Perforation of the maxillary sinus (or, as it is also called, the maxillary cavity) is an iatrogenic complication that occurs during dental procedures on the upper jaw. It consists of perforating the bottom of the sinus, which causes an abnormal communication to appear between it and the oral cavity. Air begins to flow into the mouth through the hole, bleeding from the hole and a feeling of compression in the projection of the cavity are possible. If infectious agents get into the wound, sinusitis develops.
The CELT Dentistry Department invites you to undergo a course of treatment for perforation of the maxillary sinus in Moscow. Our multidisciplinary clinic welcomes leading domestic dentists with decades of scientific and practical experience behind them. They have a modern equipment base for accurate diagnosis and treatment in accordance with international standards. Our dental department has all certificates and licenses, treatment is carried out on the basis of an official contract with guarantees. We use the most effective methods for closing maxillary sinus perforations that provide the best results.
Consultation with a dental surgeon - 1,000 rubles.
Plastic perforation of the maxillary sinus - 7,500 rubles.
At CELT you can get advice from a dental specialist.
- The cost of a consultation with a dental surgeon is 1,000
Make an appointment
Why can odontogenic sinusitis occur?
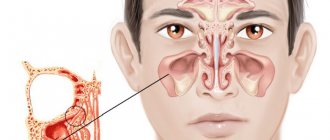
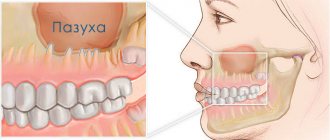
The maxillary (maxillary) sinus is a cavity with bony walls that is located inside the upper jaw. The cavity communicates with the nasal cavity through the anastomosis, which is located on the side wall of the sinus facing the nasal cavity. The lower wall has contact with the upper teeth. Quite often (in about 15% of cases) the apex of the tooth root lies directly under the mucous membrane of the bottom of the maxillary sinus, and there is no bone septum between them.
When an infection enters the maxillary sinus, inflammation of its mucous membrane or sinusitis occurs.
There are two ways of infection:
- rhinogenic - through the nasal cavity. In this case, the infection penetrates from the nasal cavity through natural or artificial (after surgery) communication;
- odontogenic - through the tooth or tissue around it.
Odontogenic sinusitis most often develops slowly against the background of chronic infection in the area of the tooth root. As a result of chronic inflammation, a cyst forms in the root area, which destroys the barrier between the sinus and the tooth. Pathogenic microbes gradually penetrate the sinus mucosa, causing inflammation.
Also, odontogenic sinusitis can occur as a result of the actions of the dentist. Often, after the removal of the upper tooth, the thin barrier between the sinus and the oral cavity may be damaged. As a result, a gateway for dental infection appears. In this case, the anatomical features of the patient with a thin bone septum between the sinus and the tooth root or its complete absence are of key importance.
Infection can occur when cleaning the canals and filling them. In some cases, the filling material gets inside the sinus, causing the formation of fungal sinusitis, and the zinc contained in the filling material promotes the growth of mold fungi (Aspergillus, Mucora). Also, odontogenic sinusitis can develop after the sinus lift procedure and the installation of dental implants in the upper jaw.
Perforation of the maxillary sinus: diagnosis
In order to accurately make a diagnosis, CELT dental surgeons:
- Anamnesis is collected, which includes the removal of an upper jaw tooth or endodontic treatment, surgery to replenish bone volume or implantation of an implant;
- An examination is carried out to identify the cause of the perforation, the hole is probed, and the patient is asked to exhale by opening his mouth and closing his nose;
- The patient is prescribed an X-ray examination of the maxillary cavities and orthopantomography;
- The patient is prescribed an endoscopic examination of the nasal cavities.
Complications
With odontogenic sinusitis, a chronic inflammatory process occurs. Dental microflora appears in the sinus, not typical for the upper respiratory tract, which can destroy bone tissue. Due to the fact that the paranasal sinuses have contact with the orbit and brain, odontogenic sinusitis can lead to severe complications:
- intraorbital (orbital phlegmon, ophthalmitis, optic nerve neuritis);
- intracranial (meningitis, encephalitis, brain abscess).
