Treatment of herpes in the mouth
Can herpes be in the mouth?
Maybe! Herpes in the mouth requires the same responsible approach and competent treatment as other diseases of the oral cavity. Despite the fact that the infection is often mild and goes away naturally, there are still risks of serious complications, and the possibility of infecting other people remains. Many factors influence the degree of development of the pathology and the presence of possible dangers for the patient. Complete diagnosis and comprehensive treatment can completely stop the manifestations of the infection, although complete elimination of the virus is considered impossible. Herpes, a viral disease known to many as a “cold sore,” is often perceived as a minor problem that does not require treatment. It is characterized by the appearance of a moderately painful blistering rash, but not many people know that this disease is not limited to appearing only on the lips , but can also develop on the oral mucosa . The disease is often accompanied by weakness, general malaise and severe itching, and in some cases can cause complications. During the active phase of the virus, a patient can easily infect others with it through household items, close contact or by airborne droplets.
2. Causes of stomatitis
We have already talked above about why irritation of the oral mucosa may begin. Now let's dwell on the question of why ulcers and herpes appear. Ulcers.
In fact, the exact causes of stomatitis in the form of ulcers are not known. But many things can contribute to their development. These include certain medications, oral injuries, poor diet, stress, bacteria and viruses, sudden weight loss and the consumption of certain foods - potatoes, citrus fruits, coffee, chocolate, cheese and nuts.
Stomatitis may be associated with a weakened immune system due to colds, flu, changes in the body's hormonal levels, as well as a lack of vitamin B12 and folic acid. Even accidentally biting the inside of your cheek or chewing on a sharp piece of food can cause an oral ulcer.
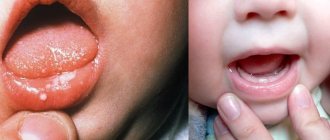
Ulcers can occur as a result of a genetic predisposition. In this case, it is considered an autoimmune disease. In general, ulcers appear in about 20% of people, but the disease is not contagious.
Visit our Therapy page
Symptoms of herpes on the oral mucosa
Symptoms of herpes are individual, have varying degrees of manifestation, and can occur in different parts of the oral cavity. For most cases, there are a number of signs that indicate the occurrence of herpes:
- Regular headache;
- Fever;
- A person gets tired quickly;
- Discomfort when eating and drinking;
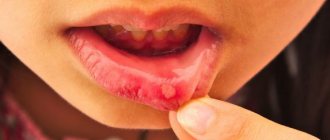
- The appearance of water bubbles filled with transparent white or yellowish exudate, up to 3 mm in diameter;
- The appearance of ulcers at the site of burst blisters;
- Inflammation of the soft tissues of the oral cavity, redness, itching, burning, swelling of the lesion.
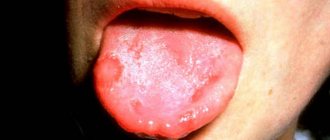
According to clinical studies, blisters in the mouth can form in different areas: on the palate, on the inside of the cheeks, on the tongue, on the gums, on the tonsils.
Experts' opinion
Research conducted at the Kazan State Academy has determined that the use of preparations from the Asepta line (gels, balms, toothpastes, rinses) increases the effectiveness of treatment of chronic catarrhal gingivitis and other inflammations, mild and moderate chronic periodontitis, hyperesthesia of hard dental tissues, which together significantly reduces the duration of treatment and increases the duration of remission in this category of patients.
Sources:
- The use of drugs from the Asepta line in the complex treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases (N.V. Berezina E.N. Silantyeva S.M. Krivonos, Kazan State Medical Academy. Kazan.) N.V. BEREZINA, E.N. SILANTIEVA, S.M. KRIVONOS Kazan State Medical Academy
- https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/sovremennye-lechebno-profilakticheskie-sredstva-dlya-individualnoy-gigieny-polosti-rta Silantieva E.N., Berezina N.V., Krivonos S.M. Complex treatment of chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis using drugs from the Asept line, Practical Medicine journal
- Clinical and laboratory assessment of the influence of domestic therapeutic and prophylactic toothpaste based on plant extracts on the condition of the oral cavity in patients with simple marginal gingivitis. Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Elovikova T.M.1, Candidate of Chemical Sciences, Associate Professor Ermishina E.Yu. 2, Doctor of Technical Sciences Associate Professor Belokonova N.A. 2 Department of Therapeutic Dentistry USMU1, Department of General Chemistry USMU2
- Clinical studies of antisensitive toothpaste “Asepta Sensitive” (A.A. Leontyev, O.V. Kalinina, S.B. Ulitovsky) A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist O.V. KALININA, dentist S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry, St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
- Report on clinical trials of anti-inflammatory balm for gums "Asepta" adhesive, St. Petersburg State Medical University, 2007
Stages of development of herpes in the oral cavity
The disease develops sequentially, including passing through several distinct stages:
- At first, the patient may experience drowsiness, malaise, and tingling or itching of the mucous membrane. Sometimes body temperature rises slightly;
- Next comes redness and swelling of the lesion, minor pain occurs due to the appearance of herpes on the tongue or lip;
- Blisters appear in the oral cavity, filled with transparent contents. During this period, the patient is most contagious, blood counts change;
- The blisters become cloudy and open, and yellowish, shallow, painful ulcers form in their place;
- A hard, fragmented crust forms on the ulcers, damage to which causes bleeding. After a few days, the crusts disappear.
