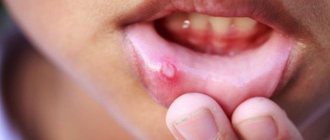
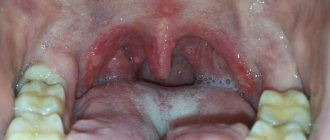
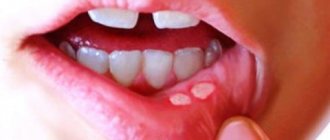
Bacterial stomatitis: before and after photos
The causes of infection may be:
- pockets of bacteria accumulation on carious teeth;
- germs entering the mouth due to herpes;
- infection during treatment - bacterial stomatitis can develop if the doctor does not comply with antiseptic rules;
- chronic diseases of various organs;
- contact with a sick person (for example, a kiss).
Symptoms of infectious stomatitis are, first of all, redness of the oral mucosa in the place where microbes entered the wound, swelling, and in the necrotic form, a rash. In children, cracks may form in the mucous membrane, and the gums begin to bleed. The damaged area is itchy and painful.
If bacterial stomatitis is not treated, the temperature rises, a headache appears, the lymph nodes and tonsils become inflamed, and due to intoxication of the body, the rash spreads throughout the body. Children may develop a sore throat and experience pain in the knee joints.
Prevention of stomatitis
You can reduce the risk of developing stomatitis using the following recommendations:
- regular washing of toys, bottles, pacifiers, breast hygiene if the baby is breastfed;
- general strengthening activities: walks, wet cleaning, a balanced diet, moderate hardening, adherence to a daily routine;
- fighting bad habits of biting nails, pencils, etc.;
- regular dental examinations and timely interventions in case of dental injuries.
The dentists of the Family Doctor clinic treat and prevent stomatitis in children.
Advanced equipment allows us to quickly and accurately assess the condition of the oral cavity and perform the necessary studies in a short time. We practice modern approaches to the treatment of inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity and adhere to an individual approach to each small patient. Consultations with a pediatric dentist are available by appointment. To make an appointment, call the single contact center or fill out a special online appointment form with a pediatric dentist on the website, or you can also visit the clinic’s reception in person.
Treatment of bacterial stomatitis
Self-medication for infectious stomatitis is completely excluded, since it is necessary to accurately identify the pathogen and select drugs that suppress it. Such studies are carried out in the laboratory. This is especially important when it comes to babies. To prevent possible complications, parents of a baby should immediately consult a doctor as soon as they see an inflamed scratch or swelling in the child’s mouth.
When treating bacterial stomatitis, the following are used:
If necrosis has developed, dead tissue is removed surgically, after which it is necessary to completely sanitize the oral cavity.
In parallel with medical measures to eliminate the symptoms of bacterial stomatitis, the patient is prescribed a diet. During this period, it is necessary to ensure maximum sparing of the oral mucosa, limit the consumption of carbohydrates and enrich the diet with vitamins and proteins.
- Superficial (catarrhal). In this case, symptoms of intoxication manifest themselves in a deterioration in appetite and an increase in temperature. There is discomfort when chewing and swallowing food, and the secretion of saliva periodically increases. When examining the oral cavity, a white coating on the tongue is found (on its lateral surfaces there are clearly visible imprints of teeth), bleeding gums, and hyperemia of the mucous membrane. Lack of treatment for catarrhal bacterial stomatitis leads to the disease progressing to the next, more severe form.
- Deep (ulcerative-necrotic). The patient's condition worsens. Symptoms of intoxication intensify: a person has a headache, the temperature rises to high levels, sleep and appetite are disturbed, weakness, irritability, and lethargy appear. Also, bacterial stomatitis in this form is characterized by pain when chewing, bad breath, and increased salivation. When examining the oral cavity, bleeding gums, hyperemia of the mucous membranes, and the presence of ulcers are revealed - first small, covered with a grayish coating, then enlarged, deep, with traces of tissue decay. Immunostimulants. They are necessary to boost immunity and prevent new outbreaks of the disease. These drugs have local and general effects. The doctor selects the optimal treatment option depending on the patient’s condition. For the same purpose, it is recommended to take a course of vitamins.
- Antibiotics. They are prescribed when bacterial stomatitis has become severe or the cause of the disease is systemic diseases of the internal organs. Effective remedies that stop infection directly in the oral cavity are ointments that contain an antibiotic. They give excellent results if the causative agent is a coccal infection. Among the drugs for oral administration in the treatment of bacterial stomatitis, penicillin, lincomycin, gentamicin, kanacimin and others are used.
