The inflammatory process that occurs in the periodontal tissues that surround the tooth root is called periodontitis. Several causes of the disease can be identified:
- untreated caries
- untreated pulpitis
- injury received
- mistakes made in dental canal treatment
The most common causes of tooth root inflammation are problems associated with caries and pulpitis. In any case, treatment should be carried out in several stages. Left to chance, this dental disease can provoke serious general somatic problems, so it is necessary to approach the treatment of tooth root inflammation with all seriousness.
For what reasons can a tooth root become inflamed?
Despite the availability of many effective methods of therapeutic treatment of inflammation under the tooth root, it is often necessary to resort to the use of surgical treatment methods. This is indicated in the following cases:
- Root canal obstruction was detected
- there is a pin or stump tab that cannot be removed without damaging the root
- there are many cysts - perihilar or growing into the maxillary sinus
- there is a perforation (perforation) of the wall of the tooth root or its cavity
- The use of conservative methods of treating root inflammation does not help
Important:
Most often, periodontitis refers to inflammation in the area of the apex of the tooth root (apical, periapical periodontitis). The cause of tooth root inflammation is untimely treatment of caries and pulpitis. Another type of disease, marginal periodontitis, is classified as periodontology; in this case, the lesion spreads to the gums in the cervical part of the tooth.
Mechanism of pain
- Trauma to soft, hard periodontal tissues;
- damage (rupture) of the connective tissue holding the tooth;
- destruction of blood vessels and nerve endings;
- swelling of the injured gum, pressure on nearby areas, poor circulation;
- irradiation of pain along the nerve trunks to other parts of the maxillofacial areas.
Pain after extraction of any dental unit is a natural reaction of the body to the intervention. No matter how carefully the surgeon acts, the integrity of the vessels, nerves, and fibers is inevitably compromised. It is normal for the extracted tooth to hurt for no more than 2-3 days.
, after removing the figure eight, the gums may bother you
for about a week
. If after 7-10 days the discomfort does not disappear, but continues or increases, you need the help of a doctor.
Symptoms and treatment
Periodontitis can be chronic and worsen. The characteristic symptoms that are revealed during examination by a dentist and as a result of anamnesis vary depending on the stage of development of the disease.
Exacerbation of periodontitis is characterized by the following signs and complaints from the patient:
- Regardless of the time of day, you are constantly haunted by a monotonous, equally intense, aching toothache.
- When pressing on the tooth, the pain intensifies
- There is a feeling that the tooth has “grown” - it interferes and does not allow the jaws to connect, since any attempt to do this ends in a painful attack
- The accumulation of purulent contents provokes pulsating pain, radiating along the branches of the trigeminal nerve
- Feeling worse, weakness appears, temperature rises
- Submandibular lymph nodes may become enlarged
Exacerbation may be accompanied by serous and purulent discharge. In case of purulent periodontitis, the doctor is first faced with the task of getting rid of pus: the tooth cavity is cleaned, the canals are treated.
Symptoms of tooth root inflammation in chronic form are not so pronounced:
- The tooth does not hurt constantly, but when pressing, unpleasant pain occurs
- A fistula may occur with frequently exacerbating granulating periodontitis. In this case, under the influence of exudate, the tissues “melt” and the exudate exits through a hole in the gum located in the area of the root apex. In the remission stage, such a formation looks like a changed area of the mucous membrane
- The presence of bad breath (halitosis) is also a sign of chronic apical periodontitis. Microorganisms that cause caries contribute to the destruction of hard tooth tissues, enter its internal cavity and provoke tissue death in the pulp, which leads to the accumulation of necrotic masses, which are the main factor of halitosis.
The chronic form of tooth root inflammation is treated conservatively in most cases; only in the most advanced cases is surgery prescribed. Modern standards of all medicine and dentistry in particular consider any disease comprehensively, that is, they do not treat fistulas, cysts or granulomas separately. In the treatment of tooth root inflammation, antibiotics, painkillers and other medications are used.
