What is periodontitis?
You need to know an enemy, and especially such a formidable one, by sight. Medical encyclopedias report:
“Periodontitis is an inflammatory disease of periodontal tissues.”
To the common man this definition will most likely seem incomprehensible. Therefore, in order to understand how insidious this dental disease is, it is worth remembering what periodontium is and its structure.
Periodontium is periodontal tissues whose main task is to hold the tooth in the socket.
Periodontium includes:
- Gums are soft tissues that surround part of the tooth root and protect it from external influences.
- Bone bed of the tooth or alveolar process. It consists of bone plates, and is penetrated by vessels and nerves.
- Periodontium is connective tissue that fills the space between the bone bed and the tooth itself.
- Cementum is the tissue that covers the root of the tooth.
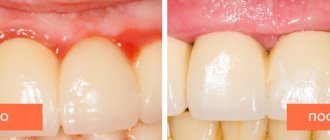
So, periodontitis is a pathological process that affects all, without exception, periodontal structures. Beginning as inflammation of the gums, over time it spreads to the connective tissue and alveolar ridge. It is easy to guess that at a late stage the disease leads to loosening and loss of teeth. And the destruction of the ligamentous apparatus and bone bed makes the process of prosthetics impossible.
Stages of periodontitis
In its development, the disease successively passes through 2 stages:
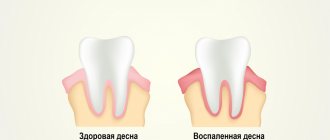
- Initial . The patient periodically begins to notice blood on the toothbrush, sometimes feels itching and numbness in the gums. At this stage, the dentist diagnoses gingivitis - inflammation of the soft tissues.
- Developed . The gums become inflamed, bleed more often, and their contour begins to change. The patient is already uncomfortable drinking cold drinks and foods, and the general body temperature rises to low-grade fever. Over time, the situation only gets worse: teeth become loose, scattered, and later fall out.
If you seek help from a dentist, you can achieve a stage of stabilization or remission
periodontitis. This is not a complete cure, but only a subsidence of the inflammatory process.
A new exacerbation is possible even after a few months, or perhaps the patient will not remember about the problem for many years. It all depends on the timeliness of visiting a doctor and on how conscientiously his instructions will be followed.
The difference between periodontitis and periodontal disease
Very often, patients confuse periodontitis with a rarer, but no less insidious disease - periodontal disease. In both cases, we are talking about pathologies of the periodontium - the tissues that hold the tooth in the bone. But there is a huge difference between these two diagnoses.
- Periodontitis is an inflammatory disease that is widespread among the population. Periodontal disease can develop quickly and aggressively, making it possible to detect it in the early stages;
- Periodontal disease is not an inflammatory process, it is a systemic lesion of the periodontium, which leads to atrophy of the bone bed of the tooth. The disease is rare: no more than 2% of the population. Periodontal disease is characterized by a slow, asymptomatic course.
If the gums in the area of 1-2 teeth are affected, bleeding is present and swelling of the soft tissues is clearly visible, we can confidently speak of periodontitis. Periodontal disease always affects the entire oral cavity, and is detected in most cases very late, when the bone tissue has already severely atrophied.
Periodontitis. Causes and prevention.
Periodontitis is an inflammatory disease of the tissues that support the tooth. These include bone, gums, mucous membrane and adhesive layer. Thus, during the development of periodontitis, the supporting apparatus of the tooth is destroyed. It is for this reason that most people lose their native units ahead of time.
It is quite difficult to cure periodontitis.
Despite this, the process cannot be left to chance. Modern dentistry has enough innovative technologies in its arsenal to combat pathology. Causes
The etiology of periodontitis requires serious consideration by specialists. The method of treatment will depend on this. After all, the causes of periodontitis are quite diverse:
- The predominance of pathogenic bacteria in the microflora of the oral cavity. This happens due to poor hygiene.
- Diseases of internal organs (atherosclerosis, diseases of the digestive system, etc.).
- Pathologies in the development of the dentofacial apparatus (bad bite, position of units in a row).
- Errors in the work of a dentist (defects in fillings, crowns, bridges).
- Presence of predisposition.
