In ENT practice, there are cases when a patient comes to an otolaryngologist with complaints of severe nasal congestion and suppuration from the nasal cavity. At the same time, the patient has an elevated body temperature and headaches. But the ENT doctor, having examined the patient, sends him to see a dentist. “Why?”, you will be surprised. Because in this case we are dealing with odontogenic sinusitis.
Sinusitis is a type of sinusitis. The development of sinusitis of odontogenic nature is not associated with colds or acute respiratory viral infections. The main cause of the disease is bad teeth. First, the development of inflammatory tooth disease occurs, after which the inflammatory process from the upper jaw extends beyond the oral cavity and is localized in the maxillary sinus.
Such a state cannot be tolerated. Timely detection of symptoms and diagnosis carried out by a competent ENT doctor will allow timely diagnosis of dental sinusitis and avoid serious complications.
What are the maxillary sinuses
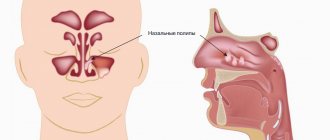
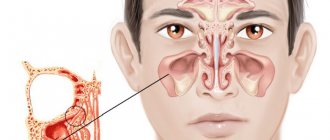
The maxillary sinuses (also called the maxillary sinuses) are special cavities on both sides of the nose that are filled with air. Each cavity is connected to the nasal passage by small openings called anastomoses. The cavities are covered with mucous membrane. The function of mucus is to trap bacteria and harmful particles in it, and then remove them from the body through those same anastomoses. When edema occurs, the excretory opening becomes very narrow, as a result of which mucus, along with harmful particles and bacteria, cannot come out and stagnates. At this time, the patient begins to experience bursting pain in the cheek area - this is how inflammation of the maxillary sinus begins. Treatment of the maxillary sinus should not be neglected, since inaction can provoke serious consequences, including sepsis and meningitis.
Classic sinusitis can be bilateral, when both sinuses are affected. In the odontogenic form, the inflammatory process starts in the sinus on which side the diseased tooth is located.
Treatment methods for acute sinusitis
The mildest disease does not require the use of any special measures or antibacterial agents for treatment. It is enough to take anti-inflammatory drugs to relieve general symptoms and use vasoconstrictor drops to relieve swelling and facilitate the release of mucus.
Sinusitis with a purulent form is treated with the help of antibiotics (for example, Amoxiclav).
Therapy for the acute form of the disease is best supplemented by rinsing the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses. The most effective method of treating sinusitis is Proetz lavage, better known as the “cuckoo” method.
Physiotherapeutic procedures and irrigation of the nasal cavity with antiseptic agents will help to consolidate the effect of treating sinusitis.
Types of odontogenic inflammation
The disease begins with a serous form. It is characterized by swelling of the mucous membrane, nasal congestion, dilation of capillaries, and increased secretion production. Swelling of the tissues leads to a narrowing of the anastomosis, the mucous masses do not find a way out and mucus with pathogenic contents accumulates in the sinus. This is how serous inflammation turns into purulent inflammation.
There are also acute and chronic forms of the disease. Chronic odontogenic sinusitis occurs due to improper treatment of acute sinusitis. Chronic odontogenic sinusitis lasts for years, worsening during a decrease in immunity or when infected.
Odontogenic sinusitis is diagnosed by an otorhinolaryngologist, and treatment is carried out by two specialists: a dentist and an otorhinolaryngologist.
Types of acute sinusitis
There are catarrhal and purulent forms of sinusitis.
Make an appointment right now!
Call us by phone or use the feedback form
Sign up
The name “catarrhal” comes from the medical term “catarrh,” meaning “to flow, drain.” That is, with this form of sinusitis, inflammation of the mucous membrane and its swelling develop quite quickly. Initially, the changes affect only the mucous membrane. Inflammation during sinusitis of this form is accompanied by severe swelling of the mucous membrane - it noticeably increases in size and, as a result, a little later transparent mucus forms. Only thanks to timely treatment, it is possible to prevent the transition of catarrhal forms into purulent sinusitis, which with a high degree of probability can become chronic.
With purulent sinusitis, direct contact of pus with the mucous membrane degenerates it, quite quickly and, what is most dangerous, irrevocably. Thus, with improper treatment or no treatment at all, you can very easily and simply join the army of people suffering from a chronic form of sinusitis.
The cause of the purulent form of sinusitis (acute sinusitis) is bacteria. The secreted mucus contains streptococci, staphylococci, and less commonly pneumococci and fungi, which leads to the appearance of purulent contents in the sinus itself.