- Antiseptics. At the initial stage and in the middle of the disease, rinsing with a chlorhexidine solution and treating the mucous membranes of the oral cavity with an anti-inflammatory gel with an analgesic effect are recommended. After the disappearance of acute symptoms, treatment of bacterial stomatitis continues with the help of epithelializing agents that promote rapid healing of defects.
Causes of childhood stomatitis
The immediate causes of stomatitis are bacteria, viruses and fungi. These microorganisms may be present in small quantities in a healthy child, but they begin to multiply and cause disease in the presence of certain factors.
Factors contributing to the occurrence of stomatitis
- Failure to comply with hygiene rules (the child may touch the mouth with dirty hands), hard plaque on the teeth;
- Weakened immunity;
- Long-term use of medications (especially antibiotics). Antibiotics disrupt the natural microflora, promoting the growth of fungus and the occurrence of fungal stomatitis.
Diagnostics
Most often, the diagnosis is made by a dentist after examining the oral cavity. In some cases, the doctor may prescribe additional examinations (bacterial culture, PCR smear, etc.) to detect candidiasis or the herpes virus. In case of massive damage to the oral cavity (severe forms of stomatitis), it is necessary to conduct a blood test and seek advice from a therapist. During diagnosis, it is important to distinguish between herpetic and aphthous forms of stomatitis, since different special therapy is chosen for them.
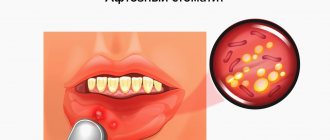
Causes of aphthous stomatitis
Aphthous stomatitis can be an independent disease or develop as a result of complex causes. Among them:
- Using aggressive agents that dry out the oral cavity (for example, sodium lauryl sulfate) during daily oral hygiene. The mucous membrane becomes more vulnerable, especially to sour and pungent tastes, and ulcers easily form on it.
- Mechanical damage to the oral cavity. Accidental biting of the inner surface, scratches from fillings and dentures, sharp chips of a tooth, rough traumatic food violate the integrity of the mucous membrane, and the resulting ulcer can serve as the beginning of the disease.
- Nervous tension and stress.
- Unbalanced nutrition, diets, nutrient and mineral deficiencies. Particularly critical is the lack of iron, zinc, folic acid, selenium, and vitamins B and C.
- Allergy to food. Products with gluten (flour), apples, tomatoes, chocolate, seafood and some food additives are critical.
- Menstrual cycle in women. Codependency with aphthous stomatitis is observed in only 10–15% of cases.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Chronic blood diseases, gastrointestinal tract, immunodeficiencies.
- Long courses of taking nonsteroidal drugs, medications for arrhythmia and high blood pressure.
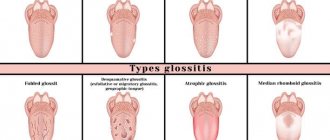
Types of stomatitis in children
Modern medicine knows a huge number of varieties of stomatitis. They can have an acute course, that is, be accompanied by pain, discomfort, and a disturbance in the general condition, or they can have a chronic course. Chronic stomatitis passes almost unnoticed for a person, pain is not expressed, general health does not suffer.
Let's look at the most common types of stomatitis in children, which dentistry in Belarus .
Acute herpetic stomatitis
Acute herpetic stomatitis is caused by the herpes virus. There are several types of herpes virus. The disease that appears on the lips and in the oral cavity is caused by the first two types of the virus. Adults remember herpes when blisters appear on the lips due to stress or hypothermia, and in children it manifests itself in the form of ulcers in the mouth and even a rise in temperature. As a rule, the disease begins with inflammation of the gums and enlarged lymph nodes. If a child looks into the mouth, you will notice several bubbles on the mucous membrane of the lip, gums, and cheeks. Over time, the membrane of the vesicles bursts and ulcers form. These ulcers are painful and the child refuses to eat. This stomatitis occurs when the baby first encounters the virus.
It is most often transmitted from parents through kissing and sharing cutlery. 98% of the world's population is infected with this virus, so it is useless to protect yourself from it. Infection with the herpes virus does not always occur with manifestations of stomatitis, and is often completely unnoticeable. But, if the latter does appear, the parents’ task is to provide proper care and alleviate the symptoms.
Traumatic stomatitis
Traumatic stomatitis is associated with mechanical damage to the mucous membrane. Children often put toys and cutlery in their mouths and can injure themselves and cause stomatitis. Stomatitis can form at the point of contact between the edges of a decayed tooth and the cheek. A bacterial infection sometimes attaches to the wound, resulting in an inflammatory process that lasts several weeks.
