Pain under the tongue can serve as one of the main symptoms of a whole range of problems, from banal mechanical injuries to a number of pathologies of the oral cavity, nervous system or internal organs. Depending on the cause and location of the pain, it can have a different nature and intensity.
If you or your loved one has pain under the tongue, there is no need to panic or self-medicate - this can only lead to aggravation of the situation. Contact a dentist at a dental clinic, he will conduct a diagnosis, determine the exact cause of the discomfort and prescribe an adequate treatment regimen to effectively eliminate the pain.
Structure of the area under the tongue
Everything that is located under the tongue is called the floor of the mouth. This:
- nerve endings;
- hyoid bone;
- hypoglossal muscles;
- salivary gland;
- connecting folds called frenulums;
- vessels.
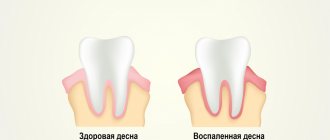
Each element of the floor of the mouth serves its own purpose and is irreplaceable. Only if all muscles, tissues, glands and nerves are healthy does the tongue function normally. If there is pain under the tongue, then we are talking about pathology.
Discomfort in the lateral areas of the tongue
When the tongue hurts on the side of any side, the causes of the discomfort may be a discrepancy in the size of the dentures, inflammation of the mucous membranes, heavy smoking, or characteristic neuralgic manifestations.
Pain on the tip of the tongue
The tip of the tongue is constantly in contact with the teeth and is actively involved in the process of creating sounds, therefore it causes special discomfort to people. The most common reasons for this condition are:
- Minor injuries at the end of the tongue
occur most often, since it is this area that first encounters food, dentures and teeth.
- Glossalgia
accompanied by a burning sensation, as well as the possibility of pain spreading to other parts of the oral cavity.
- Glossitis
– inflammatory disease of the oral cavity.
- Stomatitis
causes small painful wounds at the end of the organ.
- Allergic manifestations
occur as a result of immediate contact with certain medications or foods.
Causes of pain under the tongue
- Allergic reactions cause tissue swelling and pain.
- Harmful microorganisms that appear in the mouth during a sore throat cause acute inflammation. Often, it affects the floor of the mouth.
- Mechanical injuries from a bruise or a fall damage blood vessels, nerves, and soft tissues. Vessels may rupture, which will lead to the accumulation of blood between the muscle fibers.
- Some untreated diseases lead to phlegmon, inflammation with pus inside. In most cases, phlegmon appears under the tongue.
- Ordinary caries, if left untreated, causes inflammation that reaches the sublingual area.
- There are many ducts in the salivary gland, and if an infection gets into it, then through these ducts it can easily enter the gland tissue.
- Injury to the frenulum of the tongue. In people with a congenital short frenulum, injuries occur more often. Even a normal conversation can cause a breakup. However, people with a normal frenulum size also suffer. Inflammatory diseases and allergic reactions often lead to injury, leading to swelling of the tongue and the appearance of ulcers. But also improper oral hygiene leads to damage to the frenulum - the so-called dangerous brushing.
Some people have asymmetry of the hyoid bone from birth, and sometimes this anomaly is formed due to injury. Asymmetry prevents the organs of the floor of the mouth from functioning properly.
Tongue injuries
Another reason why the tongue hurts on the side lies in mechanical injuries to the organ. They occur when eating food with sharp parts (seeds, nuts, undercooked cereals), hitting, or biting. Damage can occur due to a seizure, sports, falls, or various accidents.
If you are absolutely sure that the soreness is the result of an injury, then you just need to give the tongue time to recover. Nevertheless, examination by a specialist to clarify the diagnosis and treatment will not be superfluous.
How is the sublingual area treated?
Considering the above reasons, if you have the slightest pain in the sublingual space, you should immediately consult a doctor. The doctor will find out the source of the pain and determine a treatment regimen. In some cases, allergists and therapists provide treatment. But more often, pain in the floor of the mouth is treated by dentists.
In case of injury to the frenulum or the tissues of the area under the tongue, rinsing will be prescribed: with a solution of soda, romazulan, stomatophyte, hexoral, chlorophyllipt or iodinol. You should rinse your mouth according to the following schedule:
- morning and evening before bedtime;
- after meal.
The doctor also treats the area of injury with an antiseptic and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Inflammations caused by dental problems require immediate treatment - the specialists at Family Dentistry will get rid of caries, pulpitis or periodontitis and prescribe a course of anti-inflammatory drugs to cope with sublingual inflammation.
But one of the most dangerous diseases in the floor of the mouth is inflammation of the salivary glands. It is important to begin treatment before an abscess appears and complications develop. In this case, the doctor prescribes:
- antibacterial therapy - the doctor injects medicine into the gland and also prescribes a broader-spectrum antibiotic;
- drugs to activate saliva secretion - either a solution of potassium iodide or pilocarpine is used, sometimes regular lemon is used;
- hot dry compresses;
- physiotherapy course.