Causes of odontogenic sinusitis
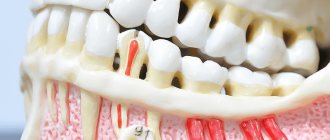
It is very easy to understand why acute odontogenic sinusitis occurs - just look at the anatomy. If you look at the structure of the skull, you can see: the 5th, 6th and 7th teeth of the upper jaw are located very close to the maxillary sinus. There are cases that these teeth even go into her cavity. An infection in a tooth easily thins the already small distance between the tooth and the wall of the sinus and easily penetrates inside, thus starting the inflammatory process.
Development in acute form occurs due to the following reasons:
- Improper oral hygiene.
The most common cause of the disease is neglect of basic rules of oral care: improper and irregular brushing of teeth, delaying a visit to the dentist when there are problems with the teeth. At particular risk are those patients who have been diagnosed with an advanced form of caries with developing necrosis of the dental nerve. - After tooth extraction.
Infection after tooth extraction is associated with the formation of a fistula - a small channel through which the infection enters the maxillary sinus. This occurs when the roots of a diseased tooth enter the maxillary cavity. - Incorrectly installed seal.
Unfortunately, there are cases when the development of inflammation is facilitated by the inept actions of insufficiently qualified dentists. Part of the filling can get into the sinus, and it will immediately be perceived by the body as a foreign particle, and the inflammatory process will start. If after visiting the dentist you have a runny nose, you need to consult an otolaryngologist. - Oral diseases.
Caries, gum disease, periodontal disease, the presence of cysts are all diseases in which there is a source of infection on the oral mucosa. - Reduced immunity.
Decreased immunity leads to the activity of bacteria that are constantly in the oral cavity.
How does an infection in a tooth cause the lining of the maxillary sinus to thicken?
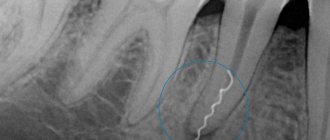
The apices of the roots of the teeth are located under the Schneiderian membrane, that is, under the mucous membrane that lines the bottom of the maxillary sinus.
This is the normal anatomical structure of the sinus - when the tops of the teeth are located in it. Some people have the tops of the fourth, fifth, sixth, seventh there. Some people only have the sixth. Some have sixth and fifth. But, one way or another, they are almost always there.
When a tooth is affected by caries, the infection penetrates through the dentinal tubules into the pulp chamber. Through it, the infection slowly progresses further through the blood and lymphatic vessels into the periodontium of the tooth.
Pulp microvessels emerge from the periodontium directly under the mucous membrane of the sinus, and over time it begins to react with inflammation.
Immune system cells responsible for protecting against infection initiate chronic inflammation. And the mucous membrane gradually thickens. This irritation happens all the time.
Infection from the carious process, which is thus restrained by immunocytes, causes a gradual degeneration of the structure of the sinus lining in the form of polyps and cysts.
Symptoms of the disease
The symptoms of the disease are similar to classic inflammation of the maxillary sinuses. Only a highly qualified otolaryngologist will be able to distinguish odontogenic sinusitis from ordinary sinusitis.
Signs of odontogenic sinusitis are:
- constant nasal congestion;
- purulent nasal discharge with a characteristic odor;
- the appearance of odor from the patient’s mouth;
- pain in the cheek area under the eyes;
- acute toothache in the upper jaw;
- elevated body temperature.
Symptoms also include a general deterioration in well-being, a persistent feeling of fatigue, and problems sleeping.
Specific symptoms of purulent odontogenic sinusitis are pain when lightly pressing on one of the cheeks or when lightly tapping on the teeth located in the area of the inflamed sinus.
Chronic odontogenic sinusitis is manifested by discomfort in the affected sinus area. In general, the patient feels satisfactory until a period of exacerbation occurs.
Are complications possible with acute sinusitis?
With delayed treatment or lack of properly selected treatment, acute sinusitis can become chronic and lead to the development of a number of other serious complications.
Friends! Timely and correct treatment will ensure you a speedy recovery!
Chronic inflammation in the sinuses is the most common complication of acute sinusitis. The chronic form requires long-term competent treatment.
An infection from the maxillary sinuses can enter the middle part of the ear and provoke a severe inflammatory process there (otitis media). Otitis is accompanied by sharp pain in the ear, hearing loss occurs, and body temperature may rise.
Diseases of the ternary nerve are associated with sinusitis, since it is located close to the source of inflammation. This condition is characterized by shooting pains in the face. Patients describe the sensations as electric shocks. Such neuritis is extremely difficult to treat.