The pathogenesis of periodontitis is such that any of the listed factors, together with a weakening of immune functions, leads to an inflammatory process.
Symptoms
Signs of periodontitis may change at different stages of its development. The first symptoms are expressed in the form of bleeding gums while brushing teeth and the addition of an unpleasant persistent bad breath.
Upon closer examination, the following symptoms can be detected:
- tartar and soft deposits above and below the gum;
- swelling of soft tissues;
- pale color of the gums due to impaired blood supply in them;
- unpleasant sensations (pain, burning, itching).
Symptoms of periodontitis in the initial stage are similar to those of gingivitis. However, in the deep layers the mechanism of pathological changes has already been launched. The formation of gum pockets filled with serous contents indicates that a person has developed dental periodontitis. If the disease is not treated, destruction of bone tissue leads to loss of stabilization of units in the row.
Kinds
The classification of periodontitis allows you to divide the disease based on the characteristics of its course. The disease comes in acute and chronic forms. These phases alternate, replacing one another:
- The acute form is characterized by a sudden onset. The most common type of periodontitis is localized periodontitis, which involves the tissue around one or more units. The generalized form, which affects almost the entire gum, is diagnosed less frequently.
- The chronic form occurs in most cases. The stages of periodontitis alternate between exacerbations and stages of remission. Most often, the disease results from gingivitis, covering the deep layers and spreading along the jaw row. Therefore, localized periodontitis in chronic form is extremely rare.
It is worth noting that if you consult a doctor in a timely manner during the acute course of the disease, in most cases you can achieve recovery.
There is also such a thing as purulent periodontitis. The disease is characterized by the release of exudate from the gum pocket. During therapy, doctors use all possible remedies for periodontitis: cleaning deposits, antiseptics, antibacterial tablets, ointments, hardware and surgical treatment.
Classification by severity
If the disease is not treated, the pathological process progresses. Periodontology has 3 stages of the disease. They differ in symptoms and treatment methods.
Mild periodontitis is diagnosed if:
- Only the gum papillae are affected;
- pocket depth no more than 4 mm;
- a small part of the bone tissue underwent resorption.
Moderate periodontitis:
- depth of gum pockets – 6 mm;
- the inflammatory process also extends to the edge of the gum;
- Symptoms include a strong odor, increased bleeding and cyanosis of the tissues.
Severe periodontitis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- the alveolar part of the gum is inflamed;
- pockets reach 8 mm;
- Severe periodontitis is characterized by noticeable tooth mobility;
- The symptoms are accompanied by a noticeable pain syndrome, which often prevents cleaning with a brush and paste.
Depending on the location, the disease can interfere with proper chewing of food.
Diagnostics
Before starting gum treatment for periodontitis, an examination is carried out. An important step is measuring the depth of the pockets. The size of the gap formed between the gum and tooth is taken into account.
To determine periodontitis and the severity of inflammation, the following diagnostic methods are used:
- visual examination and questioning of the patient;
- clinical examination allows you to identify the type of pathological bacteria;
- instrumental sounding;
- X-ray examination.
Periodontitis in children is diagnosed much less frequently than in adult patients. The examination stages are carried out according to the same scheme.
Treatment
Treatment methods for periodontitis in modern clinics are quite varied. The choice of method to solve the problem depends on the clinical picture and individual characteristics of the patient. Mild gum periodontitis can be completely cured. In severe cases, doctors strive to achieve stable remission. Let's consider treatment methods:
- The medicinal method involves the use of antiseptics (Chlorophyllipt, Chlorhexidine, Rotocan). Antibacterial drugs fight pathogenic microflora (Levomethicin, Summed, Erythromycin). Be sure to prescribe a course of immunomodulators and vitamins.
- Ultrasound procedures using the Vector device are combined with medication. The medicine, together with radiation, destroys microbes and stimulates tissue regeneration.
- Surgery is recommended in difficult cases. The doctor performs curettage or flap surgery. Splinting is used to stabilize loose units. At this point, anesthesia is administered. After the operation, the doctor prescribes antibacterial drugs.
- Laser treatment is considered the most advanced method. The result is achieved due to a good cleansing and antibacterial effect.