If the inflammation is advanced and pus appears or a stone has formed, the patient is sent to a surgeon, who cleans the gland cavity of pus and removes the stone.
Treatment and removal methods
The treatment regimen is drawn up depending on what factors caused the anomaly. But treatment is necessary so that the acute stage of the disease does not develop into the chronic phase. If this happens, the exacerbation will recur from time to time. This form of the disease is more difficult to treat. If necessary, laser treatment of gums should be carried out on time. A healthy oral cavity is the key to the overall well-being of the body.
- The doctor selects medications based on the underlying pathology. The initial manifestations of the disease are successfully eliminated with medications and local applications. According to indications, medications are recommended that stimulate saliva production. This may be Galantamine, Pilocarpine, Potassium Iodide. To maintain general condition, the doctor selects means to stimulate the immune system.
- Serious blockage of the salivary glands is eliminated by mechanical cleaning of the ducts. Today, sialoscopy, a minimally invasive procedure for grinding mineral deposits, is widely used.
- Purulent papules are opened, after which the exudate is removed. Surgical technologies such as galvanocaustics, electrocoagulation, cryodestruction, laser beams, and radio waves are used.
- Sanitation of the oral cavity to accelerate the regeneration of damaged tissue includes rinsing with Chlorhexidine, Furacilin, Rotokan, Miramistin.
To prevent pathology, you need to regularly carry out hygiene procedures with a brush and toothpaste. In addition, floss and irrigator should be used. It is necessary to visit the dentist every six months, and other doctors when the initial symptoms of the disease appear.
Prevention of inflammation of the floor of the mouth
To prevent diseases of the sublingual area, dentists give recommendations on proper oral care:
- take care of your gums;
- avoid the accumulation of bacterial plaque;
- visit the dentist 2 times a year;
- prevent the occurrence of caries;
- brush your teeth 2 times a day.
But if the patient has congenital or acquired anomalies in the development of the floor of the oral cavity, such as a shortened frenulum or structural asymmetry, then you will have to be more careful to prevent injury. Some abnormalities can be treated. Come to an appointment at Family Dentistry and experienced specialists will tell you how to get rid of defects, tumors and inflammations.
Catarrhal glossitis
If the tongue hurts on the side and a white coating covers its surface, then this is most likely catarrhal glossitis - a special case of this disease. It can be considered as a symptom of other pathologies. In particular, it is called:
- caries;
- stomatitis;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- various infections (measles, diphtheria, etc.).
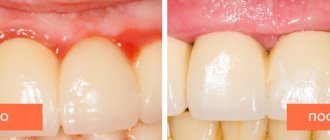
In addition to pain and plaque, symptoms of catarrhal glossitis include swelling of the tongue and a burning sensation, which is especially worse after eating or talking. The disease is treated by eliminating its causes and rinsing the mouth with antiseptic solutions.
The tongue itches - what to do if the organ literally itches
The tongue can itch not only in a figurative sense. If you experience unpleasant irritating sensations, the first thing you should do is figure out what could be the reason for the appearance of this symptom. The organ is a muscle containing a huge number of nerves and blood vessels. The occurrence of discomfort, burning, soreness, swelling and itching in the tongue always indicates some pathological condition, and the symptom itself may be associated with dental disease and disturbances in the functioning of internal organs.
Why might my tongue itch?
In any case, if this symptom develops, you should immediately see a specialist. Further in this article we will find out why the tongue may itch, what preconditions contribute to this, and what to do in such a situation.
Diagnostic measures
The only correct decision regarding the appearance of the symptoms described above is to contact a knowledgeable specialist. Only a doctor can conduct a competent examination and identify the true cause of the discomfort. Thus, the main diagnostic procedures include:
- general blood analysis,
- taking a swab from the throat.
Tests can determine the true cause of the problem.
Having the test results in hand, the doctor can significantly narrow the range of suspected diseases and even immediately make an accurate diagnosis. It is likely that at the stage of identifying the source of the problem, consultation with highly specialized specialists - a dentist, neurologist, gastroenterologist - may be required. Without knowing the exact doctor’s conclusion, you should not make any attempts to solve the problem yourself, otherwise you can only worsen the situation.
Why does swelling of the tongue still occur?
We list the most common reasons why an organ may swell:
- an allergic reaction resulting in Quincke's edema;
- glossitis disease or an inflammatory process that affects the tissues of the tongue;
- hypothyroidism or diseases of the endocrine system;
- infectious diseases, when the tongue may suddenly swell;
- injury caused by a broken piece of tooth, or incorrect prosthetics;
- disruption of the metabolic process;
- malignant formations;
- complications caused by piercing, etc.
An experienced doctor will help determine the true cause of swelling of the tongue, who will diagnose the oral cavity under the careful supervision of the patient.
Possible consequences
If the swelling is not eliminated in time, then negative consequences will not keep you waiting. They may appear as follows:
- chronic or acute respiratory dysfunction;
- violation of a person’s aesthetic appearance (almost constantly open mouth with tongue hanging out);
- psychological discomfort;
- speech distortion;
- malocclusion;
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract;
- copious amounts of saliva;
- tooth decay and loss.
