, microbes, food debris, these products enter other organs with the blood. Due to the constant inflammatory process, allergies can begin. With an exacerbation of the disease, tonsillitis can progress to the stage of acute tonsillitis (tonsillitis), parotonsillar abscess.
Symptoms of chronic tonsillitis in a simple recurrent form: the edges of the arches swell, pus accumulates in the lacunae, purulent plugs appear, pain when swallowing, enlarged lymph nodes, sensation of a foreign body in the throat, bad breath. With an exacerbation of the symptoms of chronic tonsillitis, this form turns into a sore throat, which can bother the patient up to three times a year. With angina, the body temperature rises to 38 degrees and above, weakness appears, aches in the muscles and body, headache, dizziness, lymph nodes enlarge, pain is felt when palpated, with good treatment the disease goes away in a maximum of a week.
With an exacerbation of the symptoms of chronic tonsillitis in the form of a parotonsillar abscess, the temperature rises to 38 degrees or more, weakness, headache, pain in the body and muscles, soreness and burning of the throat, fever and fever appear. After a few days, the patient has difficulty swallowing due to swelling of the throat, it is difficult or impossible to drink and eat, and open his mouth.
In the toxic-allergic form, in addition to the usual symptoms, others appear: a feeling of intoxication, pain in the joints and heart, severe fatigue, and fever. Diseases in the form of ARVI, colds and flu take quite a long time to be treated. Another option for the development of a toxic-allergic form: due to an infection that accumulates in the tonsils and spreads throughout the body, the functions of the liver, kidneys, and joints deteriorate significantly. Possible heart problems: instability of heart rhythm, heart defects.
Treatment of exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis does not differ from the treatment of sore throat. The patient should be provided with silence, complete rest and bed rest. Food should be crushed; it is best to give the patient liquid food in the form of porridges and purees. You should drink a large amount of warm liquid per day (compotes, milk with butter and honey, water, tea with raspberries). You should definitely call a doctor for further treatment instructions. Usually the doctor prescribes macrolites and penicillin antibiotics. If any drug gives a positive result, it can be used during the next exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis.
Diet
Patients with acute and aggravated tonsillitis should follow diet No. 13. It is aimed at quickly removing toxins from the body and strengthening the immune system. Products must be steamed or boiled. Meals should be fractional and in small portions. It is important to drink at least 2.5 liters of fluid per day for adults and 1.5 liters for children.
The list of recommended products includes:
- yesterday's wheat bread;
- meat and fish broths;
- steamed meatballs and cutlets;
- dairy products;
- viscous and semi-liquid porridges;
- jam, marmalade, honey;
- rosehip decoction, weak tea.
During treatment of acute and exacerbated chronic tonsillitis, the following should be excluded from the diet:
- baked goods, rye bread;
- millet, pearl barley porridge;
- fatty meat, fish;
- fatty cheeses, whole milk;
- hot seasonings, spices;
- strong tea, coffee;
- alcohol;
- cabbage, radish, radishes, legumes.
Diagnosis of tonsillitis
Chronic tonsillitis is not diagnosed during an exacerbation (sore throat), since all factors will reflect the acute course of the process, but not its chronic course. The most reliable signs of chronic tonsillitis are purulent contents in the crypts and anamnesis indicating very frequent sore throats.
Exacerbations of chronic tonsillitis occur about 2-3 times a year, rarely - up to 6 times a year. Even sore throats that occur once a year are considered frequent. However, non-angina forms cannot be excluded, when the patient does not have a sore throat, but at the same time has pronounced pharyngoscopic signs. Similar signs are typical for 4% of patients with chronic tonsillitis.
An important sign of chronic tonsillitis is an increase in regional lymph nodes (often accompanied by pain) at the angle of the lower jaw and along the sternocleidomastoid muscle. Chronic tonsillitis is almost impossible to determine using laboratory diagnostic methods (blood tests, bacteriological and cytological studies).
The best method for diagnosing chronic tonsillitis is to analyze a group of general and local symptoms and objective signs. The disease can be suspected based on the purulent contents in the crypts and frequent sore throats.
Treatment of tonsillitis
Treatment methods for tonsillitis include conservative therapy, local and general. Removal of tonsils for tonsillitis is performed if conventional treatment does not help and this can cause complications in other organs.
