Author of the article:
Soldatova Lyudmila Nikolaevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Clinical Dentistry of the St. Petersburg Medical and Social Institute, Chief Physician of the Alfa-Dent Dental Clinic, St. Petersburg
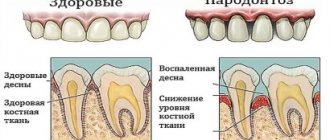
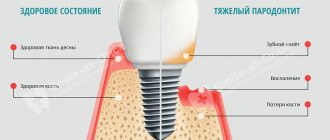
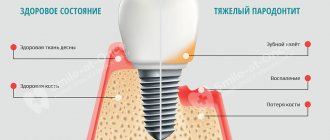
Periodontal disease is one of the most dangerous and insidious dental diseases, which can lead to the complete loss of not only single teeth, but also entire dentitions. Periodontal disease practically does not affect the teeth themselves, however, under its influence, periodontal tissue is destroyed - that part of the gum and jaw that is in direct contact with the root of the tooth and ensures its fixation. Not only the soft tissue of the gums weakens and collapses, but also the bone tissue, as a result of which the teeth become loose and there is a threat of their complete loss.
Degenerative processes in gum tissue that occur during periodontal disease develop under the influence of a number of factors, none of which researchers single out as the main and only one. Patients suffering from periodontal disease almost always exhibit certain trophic and circulatory disorders in the gum tissue, in particular of an atherosclerotic nature. However, such disorders can arise as a consequence of a wide variety of pathologies. Among the reasons that can provoke the occurrence of periodontal disease, experts name various dysfunctions of the endocrine and digestive systems, vascular diseases, neurological diseases and occlusion pathologies, single or regularly recurring injuries. Bad habits (alcohol and tobacco consumption), poor nutrition, which causes a lack of vitamins and minerals, and a persistent decrease in immunity, leading to increased activity of pathogenic and opportunistic microorganisms in the oral cavity, play a role in this process.
Unfortunately, today there is not a single drug that could completely restore destroyed tissue and reverse the process of development of periodontal disease. However, the use of a complex of physiotherapy and medications makes it possible to stop the progression of the disease, stabilize the patient’s condition and help the body regenerate damaged periodontal tissue. The leading role in achieving this result belongs to medications. You will learn about how to treat periodontal disease with medication from our material.
How to cure periodontal disease forever?
Treatment of any disease begins with diagnosis. In the case of periodontal disease, which is often asymptomatic, the following procedures are performed to make a final diagnosis:
- examination of the oral cavity;
- probing of the gingival sulcus;
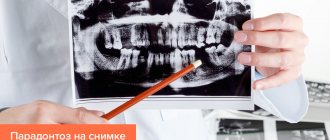
- X-ray examination (orthopantomography);
- biomicroscopy of the gums to determine the degree of microcirculation impairment.
The main factor confirming the presence of periodontal disease is a uniform decrease in the height of the interdental septa with alternating foci of osteosclerosis and osteoporosis in the deep parts of the alveolar process and the body of the jaw, as well as in other bones of the skeleton. As a rule, all these manifestations are displayed on an x-ray. The patient will also need additional consultation with a general practitioner and an endocrinologist to identify and treat metabolic disorders, diseases of the cardiovascular or endocrine systems, which often accompany the disease.
How to get rid of periodontal disease and finally prevent bone tissue destruction? Unfortunately, it is impossible to completely say goodbye to the disease. For this reason, treatment of dental periodontal disease is usually aimed at slowing down the process of periodontal dystrophy and preventing tooth loss, tissue inflammation and purulent bone damage.
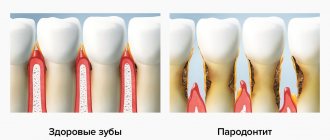
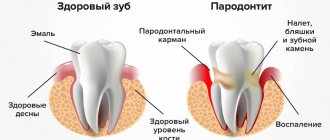
Periodontitis is an inflammatory process in periodontal tissues
Periodontitis begins with inflammation of the gums - gingivitis, which is caused by microbes from plaque. The gums become red, swollen, and may bleed when brushing your teeth, but this condition is reversible and after normal hygiene is restored, everything returns to normal.
If no action is taken at the stage of gingivitis, the inflammation penetrates under the gum, the ligament that holds the tooth in the socket is destroyed, bone tissue begins to become arthophic, and periodontal “pockets” are formed filled with soft plaque and tartar. In the absence of treatment, the destruction of periodontal tissue can proceed to the apex of the root and the inflammation will end only after the removal of the causative tooth.
