28.06.2017
Head and neck diseases | Oropharynx and face
Hypertrophy is the growth of tissue. This reaction of the body serves as a response to increased stress on the organ. The most “physiological” example is muscle hypertrophy in weightlifters and bodybuilders. An enlarged liver often indicates intoxication of the body; proliferation of left ventricular tissue - the need to compensate for circulatory disorders caused by lung diseases, hypertension, etc.
Hypertrophy of the palatine tonsils (or tonsils) in most cases indicates that “attacks” on the main entrance gates of the body (mouth and nose) are so intense and frequent that the “personnel” of the “protective garrison” can no longer cope and asks for reinforcements.
The palatine tonsils are part of the immune organ - the lymphadenoid pharyngeal ring. They contain both the birth of new protective cells - lymphocytes (some of them perform their service “in place”, others enter the bloodstream and become available to the body), as well as the formation of very accurate and effective means of neutralizing the “enemy” - antibodies (especially in childhood). Elsewhere in the body, a similar role is played by the spleen, lymph nodes, and intestinal lymphoid tissue (including the appendix).
The palatine tonsils, it turns out, are also involved in digestion in the oral cavity: they contain enzymes that break down various food components.
Causes and course of the disease
Hypertrophic changes in the tonsils are considered as an immunoreactive condition that occurs when the body adapts to changing conditions and mobilizes compensation that has arisen in the lymphoid pharyngeal ring.
This is facilitated by breathing through the mouth, which is caused by hypertrophy of the adenoids, especially in the cold season. If adenoiditis provokes the formation of mucus, which forms in the nasal cavity, infects the palatine tonsils. Hyperplasia (increased cell proliferation) is promoted by infectious diseases and repeated inflammation in the oropharynx and nasal cavity.
Also, this process is influenced by poor living conditions, insufficient nutrition, as well as other factors that can reduce immunity. The size of the tonsils is affected by various disorders in the endocrine system, especially hypofunction (weakening of activity) of the adrenal cortex, exposure to small doses of radiation over a long period of time, hypovitaminosis (lack of vitamins).
The basis for too large an increase in the lymphoid tissue of the tonsils is the active proliferation (proliferation of tissue by cell multiplication) of immature T-lymphocytes and T-helper deficiency, which does not allow the production of full-fledged antibodies. The immunopathological predisposition of the child’s body to lymphatic diathesis, which is caused by hereditary deficiency of the lymphoid system, is influenced. Allergic reactions also influence the formation of hypertrophy of the palatine tonsils.
However, do not forget that hyperplasia is a reversible process. During adolescence, involution (reverse development) of lymphoid tissue occurs.
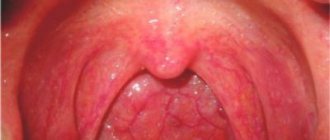
Hypertrophy of the palatine tonsils is often combined with a pathological enlargement of the entire pharyngeal lymphadenoid ring, especially often with hypertrophy of the pharyngeal tonsil (adenoids). Enlarged palatine tonsils generally have a dense and fairly elastic consistency, but in some cases they are spread out and soft on palpation. The palatine tonsils have no signs of inflammation and are not fused to the palatine arches. They have a developed lower pole and a triangular fold below, and the lacunae have a normal structure.
From a histological point of view, there is a predominance of hyperplasia of lymphoid tissue, in which there is an increase in the area of the follicles and the number of mitoses (indirect division), but plasma cells and macrophages are absent.
Hypertrophy of the palatine tonsils has 3 degrees:
- 1st degree - the palatine tonsils occupy 1/3 of the distance from the arch to the center of the pharynx (if measured along the midline of the pharynx);
- 2nd degree – already 2/3 of the distance mentioned above;
- 3rd degree – the tonsils are almost touching.
A microscopic examination reveals a large number of follicles with very frequent areas of mitosis, which indicates a very high activity of lymphoid tissue.
Friends! Timely and correct treatment will ensure you a speedy recovery!
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of hypertrophied tonsils is not difficult. The data from pharyngoscopy are used as a basis. The pathology has several degrees of severity, taking into account the stage of development. The extreme stage involves the contact of the tonsils with each other.
Despite the absence of inflammation, it is necessary to differentiate hypertrophy from chronic tonsillitis and tumors. The latter are represented by lymphosarcoma and lymphogranulomatosis, the characteristic features of which are asymmetry, increased tissue density and metastases.
According to indications, blood tests and biopsies are also prescribed, the results of which help clarify the diagnosis. The fluctuation method used during palpation helps to distinguish hypertrophy from an abscess or cyst. It is usually combined with a diagnostic puncture, which involves suctioning out the contents.
Clinical picture
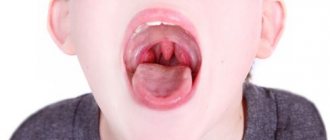
Hypertrophied palatine tonsils have a pale pink color, a smooth surface, clearly defined lacunae and a loose consistency.