How to treat tonsillitis? General methods of conservative treatment include hardening procedures: gymnastics and other outdoor sports, hardening and wiping with water, regular moderate physical activity. They play a big role in supporting the immune system, but they cannot be used for acute or chronic forms of tonsillitis and in the period in between. General therapy includes various physiotherapeutic procedures: irradiation with short-wave ultraviolet light, laser therapy, phonophoresis, diathermy. They can be carried out for general or local symptoms of tonsillitis in the interval between its acute forms.
Local treatment of tonsillitis involves lubricating the tonsils and their lacunae with solutions of iodine tincture, Lugol, iodine glycerin and others. The main effect of the solutions is not an antibacterial effect, but an anti-inflammatory, soothing and astringent property. They help relieve acute pain and normalize food and water intake.
How to treat chronic tonsillitis? The main method of treatment is taking antibiotics. Most often, the patient is prescribed protected aminopenicillins. Treatment of the chronic form of tonsillitis can be complicated by the fact that the resorption capacity of the palatine tonsils decreases and sclerotic processes occur around the lacunae.
Antibiotics for tonsillitis
Treatment of tonsillitis with antibiotics is prescribed by a doctor, who takes into account the sensitivity of the microorganism to a specific drug. It is worth remembering that if the causative agent of tonsillitis is a viral infection, then in such a situation antibiotics will simply be ineffective.
Penicillin antibiotics are most often prescribed to treat this disease. These drugs are completely and quickly absorbed in the intestine. Before their appointment, a smear must be taken in order to determine the type of pathogen.
Antibiotics for chronic tonsillitis are prescribed during an exacerbation of the disease. There are two types of antibiotics:
- First-line drugs are penicillins. Their functions include both the treatment of exacerbations of the disease and the prevention of rheumatism and glomerulonephritis, which are caused by hemolytic stretococci;
- second-line drugs - macrolides.
As for penicillins, semi-synthetic drugs in tablet form are now most often prescribed: amoxcillin, oxacillin, ticarcillin. Although, of course, the most effective are inhibitor-protected penicillins, which are resistant to microbial enzymes due to the addition of clavulanic acid.
If the causative agent of the disease is Staphylococcus aureus, then antibiotics for tonsillitis for adults are prescribed - aminoglycosides. These antibiotics have fewer kidney side effects.
The method of surgical treatment of tonsillitis cannot always eliminate a chronic infection completely, since it spreads not only to the tonsils, but also to the surrounding tissue, lymph nodes and other areas. If chronic tonsillitis continues for a long time, it can lead to the development of a pronounced infectious and allergic process.
Recently, cryotherapy has been used in the treatment of chronic tonsillitis. The tonsils and back wall of the pharynx are exposed to low temperatures. Thanks to this, the altered surface layers of tissue are destroyed and pathogenic microflora is eliminated. After cryotherapy, the pharyngeal mucosa returns to normal and is restored, the tonsils fully retain their functions. The advantage of this method compared to surgery is the absence of pain, bleeding and complete tissue restoration.
You can search for cheap medications in pharmacies after doctor's prescriptions through our website. They are also easy to book online, saving you money and time.
To treat or not to treat?
This question is often asked by patients suffering from periodic exacerbations of this disease. Many are sure that it is pointless to treat it, since the symptoms will return again. Yes, the treatment of chronic inflammation is a long, complex process that requires a lot of patience from the patient and high qualifications and experience of the otolaryngologist. The bacteria that cause the disease adapt very quickly to antibiotics. Therefore, it is extremely important and necessary to cure the disease in its acute form, all its manifestations. Others do not consider this disease dangerous in principle: unpleasant, yes, but not dangerous. Both approaches are completely wrong!
You cannot treat the disease carelessly, much less let its development take its course. If the disease is not cured, the bacteria can spread to other organs, causing serious complications: for example, joint diseases, myocarditis, glomerulonephritis.
Pregnant women are at particular risk: if a woman is planning a child, it is simply necessary to treat tonsillitis. After all, the disease can provoke miscarriage or premature birth. In addition, the disease greatly complicates the course of pregnancy and affects the fetus.
Surgical treatment of tonsillitis
If conventional treatment methods do not help and complications occur in other organs, the patient is prescribed surgery to remove the tonsils. First of all, for such complications as: rheumatism, nephritis, endocarditis and cholangiohepatitis. In most cases, removal of the affected tonsils significantly improves the patient's condition and reduces the extent of pathological complications in the affected organs. But the surgical method does not help in all cases.