Therefore, at the slightest suspicion of this disease, you should consult a doctor.
Diagnosis of “dental” sinusitis
Inflammation of the antrum can have several causes and does not necessarily have to come from the teeth. Since treatment should always be cause-and-effect, the doctor must make an accurate diagnosis. In the context of odontogenic sinusitis, unilateral onset of symptoms is typical. Other complaints, such as pain, which is usually worse when bending over, are additional symptoms.
Further investigations include rhinoscopy (nasal endoscopy) and imaging techniques:
- X-ray examinations;
- CT (computed tomography);
- DVT (digital volumetric tomography);
Treatment
The treatment of odontogenic sinusitis requires an integrated approach. As a rule, treatment requires the simultaneous participation of an otolaryngologist and a dentist. Isolated antibacterial and conservative therapy lead only to temporary relief of the condition and removal of the severity of the process.
For a complete recovery, it is necessary to eliminate the source of infection - remove or treat the causative tooth while simultaneously sanitizing the inflamed sinus.
In case of foreign inclusions in the sinus (filling material, sinus lifting material, fungal bodies), their complete removal is necessary. For this, endoscopic techniques are used. They allow you to remove these formations through the nasal cavity. If there is a connection between the sinus and the oral cavity (oroantral fistula), it must be closed using special bioinert collagen-based membranes and mucosal flaps.
What are the maxillary sinuses
The maxillary sinuses (also called the maxillary sinuses) are special cavities on both sides of the nose that are filled with air. Each cavity is connected to the nasal passage by small openings called anastomoses. The cavities are covered with mucous membrane. The function of mucus is to trap bacteria and harmful particles in it, and then remove them from the body through those same anastomoses. When edema occurs, the excretory opening becomes very narrow, as a result of which mucus, along with harmful particles and bacteria, cannot come out and stagnates. At this time, the patient begins to experience bursting pain in the cheek area - this is how inflammation of the maxillary sinus begins. Treatment of the maxillary sinus should not be neglected, since inaction can provoke serious consequences, including sepsis and meningitis.
Classic sinusitis can be bilateral, when both sinuses are affected. In the odontogenic form, the inflammatory process starts in the sinus on which side the diseased tooth is located.
Sinusitis or tooth – what to treat first?
In this case, many otolaryngologists prescribe tooth extraction.
In our clinic, we collaborate with specialists who treat odontogenic sinusitis or help the patient prepare the sinus mucosa for sinus lifting.
Of course, it is not always possible to prosthetize and treat a tooth with a source of infection in the periodontium in the upper jaw. Therefore, such teeth often still need to be removed.
Tooth extraction surgery is a major source of irritation for the body and the immune system. After it, you need to wait 4-6 months until the porous bone tissue of the alveoli is restored.
In this case, conservative anti-inflammatory therapy, antibiotics, and active copious rinsing of the nasal sinuses are prescribed. Treatment lasts about a month after tooth extraction.
If CT and diagnostics revealed a source of infection (cyst or granuloma) on the tooth, then treatment for odontogenic chronic sinusitis begins immediately after removal. Then the chance to reduce inflammatory changes in the mucosa is quite high.
Otherwise, the patient risks getting large growths, which sometimes occupy more than half the height of the sinus.
This is manifested by nasal congestion, because when we have ARVI, the nasal mucosa swells greatly. And our nasal mucosa is exactly the same as in the sinus: the same columnar epithelium. It swells very much when initially, as a result of constant irritation, the infection has already grown by more than half.
In this case, the half of the nose that is more blocked will be an indicator to check what is wrong with the teeth on the same half of the jaw.
Features of the maxillary sinuses
Sinus lift surgery is closely related to the anatomy and functioning of the maxillary sinuses. Each maxillary sinus has the same structure, but has certain differences that the dentist must pay attention to when planning the operation.