Treatment of periodontitis in children is carried out practically as in adults:
- professional cleaning of deposits accumulated in the child;
- eliminating the cause of periodontitis;
- teaching children proper oral hygiene;
- prescription of rinses with anti-plaque effect;
- antiseptic rinsing solutions (Chlorhexidine, Givalex, Etonium);
- anti-inflammatory drugs (Traumwell, calendula tincture, Rotokan, Stomatofit).
If necessary, the doctor prescribes antibiotics, determines the dosage and duration of therapy.
Possible complications
Neglect of treating an inflammatory disease can provoke the development of other ailments. Let's consider possible complications:
- Periodontal abscess.
- Early tooth loss.
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- Endocrine disorders.
- Respiratory diseases.
- Various pathological processes during pregnancy.
Preventing the development of the inflammatory process in the oral cavity and its progression will preserve the health of the entire body.
Preventive measures
Following simple rules significantly reduces the risk of illness. Prevention of periodontitis consists of proper oral care and timely treatment of any dental diseases:
- Regular teeth cleaning.
- Correctly selected products
- personal hygiene.
- Healthy lifestyle.
- Balanced diet.
- Strengthening the immune system.
An important role in preventing all dental problems is played by the habit of going to the dentist once every six months for a preventive examination. You should have your teeth professionally cleaned of plaque at least twice a year. These simple rules will preserve the aesthetics of your smile for many years. After all, healthy gums that frame the teeth are no less important in this matter.
Oral hygiene in persons with periodontal diseases
The general principles of oral hygiene are the same as at a young age. But in case of periodontal diseases, it is necessary to pay much more attention to the individual selection of hygiene products and more carefully follow all stages and rules of oral care
Preventative manual toothbrush.
Preference is given to bristles of medium hardness (medium), but if there is a slight reaction of the teeth to cold/hot, sour/, sweet or other external irritants, you should use a “Soft” type brush. If there are wedge-shaped defects of significant depth, pathological abrasion of teeth, exposure of the necks and roots of teeth against the background of periodontal diseases and characterized by a pronounced pain reaction to external stimuli, it is necessary to use a “Sensitive” type brush. But in any case, it should have rounded and polished bristle tips, a multi-level brush field consisting of a power protrusion and an active recess, micro-textured bristles and an indication of the degree of wear. These are the main parameters that can significantly increase the cleaning efficiency of a toothbrush and transfer it from hygienic to preventive.
Therapeutic and prophylactic toothpaste.
For periodontal diseases, it is recommended to use special-purpose toothpastes that have anti-inflammatory and astringent properties (due to extracts and/or oils of herbs and/or plants) and pronounced antimicrobial properties. First of all, preference is given to “herbal” pastes. With increased bleeding of the gums, pastes with pronounced astringent and hemostatic properties are needed. If the teeth have slight hypersensitivity, then you can limit yourself to a paste of the “Sensitive” type; if it is significant, you can use a paste with pronounced desensitivity properties, belonging to the “Oral - B Sensitive original” type.
Therapeutic and prophylactic mouth rinses.
It is advisable to use mouth rinses from the same brand and series as preventive toothpastes. For periodontal diseases, rinses are recommended that reduce the formation of dental plaque and have antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects.
Dental floss (floss).
With periodontal disease, over time, gaps appear between previously tightly standing teeth, and the gums do not adhere tightly to the surface of the tooth root (a periodontal pocket appears). All this makes it difficult to maintain oral hygiene using conventional means. Superfloss (ultrafloss) is an integral component of a hygiene kit for people with periodontal diseases. Due to the rigid guide, superfloss is inserted into the spaces between the teeth or periodontal pockets, and the loosened part most effectively collects and then removes plaque from the lateral surfaces of the teeth and underlying gums.
Special purpose toothbrushes.
Mono-beam toothbrushes are used to clean the cervical (near-gingival) areas of teeth, as well as the distal (far) surfaces of distant teeth or periodontal pockets. If periodontal pockets and interdental spaces are not sufficiently cleaned with a monotuft toothbrush, it is recommended to select a brush-brush, which come in various sizes and are more convenient for use in periodontal pockets.
Oral deodorants.