HPV vaccinations
HPV vaccine
You can protect yourself from the formation of growths in the oral cavity by getting vaccinated against the papilloma virus. There are many different rumors around this vaccine, but they have no basis in terms of effectiveness.
The product contains substances of organic origin that promote the production of cells in the body that resist the development of condylomatosis.
Effective means are used for vaccination:
- Cervarix;
- Gardasil.
These vaccines are not used in the treatment process; they are intended solely for preventive purposes. The procedure must be performed before sexual activity begins; the maximum age of the patient is 26 years. When using the product at an older age, the effectiveness decreases significantly.
One vaccine protects the body from the papilloma virus for 8 years.
How inflammation develops
To prevent such inflammation, teach your child to follow simple hygiene standards. It is very important to brush your teeth regularly. If a child finds a wound in his mouth, it should be immediately treated with brilliant green or iodine. Invite your child to rinse his mouth thoroughly with a decoction of chamomile, calendula, sage, a weak solution of potassium permanganate or soda. All these products have an antibacterial effect. If swelling or painful redness appears, take your child to the doctor immediately. He will recommend how to proceed further. Don't risk your child's health and don't waste time on self-medication! Under no circumstances should this swelling be rubbed, iced, or heated. Because of this, the abscess can burst inside.
Treatment of tongue tumors: strategies and methods of combating malignant tumors
In order to choose the right treatment method, it is imperative for a specialist to conduct a series of diagnostic and biochemical studies. To determine the type, shape, type and stage of cancer, a biopsy is done, after which the resulting biopsy is examined histologically, finding out which treatment method can kill these particular cancer cells. You can see how much tissue is affected and how deeply the metastases have grown using CT.
Radiation therapy
The main treatment for tongue cancer is still radiation therapy. In particularly advanced cases, when there is a need to prescribe combination therapy, treatment with medications is resorted to. In the first and second stages of cancer of the lower and lateral surfaces of the tongue, radiation therapy is used using the contact method; in later stages, a remote type of exposure is used.
Surgery
Surgery is indicated only as a radical method of treatment. Since excision of tissues in the mouth will inevitably lead to their subsequent scarring, and therefore to a sharp deterioration in the patient’s quality of life. With extensive metastasis, invasive interventions do not make sense, since it is not possible to completely remove the affected tissue. When predicting a favorable outcome, the following manipulations are performed: partial resection of the tongue, cheeks, palate, mouth and jaws.
After a successful operation using the Krail method, patients have the opportunity to live for at least another five years. And if for objective reasons, for example, if the patient refuses surgery, resection cannot be performed, then the patient is prescribed a course of dosed chemotherapy. In any case, the type and method of treatment will depend on the patient’s age, stage, shape, rapidity of growth, abundance of metastasis and general health of the patient.
Abscess of the root of the tongue: Symptoms
The symptoms of an abscess will differ depending on the depth at which the abscess is located. There are two types of abscess:
- Superficial abscess - the epicenter of inflammation is located directly under the layer of mucous tissue. In this case, swelling and redness are clearly visualized. The swallowing process is accompanied by severe pain and body temperature rises. Spontaneous opening of the abscess is possible, after which relief occurs.
- A deep abscess is an inflammation in the thickness of the tissues of the tongue, during which the general condition can sharply worsen: a headache appears, the temperature reaches the maximum level, and fever is possible. The mental lymph nodes may also be enlarged, the tongue becomes bluish, and there is a putrid odor from the mouth.
With an abscess of the root of the tongue, severe swelling is observed, which makes it difficult not only to speak, but also to breathe.
Important! If you have any discomfort while swallowing or a feeling of tightness at the root of your tongue, you should immediately consult a doctor. Rapidly developing swelling of the tongue can lead to suffocation.
Frequently recurring abscesses in the center of the tongue may indicate a pathology of the structure of the organ (unfused blind foramen).
Appearance in children
Children often face this problem. The appearance of similar symptoms in a child almost always indicates the development of candidiasis. Here it is necessary to conduct a careful visual examination of the oral mucosa for the presence of a dense white coating with a cheesy consistency - this is the very first sign of the pathology in question. If your baby is still very young and cannot tell you about the symptoms that are troubling him, pay attention to whether he is constantly sticking out his tongue. This is how little children usually make it clear that they feel discomfort in the organ.
Stomatitis is common in infants
A common accompanying symptom is burning, and this is a good reason for parents to worry. Here you need to monitor the child’s psycho-emotional state, make sure that he does not experience any serious worries or stress. If you suspect that the cause of the itching lies precisely in the psychological state of the baby, it makes sense to show him to a neurologist. If the diagnosis is confirmed, the doctor will prescribe a course of sedatives. A childhood disease such as scarlet fever can also provoke itching in the tongue and even in the throat. In any case, if suspicious signs of pathology appear, the child should be shown to a doctor as soon as possible.