Depending on the severity, the disease manifests itself as follows:
- Soreness, swelling and bleeding of the gums.
- Exposure of the roots of the teeth and the appearance of tooth mobility.
- Discharge from periodontal pockets, accompanied by an unpleasant odor or taste in the mouth.
The rate of development of periodontitis depends on the composition of the microbial flora, the patient’s immunity, genetic predisposition, and the presence or absence of treatment. Unlike periodontal disease, which always affects a group of teeth, periodontitis can be limited to 1-2 teeth, in the case of:
- An “inflated” filling, which creates an increased chewing load that is transmitted to the periodontal tissue.
- The “overhanging” edge of a filling or crown, which irritates the gums and makes hygiene difficult.
- “Overload” of periodontal tissues caused by uncomfortable orthopedic structures or problems with bite.
Usually, eliminating the traumatic factor stops the destruction process and the bone tissue can partially recover.
Treatment methods for periodontal disease
The development of the disease can be slowed down by treating periodontal disease with medications and carrying out the following procedures:
- professional hygiene for timely removal of dental plaque;
- splinting to normalize occlusal relationships;
- the use of drugs for periodontal disease, vitamins and agents to improve microcirculation in tissues (nicotinic acid, aloe extract, heparin);
- massage to strengthen gums during periodontal disease;
- grinding of teeth;
- prosthetics;
- darsonvalization of gums;
- filling erosions.
Modern methods
The most effective treatment for periodontal disease is based on the use of more modern methods, listed below:
- exposure to high pressure oxygen in hyperbaric chambers;
- ultrasonic device for the treatment of periodontal disease;
- local hypo- and hyperthermia;
- diadynamic currents;
- amplipulse therapy;
- electrophoresis;
- UHF therapy.
Which doctor treats periodontal disease? Most patients do not know the answer to this question. A doctor who treats periodontal disease is called a periodontist. Be sure to contact this specialist if you notice pale coloration and receding gums, increased tooth sensitivity, or a wedge-shaped defect. Where to treat periodontal disease? Of course, in a dental clinic.
Always treat gum problems
When a patient comes to the doctor, he complains about something. What symptoms does he see a doctor with before receiving a diagnosis of periodontal disease? What worries him?
Literally, patients tell the doctor this: my gums have sagged, my gums have become exposed, my lower gums have receded. And for some reason the symptom of gum subsidence automatically means that the patient has the so-called. periodontal disease.
More experienced patients, who have already heard a lot of professional terms, who delve into the professional colloquial language of doctors, say this: “The necks of the teeth have become exposed a little, the teeth have become a little higher.” But, according to statistics, most patients complain about sagging gums.
And so, when patients come to the doctor with complaints about the problem of exposed tooth necks, the doctor diagnoses them with periodontal disease. Of course, he begins to treat them. And to treat it specifically for periodontal disease.
But time passes, money also goes away, and the question of why the gums recede and the necks of the teeth become exposed, why the gums recede, has not been resolved. And the patient still has periodontal disease.
Surgical treatment of periodontal disease
Is it possible to cure advanced periodontal disease? The answer to the question is also negative. However, when treating advanced periodontal disease, surgical intervention is most appropriate. We are talking about the stage of the disease when the alveolar process is almost completely atrophied, and in order to prevent the loss of all teeth, the patient undergoes an operation to restore bone tissue during periodontal disease, which will keep the teeth in their places.
What does splinting teeth do?
When mobility occurs, it is important to connect stable and mobile teeth into a single system. The lateral and anterior teeth are splinted separately. A groove is cut on the chewing surface of the teeth into which a splint - a fiberglass thread - is placed.
The front teeth are splinted using a method similar to fixing the bite after wearing braces.
Splints allow you to feel more confident about your teeth while eating.
Splinting teeth makes it difficult to maintain interdental hygiene. Instead of dental floss, you will need dental brushes, it is advisable to use an irrigator and resort to professional hygiene more often.
Read the article To prevent periodontitis, do professional hygienic teeth cleaning 2 times a year.
If you pay due attention to your teeth, the condition of your gums and the general health of your body, then with a diagnosis of periodontitis or periodontal disease, you can save your teeth for many years.
Remedies for periodontal disease
There is no best cure for periodontal disease, and a specific cure has not yet been invented. At the moment, relief from the symptoms of this disease is achieved only through special procedures and complex treatment of periodontal disease with drugs rich in amino acids, proteins and antioxidants. Taking vitamins for periodontal disease also helps accelerate metabolism in periodontal tissues. What vitamins can a doctor prescribe? Typically, as part of drug treatment for periodontal disease, dentists recommend taking the following vitamins and minerals:
- vitamin B6 and vitamin B12 – if periodontal disease develops against the background of pathologies of the digestive system, diabetes mellitus, neurasthenia;
- folic acid – to activate all metabolic processes in the body;
- zinc – for bone tissue regeneration;
- calcium – for mineralization of bones and teeth;
- selenium - for antioxidant and immunomodulatory effects.