Oral deodorants can be used during the day if mouth rinses are not possible.
Oral irrigators.
Oral irrigators are compact devices that can be used to wash away food debris and plaque from hard-to-reach areas, such as periodontal pockets, with a stream of water or antiseptic. They are very effective for washing away food debris in the “jet” mode and massaging the gums in the “shower” mode. Jet - before starting hygiene procedures; shower at the end.
Symptoms of periodontitis
The onset of periodontitis is almost invisible to the patient. Few people consider itching in the gums, minor discomfort during chewing and bad breath to be a good reason to visit a dentist. Patients begin to think about the need for treatment later: when the gums begin to bleed, react painfully to brushing their teeth, become inflamed and swell. If no action is taken at this stage, the teeth will soon begin to loosen. Advanced periodontitis can no longer be ignored. It is characterized by: increased body temperature, inability to chew due to sore gums, displacement and loss of teeth.
Traditional methods of treating periodontitis
Today, dentists can offer many medicinal methods for treating periodontitis. However, some still prefer to deal with this problem with the help of “grandmother’s recipes.” Is it worth starting treatment for periodontitis with folk remedies or is it still necessary to go to the doctor?
Periodontitis is an unpleasant disease from any point of view. It causes not only bleeding and painful sensitivity of the gums, loosening and displacement of teeth, but also bad breath, and also makes a person’s appearance rather unattractive. If treatment is not started in time, the acute local process will become chronic, and may even lead to tooth loss.
How to fight periodontitis
A dentist’s help with periodontitis involves making a correct diagnosis and prescribing adequate treatment, depending on the severity of the disease and the individual characteristics of the patient’s body. After carrying out the necessary medical procedures in a dental clinic, treatment of periodontitis should be continued at home. For this purpose, special solutions, medicinal herbs and various folk remedies are used.
Folk remedies
Improving and treating gums with periodontitis using folk remedies is possible only after professional sanitation of the oral cavity. If plaque and tartar are not removed, the gum mucosa will be constantly injured, and pathogens will cause inflammatory processes. Let's say you did everything right: you visited a doctor, performed professional hygienic cleaning, took a course of medication (if it was prescribed). Here's what else might help:
- Beekeeping products Honey and propolis have always been used for stomatitis - their safety and effectiveness make it possible to recommend them even to small children. And if you add viburnum or chokeberry to healing honey, you can get an excellent remedy for periodontitis. The mixture is prepared from one type of ground berries and honey in a 4:1 ratio, and is used as a dessert after meals. You can alternate viburnum and chokeberry daily. The duration of taking this tasty “medicine” is 25–30 days.
- Medicinal herbs For rinsing, a decoction of comfrey or an infusion of oak bark with linden flowers are useful. Crushed comfrey roots should be simmered over low heat for 20 minutes, then cooled and used for daily rinsing twice a day. An infusion of oak bark is prepared in the same way, but after boiling, linden flowers are added to it and allowed to brew. The ratio of oak bark and linden blossom should be 2:1. You should rinse your mouth with this infusion 4-5 times a day until the symptoms disappear completely.
- Vegetable oils A mixture can be prepared from sea buckthorn and fir oil to lubricate the gums. the procedure using it is carried out twice a day, carefully rubbing the mixture into the gums using gauze, which is wrapped around a finger. To achieve the desired effect (that is, relieve inflammation), you need to carefully, with smooth circular movements, massage the gums in this way both from the outside and from the inside.
Modern means
To treat periodontitis at home, modern pharmacological agents are also used - ready-made medicinal rinses and special toothpastes. The solutions have anti-inflammatory, disinfecting, antimicrobial and analgesic effects. Many of them contain not only chemicals, but also extracts of medicinal herbs, some contain antibiotics. Therefore, when choosing a medicinal solution or toothpaste, consult your dentist to ensure that the product is not only effective, but also safe.