Treat or remove baby teeth
Before talking about how baby teeth are treated, it is necessary to note their features that distinguish them from permanent teeth. First of all, baby teeth have thinner enamel, making them very vulnerable to tooth decay and other damage. In addition, contrary to popular belief, baby teeth also have roots, although they are smaller and thinner than the roots of permanent teeth.
In this regard, the question arises: are milk teeth treated in children, or can they be removed if problems arise - after all, after some time, permanent teeth will appear in their place. It is important to understand here that most often a very short period of time passes between the spontaneous loss of a baby tooth and the appearance of a permanent one. In fact, the baby tooth falls out at the moment when the permanent tooth is ready to develop. But if a baby tooth is removed before its due date, an empty socket will appear on the child’s jaw, which may remain without a tooth for many weeks and even months. In this situation, neighboring teeth will begin to shift towards the socket, which will increase the gaps between them and create obstacles for the growth of a permanent tooth. It may begin to hurt, it will grow crooked, the formation of the bite will not occur correctly - and the child, in order to avoid serious problems and return a beautiful smile, will have to endure many dental procedures and even, probably, wear braces. Therefore, modern dentists are trying their best to preserve baby teeth until they naturally fall out - using different methods, including installing crowns.
In addition, when thinking about why we should treat baby teeth, we should not forget about the main function of teeth - chewing. If we simply remove a child’s diseased baby teeth, what will he chew on? In this case, the child will have to get a prosthesis, since it may take a long time for permanent teeth to emerge in place of the removed milk teeth.
Relieve pain before going to the doctor
For any form of periodontitis, it is necessary to make an appointment with a doctor, but often the aching tooth “does not want” to wait for the appointed time and hurts unbearably. Taking a pain reliever will help relieve the condition. For toothache, experts advise taking medications that are most optimal for such cases. The pill will not cure, but it will relieve the pain. This does not mean that you can postpone a visit to the doctor - after the pill wears off, the pain will return, so a trip to the dentist should not be postponed or put off “for later”.
At what age should children have their baby teeth treated?
It is necessary to treat baby teeth at any age. In the first years, when baby teeth erupt, children are often limited in sweets and caries develops infrequently. At the age of 3-5 years, the situation becomes more complicated due to the fact that sweets become more accessible, and teeth brushing is often carried out irregularly and without due diligence.
At about 5-6 years old, baby teeth begin to be replaced by permanent ones. Usually this process is completed by the age of 14, although deviations in one direction or another are often encountered. It makes no sense for parents to wait for a certain time to start seriously taking care of their child’s teeth and taking him to the dentist. As we have already said, diseases of baby teeth can lead to their untimely loss and even cause damage to future permanent teeth. Decayed and prematurely lost baby teeth can cause problems with diction, prevent a child from chewing food normally, and cause digestive problems.
Therefore, from the very beginning, it is important to accustom children to regular oral hygiene, limit their insatiable love for sweets, and periodically take them for preventative visits to the dentist. In order for children not to be afraid of the dentist, it is important to choose a good clinic that employs pediatric dentists, with experience in treating primary teeth and attentive attitude towards young patients. If a child knows that a visit to the dentist does not necessarily mean that their teeth will be drilled, then they will be able to accept these regular visits with greater peace of mind, and their smile will always be flawless.
Features of the treatment of periodontitis with fistula
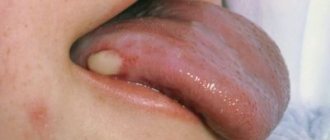
The inflammatory process can occur with complications, one of them is odontogenic fistula. More often it occurs with granulating periodontitis. These are holes in the mucous membrane, formed as a result of the proliferation of granulations and destruction of the tissues surrounding the tooth. Through the resulting fistula, pus is released, which is formed during inflammation under the root of the tooth.
To some extent, the resulting fistula helps to reduce the pain experienced by a person: the purulent contents do not linger in the tissues, but come out, easing the course of the disease. But you should not delay the examination by the dentist and the appointment of treatment - this is fraught with tooth loss.
The fistula will not disappear on its own; it is necessary to remove the cause that caused it – inflammation in the periodontal tissues. The treatment regimen for root inflammation is standard in all cases:
- thorough mechanical cleaning of the canals
- carrying out disinfection
- temporary filling with a drug until inflammation in the periodontium disappears
In particularly advanced cases, overgrown granulations are surgically removed.
