Walking in the fresh air is useful at any time of the year, but still a long stay outside in sub-zero temperatures can sometimes unexpectedly lead to local hypothermia of the face and head. Often the consequence is an inflammatory process in the dental nerve.
In such cases, patients usually say that they “have caught a cold on the dental nerve.” Experts call this phenomenon “local hypothermia of the dental nerve.”
Inflammation in this case usually has nothing to do with the penetration of infection. The reason is directly related to the experience of severe hypothermia.
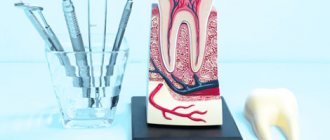
To understand the reason for the development of inflammation in the dental nerve after exposure to cold temperatures, you should first pay attention to the anatomy. The center of the tooth is the pulp.
The pulp is a soft tissue with its own system of blood vessels and nerves. It has a loose structure. Each pulp tissue performs a specific function. It is known that large nerves of the pulp have a connection with the root processes. If toothache occurs, it is always associated with the dental nerve in the pulp.
Why might this happen?
The reasons are obvious:
- Dental nerves are sensitive to cold.
- Prolonged exposure to wind on an unprotected face.
- Lack of headwear in cold weather.
- General hypothermia of the body.
Possible provoking factors should also be highlighted
- Development of caries.
- Tooth chips and injuries.
- Tooth infection.
- The use of low-quality fillings in dental treatment.
- Poor quality prosthetics.
Possible risks and complications
As a rule, the virus enters the body through the mucous membrane of the throat or nose, therefore the tissues of these organs become inflamed first. Since the treatment site is close to the source of infection, the virus can easily penetrate the tooth tissue along with saliva. It can slow down the recovery process and cause complications after procedures, for example:
- Sinusitis. Occurs when a virus or bacteria enters the maxillary sinuses. In the sinuses close to the eyes and brain, pus appears, which causes intoxication of the body. If left untreated, sinusitis can lead to meningitis, otitis media and sepsis.
- Otitis. Occurs when an infection enters the middle ear cavity and causes inflammation. Acute purulent otitis media can contribute to the development of labyrinthitis - the spread of infection to the inner ear. An unfavorable outcome of this disease can be complete hearing loss.
- Pneumonia. Pneumonia begins when an infection enters the respiratory tract. Treatment should not be delayed as the disease can be fatal. The consequences of advanced pneumonia include: acute respiratory failure, abscess, pulmonary gangrene, pleurisy, pleural empyema, obstruction, endocarditis, pericarditis, meningitis, pulmonary edema and sepsis.
- Meningitis. Through the circulatory system, a virus or bacteria can enter the brain and cause inflammation of its membranes. If treatment is delayed, the disease can cause problems with mental development in children or lead to complications such as deafness, epilepsy and hydrocephalus.
- Osteomyelitis. It develops when the infection enters the bone tissue through the bloodstream or infected surrounding tissue. The disease can lead to bone deformation, the appearance of tumors at the site of inflammation, pathological fractures, and ankylosis of the joints.
In order to reduce the risk of complications after dental treatment with fever, it is necessary to follow the doctor’s recommendations before and after the procedure, take medications, and monitor oral hygiene.
What symptoms indicate a cold dental nerve?
Pain. Local hypothermia of the dental nerve is manifested by severe pain. It usually occurs unexpectedly without any mechanical impact.
In some situations, patients complain of pain in the ear, jaw, and temples. With temperature and mechanical influence, such pain may intensify.
Heat . Not in all situations, but it still sometimes happens that the inflammatory process in the pulp after hypothermia leads to an increase in body temperature. Usually it rises to a maximum of 37.5° C. If the temperature is higher, this may indicate general intoxication of the body.
The appearance of skin sensitivity . Sometimes pronounced redness appears on the face in the area where the inflamed tooth is located, associated with increased sensitivity of the skin in this area.
Patients may complain not only of pain when touching a “chilled” tooth, but also to the skin of the face in the approximate area of its location.
Treatment and prevention
Anyone can get a toothache, but only experienced specialists can make an accurate diagnosis. If the cause of inflammation is caries , the doctor will clean the tooth, remove the affected areas and put a filling. If the pulp is damaged, the nerve will have to be removed and the root canals filled. In any case, inflammation can be relieved only by removing the source of the disease.
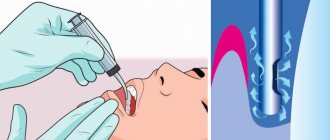
To treat teeth under anesthesia , you don’t have to be a hero, because modern dentistry allows you to do this without fear and pain. Thanks to the use of drug sedation, patients no longer complain of discomfort and pain during treatment. Sedation helps us relax and fall asleep, while the pain threshold increases significantly, salivation decreases, and all vital organs remain active. You can treat your teeth in your sleep at the Medexpert Family Dentistry Center. Treatment without stress and pain - come to us!
How to properly treat a chilled tooth nerve?
If the dental nerve is cold, you should not postpone a visit to the dentist, as the inflammatory process and pain will intensify over time, which will lead to dangerous negative consequences.
For temporary pain relief:
- Moisten a piece of sterile cotton wool with alcohol (another option is vodka) and apply it to the tooth. This will slightly suppress the inflammatory process and relieve pain. But it is important to avoid contact of the mucous membrane with the cotton wool to avoid burns.
- Add chlorhexidine (no more than 5 drops) to a glass of warm water from a kettle. The solution should be used to rinse the mouth to “pacify” inflammation.
- Use dried sage leaves in small quantities. Pour boiling water over them, let cool. After this, you can rinse your mouth with the resulting infusion.