They protrude somewhat beyond the edges of the anterior palatine arches. Patients complain of coughing, difficulty swallowing and breathing. There may be a speech disorder that occurs due to changes in the upper resonator, as a result of which the voice becomes nasal. Make an appointment right now!
Call us by phone or use the feedback form
Sign up
Due to brain hypoxia (oxygen starvation), patients sleep very restlessly at night, insomnia and night cough are possible. As a result of relaxation of the pharyngeal muscles, attacks of obstructive apnea (temporary cessation of breathing during sleep) may occur. Due to tubular dysfunction (the initial stage of dysfunction of the system), hearing impairment occurs, and the formation of exudative otitis media (ear inflammation) is possible.
Hypertrophy of the palatine tonsils in children
Often patients are children aged 5 to 7 years with a complicated history of adenoiditis. In such cases, both tonsillectomy and adenoid removal are performed as part of one intervention. The postoperative stage requires you to follow a diet. Food should be non-irritating, gentle, without adding seasonings. The drink is warm.
You can call an ENT doctor at home or make an appointment with a doctor through the form on the website or by calling the clinic. The doctor will examine the throat and, if hypertrophy is diagnosed, prescribe treatment.
The operation can also be performed on an outpatient basis. In this case, it is necessary to ensure constant monitoring of the patient, which is carried out until the final healing of the wound.
Treatment
If there are complaints of difficulty swallowing and breathing, cough, or speech disorders, it is recommended to partially remove the tonsils (tonsillotomy) when the child reaches 5-7 years of age.
But such an operation has the following contraindications: acute infectious diseases, blood diseases, diphtheria bacilli carriage. Tonsillotomy is not recommended for polio outbreaks. ENT surgery can be performed on an outpatient or inpatient basis, both under anesthesia and local anesthesia. It is not uncommon to perform a bilateral tonsillectomy - complete removal of the tonsils.
Tonsillotomy as a method of treating hypertrophy of the palatine tonsils
Far from being the rarest diagnosis in children is hypertrophy of the palatine tonsils. Enlarged tonsils cause one or more problems at once:
- difficulty breathing through the nose
- sleep apnea
- snore
- shortness of breath, shallow breathing
- a sore throat
- speech disorders
- headache
- disturbances in concentration, work ability
Causes of enlarged tonsils
Doctors believe that the sharp growth of cells in the tissues that make up the tonsils is associated with the body's immune response. At an early age, a person is more susceptible to infectious diseases than as an adult. Tonsils, as one of the barriers to infection in the body, are under attack from diseases that can provoke hyperplasia - unusually rapid growth of cells in tissues without signs of inflammation.
How to determine that a child has enlarged tonsils?
Firstly, you need to visit an ENT doctor at least once a year. Upon examination, he will be able to clearly establish the pathology.
Secondly, if a child breathes predominantly through the mouth, this is an alarming symptom; nasal breathing may already be impaired.
Third, pay attention to your child's sleep. Snoring or sudden stops in breathing (apnea) are also evidence of enlarged tonsils.
How to treat hypertrophy of the palatine tonsils?
Often patients do not want to take action if tonsil enlargement does not interfere and does not affect the quality of life. However, it is necessary to treat problems in the throat - there are other organs located near the palatines to which hyperplasia can spread. Often the process involves the pharyngeal tonsils.
There are three types of treatment methods for tonsil hypertrophy: physiotherapy of the throat, surgery and the use of medications.
Physiotherapy of the throat and its organs:
- UHF;
- ozone therapy;
- mud therapy;
- ultrasonic massage.
Drug treatment for enlarged tonsils consists of a combination or isolated use of immunostimulating drugs, corticosteroids, and antibiotics. A solution of silver nitrate is also often prescribed. The drug treatment strategy is determined only by the doctor; you cannot use the drugs yourself.
Operation tonsillotomy
While monitoring the development of tonsil hypertrophy, the doctor may suggest their removal - tonsillotomy. This is a fairly common procedure and the risk of undergoing it is minimal, especially considering the possible consequences of refusing treatment.
With tonsillotomy (as opposed to tonsillectomy), the tonsil is not completely removed, but only the affected part is affected. At the same time, in the future, the tonsils will recover and will be able to continue to perform their function.
This operation is not one of the most complex, but it is performed only by the operating ENT doctor. In Voronezh you can apply for this. Our operation is performed using laser surgery. Laser tonsillotomy does not require general anesthesia; local anesthesia is used.
This operation belongs to the so-called “one-day operations” - after the procedure, the patient does not remain in the hospital, but can safely spend the night at home. The ENT doctor operating on the patient schedules a follow-up appointment in a week to ensure proper regeneration of the mucous membrane.
Contraindications to tonsillotomy surgery
The operation is not performed if:
- The child was diagnosed with diphtheria bacilli
- An infectious disease occurs in an acute form
- History of blood disease
Do I need to remove my tonsils completely?