What are the possible complications?
The intensity of pain must be carefully monitored. Unpleasant sensations must subside, otherwise it indicates the development of pathology. The gums hurt especially painfully after difficult removal if inflammatory complications develop:
- Alveolitis is an inflammation of the bone socket and surrounding tissues. accompanied by acute, throbbing pain, redness, swelling, the formation of yellow, greenish, dark gray plaque, cloudy pus with a putrid odor. The cause of the complication is poor hygiene in the postoperative period, ignoring the drug therapy prescribed by the doctor.
- Dry socket - there is no blood clot in the socket, it is dry, empty, there is a yellowish-gray coating, a putrid odor. The reason is that the clot was not formed due to a blood clotting disorder; the clot was removed from the socket by the patient during hygiene, intensive rinsing, etc.
- Socket bleeding - may be associated with a blood clotting disorder, excessive damage to tissues, blood vessels, or a fracture of part of the alveoli.
- Facial neuralgia is a rare complication that occurs due to damage to the facial nerve during tooth extraction. Accompanied by numbness in the cheeks, tongue, lips.
- Periostitis is a purulent inflammation of the periosteum that develops for the same reasons as alveolitis. Accompanied by acute, diffuse pain that cannot be relieved with an analgesic. Swelling is pronounced, can spread to the neck, temperature is above 38℃, general intoxication of the body is observed (headache, weakness, etc.).
- Osteomyelitis is a purulent-necrotic lesion of the jaw bone, accompanied by throbbing pain radiating to the ear, temple, fever, swelling of the gums and oral mucosa, spasms of the masticatory muscles, deterioration in general well-being, and enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes.
Cheek pain after tooth extraction is a very common symptom, the duration of which depends on the complexity of the intervention. Normally, aching pain completely subsides after 2-3 days
. The picture is completely different when complications develop. With inflammatory complications, purulent foci form in the tissues, and the risk of spread of purulent contents through the general bloodstream increases many times over. There is a high probability of phlegmon, abscess, and destruction of bone tissue. Serious surgery and long-term rehabilitation are inevitable.
Treatment methods
As already noted, in modern dentistry, preference is given to conservative treatment. However, it is often impossible to fully treat tooth root inflammation without surgical intervention.
Conservative treatment
This is a complex methodology that includes several types of activities:
- mechanical cleaning of channels
- disinfection of canals using medications
- Temporary filling with medication
Conservative therapy includes the prescription of antibiotics for inflammation of the tooth root.
Surgery
Involves the operation:
- removal of 1/3 of the root tip
- removal of part of the root (hemisection)
- removal of a tooth from the dental socket
Important: Doctors try to save teeth using all conservative treatment methods available today, since they are successful in 70-90% of cases.
Is it necessary to treat caries of baby teeth?
Due to their thin enamel, baby teeth are very susceptible to tooth decay. At the earliest stage, caries does not even require drilling and filling - you can get by with polishing the tooth and applying a special mineralizing paste. But if the moment is missed and a hole has formed, then the treatment will be more serious. But in any case, parents who doubt whether it is worth treating caries of baby teeth should remember that on delicate baby teeth with thin enamel, caries develops much more rapidly than in adults. Therefore, severe toothache can suddenly overtake a child in the most inopportune situation - at the grandmother’s dacha, on a trip abroad. You will have to urgently look for a suitable clinic, possibly spend a lot of money and risk the child’s health, because if the tooth is removed poorly, parts of the roots may remain in the socket, which will interfere with the eruption of the permanent tooth.
Caries of baby teeth in children is also treated because it can become a source of infection, lead to periodontitis, and damage nearby permanent teeth. As in adults, caries in children must be treated promptly and as early as possible in order to preserve the tooth and not damage the normal development of the child’s jaw and bite.