In the best case, the disease resolves naturally within two weeks and without treatment. All wounds heal quickly and without scars.
But there are also complications that lead to infection of internal organs. Suppuration occurs at the site of the wounds, the temperature rises to 40 C. Inflammation of the lymph nodes in the jaw and neck may begin.
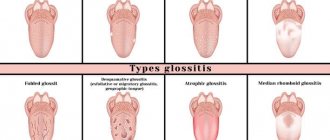
1.What is stomatitis, its types and symptoms
The term stomatitis refers to inflammatory processes in the oral cavity
that cause pain.
Stomatitis can cause discomfort and pain and interfere with eating, sleeping, and other daily activities. Canker sores can occur anywhere in the mouth, including the inside of the cheeks, gums, tongue, lips, and roof of the mouth
.
Types of stomatitis
There are several types of stomatitis, the main ones being:
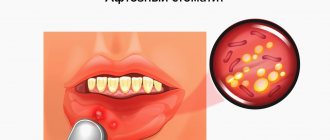
- Ulcers
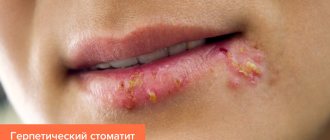
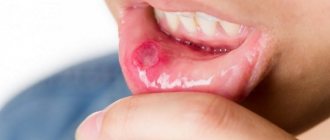
, also called aphthous ulcers. They usually appear in the mouth on the cheeks, tongue or lip, and appear as pale or yellowish sores with a red outer border; - Herpes
. Cold sores are fluid-filled sores that are located on or around the lips. Herpes on the gums and upper jaw also occurs, but very rarely. Herpes on the lips first looks like blisters filled with liquid, and then a crust or sore forms on it. Before a cold sore appears, there is often an itching, tingling or burning sensation on the lip. - Irritation of the oral mucosa
. It can be caused by biting the cheeks, tongue or lips, wearing braces, damage to the mucosa from a broken or sharp tooth, burns to the mouth from eating too hot food or liquids, gingivitis and other gum infections, and some autoimmune diseases. For example, systemic lupus, Crohn's disease or Behçet's disease. Mucosal irritation and stomatitis can be a side effect of treatment for other diseases - chemotherapy, antibiotics, drugs used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, epilepsy.
Symptoms of stomatitis
Symptoms of stomatitis depend on what type of stomatitis appears. So, mouth ulcer
usually painful and lasts 5 to 10 days. Often the ulcer appears again. And it is usually not associated with any colds.
Herpes
on the lip is not always painful. Rather, it causes discomfort. Herpes goes away in 7-10 days and its appearance is often a consequence of colds and flu.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Causes of oral herpes infection
Herpes that affects the oral cavity develops when infected with the herpes simplex virus type 1, which not only provokes the appearance of a blistering rash, but can also cause complications in 10% of cases. The second type of herpes virus (genital) also causes a rash in the mouth, but does not cause serious disruption to the body and differs in its mode of transmission (through sexual contact).
Most often, primary infection with a herpes virus occurs in childhood, after which it is introduced into the genome and remains in an inactive form for life.
The main routes of infection with a viral agent are close conversation, skin-to-skin contact, kissing, and the use of shared hygiene products or utensils. However, the entry of viral particles into the body does not guarantee that the disease will develop, since the immune system can suppress the action of the pathogen. In this case, situations that worsen the overall health of the body, on the contrary, provoke a clear manifestation of infection:
- surgical interventions;
- emotional and physical stress;
- lack of sleep, overwork;
- colds;
- chronic pathologies;
- long-term use of antibiotics;
- periods of menstruation, pregnancy or lactation;
- vitamin deficiencies;
- AIDS;
- abuse of nicotine or alcohol;
- the appearance of microtraumas from excessive exposure to the sun or frost.