You should not self-medicate. The doctor determines which drugs for periodontal disease should be used in each specific case, based on the results of dental diagnostics and the general condition of the patient’s body.
Antibiotics for periodontal disease
Patients are often interested in whether antibiotics are used for periodontal disease in adults? In the initial stages, this is not necessary, since there is no inflammatory process. However, severe degrees of the disease are sometimes accompanied by inflammatory complications. Here, treatment of periodontal disease with antibiotics is considered justified. What antibiotics do doctors usually prescribe for periodontal disease with inflammatory complications? These can be various drugs that help quickly stop inflammation.
Stages of disease development
There are 3 stages of periodontal disease:
- Easy.
The patient has no complaints; very rarely there is a reaction to cold or hot food. The presence of periodontal disease can be determined during a dental examination. The mild stage of the disease is best treated.
- Average.
The roots of the teeth are exposed by an average of 4-6 mm. The patient begins to experience a burning sensation in the mouth, and there is an acute reaction to eating hot, cold or sour foods.
- Heavy.
The roots of the teeth are exposed by 8-10 mm. Chewing food causes severe pain.
Injections into the gums for periodontal disease
In addition to drug treatment, injections for periodontal disease are also used. These are injections of aloe extract, which is an effective biogenic stimulant. Typically, the course of treatment consists of 20 - 25 injections with a break per day. What injections for periodontal disease are prescribed if the disease has become severe? In the presence of an inflammatory process in the later stages of the disease, dental periodontal disease can be treated with injections with synthetic tissue regeneration stimulators according to the same scheme.
Tips for strengthening bone tissue
Experts give several recommendations that may be useful if you have periodontal disease :
- combine myrrh (20 g) with mint and raspberry leaves (15 g of each component). Mix, add wine alcohol (80 g) and vinegar (25 g). Mix again and place in a glass container of suitable size. Infuse for three days in a place protected from sunlight. Rinse your mouth with the prepared mixture a couple of times a day;
- pour sage (50 g) with boiling water (100 g). Leave for about an hour, covering with a lid. Rinse your mouth thoroughly;
- Chop and crush fresh plantain. Use the resulting juice to soak a cotton swab. Wipe gums;
- pour dried calamus (30 g) with vodka (0.5 l). Infuse the mixture for a week in a place inaccessible to light. Strain through cheesecloth. Dilute the product (3 tbsp) with water (200 ml). Rinse your mouth for about 3-6 minutes;
- Chop pine needles (6 tbsp) and pour boiling water (1 l). Bring to a boil, strain, and leave until the mixture cools completely. Rinse your mouth in the morning and evening.
Plates for periodontal disease
Often solutions and ointments for the treatment of periodontal diseases are not effective enough, as they are quickly removed from the mouth with saliva. Therefore, it is necessary to apply products in the form of applications for periodontal disease. However, modern treatment of periodontal disease involves the use of an alternative form of drugs that allows active substances to better penetrate the epithelium to achieve a high regenerative effect. These are plates made from natural polymers (gelatin, collagen, sodium alginate) and medicinal substances that improve metabolic processes in tissues and increase vascular tone (mineral components, enzymes, herbs, vitamins, amino acids, organic acids, phytohormones).
How is periodontal disease treated with plates?
The product is applied to the gingival margin after brushing the teeth and gently pressed into the interdental spaces. Thanks to their adhesive properties, the plates can be held on the gums for 6 to 10 hours. Then their remains are removed with warm water.
The instructions for these plates say that they are intended to protect and improve periodontal tissue. But is it possible to cure advanced periodontal disease with their help? The answer is negative. This product is not intended specifically for the treatment of periodontal disease. It has a general strengthening effect on the entire periodontium as a whole and is more suitable for alleviating the symptoms of gingivitis and periodontitis in the form of bleeding and inflammation of the gums.
Clinical researches
The effectiveness of ASEPTA products has been repeatedly proven clinically. For example, clinical trials of ASEPTA gum gel have proven that using ASEPTA gum gel with propolis for a week can reduce gum inflammation by 31%.
Repeated clinical studies have also proven that the two-component mouth rinse ASEPTA ACTIVE more effectively combats the causes of inflammation and bleeding compared to single-component rinses - it reduces inflammation by 41% and reduces bleeding gums by 43%.