Stages of periodontitis treatment
How many times you will have to come to the doctor to treat inflammation at the root of the tooth depends directly on the form of the disease, in remission or during an exacerbation. The course of treatment is also influenced by the method chosen by the doctor. Often, therapy requires a course consisting of several stages of treatment and a visit to the dentist. Until the inflammatory process is eliminated, the tooth cannot be filled, so you will have to visit your doctor several times:
- Preparatory stage. Diagnosis of the condition of the tooth root using x-rays
- When removing the old filling, the tooth is drilled to open access to the canals and remove the nerve
- Channels are expanded to the required size
- Treating the canals with antiseptic drugs and applying medication
- A temporary filling is installed
- At the next visit, the temporary filling is removed and the canals are treated with antiseptic. This stage can last for weeks, or even months - the process will be repeated until the inflammatory focus is completely eliminated and the number of visits will depend on this
- A permanent filling is placed and x-rays are taken again for control.
In addition to the procedures performed in the clinic, the patient must undergo antibacterial and anti-inflammatory therapy. At home, he should do warm rinses with special antiseptic solutions (herbal, medicinal - as recommended by a doctor).
What to do when the process of tooth decay begins
Modern dentistry is not about pain at all. This is about caring for the patient and the desire to preserve his teeth.
Dentists' advice is simple, but how many people follow it?
How to prevent teeth from rotting:
- Lead a healthy lifestyle
- Takes good care of your teeth
- Carry out hygiene procedures regularly
- Monitor your general health
Plaque on teeth is the beginning of the decay process. Regular cleaning of tartar is one way to keep your teeth healthy.
Prevention
- Preventing any disease is easier than treating it afterwards. This is a true statement, so regular dental checkups should become a good habit. If you live in St. Petersburg, Krasnodar, Novorossiysk or Moscow, then you can contact any of the branches of the INTAN dental network for the best qualified help
- Also, timely treatment of caries and pulpitis will help to avoid periodontitis and its attendant complications. The cost of treating them will be higher and more time will be required.
- In case of acute inflammation at the root of the tooth, a quick visit to the doctor and timely treatment will relieve complications and prevent the process from becoming chronic.
- If caries is detected at any stage, you need to make an appointment with a doctor as soon as possible, undergo an examination and prescribed treatment (remove damaged tooth tissue, filling)
- Compliance with hygiene rules (brush your teeth twice a day with a properly selected brush and toothpaste, use dental floss)
- Diet is important. Dairy products and protein-rich foods, fresh vegetables and fruits should always be on the table. Minimize the consumption of sugar-containing foods and sweet carbonated water.
- Visit your doctor every six months for a check-up and professional teeth cleaning
Following simple rules for oral care will help you avoid inflammation of the tooth root and all the troubles associated with it.
Is it necessary to treat pulpitis on baby teeth?
Pulpitis is inflammation of the pulp, i.e. nerve and surrounding soft tissues. Sometimes for some reason they believe that pulpitis does not occur in children. But baby teeth also contain nerves and they can become inflamed in the same way. The reasons are:
- advanced caries,
- tooth injury,
- an error in the treatment of caries (the dentin of a baby tooth is very thin and a dentist who does not have much experience in treating baby teeth in children may accidentally open the pulp chamber),
- infectious disease (for example, severe sore throat, as a result of which the infection penetrates the tooth from the inside, through the blood).
Pulpitis in children is uncommon, but does occur. Therefore, it is necessary to treat it. Otherwise, it can become chronic and not only lead to tooth loss too early, but can also transmit inflammation to the new emerging permanent tooth.
Pulpitis in baby teeth is now treated in three ways:
- Classical devital amputation: the diseased nerve is killed with a special paste, after a few days the pulp is removed and the tooth is filled. Now this method is considered outdated, but nevertheless is sometimes used.
- Vital amputation: if only part of the nerve is inflamed, then at the very beginning of the inflammation it is possible to remove the affected part of the nerve under anesthesia, and an antiseptic anti-inflammatory agent is applied to the rest and the tooth is filled. The operation is complex and leaves the possibility of re-inflammation of the pulp.
- Vital pulp extraction: under strong anesthesia, the inflamed pulp is completely removed and the pulp chamber is filled with a special zinc-eugenol paste, which in the future will be absorbed along with the roots of the baby tooth. The method is effective, but expensive and requires a highly qualified dentist.