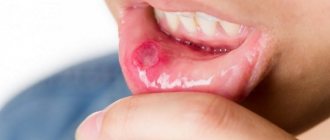
Chronic aphthous stomatitis
Chronic aphthous stomatitis manifests itself in the form of white spots (aphthous) on the mucous membrane of the lips, cheeks and sometimes gums. In the first days, the spot is surrounded by a red rim. Then a small ulcer forms at the site of the spot. After 7-10 days, the ulcer heals. The causes have not been fully elucidated, but it is believed that it often occurs in children with allergies, intestinal diseases and weakened immune systems.
Candidal stomatitis
Candidal stomatitis is caused by the fungus Candida Albicans. You can see red spots and ulcers in the child’s mouth. A cheesy white coating can be seen on the cheeks and tongue. Often this stomatitis appears after prolonged use of antibiotics. Children complain of pain and refuse to eat.
Causes
There is still no consensus on why aphthous stomatitis occurs. However, most doctors believe that the main reason for the development of the disease is weakened immunity.
Often the occurrence of stomatitis is a consequence of other diseases: influenza, tonsillitis, tonsillitis, gastrointestinal diseases. Provoking factors include a sharp change in climate zone and a large amount of stress in everyday life.
Many microorganisms enter the human body through the oral cavity: a decrease in the overall immunity of the body entails a decrease in the level of resistance of the mucous membrane. As a result, the concentration of microbes in the mouth increases, the result of which is the development of the disease.
Forecast and prevention of the disease
If you consult a doctor in a timely manner, the treatment prognosis is favorable. Strict adherence to the doctor’s recommendations allows you to achieve remission.
The main prevention of stomatitis is maintaining oral hygiene. In order not to injure the mucous membrane, it is recommended not to use a hard brush. From time to time it is worth using pastes with an anti-inflammatory effect (contain oak bark).
After each meal you need to rinse your mouth with an herbal solution or special compositions. Regular visits to the dentist twice a year increases the chance of noticing the first manifestations of the disease.
It is the responsibility of parents to ensure that the child washes his hands frequently and thoroughly with soap and rinses vegetables and fruits before eating them.
Features of treatment
To diagnose a disease, only a visual examination is often sufficient, but in some cases laboratory diagnostics are required to determine the causative agent of the inflammatory process and the sensitivity of bacteria to antibiotics. Treatment should be carried out by a dentist, and the treatment regimen is developed individually, taking into account test results, the age and well-being of the child, the causes of the disease, the area of mucosal lesions and other conditions.
If the question of how to treat aphthous stomatitis in children is decided individually, then recommendations regarding eating behavior and hygiene are general for all cases. Such recommendations include the following:
- avoidance of too hot or cold drinks and foods;
- following a hypoallergenic diet;
- refusal of food that irritates the mucous membrane. This list includes fatty, salty and spicy foods, marinades, solid foods;
- adding pureed and soft foods to the menu. This includes cream soups, porridges, pre-boiled meat;
- drinking enough liquid;
- careful adherence to oral hygiene: using brushes with soft bristles, rinsing the mouth after each meal.
Local drug treatment consists of the use of such agents as:
- rinses or irrigation solutions (for children who do not yet know how to rinse their mouths) with an antiseptic effect;
- ointments and gels that stimulate the restoration of mucous membranes;
- drugs for pain relief and burning sensation.
It is important to test the product before use: apply a small amount to the crook of your elbow. If there is no redness, burning, or rash, we can say there is no allergy - the product can be used for treatment.
In some cases, systemic drug therapy is indicated. Your doctor may prescribe antihistamines to combat the allergic reaction and relieve swelling. In order to increase the resistance of the child's body, immunomodulators may be recommended. The decision on the need for antibacterial therapy is made in the case of an extremely severe course of the disease, a persistent increase in body temperature, and identification of a bacterial pathogen in a smear.
Elevated body temperature and pain are indications for symptomatic therapy. The doctor may recommend non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in a dosage and form appropriate to the age of the young patient. Sometimes it is advisable to use suppositories if taking the medicine in the form of a tablet or syrup causes pain or anxiety.
Treatment of infants additionally includes disinfection of toys and teethers that the baby may put in his mouth. A nursing mother should pay attention to breast hygiene: thoroughly wash her breasts after feeding using warm water and special products.
Sometimes it is advisable to use folk remedies. Thus, rinsing the mouth with chamomile can soothe inflamed mucous membranes and speed up the healing process. However, it is important to remember that such prescriptions can only complement the main course of treatment. Don't forget to consult your doctor about the possibility of using them. Some herbs are strong allergens, so it is important to ensure that you are not hypersensitive to them.
Warming, the use of honey and alcohol tinctures are prohibited, as all this can lead to a worsening of the condition and lead to serious complications. It is better not to self-medicate, but to show the child to a qualified specialist.
Treatment of aphthous stomatitis in children usually takes no more than 7–12 days. It all depends on the state of the child’s immune system, the severity of inflammation, the number and depth of ulcers.