Complications of sinusitis associated with the eyes are possible. With inflammation, we observe swelling of the eyelids, pain when pressing on the eye socket, and vision may begin to “deteriorate.” Pus entering the eye socket and vein thrombosis can lead to loss of vision and even loss of the eye itself (panophthalmitis).
The worst consequence of sinusitis is inflammation of the lining of the brain (meningitis). A similar complication develops with prolonged and incorrect attempts to independently cure sinus inflammation.
Other common complications of sinusitis in adults: periostitis of the jaw, meningoencephalitis, sinus thrombosis, up to generalized blood poisoning (sepsis).
Remember, sinusitis with complications is much more difficult to treat, so it is very important to promptly seek qualified help from an ENT specialist.
Medications
Painful sensations in the dentition can be eliminated before going to a medical facility. To do this, you will need an anesthetic drug. For example Nurofen or Nise.
Ketanov is considered a highly effective medication against dental pain, but its use for more than 3 days in a row is unacceptable. Before taking pain medication, it is strongly recommended that you carefully read the instructions for use. The drug is able to eliminate the clinical sign of the pathology, but does not relieve the patient of the provoking factor.
Puncture for sinusitis
If all conservative methods of treating sinusitis do not help, the ENT doctor will suggest a puncture of the maxillary sinus. This measure is necessary because pus accumulated in the sinus, as we already know, can lead to serious consequences, including inflammation of the brain.
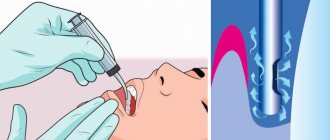
During the procedure, the otolaryngologist releases the purulent contents of the sinuses and injects medication into the sinus. There is no need to be afraid of a puncture - before the procedure, anesthesia is performed: the ENT doctor inserts a cotton swab soaked in a lidocaine solution into the nasal passage of the patient sitting in a chair. It is completely safe and does not require patient preparation.
As soon as the anesthesia takes effect, the otolaryngologist, using a Kulikovsky needle, carefully inserts it into the sinus through the nasal cavity. Using a syringe, the purulent contents are sucked out. As soon as the purulent masses are completely removed, rinsing is carried out. The sinus should continue to be rinsed for several days after the procedure.
Specialists who took part in the treatment:
- Dentist-endodontist – diagnosis of periodontitis, treatment of tooth canals under a microscope, tooth restoration with a ceramic inlay.
- ENT A.V. Arkhandeev – diagnosis and treatment of sinusitis.
- Dental assistant A. Antoshkina.
- ENT assistant E. Shilova.
See other examples of the work of specialists from the Dial-Dent clinic here.
Make an appointment for a consultation by phone +7-499-110-18-04 or through the form on the website. You can ask questions about dental treatment to the chief doctor of the clinic, Sergei Vladimirovich Tsukor, at
Washing “cuckoo”: description of the method of treating sinusitis
The “cuckoo” method is a painless and, most importantly, effective procedure. Thanks to conservative treatment, purulent masses, mucous secretions along with pathogenic microorganisms are effectively washed out of the sinuses, the mucous membrane improves its function, nasal congestion decreases, and inflammation subsides. In some cases, thanks to Proetz lavage, puncture can be avoided. How is this procedure carried out?
The patient is positioned comfortably, lying on the couch, face up. The ENT doctor carefully pours an antiseptic into one nostril (Chlorhexidine, Furacilin, Miramistin, etc.). And at the same time, with the help of a special metal olive connected by a medical suction device, it sucks out this rinsing solution, but from the other nostril. The manipulation is repeated three times on each side, using a sterile plastic syringe with a volume of twenty ml. The entire procedure lasts about five minutes.
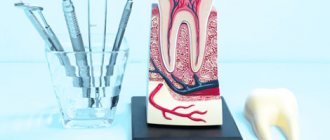
Treatment of periodontitis
The endodontist explained to the patient that in order to stop the inflammation, it is necessary to eliminate its cause - that is, eliminate the infection in the tooth canals. Retreatment of the tooth canals will be carried out under a microscope, which allows you to better clean the canals and see the branches along the canals.
Commentary by endodontist T.I. Matienko: “When periodontitis with an abscess develops, it is most often suggested to remove the tooth, but at the clinic we try to save the tooth, which is why treatment is carried out under a microscope, which improves the quality of treatment and helps to see many problems (narrow canals, canal branches, organic residues on the canal walls etc.) that are not visible to the naked eye. The decision on the choice of treatment tactics is made very carefully, after a thorough analysis of the computed tomogram. Not all teeth can be saved by retreatment. Sometimes I recommend removing a tooth because, based on some signs visible on a CT scan, its treatment will not be effective.”