Much more often, doctors suggest simply removing a baby tooth affected by pulpitis. This is both simpler and cheaper, but, unfortunately, there is a possibility of displacement of adjacent teeth (if the permanent tooth does not erupt soon), which can lead to the formation of a malocclusion. To avoid such a situation, it is best not to let the situation develop into pulpitis, but to treat caries as early as possible.
Correcting your bite with braces is harmful because the teeth underneath them begin to deteriorate.
This is an incorrect statement. After all, braces are small clasps that are attached to the teeth using a special photopolymer composite orthodontic material that contains fluoride and is completely harmless to tooth enamel. Carious lesions in patients who wear braces can only occur due to poor oral hygiene. If they eat foods that are prohibited by the orthodontist, do not brush their teeth and the system itself after eating food or do not do so at all, and do not use rinses and special orthodontic brushes for teeth, then they are immediately automatically placed at risk of developing caries.
Are all sweets bad for your teeth?
Very often, parents are of the opinion that dried fruits and honey are not sugar, so they cannot harm the teeth, especially if the package says “Organic”. But this is a mistaken opinion. Healthy sweets also contain adhesive sugars that can cause tooth decay. This also applies to various sweet drinks - compotes, fruit drinks, juices, as well as children's cookies and sweet buns. Dentists do not prohibit eating sweets, but urge you to choose the least harmful ones - marshmallows, marshmallows, cocoa, chocolate containing a lot of cocoa. By the way, these experts believe that it is better to eat several candies at once than one every hour.
But if, despite all your efforts, your baby’s teeth are still constantly deteriorating, this may be a signal that a thorough examination of the body is necessary. Bad teeth can occur if something is wrong with the child’s health.
Reason four: financial
In the initial stages, caries treatment is relatively inexpensive and absolutely affordable for everyone. However, with the development of complications up to the loss of a tooth, treatment becomes increasingly more expensive: treating pulpitis is already noticeably more expensive than caries, since the volume of manipulations and materials consumed are greater. As for the loss of a tooth that has not been treated in time, prosthetics will cost quite a hefty sum. Therefore, those people who do not care too much about their health may benefit from the financial argument.
Stages of disease development. Where does the disease begin?
The most unexpected microorganisms can cause severe and fatal illnesses. Now let's look at the chain of development, that is, the cycle of transformations from health to illness and the death of an individual. At school we studied the cycle of life in nature, the water cycle, watched interesting films about animals, about the food chain.
But at the same time, we have always considered ourselves “Kings of Nature,” not assuming that inside us, in our body, the same cycle of different lives is possible, coming and going, but living by eating our cells, each other, or feeding on other people’s scraps. Everyone has the same motto: “Survive at any cost, winners are not judged!” This means infiltrating into the best place, individual for each specific type of parasite, finding food for growth, reproduction, protecting its offspring and helping it spread.
So let's look at this process. Sparing the feelings of convinced atheists, I will start not with the true causes of the development of diseases - spiritual, energy-informational, but with “materialized” ones, that is, those that can be seen, touched, identified, calculated and measured. These reasons are the microorganisms living in us. I will paraphrase the Bible saying “what is outside of us is also in us” to “what is on the earth and in the air is also in us.”
Let's consider the process of disease development and the role of various microorganisms involved in it. The trigger mechanism for the development of the disease is viruses. They are able to penetrate cells, weakening them or completely destroying them. These do not necessarily have to be formidable viruses specific to immune cells. Any other viruses that penetrate us from childhood gradually lead to a weakening of the immune system, a weakening of the protective properties of cells, organs, and systems.
Bacteria
Next, bacteria are introduced into the already weakened cells, which are able to completely destroy the cell, feeding on its insides. According to the nature of their development, they are divided into those that are able to divide and grow only inside the cell (chlamydia, etc.) and those that multiply both inside and outside the cell (mycoplasma, legionella, listeria, rickettsia, etc.). The variety of lesions they cause is explained by their sensitivity to different types of host cells (human, animal).