Expert opinion
The use of folk remedies in the treatment of periodontitis at the initial stage is quite effective - provided, of course, that the disease is not in an acute phase and does not require urgent dental intervention, for example, to remove tartar that causes inflammation. “Medicines from the people” cope well with the problem of bacterial plaque during the prevention of various inflammatory diseases. And for chronic periodontitis, treatment with folk remedies is the most effective “weapon” from the entire arsenal of preventive measures that can prevent relapses of the disease. However, it is recommended to use folk remedies only under the supervision of a doctor, since they often cause serious allergic reactions that complicate the course of the disease. Therefore, before you undertake periodontitis treatment on your own, visit a dentist who will give you all the necessary recommendations taking into account the characteristics of your body.
Causes of periodontitis
Dentists say the main culprit in the occurrence of periodontitis is bacterial plaque. If you do not remove it from the surface of your teeth in time, over time it hardens and turns into tartar. It, in turn, contributes to the formation of a gap between the gum and tooth, which is commonly called a periodontal or periodontal pocket. As a result, it becomes increasingly difficult to maintain oral hygiene: food debris gets clogged into the resulting gap and provokes an inflammatory process.
The rapid formation of tartar is not necessarily a sign of poor hygiene. The cause of the pathological process may be reduced secretion of saliva, which naturally cleanses the oral cavity. This problem often occurs during long-term use of antidepressants and anti-inflammatory drugs.
The disease can also develop due to a lack of vitamins and microelements. Thus, a lack of calcium will certainly affect the entire skeletal system of the body, and a deficiency of vitamin C reduces the strength of connective tissue. In adults, periodontitis can be a payback for the habit of chewing on one side and a dislike for solid foods: raw vegetables and fruits - ideally, the load on the teeth should be even, and the gums need daily training.
Treatment of periodontitis in dentistry
Periodontitis is an insidious disease: it never heals spontaneously. But you just need to start the process a little, and you can no longer talk about a complete cure, but only about going into remission. Therefore, at the first symptoms of gum inflammation, it is worth carving out a few hours from your busy work schedule and contacting an experienced dentist.
Modern medicine is not at all helpless in the face of illness. Doctors have a variety of conservative, hardware and surgical methods of treating periodontal disease in their arsenal. Which one will be most effective in each specific case can only be determined by a specialist.
Surgical intervention
The main criterion for the need for surgical intervention is an increase in the depth of the periodontal pocket and obvious progression of the inflammatory process, despite drug therapy.
There are several methods of surgical treatment of periodontitis. All of them are aimed at stopping the pathological process, eliminating periodontal canals, and preventing the patient from losing teeth.
Open curettage or flap surgery. Allows you to clean the deepest periodontal pockets, and is performed under local anesthesia. To reach the affected areas, the doctor makes an incision and peels away the gum. And then, using hand tools or using ultrasonic devices, he carries out a thorough cleaning. After this, the cavity of the pockets is filled with osteogenic preparations, and a suture is placed on the gum.
Gingivectomy. This is an operation to remove the excess edge of the gum when it grows excessively. Its goal is to eliminate periodontal pockets in order to prevent the spread of the process from soft tissues to the ligamentous apparatus and bone bed of the tooth. It is performed either under local or general anesthesia.
Splinting. It involves installing a removable or non-removable splint on the inner surface of the teeth, the task of which is to fix the teeth in the correct position and prevent them from moving. This procedure allows you to save teeth even with advanced periodontitis and severe loosening.
If the cause of periodontitis is a malocclusion or a shortened frenulum, the first thing a specialist will do is correct the anatomical disorders. And there are no age restrictions for this.
100% discount on periodontist appointments!
Moscow
Laser treatment
Very often, surgical treatment of periodontitis is supplemented or replaced by a laser curettage procedure. This is a bloodless, minimally invasive method that requires local anesthesia only in patients with a low pain threshold.
In Western Europe, laser curettage has been used for the treatment of periodontitis for about 15 years. Experience has shown that the method is effective for all forms of the disease and guarantees a stable, long-term effect.
During the procedure, the doctor applies a photosensitizer gel to the gums. Then the light guide of the device is inserted deep into the affected periodontal pocket. The next step is to activate the gel with a thin laser beam, which instantly coagulates the infected tissue. Moreover, only pathogenic flora is subject to destruction; neither the laser nor the photosensitizer has any effect on healthy areas of the gums.