Professional treatment
The treatment method for a cold dental nerve depends on the cause, the nature of the symptoms, the general well-being of the patient, the condition of the tooth, its pulp and oral mucosa. In case of severe complications, there is usually a need for urgent hospitalization of the patient.
If for now the symptoms are limited to acute pain, the dentist will provide emergency treatment to eliminate the inflammatory process.
If there are chips, other signs of mechanical damage to the tooth, or signs of caries, the diseased tooth is cleaned and filled.
In case of necrosis of the soft tissue of the pulp or its complete damage, surgical treatment and antibacterial therapy will be required after removal of the pulp.
First aid or how to relieve symptoms
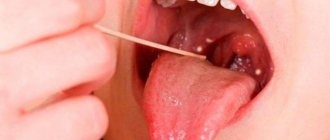
to make a diagnosis on your own if your tooth has caught a cold . Sometimes obvious symptoms become a sign of inflammation of the gums or pulp, and not the tooth itself. Only a specialist can identify the disease and prescribe appropriate treatment. But what to do if, for example, you make an appointment with a doctor only for tomorrow or late evening, but the pain bothers you? The right solution would be to rinse your mouth with a soda solution, apply a piece of lard or a little cotton wool moistened with alcohol to the gum. By the way, you need to rinse your mouth 4-5 times a day.
How to protect the dental nerve from hypothermia?
- During the cold season, use warm hats, scarves and outerwear with a high collar.
- In low temperatures and strong winds, it is advisable to cover your face with clothing.
- Do not use a thermos with hot water. Temperature changes may cause inflammation of the dental nerve and the appearance of an acute painful reaction.
Study the condition and appearance of your teeth, as well as the oral mucosa, regularly on your own. This way you can see suspicious changes in a timely manner.
Causes
Accurate diagnosis is important for a positive treatment outcome. It is this that allows you to determine why the tooth is inflamed. There are 3 diseases hidden under the general term.
Pulpitis
Microbes penetrate through the dentin layer to the neurovascular bundle - the pulp. People call it a nerve. Usually, this happens with deep caries. The pulp is penetrated by nerve endings. The pain is often acute and difficult to endure. But sometimes it is not strong, periodic. We ignore it and the inflammation becomes chronic, destroying the pulp. A small bun makes a huge difference:
- produces secondary dentin, therefore, although the height of the teeth changes throughout life, they do not disappear completely;
- participates in tissue metabolic processes;
- conducts nerve impulses.
When the pulp dies, the tooth is said to become “dead.” Such teeth are quickly destroyed.
To treat pulpitis in dentistry, therapeutic and surgical methods are used. In the first case, medications are placed into the tooth cavity and closed with a temporary filling. After some time, the tampon with the medicine is removed and the tooth is filled. This method does not always help relieve inflammation inside the tooth.
If the process has gone far, the pulp or part of it is removed and then a permanent filling is placed.
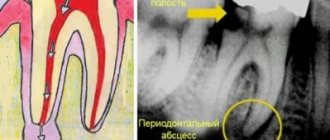
Periodontitis
Under the crown of the tooth there is connective tissue - periodontium. As a result of injury or poor treatment, microbes penetrate there, causing inflammation of the tooth root - periodontitis.
.
There is an apical form, when only the apex is affected, and a marginal form, when all the tissue around the root is infected.
Symptoms of periodontitis:
- pain while eating or when jaws touch;
- feeling that the tooth stands out from the row (has become taller);
- temperature increase;
- tissue redness;
- tooth mobility;
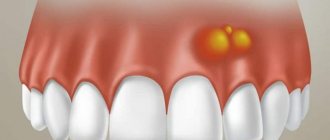
- discharge of pus.
Periodontitis is an insidious enemy. Often the disease occurs without symptoms. It can only be suspected when the signs of the disease become pronounced: roots are exposed, gums bleed, pus is released, bone tissue decreases.
Treatment depends on the type of periodontitis and severity:
- Therapeutic method
The doctor opens access to the root canals, removes part or all of the pulp, and installs drainage to drain the pus. After a few days, the drainage is removed, the canals and tooth are processed and filled. It is recommended to place a crown on such a tooth.
- Surgical method
They resort to it if fibrosis has developed or there are granulomas.
Dentist:
- Cuts off the root tip
- Removes 1 root in multi-rooted teeth
- Amputates the root but leaves the crown intact
- Removes a tooth
- Performs separation (cuts the tooth in half, cleans it and puts it back together)
A course of antimicrobial tablets helps relieve inflammation inside the tooth.
Periodontitis
Periodontium is the fibers that hold the tooth in its socket. Plaque allows bacteria from it to penetrate into the periodontium and begin to rapidly multiply, forming a periodontal pocket. From the pocket, it is easy for them to get under the crown of the tooth and cause an inflammatory process there.
Before treating tooth inflammation under the crown, periodontal pockets are curetted, freeing the surface from tartar and plaque. Then they begin other manipulations: getting rid of caries, splinting teeth. Often, for periodontitis, a course of antibiotics is prescribed. The inflammation must be stopped so that the tooth does not have to be removed.
Colds and viral diseases
They undermine an already weak immune system. He fights them, and all sluggish infections immediately “spread their wings.” If there was such a hidden infection in the teeth, which was previously controlled by the immune system, and the person did not even know about it, now, left without supervision, it begins to gain strength. As a result, a toothache suddenly appears and the temperature begins to rise.
By lowering the temperature, you don’t need to wait for the tooth to “somehow” go away. The infection “lived” there for a long time, and a decrease in immunity made it possible to detect it, so it is necessary to begin treatment immediately, otherwise it is unknown how all this will affect the condition of the teeth.