According to antiplagiat.ru, the uniqueness of the text as of October 16, 2018 is 99.4%.
Key words, tags: implantation, installation of Astra Tech Implant System implants, sinus lift, radiography.
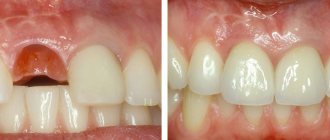
Dental implantation sometimes requires restoration of the lost volume of the jaw bone. And although at first glance this sounds scary, bone augmentation in the oral cavity is today a widespread type of surgical intervention throughout the world and in Russia, in particular.
Historical reference
“Augmentation (Latin augmentatio, from augmentare to increase, strengthen) is the process of restoring or replacing jaw bone tissue. This is not as new a direction in dentistry as it might seem. Bone augmentation began to develop tirelessly in the 19th century, so scientifically based plastic bone transplants were carried out by Walther (Ph. Walther, 1821) and Wolff (1. Wolff, 1863). In our country, the founder of osteoplastic surgery is N.I. Pirogov, who in 1852 performed an operation and initiated bone transplantation on a pedicle. And the first attempts to carry out bone tissue transplantation in the maxillofacial structure were carried out in 1891 by doctors P.I. Dyakonov. and Deshin A.A.”*
Anatomy of human jaw bone tissue
Bone tissue is a special, hard form of connective tissue. Bone tissue cells are represented by osteoblasts, osteoclasts, and osteocytes, which participate in the continuous process of tissue resorption (resorption) and repair (restoration). In both cases, these are normal physiological processes of bone tissue. It is also worth noting that bone resorption (resorption) can simultaneously be a pathological process, provoked by injuries, infections, various types of formations and due to tooth loss. For example, after 2-3 months after tooth extraction, characteristic signs of bone tissue atrophy are observed, since there is no fixation of the roots of the teeth and the bone does not receive the necessary load. This process is characterized by a noticeable decrease in its volume.
The bone tissue of the jaw consists of a spongy and compact layer , which in turn is covered by the periosteum , with the exception of the articular surfaces. Periosteum is a connective tissue rich in blood vessels, has a complex structure and is responsible for nutrition and bone regeneration. Compact bone is a dense and homogeneous bone tissue that makes up the surface layers of bones filled with spongy substance. The spongy layer (substance) has a developed blood vascular network, consisting of trabeculae or bone plates located in different directions and forming a system of cavities in the bone tissue, which makes it look like a sponge. In dentistry, it is the spongy part of the bone tissue that is most used for fixing implants. If the volume is insufficient, this layer has to be restored using augmentation.
Types of Augmentation
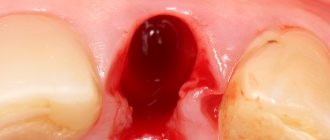
The formation of extensive bone tissue defects is usually caused by infectious processes at the apexes of the roots of the teeth; subsequent removal of such teeth often increases the size of these defects. In the frontal region of the upper jaw, bone loss also often occurs due to dental trauma. All this results in the fact that the volume of bone tissue is not enough to install implants: the alveolar ridge can be very narrow, or its height can be significantly reduced. Depending on this, alveolar process augmentation surgery is divided into horizontal and vertical, according to the direction in which the bone tissue is built up.
Horizontal augmentation is an increase in the width of the alveolar ridge; it is most often performed in the anterior part of the upper jaw and posterior parts of the lower jaw. This is a relatively standard and predictable procedure. The preserved height of the alveolar ridge allows you to use the existing bone volume and gain its width.
With vertical augmentation, the height of the alveolar ridge increases. If there is insufficient volume of bone tissue in height, it is more difficult to isolate and immovably fix the augmented augmentation. Therefore, in dental practice, this operation is considered more responsible, time-consuming and less predictable than horizontal augmentation.
Alveolar ridge augmentation is a preparation for implantation and is usually done several months before. In some cases, bone augmentation is carried out simultaneously with the installation of implants.
