The main criteria for the treatment of gingivitis are:
- Complexity
Each specific case requires a number of therapeutic procedures. Both local and general treatment are necessary. Therapy should be aimed not only at relieving symptoms, but also at the causative factors.
- Individuality
The features of the clinical course, associated problems (their presence and nature), as well as factors of local and general defense of the patient’s body (the state of the immune system) must be taken into account.
- Systematicity
Chronic forms of the disease require regular courses of maintenance therapy to bring the disease into stable remission.
Treatment tactics depend, first of all, on the form of the disease. Let us consider in detail the specifics of treatment of three forms of gingivitis. This will help you understand the basic principles of therapy and roughly explain how your dentist will treat gingivitis.
Which doctor should I contact?
If alarming symptoms appear, contact your dentist. If your diagnostic exam reveals signs of periodontal disease, your dentist will refer you to a periodontist. This is a doctor specializing in the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of pathology of periodontal tissues.
Up to contents
“The information in this article is for reference only and does not replace professional advice from a doctor. To make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment, consult a qualified specialist."
Sources:
- Anne E. Beall, Can a New Smile Make You Look More Intelligent and Successful? // Dental Clinics of North America, Volume 51, Issue 2, April 2007, Pages 289-297.
- NHS, The health risks of gum disease, Page last reviewed: 31 August 2022, URL: https://www.nhs.uk/live-well/healthy-body/health-risks-of-gum-disease/
- Therapeutic dentistry: Textbook for medical universities, ed. E.V. Borovsky // MIA, - 2011, - pp. 181, 216, URL: https://www.rulit.me/books/terapevticheskaya-stomatologiya-uchebnik-read-301411-1.html
- CLINICAL GUIDELINES (TREATMENT PROTOCOLS) FOR A DIAGNOSIS OF GINGIVITIS Approved by Resolution No. 15 of the Council of the Association of Public Associations “Dental Association of Russia” dated September 30, 2014, - URL: https://minzdrav.gov-murman.ru/documents/poryadki-okazaniya-meditsinskoy -pomoshchi/5_gingivit.pdf
- Handbook of Dentistry, ed. A.I. Rybakova // Medicine, – 1977. – p. 78-79, 91-100.
- Rybakov A.I., Banchenko G.V. Diseases of the oral mucosa // Medicine, – 1978, p. 75-78.
- Dentistry: Textbook edited by professors V.N. Trezubova and S.D. Arutyunova // Medical book, – 2003, – p. 336, URL: https://studfile.net/preview/5346704/
- Dental gel for gums “Metrogil Denta®” in the treatment of periodontal diseases and oral mucosa // Practical Medicine, – 2003, – No. 1 (33), – p. 105.
Up to contents
Treatment of chronic catarrhal gingivitis
- The first and mandatory step in therapy is professional teeth cleaning - removing tartar and smoothing the surface of the teeth using ultrasonic and sandblasting devices. The steps of the procedure are shown in the figure below.
- Training in proper individual oral hygiene.
- Elimination of local factors that contribute to the formation of plaque - treatment of caries, correction of orthodontic and orthopedic structures.
- Relief of a problem that aggravates the effect of a microbial factor - elimination of injuries, treatment of pathology of the attachment of the frenulum (plastic surgery to enlarge the frenulum).
- Antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs in the form of oral baths, applications, irrigations are used for gingivitis at the stage of a pronounced inflammatory process.
- To improve the process of tissue regeneration, keratolytic agents are used (sea buckthorn and rose hip oil, solcoseryl, vitamins A and E).
- General strengthening therapy is necessary - the use of vitamins, adaptogens, antioxidant therapy, and means to normalize metabolism.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of gingivitis is carried out in several ways, which are used in combination. At the initial stage, the doctor collects anamnesis:
- The diet and bad habits are revealed;
- The reasons for tooth extraction/loss are clarified;
- Genetic predisposition is determined.
After this, an examination of the oral cavity is carried out, the depth of the dental canals is studied with a special probe. Additional methods of diagnostic testing include x-rays and testing the sensitivity of the pulp.
The following methods can be used to diagnose gingivitis:
- Fedorov-Volodkina index;
- RMA index;
- Schiller-Pisarev test.
Treatment of ulcerative gingivitis
Therapeutic measures should be aimed at eliminating the inflammatory process, increasing the patient’s body’s resistance to microbes, and preventing the influence of local factors that provoke necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis. Let's consider the main stages and principles of the treatment.
- Professional oral hygiene.
- Antibacterial and anti-inflammatory therapy.
- One of the features of the treatment of necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis is the removal of necrotic areas of tissue; Hydrogen peroxide and chlorhexidine are usually used.
- The use of keratolytic agents, vitamins, adaptogens.
- Training in the rules of proper oral hygiene, as well as monitoring hygienic skills.
- One of the features of the ulcerative form of the disease is severe pain, therefore the treatment of gingivitis, due to the difficulty of carrying out normal hygienic care, is accompanied by the use of antiseptics and anti-plaque agents.
- Elimination of factors contributing to the formation of plaque on the surface of teeth.