The result of laser treatment of periodontitis is complete sterilization of periodontal pockets, on the walls of which a protective photocoagulation film is formed immediately after the procedure. It prevents the penetration of pathogenic bacteria between the gum and tooth, and promotes the rapid closure of the periodontal pocket.
The duration of the laser curettage procedure is no more than 3 minutes. If the disease is detected at an early stage, the affected areas can be completely cured in just one visit to the dentist. In advanced cases, 2 or more procedures may be required, which are carried out with a break of 1 week.
Ultrasound treatment
At the initial stage of development of periodontitis, gum inflammation can be eliminated by simply removing tartar. This type of teeth cleaning is called scaling and is carried out using ultrasonic instruments. One of the most common is the Vector device, developed by the German company Durr Dental.
Unlike traditional scaling, Vector deals with deposits painlessly for the patient. Under high pressure, the device delivers a Fluid Polish polishing suspension to the treated area, which destroys the biofilm on the tooth surface without affecting the root cement and without injuring the soft tissue. This delicate approach allows not only to shorten the treatment period for periodontal disease, but also to avoid the use of antibiotics.
Vector therapy is indicated for patients with any stage of periodontitis. At an early stage, the method leads to complete cure. In more advanced cases, ultrasound scaling precedes surgical treatment.
Antioxidant treatment
Among this group of drugs, the most famous are the following:
- Mexidol. It is a modern antioxidant drug that effectively eliminates periodontitis. Taking this medicine can significantly reduce the treatment time for the disease. If the dosage is correctly chosen, the positive effect becomes noticeable after two weeks.
Mexidol not only has a detrimental effect on bacteria, but also promotes the rapid restoration of the immune system, normalizes cell metabolism and prevents the spread of infection. This drug is recommended by experts for the treatment of not only periodontitis, but also any other inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity.
- Carotenoles. A very new drug that has already gained significant recognition among dentists. Helps restore immunity by attacking bacteria.
Treatment with medications at home
Treatment of periodontitis is always complex. But if surgical methods are not indicated for everyone and not always, and they are increasingly being replaced by hardware procedures, then drug therapy is a mandatory element of treatment. It includes the following:
- antiseptics;
- steroidal and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- immunomodulatory agents.
It is impossible to cope with periodontitis on your own at home! No miraculous toothpastes, magic toothbrushes or even injections will help if you do not eliminate the main cause of inflammation - bacterial plaque and tartar. Therefore, the medicinal method of treating periodontitis will bear fruit only after the dentist has cleaned the teeth, and, if necessary, undergone surgical intervention.
In almost all cases, dentists insist on treating periodontitis with antibiotics. They can be local, in the form of ointments or gels. But more often, broad-spectrum drugs are prescribed: Trichopolum, Doxycycline, Metronidazole. It is recommended to take them in the form of tablets; less often, the dentist may recommend injections.
Treatment with folk remedies
Methods known to our grandmothers help strengthen the gums and relieve inflammation, especially at the initial stage of the disease.
The main thing to remember: alternative treatment must be agreed with the attending physician and carried out under his supervision.
The most effective means for treating gums are:
- Massage the gums using circular movements of the pads of the thumbs. You need to do it in the morning and evening for 5-10 minutes. To make the effect more noticeable, simultaneously with the massage, it is worth rubbing honey, sea buckthorn or fir oil into the soft periodontal tissues.
- Rinse. They are performed immediately after brushing your teeth with comfortable-temperature decoctions and tinctures diluted with water. To make them, they use calendula flowers, oak bark, string, celandine and pine needles.
- Applications. For them you can use honey, beeswax, sea buckthorn oil, Kalanchoe juice.
Herbal medicine: healing herbs and plants
When treating periodontitis using traditional methods, the use of medicinal plants and medicinal herbs is very effective, since most of them have excellent anti-inflammatory and healing properties.
Let's look at the most effective recipes:
- Dry comfrey root is infused in a liter of boiling water for a day. Rinse the mouth with the strained decoction. The procedure is performed three times a day. This will relieve inflammation and pain due to periodontitis.
- Boil two tablespoons of crushed oak bark for 15 minutes in half a liter of water. The decoction should be used to rinse your mouth regularly. Treatment is continued until all clinical manifestations of the disease disappear. Oak bark not only relieves inflammation, but also eliminates bleeding gums.