It may happen that treatment of acute tonsillitis with standard methods does not bear fruit. The tonsils can swell so much that it will be extremely difficult for the patient to breathe any further. Then they are simply removed surgically. No one disputes that tonsils are an important part of the body's immune system throughout life and that everything should be done to avoid having them removed. But such a procedure is still better than the prospect of constantly suffocating from lack of oxygen. There are also nuances here. Most operations are performed using a scalpel. However, there are many alternatives to this traditional method. Many countries practice removal of tonsils using lasers, radio waves, ultrasound energy or electrocoagulation. These methods are much less painful than using a scalpel.
Like all surgical procedures, each has its own advantages and disadvantages. Here you need to consult a doctor to choose the best option.
Complications
Chronic tonsillitis is very dangerous due to rapidly occurring complications. The most severe of them are heart disease - myocarditis, inflammation of the joints - rheumatism and serious kidney damage - glomerulonephritis.
Some toxins that are produced by microbes in the tonsils and then enter the bloodstream can damage cartilage and ligament tissue. The result is inflammation and pain in the muscles and joints. Other toxins often cause persistent fever, changes in blood tests, fatigue, depression, and severe headaches.
Chronic tonsillitis can affect the functioning of such a vital organ as the heart. The tonsils are often parasitized by group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus, the protein of which is very similar to the protein found in the connective tissue of the heart. Because of this, the immune system can show retaliatory aggression not only to the emerging streptococcus, but also to its own heart. As a result, heart rhythm disturbances, heart valve prolapses, and even the development of severe myocarditis and bacterial endocarditis occur.
For the same reason, articular surfaces and kidney tissue are at great risk. Unfortunately, the development of diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and glomerulonephritis is extremely high.
Due to the fact that the source of infection remains in the tonsils for a long time, a distortion of the body’s reactivity occurs, resulting in allergic changes. In some cases, just one course prescribed by a doctor can get rid of itching and allergic rashes, and in some cases stop the development of bronchial asthma attacks.
Treatment of chronic tonsillitis at home
The principles and approaches to home treatment are influenced by the patient’s age, the frequency of manifestations of chronic tonsillitis and other factors. In general, there are three important factors that must be performed at home.
The most important thing is to cleanse the mouth and throat and cleanse the body. Chronic tonsillitis (if the tonsils are not removed) provides a slow negative effect on the body, provoking a number of serious diseases over time. Therefore, you need to pay close attention to the health of the liver, kidneys, heart, and gastrointestinal tract. The doctor will tell you what preventive measures to take based on a study of your medical history.
Physiotherapy, rinsing, and the use of traditional medicine are important in the home treatment of chronic tonsillitis. It should be noted that this is not a panacea - it only supports and increases the effectiveness of conservative treatment prescribed by the doctor. In addition, strengthening the body's protective functions makes it possible to reduce the number of transitions of tonsillitis into acute phases.
Rinse for tonsillitis
The goals and objectives of rinsing are as follows:
- wash away purulent deposits, therefore, remove viral, bacterial and fungal agents that provoke inflammation from the throat;
- remove purulent plugs, destroying the breeding ground for bacteria;
- create an environment unacceptable for the life of infectious agents;
- soften and moisturize the mucous membrane of the pharynx, reducing discomfort and pain;
- accelerate the healing process of the mucous membrane, promote epithelial repair.
Rinse solutions for tonsillitis
Most ready-made solutions that are sold in pharmacies are capable of destroying infection in the mucous membrane: Furacilin, Chlophyllipt oily or alcoholic, Miramistin, Lugol's solution, Iodinol, Hexoral, Chlorhexidine, Rivanol.
In addition, you can use folk remedies:
- baking soda solution – creates an alkaline environment. Proportion – 1 teaspoon per 1 glass of water. Effective, has virtually no side effects, does not cause allergic reactions;
- chamomile decoction - restores mucous membranes and relieves inflammation. Chamomile should be boiled in a water bath, strained, left to stand in an earthenware or enamel bowl for up to 40 minutes, strained, and gargled once a day;
- table salt solution - washes out the purulent contents of the lacunae. Can be used in combination with soda solution;
- sage decoction - acts like chamomile decoction;
- A decoction of celandine is one of the most effective remedies. Rinsing with celandine for tonsillitis should be done by preparing tea from the celandine herb at the rate of 1 tablespoon of herb per 1 glass of boiling water. You can use it after 15 minutes of infusion. For each rinse, you need to prepare a fresh solution.