It is possible, but not recommended unless absolutely necessary. The tonsils still act as a kind of barrier to infections that seek to penetrate the lungs, bronchi or trachea. After partial removal, the organ is regenerated and its functions are restored. Tonsillectomy does not leave the body the opportunity to restore the tonsils - complete and final removal occurs.
You can make an appointment with an ENT doctor by phone +7 or through an online appointment on the website
Complications of treatment
Indeed, there are two directions in the treatment of tonsil cancer with the same outcome, but different techniques: surgical treatment and radiation therapy. It is important to note that these approaches will have different complications.
Radiation therapy may be complicated by bone or soft tissue necrosis and swallowing problems, especially in patients with advanced tonsil cancer. Myelitis, trismus, hypoglossal nerve damage, and long-term risk of another malignancy are also possible.
Complications of surgery include difficulty swallowing, fistula formation, failure of flap healing, poor wound healing, and aspiration of food and saliva, sometimes leading to laryngectomy. The risk of severe and/or fatal complications after surgery is higher than with radiation therapy.
Complications of systemic therapy include fatigue, skin toxicity, mucositis, diarrhea, hepatotoxicity, pneumonitis, hypo- and hyperthyroidism, myelotoxicity, neuropathies, metabolic disorders, etc.
Causes and symptoms of chronic tonsillitis
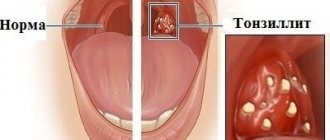
If general immunity is reduced and/or the body has had to face a powerful infectious attack (for example, a sore throat or infection with herpes viruses), a real battle between the immune system and microbes unfolds in the lacunae of the tonsils. As a result, pus, consisting of dead microbes and cells (purulent-caseous plugs), accumulates in the lacunae. Tonsils clogged with pus stop working as an immune organ , and pathogenic microbes thrive in the purulent contents of the lacunae and multiply. These are the so-called plugs in the tonsils. At this stage of the process, it is enough to wash the tonsils from pus and provide a little help to the immune system, after which the normal function of the tonsils is restored.
Chronic tonsillitis, tonsil in section. 1 – lacunae of the tonsil. 2 – the entrance to the lacuna is blocked by a purulent plug. 3 – entrance to a clean lacuna. On the right - vacuum rinsing of the tonsils - a painless and quick procedure. 8-10 seconds - and the plugs are washed with a disinfecting solution.
Symptoms of chronic tonsillitis:
- Painful sensations in the throat area
- Enlarged lymph nodes
- Bad breath
- Sometimes there are headaches
- Sometimes there is discomfort in the ears
- The waste products of microbes from the tonsils enter the bloodstream , poisoning the body (tonsillogenic intoxication); hence fatigue, pain in muscles and joints, headaches, decreased mood, and even, in some cases, a prolonged increase in body temperature;
- Tonsils become a reservoir of infection , from where it can spread throughout the body and cause inflammatory processes (acne, cystitis, prostatitis, adnexitis, dysbacteriosis, inflammation of the paranasal sinuses, etc.);
- Bad breath - it is caused by organic substances decomposing in the gaps; 4. The tonsils stop working as an immune organ , immunity decreases, and the slightest provocation (hypothermia, overwork, stress) can “finish off” the immune system and open the way for germs.
Forecast
The prognosis for patients with HPV-associated tonsil cancer is significantly better than for patients with other etiologies of cancer. It is impossible to predict with high accuracy the life expectancy of a particular patient, but there are average graphs that can be used to determine what percentage of patients with a certain stage are alive after n years: for example, almost 90% of patients with stage I HPV-associated oropharyngeal cancer are alive 4 years after diagnosis, while for HPV-unassociated oropharyngeal cancer at the same stage, only 80% are alive 4 years after diagnosis.
Overall survival of HPV-associated and HPV-non-associated oropharyngeal cancer according to TNM classification 7. ICON-S
Why is chronic tonsillitis dangerous?
Chronic tonsillitis is dangerous due to its complications associated with the spread of infection throughout the body. We often see that after treating tonsillitis, our patients are no longer bothered by all sorts of chronic diseases and allergies. The most severe complications of tonsillitis are rheumatism and severe kidney damage - glomerulonephritis. Toxins produced by some microbes tend to damage ligamentous and cartilage tissues, cause inflammation, as well as pain in joints and muscles.
How chronic tonsillitis affects the heart. Heart valve prolapses and heart rhythm disturbances are common findings when examining the heart in patients suffering from chronic tonsillitis. The fact is that the protein of beta-hemolytic streptococcus group A, which often parasitizes the tonsils, is similar to the protein of the connective tissue of the human heart and joints. Therefore, response aggression of the immune system is possible not only against streptococcus, but against one’s own heart and joints.
Chronic tonsillitis and allergies. Sometimes one course of treatment for tonsillitis is enough for allergic rashes, itching and even attacks of bronchial asthma to “magically” go away. The fact is that the long-term presence of an infectious focus in the tonsils not only reduces immunity, but also distorts its reactivity, causing allergic changes.