- Elimination of the problem that aggravates the proliferation of microorganisms and their pathogenic effects.
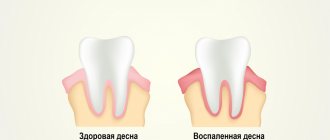
Gingivitis - classification
Based on the form of the disease and the nature of its course, acute and chronic gingivitis is distinguished.
- The acute form begins with noticeable redness and bleeding of the gums. They swell and the interdental papillae enlarge.
- The chronic form is not so obvious, but the pathological process leads to the growth of gingival tissue and its “creeping” onto the tooth.
Depending on the type of inflammatory process, gingivitis occurs:
- Catarrhal
— exudative processes predominate, fluid is released from hyperemic gum tissue. There is a burning sensation in the oral cavity, there is heavy plaque on the teeth, and the papillae are swollen.
- Hypertrophic
— proliferative processes (tissue proliferation) predominate. In turn, hypertrophic gingivitis comes in two forms - edematous and fibrous. In the first form, the gums bleed and are painful, and in the second form, the gums are dense and no bleeding is observed.
- Ulcerative-necrotic
- the process goes deeper into the periodontal tissue, causing, in addition to pain and bleeding, ulceration of the gums. The general condition suffers, the lymph nodes enlarge. If left untreated, this type of gingivitis can develop into Vincent gingivitis, which affects the entire mouth.
Dentists also distinguish mixed varieties of the disease.
Treatment of hypertrophic gingivitis
The principle and procedure for carrying out treatment procedures is similar to those for catarrhal gingivitis. However, the hypertrophic form sometimes requires surgical intervention.
Gingivectomy is a procedure performed to remove diseased tissue. Its stages can be seen in the figure below. Gingivectomy allows you to get rid of a large amount of excess tissue and prevent the accumulation of plaque, as well as stop the intensification of the inflammatory process.
Stages of gingivectomy
Treatment of gingivitis at home
Gingivitis is an inflammatory process that can be eliminated without serious medical intervention. At this stage, treatment with folk remedies is effective. But if the disease is left to chance, gingivitis can cause periodontitis, a disease that is much more difficult to cure. Therefore, treatment of gingivitis in children and adults is also reliable prevention.
A decoction of oak bark, medicinal chamomile, sage, as well as commercial anti-inflammatory drugs are used to treat gingivitis at home. They have a soothing, antimicrobial and astringent effect.
Simple ways to get rid of a difficult disease: prevention of gingivitis
The best and main method of prevention is compliance with oral hygiene measures.
Personal hygiene
Regular and high-quality teeth brushing (at least twice a day). It is important to know how to choose the right toothbrush; its bristles should not injure the gums, but at the same time remove plaque well. And also use the toothpaste that is suitable for you.
Brushing your tongue is an important part of oral hygiene and should be cleaned as often as your teeth.
It is necessary to use a mouthwash whose antiseptic properties kill most known microorganisms. It is advisable to use it after every meal.
Cleaning the interdental spaces with dental floss at least once a day. It helps remove all food particles that the toothbrush cannot reach, thereby preventing plaque from accumulating in between the teeth.
If you are the owner of dentures, veneers, crowns or implants, then you cannot do without an irrigator. It perfectly cleans the surface of artificial structures, as well as the joints between them and natural teeth.
Visit the dentist every six months
In addition to the consultation appointment, the periodontist will, if necessary, perform professional teeth cleaning. It includes:
- removal of hard dental deposits and soft plaque from tooth surfaces. This cleaning can be carried out using ultrasound or an Air Flow device;
- polishing teeth with a special paste that prevents tartar deposits. In addition to the polishing effect, it has the property of remineralizing tooth enamel, as it contains calcium and fluoride;
- carrying out medical applications on the gums with an antiseptic solution.
Following these really simple methods will help you avoid a whole host of gum and dental problems.
Cure gingivitis is the last opportunity to stop the serious process of inflammation of periodontal tissues - periodontitis, which leads to the loosening of healthy teeth and their loss. In addition, treatment of periodontitis is much more difficult and less effective. Therefore, if you have the slightest problem with your gums, do not forget to see a doctor.
Symptoms and consequences
Symptoms of gingivitis are determined by stage. The disease can begin with the following manifestations:
- swelling, redness, looseness of the gums;
- increased sensitivity of tissues, bleeding during brushing teeth and eating due to fragility of blood vessels;
- pain when chewing and touching;
- bad breath.
As the disease progresses, the necks of the teeth may become exposed, which leads to increased sensitivity of the teeth - it becomes difficult to accept hot and cold drinks and foods. The pain also increases over time, and severe difficulty chewing food may occur. In addition to general symptoms, there are also specific ones characteristic of a particular type of gingivitis.
The consequences of gum inflammation can be very serious: the pathological process often spreads to the ligamentous apparatus of the tooth, and periodontitis occurs. This condition is dangerous due to the mobility of teeth and the high probability of their loss. A chronic focus of inflammation in the mouth is a risk factor for the development of diseases of the ENT organs.