To treat periodontitis, the canals were unfilled, cleaned with special endodontic instruments, washed with medicinal solutions and dried. A medicinal paste is placed in the canals to completely suppress the infection inside the tooth and surrounding tissues. After 3 weeks, the process of washing, drying and adding the medicine was repeated. After another 3 weeks, the patient did not experience any unpleasant sensations either in the tooth area or in the maxillary sinus area, so the canals were again washed, dried and hermetically sealed with hot gutta-percha, which penetrates well into all branches and bends of the canals.
The duration of each visit is about 1.5-2 hours, since root canal treatment requires careful adherence to the treatment protocol (use of a rubber dam, adherence to the time of exposure to medicinal substances) and attentiveness from the doctor.
After canal treatment, a ceramic inlay is installed in the tooth (E.max ceramics). An inlay in a tooth increases the strength of the tooth and its resistance to chewing loads. In this case, the tooth was badly damaged, and a large filling would have been unreliable.
Solution
After a consultation of dentists (surgeon, orthopedist and therapist), the following treatment plan was adopted:
- removal of the entire prosthetic structure (!), removal of 14, 26, 27 teeth with elimination of the infectious focus.
- in the second stage (approximately a month later) bone grafting in the area of the formed defect
- the third stage (approximately after 3 months) is the implantation of artificial roots in place of teeth 24, 25, 26, 27
- after another 3 months, installation of crowns on these implants.
During this period, the patient will wear a temporary prosthesis to replace missing teeth and undergo therapeutic tooth-preserving treatment of teeth 37, 47, 13.
After presenting this information, the entire team of doctors was present at a very sad scene - an adult respectable man, almost crying, talked about the fact that just 2 years ago, for three months, he was treating his teeth, spent 120 thousand rubles on 15 crowns, and now it turned out that his problem has not only not been solved, but has also worsened and requires new physical and moral efforts and new financial costs. After the first shock passed, he asked us a fair question: why did such complications arise?
Treatment result
A follow-up visit was scheduled 6 months after treatment, but since nothing bothered her, the patient refused the visit and came to the dentist 3.5 years later with another problem.
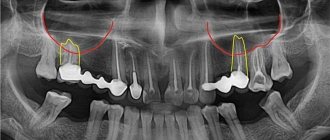
The CT scan shows:
- calm state of the maxillary sinus mucosa;
- complete restoration of bone tissue around the roots of the tooth;
- high-quality sealed canals;
- hermetic tooth restoration with an inlay to replace the old filling;
- complete restoration of bone tissue in the area where there was an abscess.
Analysis of computed tomography confirms that the treatment was very high quality and effective.
The cost of retreatment of a tooth with 3-4 canals as of September 2019 is 27,500 rubles, the cost of a ceramic inlay per tooth is 45,000 rubles, the cost of a dental CT scan is 2,900 rubles.
Ways to relieve pain
Measures to help relieve pain in case of sinusitis:
- Washing. Saline solutions and decoctions are used. The nasal cavity is cleared of pus.
- Warming up. There is an increase in the outflow of secretions.
- Inhalations. Sea salt and herbs are used. The functions of the mucous membrane are restored, irrigation is restored, and swelling is relieved.
- Vasoconstrictors. Applicable in case of clearing the nasal cavity from pus. Effectively relieve congestion and reduce headaches.
In case of frequent nosebleeds, rinsing is contraindicated. Likewise, it is necessary to avoid warming the sinuses if the patient has a fever.
How to relieve pain after filling at home?
Post-filling pain can be relieved by rinsing with warm saline and soda solutions.
Baking soda and salt are used in folk medicine to solve many diseases. After all, they remove inflammation and have an antiseptic effect. Salt can draw out pus, so it is used simultaneously with soda even for.
Warm rinses with soda and salt should be used in the early stages of pain. So, the tooth is heated from the inside. At the same time, warming the cheek from the outside is strictly prohibited.
The solution is prepared from hot water (which the mouth can tolerate). Place one teaspoon of soda and salt in a glass of water. You need to rinse four to five times per hour until the pain completely disappears.
Sometimes a couple of drops of iodine are added to the saline-soda solution. But not all patients can use iodine (for example, in case of thyroid diseases it is better to exclude it).
Medicinal pain relievers will also help relieve pain. Baralgin, ketanov, ketorol, etc. are suitable.