- Infuse walnut leaves for 2 weeks in a liter of vodka or alcohol. A solution of a tablespoon of tincture and 200 ml of water is used to rinse the mouth. The procedures are carried out for quite a long time, for several minutes, in the morning and evening.
- A decoction of a mixture of linden blossom and calendula flowers is also used to rinse the mouth in the treatment of this disease. Pour 0.5 liters of boiling water over a tablespoon of dry plants. After cooling, rinse your mouth morning and evening.
- Crushed fresh rowan and viburnum berries are taken orally, 3 tablespoons with honey for a month. Berries are a source of vitamins and minerals that stimulate periodontal restoration.
- A mixture of crushed propolis and St. John's wort leaves is infused for two weeks in a bottle of vodka. A teaspoon of the resulting infusion is dissolved in a glass of water and used for rinsing. This procedure will quickly relieve inflammation and remove discomfort in the gums.
- Rubbing the gums with fresh yarrow juice effectively eliminates inflammation during periodontitis. The course of therapy continues for two weeks, and if necessary, it is repeated after five days.
- Pour a glass of boiling water into a mixture containing a teaspoon each of chamomile and sage, and let it brew for at least 15-20 minutes, after which the infusion is filtered. Rinse your mouth with a warm solution, holding it over the affected areas for about a minute. This manipulation is repeated for 10-15 days in a row. As a result, the symptoms of inflammation and bleeding gums are relieved.
- For periodontitis, rinsing with an infusion prepared from string and violet is effective. Pour a tablespoon of the components with hot water and leave for about an hour. This infusion has a beneficial effect on the course of the disease and promotes a speedy recovery.
Is it possible to restore gums?
Periodontitis is a disease that greatly impairs the aesthetics of a smile. That is why dentistry has long and successfully used a surgical method of gum restoration - gingivoplasty. With its help, you can change the height of the gum, improve its structural condition, restore atrophied tissue or, conversely, remove excess.
Contraindications to the operation are: diabetes mellitus, cancer, decreased blood clotting, and inability to use anesthesia.
In other cases, after carrying out anti-inflammatory procedures and achieving stable remission, you can safely start a conversation with your doctor about gingivoplasty.
Types of periodontitis
To select an effective treatment, the dentist must first determine the causes of periodontitis and identify the nature of the disease. Therefore, the classification of periodontitis is not so much of scientific interest as it contains the ability to predict the further development of the situation and select those treatment methods that will give the best result.
One or another type of periodontitis can be diagnosed based on 3 criteria: severity, course of the disease and localization of the process.
By severity
To determine the severity of the disease, dentists evaluate the depth of the periodontal pocket, tooth mobility and the degree of bone tissue resorption:
- with mild periodontitis,
the teeth are immobile, the depth of the periodontal canal does not exceed 3.5 millimeters. The height of the interdental septa is still slightly reduced: no more than one third of its length; - with moderate periodontitis,
the height of the interdental septa is reduced by half its length, the periodontal pockets deepen to 5 millimeters, and the teeth begin to slowly shift; - Severe periodontitis
is visible to the naked eye even when talking to a person. The teeth are displaced and gaps form between them. And the patient complains of severe pain, bleeding, and sometimes the discharge of pus from the periodontal canals.
Severe periodontitis is statistically observed in 15-20% of people over 35 years of age.
With the flow
The course of the disease can be acute or chronic. The acute form of periodontitis is very rare and does not affect the entire oral cavity, but a small area of the gums. It occurs as a result of injury to soft tissues as a result of an impact, an incorrectly installed crown, or a broken piece of tooth.
Acute periodontitis develops at lightning speed and causes severe pain, with which the patient usually rushes to the dentist. The chronic process is characterized by a wave-like course and coverage of the entire oral cavity. When the disease enters the remission stage, the patient mistakenly believes that he is completely cured. But after a few months everything repeats itself, and this time the signs of inflammation will be more pronounced.
With timely consultation with a doctor, acute periodontitis can be cured quickly and effectively. If periodontitis has entered the chronic stage, the prognosis is less favorable.