For chronic tonsillitis with frequent exacerbations, you should gargle with sea salt purchased at the pharmacy. The recipe for the solution is also simple - 1 teaspoon of salt per 1 glass of water. Rinse can be repeated 2-4 times a day.
Honey is also suitable for gargling with chronic tonsillitis: add 2 teaspoons to a glass of warm water and stir until completely dissolved. Repeat rinsing 4-5 times a day. With the help of honey, you can treat abscesses and reduce the degree of inflammation of the tonsils. You can add 1 tablespoon of beet juice and 1 teaspoon of apple cider vinegar to the solution to enhance the effect.
It is recommended to alternate rinses throughout the day - this will provide diverse protection for the throat, as well as get rid of possible negative consequences (for example, when rinsing with soda more than 2 times a day, excessive drying of the mucous membrane may occur).
When treating tonsillitis at home, you can lubricate the throat to enhance the effect of treatment. Lubrication is carried out with sea buckthorn oil, propolis infusion (if there is no allergy), Lugol's solution, fir oil, aloe juice with honey (1:3).
Inhalations for the treatment of tonsillitis at home
You can effectively perform inhalations at home. It is important to note that they are contraindicated at high body temperature and severe signs of general intoxication. It is better to carry out inhalations for children after consultation with a doctor. To carry out inhalations, you can use a compact device - an inhaler, which can be purchased at a fairly affordable price.
For inhalations, decoctions of plants that have antibacterial and antiseptic effects are used (peppermint, eucalyptus, sage, pine buds, coltsfoot). You can also use an alcohol solution of propolis, an oil solution of chlorophyllipt. Garlic inhalations are very effective (crush 100g of garlic and stir in 1 liter of boiling water). Inhalations from infusions of eucalyptus, chamomile flowers, and walnuts have a good effect.
Folk remedies for internal use
Conventionally, remedies for folk treatment of chronic and acute tonsillitis by oral administration are divided into decoctions (herbal teas) and tinctures (alcoholic and non-alcoholic), as well as vegetable juices.
Herbal decoctions that provide a certain effect in the treatment of tonsillitis are prepared from medicinal mixtures that can be purchased at a pharmacy or made from herbs that are sold in markets (the first option is still preferable). Herbal decoctions can relieve inflammation, act as antiseptics, and strengthen the immune system. This is achieved due to the presence of essential oils, phytoncides and tannins, vitamins, alkaloids and beneficial resins.
Decoctions for the treatment of tonsillitis
It is better to notify your doctor about taking decoctions so that he can evaluate the correct interaction of herbs and medications. Several recipes for preparing decoctions:
- for an antibacterial effect - mix St. John's wort, coltsfoot, dill, wormwood, thyme, sage, chamomile and calendula flowers in equal proportions. Add crushed eucalyptus leaves. Pour boiling water over the mixture at the rate of 1 glass of water per 1 teaspoon of mixture. Leave for about 4 hours, bring to a boil, strain and drink warm;
- to stimulate the immune system - a pharmaceutical collection of wild rosemary, horsetail, St. John's wort, calamus root and licorice. You can add crushed dry rose hips to it. Prepare a decoction at the rate of 1 teaspoon per 1 cup of boiling water. Drink with honey;
- for general strengthening and effective treatment - teas from sage, rose hips, and medicinal chamomile.
Infusions for the treatment of tonsillitis
The most effective infusions (use after consultation with a doctor):
- Mix fresh coltsfoot juice with red wine in equal proportions. Add onion juice and leave in the refrigerator. Drink 3 times a day, shaking beforehand;
- Mix beet juice, rosehip syrup and lemon juice in a ratio of 5:3:1, leave in the refrigerator for a day. Drink 1-2 teaspoons 3 times a day after meals;
- chop 2 heads of garlic to extract the juice. Add freshly squeezed juice of 1 lemon to them, pour 1 glass of water. Drink 1 tablespoon. The intensity of use depends on the severity of tonsillitis.