How does the virus become infected?
The virus can be infected in different ways: airborne droplets, contact (through shared towels, cutlery, through kissing), sexual intercourse, self-expression (when the virus from ulcers enters healthy mucous membranes and infects them). You can become infected through a blood transfusion and a child can receive the virus from the mother in utero. The incubation period (from the moment of contact until the first signs appear) is 2-14 days. A person becomes contagious as soon as sores appear on the lip, and is contagious to others until the scabs fall off .
Photo: One of the most common ways of transmitting herpes is contact.
Diagnosis and treatment of herpes infection
It is better to start treatment of herpes in the mouth at earlier stages of development to reduce the risk of complications and reduce the likelihood of infecting other people. In order to identify the disease, specialists carry out diagnostic measures:
- collect anamnesis;
- conduct an examination, determine the location of the rash and its nature;
- take a smear to identify the herpes virus and determine its type;
- laboratory tests are prescribed.
Modern methods for identifying the pathogen are a patient’s blood test to detect antibodies to the pathogen and a PCR study of tissues aimed at searching for the DNA of the viral particle. Differential diagnosis is of great importance, since herpetic infection must be distinguished from other similar diseases: stomatitis (not herpetic), tonsillitis, etc.
How to treat herpes on the lip, tongue or gum? Herpes therapy is based on an integrated approach that combines:
- The use of local antiviral agents to stop the process of reproduction and spread of the pathogen;
- Prescribing antiviral medications for internal use (usually indicated for those whose symptoms occur frequently and acutely, or who are immunosuppressed);
- The use of antiseptic drugs for treating blisters and ulcers, rinsing;
- Use of topical anesthetic gels;
- Prescribing non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to alleviate general well-being;
- Strengthening the immune system by taking vitamins and immunomodulators.
To eliminate symptoms, advanced technologies such as laser radiation are also used. The technique allows you to quickly and painlessly destroy viral particles without harming mucosal cells and effectively healing damaged tissue. In most cases, several short procedures are sufficient for complete disappearance of symptoms in 2-4 days.
Antiviral drugs
Their goal is to suppress the pathogen, shorten the duration of the exacerbation, and reduce the intensity of symptoms. The most popular products are Acyclovir and Zovirax in the form of tablets and creams. Using cream in the mouth is difficult, so tablets are optimal. They drink them in a course.
It is better to start treatment at the first signs of the disease. In some cases it can be stopped. Interferon nasal drops have also shown their effectiveness in the initial stages of herpes. At the very least, they prevent the spread of infection into the respiratory tract.
We have already found out that the main reason for the manifestation of herpes is weakened immunity. Conclusion: to avoid relapses, it is necessary to increase the body's defenses. To do this, you should contact an immunologist, who will refer you for diagnostics and prescribe individual treatment. Sometimes it includes immunomodulators - drugs that can increase immunity (Immunal, Imudon and others), folk remedies (for example, echinacea tincture), vitamin and mineral complexes. You can also take specialized complexes of vitamins and minerals, for example, ASEPTA® Parodontal to strengthen teeth and gums: its active components help not only reduce bleeding and inflammation in the oral cavity, but also maintain general immunity.
General recommendations on how to strengthen the body and increase its protection:
- avoid stress, improve sleep;
- include as many fresh vegetables, fruits, and herbs in your diet as possible;
- to drink a lot of water;
- exercise or swimming.
In case of exacerbation of herpes on the gums, it is recommended to adhere to a diet: remove spicy, fatty, too hot foods from the diet, exclude hot and alcoholic drinks. To avoid irritating the mucous membranes, avoid smoking.
The difficulty of using creams and ointments is not a reason to refuse local treatment for herpes. Rinsing and irrigating the oral mucosa will help relieve symptoms and prevent the spread of infection. Good products: Hexoral, chlorhexidine, hydrogen peroxide solution, furatsilin, as well as anesthetic sprays, rinsing solutions, gels with anesthetics (for example, Lidoxor gel, which relieves burning and irritation). Adhesive gum balm ASEPTA® is an effective combined antimicrobial agent that has a wide spectrum of action against gum disease pathogens, thanks to the combination of metronidazole + chlorhexidine, and guarantees long-term fixation on the gums.