There are two main types of maxillary sinus:
- Hyperpneumatized. It is a large volume cavity with increased airiness.
- Hypopneumatized. A small space characterized by sclerotic areas.
When assessing the results of radiography or computed tomography, the dentist always pays attention to the structural features of the maxillary sinus in order to accurately calculate his actions during the operation. In addition, examination of the maxillary sinus is required in order to exclude any signs of an inflammatory process, which the patient may not even be aware of.
Features and difficulties during removal
Extraction of the upper wisdom tooth is complicated by its specific anatomical features.
“Eights” erupt late, when the dentition is already formed. Therefore, very often they are incorrectly located, grow together with the roots of neighboring teeth, grow towards the cheek or even horizontally. Each of these factors complicates the extraction process placed on top of the 8th tooth. But if we compare wisdom tooth removal from above and below, then in the first case the surgical procedure is much simpler. In the upper dentition, the bone is less dense and massive, there are much fewer blood vessels in the soft tissues and the risks of damage to the trigeminal nerve are lower. Therefore, the operation to remove the G8 is easier and safer.
What to do if the bleeding does not stop
Immediately after removing a molar, the surgeon places a tampon on the socket to stop capillary bleeding. The patient needs to clench his jaw and not remove the tampon for 20 minutes. During this time, the blood coagulates and a clot forms in the hole, protecting the fresh wound from the penetration of bacteria into it.
If the patient has high blood pressure or poor blood clotting, the tampon should be kept in place for 40-60 minutes.
When a person strictly adheres to medical recommendations, but the bleeding does not stop, he should contact a dentist for help.
General information about sinus lift surgery
A sinus lift is a surgical procedure that uses the human maxillary sinuses (maxillary sinuses) to fill the bone deficiency in the area of the anterior chewing teeth. The essence of the operation is to separate the mucous membrane from the jaw bone and fill the resulting space with osteoplastic material.
Surgery requires preliminary anesthesia, which can be either local (with or without sedation) or general. Access to the maxillary sinus depends on the type of sinus lift:
- Open method. An incision is made on the front surface of the upper jaw. The technique is performed in cases of severe bone volume deficiency and is considered quite traumatic. The graft healing process lasts on average 3-6 months, after which dental implantation can be performed.
- Closed method. This sinus lift is often performed together with implantation, since the incision is made at the site of the future installation of the artificial root. This operation involves less trauma, but is used only for small deficits, up to 4-6 mm.
The duration of the operation depends on its type, but on average it lasts 1-2 hours. During the rehabilitation period, the patient must strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations in order to prevent serious complications from occurring. These include, first of all, proper oral hygiene, as well as taking the necessary medications.
Carrying out a sinus lift after a maxillary sinusotomy
Sinus lifting for sinusitis is not performed under any circumstances, so the patient is first treated for the inflammatory process. Surgical intervention to replenish bone tissue deficiency after a manipulation such as maxillary sinusotomy is considered possible. The doctor must take into account that the patient has a history of a similar procedure and act much more carefully.
Sinus lifting after perforation of the maxillary sinus is dangerous because the risk of infection in the sinus increases. This occurs due to perforation of its wall, especially with an open operating technique. To avoid such complications, the doctor carefully plans each step of the future surgical intervention, focusing on the data of instrumental studies, in particular computed tomography.
Safe and high-quality removal of wisdom teeth in Balashikha
The Berezka dental clinic offers qualified assistance to anyone who, for certain reasons, requires the removal of a wisdom tooth from above or below. The operations are performed by experienced surgeons using safe anesthesia and modern instruments.
Before the procedure, the dentist collects the patient’s medical history, conducts all the necessary examinations, and only if the clinical picture is present is it possible to extract the wisdom tooth.
The operation is performed in a comfortable environment for the patient. Innovative equipment and professional dentists ensure successful and safe removal of the most complex teeth.