Preparatory activities
Before performing augmentation, the specialist prescribes a number of diagnostic studies to determine the volume of bone tissue and the presence of contraindications:
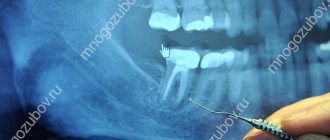
- X-ray examination. Helps identify the presence of chronic pathologies.
- Simulation of the procedure. It is carried out using special programs. Helps the doctor create an action plan.
- Study of bone tissue at the site of implant installation.
The patient should also undergo a number of laboratory tests:
- General and biochemical blood test.
- Urine and stool analysis.
- Blood test for sugar levels and coagulation.
- Analysis for tumor markers.
- A study to determine hormone levels.
- HIV test.
All prescribed procedures must be completed in advance. Shelter is donated in the morning on an empty stomach.
The patient must also properly prepare for the operation and follow a number of recommendations:
- Three days before surgery, avoid all alcoholic beverages and stop smoking.
- Take antibiotics prescribed by your doctor.
- Avoid long-distance travel.
Within two days, a complete sanitation of the oral cavity is carried out to prevent the further development of serious consequences.
Indications and contraindications for implantation using the All on 4 method and technique.
In this publication we will discuss the pros and cons of laser dental implantation.
Here we will talk about the causes of complications after dental implantation.
Types of osteoplastic materials
Currently, a wide selection of both biological and synthetic osteoplastic (osteoplastic) materials are available to restore lost bone volume.
The most important characteristic of augmentation materials is their ability to osteogenesis (bone formation). They are classified according to the severity of this ability. Thus, a distinction is made between osteoinductive materials, which directly affect bone growth, and osteoconductive materials, which are used only as a framework for new bone tissue formation.
In addition, bone material is distinguished by its origin. Thus, the patient’s own osteoplastic material can be used for transplantation. It has always been considered the “gold standard”, since in this case there is complete biocompatibility and they are called autogenous materials. Also, when performing alveolar process augmentation, material from another person is used - allogeneic, of animal origin - xenogeneic, or artificially made materials - alloplastic. The choice of this or that material is determined solely by the dental surgeon, depending on the clinical situation and the desired result.
Recovery period
The sutures are removed 5-7 days after the operation . After this, the patient must follow a number of recommendations in order to prevent material displacement and inflammation:
- Avoid physical activity.
- Follow a special diet for two weeks. Food should not be hard or tough.
- Take medications prescribed by your doctor.
- When sneezing or coughing, do not cover your mouth. A sharp change in the position of the jaws leads to displacement of the material.
- For the first few days, apply cold to the operated area. This helps reduce swelling.
- Regularly clear the nasal cavity of mucus. In this case, it is better to use a cotton pad or napkin. You should only blow your nose with your mouth open.
- Refrain from diving.
- Eliminates air travel.
You should also not drink liquids through straws. If pain, inflammation or other unpleasant symptoms appear, you should consult a specialist.
Indications
Augmentation may be required if the patient, for one reason or another, does not have enough volume of his own bone tissue for reliable fixation of the implant, as well as functional and aesthetic rehabilitation. These reasons may be long-term tooth loss, trauma during tooth extraction, infections, household or sports trauma to the jaw, and other diseases. In addition, bone augmentation is used for periodontitis, when there is a high risk of complete tooth loss, to fill the cavity after removal of a dental cyst and to reduce the depth of the maxillary sinuses, the so-called sinus lift. But in any case, this type of surgical intervention is performed solely for medical reasons.
How to obtain membranes from blood plasma - plasmapheresis procedure
Plasma therapy uses not venous blood taken from the patient, but centrifuged plasma isolated from peripheral blood. The condition of soft and bone tissues is improved through the injection of autoplasma. This autoplasma is also called PRP (platelet-rich plasma), platelet concentrate or gel.
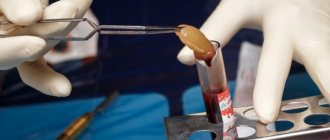
The best results are obtained from plasma containing at least 1 million platelets per 1 μl. To obtain such a concentrate, a plasmapheresis procedure is performed:
- 15-20 ml of blood is taken from the patient’s dental office from the ulnar vein.