Traditional treatment of tonsillitis with honey and products
1 hour before meals you can take 10g of propolis, mixing it with butter. As an option, take 20-30 drops of propolis 3-4 times a day, diluting it in warm water or milk. For prevention, as well as during exacerbations of chronic tonsillitis, you should use an alcohol tincture of propolis, washing it down with warm tea sweetened with honey. It is recommended to add honey to all decoctions and take it orally separately. It effectively strengthens the immune system.
In any case, you should not self-medicate, and your doctor should be notified of any change in condition.
Home treatment for tonsillitis with cold
It is widely believed that proper exposure to cold can strengthen the body's defenses and serves as an effective prevention of tonsillitis. This is generally true, but it is very important to perform these procedures only during periods of remission. In case of acute tonsillitis, this form of treatment will only aggravate the patient’s serious condition and provoke purulent damage to the tissues of the throat. The so-called “cold treatment” consists of moderate consumption of cold drinks and ice cream.
All procedures should be carried out with extreme caution - preferably after consultation with a doctor. Tonsillitis does not respond to traditional or home treatment, so such methods are used to complement basic medical treatment methods.
Prevention of tonsillitis
Prevention of tonsillitis includes hygiene measures and health procedures. It is necessary to keep the room clean, carry out wet cleaning and disinfection, especially in the children's room. It is necessary to regularly visit the dentist to monitor the health of the teeth and oral cavity, where additional infection may accumulate. Rinse your mouth regularly after eating and use the right toothbrush. It is especially important to visit a dentist in childhood, since the development of tonsillitis in children can cause serious complications in all organs and systems.
Measures to prevent tonsillitis include hardening the child, which should begin from a very early age, gradually increasing the temperature and duration of the procedure. Children should walk longer in the fresh air and breathe sea air to clear their airways. It is recommended to regularly engage in gymnastics, swimming and other types of physical activity. Nutrition should be complete, contain nutrients and vitamins to strengthen the child’s immunity. Women during pregnancy should also pay attention to the completeness of their diet and take strengthening vitamins.
During the cold season and periods of flu outbreaks, you should avoid contact with sick people and avoid places where there are many people. You should get a flu vaccination before the cold season. In the autumn and winter, avoid hypothermia, which can cause a sore throat, and subsequently tonsillitis.
Tonsillitis during pregnancy
The inflammatory process in the tonsils with chronic tonsillitis can last a very long time. The disease either subsides or worsens, and symptoms of intoxication caused by waste products of bacteria appear. This process affects the state of the nervous system - drowsiness, lethargy, weak appetite, and in some cases also surges in blood pressure. Upon examination, the doctor finds white cheesy plugs in the gaps, which are particles of dead tissue and leukocytes.
This disease sometimes causes severe toxicosis in late pregnancy. There is a risk of intrauterine infection of the fetus, since microbes from the tonsil area enter the blood. In certain cases, the disease can even cause miscarriage.
In addition, tonsillitis during pregnancy is usually accompanied by a weakened immune system. As a result, the expectant mother’s body cannot properly resist various infections. There is also a risk of premature birth or weak labor activity.
To prevent the negative impact of this disease on the course of pregnancy, the expectant mother needs to eat well and avoid hypothermia. You should also visit doctors in a timely manner, in particular the dentist, in order to promptly identify foci of infection in the body.
The best way to minimize all risks to the fetus is to plan a pregnancy, which means getting rid of the disease before conception. However, most women come to see a doctor already pregnant. When the expectant mother is registered, a chronic inflammatory process in the tonsil area is detected.
Having heard the diagnosis, you should not worry prematurely, and even more so you should not try to get rid of the disease with dubious folk remedies. If an exacerbation of tonsillitis occurs during pregnancy, an experienced doctor will be able to prevent negative consequences for the fetus. The following activities may be prescribed:
- gargling with decoctions and herbal infusions;
- washing the tonsils by introducing an antiseptic solution into the lacunae;
- lubricating the tonsils with antiseptic agents;
- local treatment with sprays.
Treatment of tonsillitis during pregnancy is complicated by the fact that some effective drugs are strictly contraindicated during this special period. Physiotherapy, many antibiotics and antihistamines are prohibited.
Before treating tonsillitis during pregnancy, the doctor weighs the benefits of the drug against the potential harm it can cause to the child. The most gentle medications are selected that will improve the mother’s condition without harming the baby.