Intracellular bacteria:
Chlamydia:
- chlamydia trichomatis (trachoma, urogenital chlamydia and pneumonia of newborns, lymphogranuloma venereum, arthritis, arthrosis, heart damage)
- chlamydia from birds (ornithosis - pneumonia, fever)
- chlamydia pneumoniae (pneumonia, acute respiratory infections, atherosclerosis, bronchial asthma)
Rickettsia:
- rickettsia (rickettsiosis, typhus)
- rohalimia (trench fever, cat scratch disease)
- Klebsiella (Congo red fever)
Escherechia:
- Escherechia (maculopapular rash)
- bartonella (bartonellosis)
By multiplying in cells, intracellular bacteria are protected not only from various influences from the human body, but also from the effects of most antibacterial drugs that are not able to penetrate inside cells. Extracellular bacteria feed on already decomposed cells, “melting” them and turning them into pus. They are a kind of orderlies (cleaners) of the body, cleaning out diseased organs and systems.
Extracellular bacteria:
- Staphylococcus (skin pustular infections, endocarditis, pneumonia, arthritis, osteomyelitis, peritonitis, eye infections, toxic shock syndrome, food toxic infections)
- Oral sticks (gingivitis, stomatitis, endocarditis, sepsis)
- Streptococci (pharyngitis, postpartum infections, neonatal sepsis, bacteremia, meningitis, arthritis, genitourinary tract infections, pneumonia, sinusitis, otitis of the middle ear, rheumatic attack, abscesses of the lungs, liver, brain)
- Bacilli (Anthrax, bacteremia, septicemia, meningitis, eye infections, pneumonia, endocarditis, food poisoning
- Corynebacteria (diphtheria, erythrasma, skin lesions in the axillary and groin area, cellulitis, septicemia, brain abscesses and osteomyelitis)
- Clostridia (gas gangrene, foodborne illnesses, necrotic enteritis, tetanus, botulism)
- Gonorrheal bacillus (infections of the lower parts of the genitourinary tract (cervicitis, urethritis, abscesses of the glands adjacent to the vagina), infections of the upper parts of the genitourinary tract (endometritis, epididymitis, pelvic inflammatory diseases), infections of other organs and tissues (proctitis, pharyngitis, blenorrhea, pelvic peritonitis and perihepatitis, pharyngeal gonorrhea), disseminated gonococcal infection; meningococcal infection)
- Pseudomonas (skin lesions, abscesses, infection of burn lesions, keratitis, conjunctivitis, otitis of the external ear, meningitis, bacteremia, endocarditis, enteritis, para- and rectal abscesses, pneumonia, urinary tract infections, osteomyelitis and arthritis)
- Flavobacteria (colonize wounded surfaces, respiratory, intestinal tracts, organs of the genitourinary system, severe meningitis of newborns, septicemia, endocarditis, pneumonia).
Intracellular and extracellular bacteria not only get along with each other, but, participating in the cycle, eat what the previous microorganisms destroyed. They can be compared to jackals and hyenas, eating what is left of the victim after a tiger.
Types of fungi
Candida are representatives of normal microflora. Several types of candida are known, which can also be pathogens. Fungal gastroenteritis is observed in severely weakened children and the elderly, as well as people of any age with significant immune deficiency of various origins. They are characterized by a gradual onset, bloating, infrequent loose foamy stools, rumbling and various soreness, nausea, vomiting, and cramping abdominal pain. In very severe cases candidasepsis may occur. Secondary infection easily develops on the affected surfaces. The disease is getting worse. Such a course of candidiasis is possible only in a dirty intestine, with blockages from a mixed meat and dairy diet in the body with a high deficiency of silicon, which is capable of excreting candida with feces. In practice, 90% of those consulted suffer from candidiasis.
Cryptococci - cause subacute or chronic deep mycosis. Most often (70%) this disease occurs in people with a mixed diet who have overloaded the enzymatic apparatus of the stomach. In such cases, even baker's yeast can cause cryptoccosis due to the infinitely large expenditure of acid to neutralize alkaline enzymes coming from the mouth with carbohydrate foods that were eaten along with protein. To get rid of this disease, it is necessary to remove the root cause of the disease - overload of the acid-forming gastric mucosal bioapparatus, use only separate nutrition, cleanse the intestines, and only then will antimycotic treatment be successful.