- A test tube with blood is run twice in a separator centrifuge for 15 minutes. This is done to separate excess fractions containing red blood cells and white blood cells.
- Fractions used in dentistry - plasma and fibrin clot - are taken from the test tube.
Platelets, fibrin and other biologically active substances are concentrated, forming thick autoplasma (platelet gel). The resulting concentrate is injected into the marginal gum, dentogingival papilla or transitional fold.
In addition, a fibrin clot (blood plasma membrane - PRF membrane) is formed in the test tube. Such a membrane can be cut and stitched for use in various techniques - osteoplasty, tooth extraction surgery after extraction to stimulate reparative processes in the socket.
Membranes for bone grafting are stored for no more than four hours, so plasmapheresis is performed on the day of surgery.
Contraindications
All the main contraindications typical for any type of surgery, including implantation, also apply to augmentation. This operation is contraindicated for people suffering from chronic diseases in the decompensation stage and some mental illnesses in the acute stage. Patients undergoing courses of radiation/chemical therapy, with infectious diseases in the acute stage, as well as during periods of recovery and rehabilitation, during pregnancy and breastfeeding, are also not recommended to undergo surgery to increase the volume of the jaw bone.
Reviews
Augmentation is an important step before implant installation and the procedure cannot be abandoned if indicated.
In the comments, you can leave your feedback about this procedure, how the recovery period went, and what difficulties arose.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Tags augmentation implantation
Did you like the article? stay tuned
Previous article
What are teeth straightening trays and how do they work?
Next article
Improving the quality characteristics of a denture using reinforcement
Age restrictions
There are no obvious age restrictions for alveolar bone augmentation. Thus, this surgical intervention can be performed on children and adolescents to treat bone tissue defects resulting from accidents or diseases, as a result of defective or delayed development of the jaw bones. As for the older generation (adults over 55-60 years of age or more), the main thing is that health indicators are within acceptable limits, which must be taken into account when carrying out this type of operation.
Possible complications
Among the complications and consequences, the development of the inflammatory process as a result of infection is most often diagnosed.
Failure to follow the rules of oral care after surgery causes such a complication.
In order to prevent infection, you should follow all recommendations and take prescribed antibacterial drugs.
Also after augmentation the following is observed:
- Fistula formation.
- Bleeding gums of varying intensity.
- Development of chronic rhinitis.
- Implant mobility.
- Deformation of the maxillary sinuses.
Complications arise due to swelling, hyperthermia and inflammation of soft tissues after surgery.
To reduce the risk of their occurrence , you should carefully observe hygiene rules, take medications and be careful when coughing and sneezing.
Price
The cost of augmentation consists not only of the cost of the operation itself, but also of other factors, including the size and shape of the operated area. It is also important what material will be used for replanting, its volume and manufacturer. It is also necessary to know that augmentation is a complex operation and its successful outcome will require a highly qualified maxillofacial surgeon and an experienced operating team. After all, augmentation can be called a qualitative test of a doctor’s professionalism, since it requires pinpoint precision and places great responsibility on the doctor’s shoulders. Accordingly, the better the specialists performing the operation, the higher the cost of providing the service. Additional costs to consider are x-rays and CT scans. In individual cases, consultation with specialists may also be required for a more complete clinical picture.
It is important to remember that augmentation is one of the main manipulations before implantation and cannot be neglected. After all, the reliability of implant fixation depends on the density of bone tissue, which means the beauty and durability of your smile!
According to antiplagiat.ru, the uniqueness of the text as of October 16, 2018 is 99.4%.
Key words, tags: implantation, installation of Astra Tech Implant System implants, sinus lift, radiography.
* History of the Department of Human Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, Russian National Research Medical University named after. N.I. Pirogov. **Images: Maxillary atrophy: classification and surgical protocols. Astra Tech DENTSPLY Implants. BioHorizons.