In case of exacerbation of the disease, it is necessary to adhere to bed rest. It is recommended to drink as much fluid as possible. Drinks include various fruit drinks and fresh juices, warm milk, and raspberry tea. You need to give up food that irritates the throat, that is, smoked, spicy and salty foods. It is better to focus on purees and cereals, since they do not cause difficulty in swallowing.
Antibiotics are usually prescribed for the purulent form of the disease. In the first trimester, drugs from the penicillin group are prescribed, and in the second and third - macrolides.
Gargling during exacerbation of tonsillitis is carried out almost hourly. In this case, Chlorhexidine, Miramistin, decoctions of medicinal herbs, and salt solution are used.
Surgical treatment of tonsillitis in pregnant women is carried out only when conservative therapy has no effect, as well as when complications develop. Tonsil removal is performed in a hospital setting under local anesthesia. This operation cannot be performed in the last weeks of pregnancy.
Risk group
It is believed that the occurrence of tonsillitis in children and adults is facilitated by factors that negatively affect the functioning of the immune system. Namely:
- frequent stress and anxiety;
- general and local hypothermia;
- living in polluted and dusty areas;
- eating monotonous foods that contain little vitamins B and C;
- disorders of the autonomic/central nervous system;
- injury to the tonsils due to too rough food;
- lymphatic diathesis (enlarged tonsils, lymph nodes, thymus gland);
- chronic inflammatory processes in the nasopharynx.
Tonsillitis in children
Treatment of tonsillitis in children is aimed at alleviating symptoms. Local therapy includes:
- washing the lacunae of the palatine tonsils with antiseptics (chlorophyllipt solution, etc.);
- treatment of the tonsils and posterior pharyngeal wall (fucorcin, lugol);
- frequent rinsing with herbal decoction or warm water with salt;
- inhalation;
- antiseptic aerosols;
- resorption of tablets that have an antimicrobial effect.
Antibiotics are necessary for severe symptoms in cases where clinical signs of the disease do not disappear and the immune system is extremely weakened. In such situations, an antibacterial course is prescribed for 10 days. Erythromycin and penicillin are used to treat tonsillitis in children. While taking a course of antibiotics, relief from the symptoms of the disease may occur as early as 3-4 days. Despite this, it is important to complete the entire course of treatment.
Inpatient treatment of tonsillitis and surgery
Inpatient treatment is only necessary in extremely severe or persistent cases of bacterial chronic tonsillitis in a child—especially in situations where treatment does not respond to oral antibiotics. In such cases, intravenous antibiotics are necessary.
Since tonsils are an important part of the immune system, their removal is best avoided. In exceptional cases, surgery to remove the tonsils is necessary - tonsillectomy. This operation is recommended to reduce the likelihood of recurrence of tonsillitis. It is necessary if:
- the child gets a sore throat five or more times during the year;
- conservative treatment is ineffective;
- symptoms recur within a year;
- there are complications from internal organs.
Most often, a tonsillectomy involves using a scalpel to remove the tonsils. However, recently more and more specialists are using ultrasound, lasers, radio waves or electrocoagulation. Each of these methods has its own advantages and disadvantages. Therefore, it is imperative to discuss with the surgeon which removal method is best for the child. The operation is performed under general anesthesia. Its duration is 30-45 minutes.
Postoperative period
After the operation, the patient can leave the hospital on the same day. And complete recovery takes 10-14 days. The postoperative period is characterized by pain at the surgical site. Therefore, children need to be given painkillers. Children after such operations do not attend kindergarten or school for two weeks. This measure is necessary to reduce the risk of contracting the infection from other children.
Children definitely need to drink plenty of fluids. But it is important to avoid sour, carbonated drinks, as they are a strong irritant. It is imperative to maintain good oral hygiene: regularly brush your teeth and rinse your mouth.
Treatment or removal of tonsils?
Dear patients! If you have visited several specialists in this field, if a course of treatment for chronic tonsillitis has been carried out and none of the methods has brought the expected result, then only in this case should you think about removing the tonsils.
If a conservative approach gives lasting results for 4-6 months or more, then the palatine tonsils are able to fight on their own. Your task is to help the tonsils by regularly sanitizing them and stimulating their work physiotherapeutically.