By localization
Depending on how extensive the area is covered by the pathological process, periodontitis is distinguished:
- localized
or
focal
; - generalized
.
In the first case, the disease manifests itself in only one or several teeth. And dentists talk about the activation of secondary factors. This means that the development of periodontitis could be triggered by a poor-quality filling, contact with arsenic paste or filling material on the gums, careless installation of a prosthesis, and even injury to the gums by dental floss.
In the generalized form of periodontitis, the gums, connective and bone tissue on two rows of teeth are affected. This is typical for the chronic course of the disease, which is much more difficult to treat.
Treatment with leeches
Hirudotherapy is also very effective for dental diseases, including periodontitis. The action of leech secretion is effective in fighting infection, which often provokes the development of this disease, and also stimulates the body’s protective functions, forming a powerful immune system. Treatment of periodontitis in this way begins with treating the gums with antiseptic solutions. After this, 1-2 leeches are placed in the area of the transitional fold of the gum in the projection of the apex of the tooth root for 5-10 minutes. The course of treatment, depending on the extent of the inflammatory process, is 1-5 procedures daily or every other day.
Hirudotherapy is contraindicated for:
- pregnancy
- hemophilia
- severe anemia
- hemorrhagic diathesis
- persistent hypotension
- oncological diseases
- individual intolerance
Diagnosis of the disease
The main diagnostic method for suspected periodontal disease is measuring the depth of the gap between the gum and tooth. In a healthy person it does not exceed 1-2 millimeters. The procedure is carried out using a periodontal probe, a thin instrument with millimeter notches.
If the process is generalized, the doctor measures the periodontal pockets of each tooth, records the obtained indicators and draws up a periodontogram. In the future, it will make it possible to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment or, conversely, to detect the progression of the disease in time.
X-ray examination is important for diagnosing periodontitis: panoramic X-ray or layer-by-layer scanning. It allows you to identify loss of bone tissue and its sclerotic changes.
In very severe cases, the doctor may refer the patient for further examination: measure the degree of hypoxia in the gums, determine the quality of the periodontal microvasculature, examine bone tissue for density.
Prevention of periodontitis
The best prevention of periodontitis is proper oral care. You need to brush your teeth at least 2 times a day: before breakfast and before bed. Moreover, the procedure should take at least 3 minutes, and the main movement when cleaning is from the root to the cutting edge of the tooth. Don't ignore dental floss. They perfectly clean the interdental spaces and prevent the development of pathogenic bacteria.
If the disease has already manifested itself, pay attention to your toothbrush. Her stubble should be stiff. And even if at first brushing your teeth with its help seems uncomfortable, over time your gums will get used to it. You need to change your toothbrush every 1.5 months.
Author: Maria Kozodaeva Candidate of Medical Sciences. Dentist-therapist, endodontist, periodontist, implant surgeon. Work experience more than 11 years.
The information is for reference only. Before treatment, consultation with a doctor is necessary.
Antibacterial agents against Helicobacter pylori
One of the tests prescribed by your doctor may be a blood test for antibodies to Helicobacter pylori. And this is not accidental, since according to data from various sources, it is this bacterium that is resistant to hydrochloric acid that in the vast majority of cases is the cause of peptic ulcer disease.
Medicines for stomach and duodenal ulcers: De-Nol
If this bacterium is not eliminated, regardless of the effectiveness of the drugs used to treat the ulcer, the risk of relapse of the disease and a decrease in periods of remission are very high. There are several treatment regimens for such bacterial infection, the main drugs in which are antibiotics of the nitroimiazoline group - Tinidazole, Metronidazole, Tetracycline.
Since these drugs have been on the drug market for a long time, their effectiveness is increasingly being questioned. This is due to the increased resistance of bacterial strains to this group of antibiotics. They were replaced by more modern antibiotics from the macrolide group. They have many advantages, and significantly fewer side effects and contraindications.
We must not forget about the extremely aggressive environment in which antibiotics have to “work” in the gastrointestinal tract. They must resist the effects of hydrochloric acid, the production of which increases significantly during peptic ulcer disease. The most stable antibiotic in this group is Clarithromycin. It is used in combination with other drugs in a dosage of 0.5 g twice a day.