Penicildia - cause deep mycoses, caused by a variety of green molds that can affect the skin, mucous membranes, external auditory canal, and internal organs. Penicilliums occur after the use of antibiotics. Nocardia asteroides are aerobic, immobile formations that occupy an intermediate state between fungi and bacteria. Most are saprophytes, but can cause diseases in humans and animals. Nocardiosis can be expressed as mycetoma -. a tumor in the lungs consisting of a dense plexus of mold.
A close relative of Nocardia asteroides is Actinomycetes isrielii. They cause severe mycotic lesions of the cervicofacial region, chest and abdominal cavities - granulomas. This fungus is most often found in people living in areas of high radiation, as well as working in hazardous chemical production.
Mucor fungi cause a disease very similar to tuberculosis - mucophomycosis.
Aspergillus is a fungus that includes many species. Some of them are pathogenic. They are capable of deeply affecting tissues. They release toxins and give rise to malignant formations.
Geotrichosis is a disease caused by fungi that attack the mucous membranes. They accompany diseases - otitis media, sinusitis.
Trichophyton is a fungus that causes diseases of the skin, hair, and nails. It is rare to find a person who is not contaminated with trichophyton.
Trichophytis - causes ringworm disease. Trichophytosis can be superficial or chronic. Superficial trichophytosis is characterized by the appearance of erymatous peeling on the scalp. The fungus penetrates the hair, destroys it, the hair breaks, which is why the name “ringworm” is associated.
Epidermophyton floccosum is the causative agent of lichen nigricans. This disease manifests itself as slightly scaly dark brown or black spots, most pronounced on the extremities. Penetration of the fungus into the skin can be deep, and upon recovery, when the black spots disappear, the skin regains its ability to pigment (change color from exposure to the sun) for 2-3 years. At this time, non-tanning spots from ringworm black appear on the arms and legs. The disease recedes with the usual antimycotic treatment with celandine juice.
Microsporiums are fungi that cause the disease microsporia, which affects the skin, hair and nails. Exposure to all kinds of creams, ointments, powders and rubs either does not give a healing effect, or gives a very short-term improvement in health. To completely get rid of microsporia, it is necessary to take antimycotic treatment from inside the body.
Mycosis fungoides - causes the disease mycosis fungoides - a malignant tumor lesion of the lymph vessels, the fungus initially settles on the skin, and then colonizes the lymphatic system.
Mycoplasmas Fluor - cause inflammatory processes mainly in the respiratory organs and in the genitourinary system.
Sporothrix is a fungus that attacks muscles, bones, and internal organs.
All fungi produce poisons that cause a wide variety of allergic reactions. Toxins from aspergilus fungi have a toxic effect on the liver.
Yeast species: Candida, Candida albicans, Cryptococcus, Trichosporum, Saccharomyces.
Molds: trichophyton, microsporium, epidermiphyton, aspergillus, mycosis.
The child can brush his teeth independently
Any child must brush his teeth on his own, and then his parents must finish what he cannot yet do on his own. Gradually, children begin to perform all movements correctly. In no case should adults rush this process so that it is not difficult for the little one. After all, this way they can instill a dislike for the procedure of brushing their teeth. Dentists advise parents to actively participate in brushing their teeth up to the age of seven, and for children over 7 years old to also do this, but only passively. It is even sometimes advisable to supervise teenagers while brushing their teeth.
How to reduce pain?
Analgesics will help relieve pain after removal of a molar (or any other tooth) - it is better if it is one of the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Antihistamines will help remove swelling, and antibiotics will help prevent inflammation. The doctor will prescribe effective medications according to the clinical picture. Medicines should be taken strictly as prescribed. Treatment for pain after tooth extraction depends on the cause of its occurrence. The most important thing after the intervention is to scrupulously follow the dentist’s instructions and recommendations. This will help reduce recovery time and avoid complications.
Author of the article Voznyuk Vladimir Aleksandrovich Maxillofacial surgeon-implantologist of the highest category
Work experience: 28 years.