Sources:
- The use of drugs from the Asepta line in the complex treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases (N.V. Berezina E.N. Silantyeva S.M. Krivonos, Kazan State Medical Academy. Kazan.) N.V. BEREZINA, E.N. SILANTIEVA, S.M. KRIVONOS Kazan State Medical Academy
- The use of adhesive balm "Asepta®" in the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases L.Yu. OREKHOVA*, Dr. med. Sciences, Professor, Head of Department V.V. CHPP**, Dr. med. Sciences, Professor, Head of Department S.B. ULITOVSKY*, Dr. med. Sciences, Professor A.A. LEONTIEV*, dentist A.A. DOMORAD**, O.M. YAKOVLEV** SPbSMU named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, St. Petersburg - *Department of Therapeutic Dentistry, **Department of Microbiology
- Study of the clinical effectiveness of treatment and prophylactic agents of the Asepta line in the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases (A.I. Grudyanov, I.Yu. Aleksandrovskaya, V.Yu. Korzunina) A.I. GRUDYANOV, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department I.Yu. ALEXANDROVSKAYA, Ph.D. V.Yu. KORZUNINA, asp. Department of Periodontology, Central Research Institute of Dentistry and Maxillofacial Surgery, Rosmedtekhnologii, Moscow
- The effectiveness of the use of Asept “adhesive balm” and Asept “gel with propolis” in the treatment of chronic generalized periodontitis and gingivitis in the acute stage (Municipal Dental Clinic No. 4, Bryansk, Kaminskaya T. M. Head of the therapeutic department Kaminskaya Tatyana Mikhailovna MUZ City Dental Clinic No. 4, Bryansk
How to treat periodontal disease with folk remedies?
Treatment of dental periodontal disease with folk remedies will not bring results. No rinses or decoctions can cope with bone tissue degeneration. And following advice from articles on the Internet that recommend using hydrogen peroxide or other chemicals to eliminate periodontal disease is not only pointless, but also dangerous to your health. It is important to understand in time that this is a serious disease that requires qualified assistance from a periodontist, and to seek treatment for periodontal disease at the dentist.
Prevention of periodontal disease
There are few preventive measures to prevent the appearance and development of periodontal disease, since the pathology is associated with genetic predisposition and metabolic disorders in the body. In general, doctors recommend maintaining overall oral hygiene through regular brushing and flossing.
You should also follow a certain diet for periodontal disease and to prevent the disease. It is recommended to eat more milk, vegetables, seafood, unrefined vegetable oils, and limit carbohydrate intake. The diet for the prevention and treatment of periodontal disease in adults should include a sufficient amount of raw vegetables and fruits, which promote self-cleaning of teeth from plaque and have a massaging effect on the gums, improving their microcirculation.
Regenerating drugs
The main problem in the treatment of periodontal disease is the restoration of tissues damaged or destroyed during the development of the disease. For this purpose, a variety of drugs are used, including stem cells and other biogenic stimulators of regenerative processes. They are most often administered by injection directly into the affected areas of the gums. Modern methods of treating periodontal disease include the use of the following drugs:
- Fibroblasts
Fibroblasts are connective tissue cells that play an extremely important role in the healing process of wounds and injuries, and also participate in the synthesis of collagen and elastin fibers, which make the soft tissues of the body more elastic. The introduction of fibroblasts helps restore the elasticity and firmness of sagging gum tissue, and also increases the protective properties of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity. The strength of fabrics and their resistance to destructive influences of various natures also increases significantly.
- Stem cells
The anti-aging properties of stem cells are widely known in modern medicine and, especially, cosmetology. Stem cell preparations can stimulate regenerative processes and promote accelerated restoration of cellular structures. Under their influence, the healing process of damage is accelerated, which is extremely important in the treatment of periodontal disease and related diseases.
- Platelet-derived growth factor
Platelet growth factor is a special protein synthesized by the body and involved in the processes of tissue growth and repair. In addition, the growth factor promotes accelerated synthesis of collagen, glycosaminoglycans and other components of connective tissue.
The use of biogenic drugs is an extremely promising direction in modern medicine, but these methods are not widely used today due to technological complexity and high cost. To stimulate recovery processes, you can use more accessible means, in particular propolis. This substance is included in a wide variety of hygiene, therapeutic and prophylactic products; in particular, it is the main active component of the antimicrobial gel for gums ASEPTA. In addition to stimulating tissue restoration, propolis also has a pronounced antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effect, reduces the sensitivity of damaged gums, and eliminates bleeding.