A mouth smear is not the most common test in dermatovenerological practice.
However, venereologists sometimes suggest that their patients be examined for sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) in this way.
It happens that such patients are referred to a dermatovenerologist by doctors of other specialties - dentists, therapists, otolaryngologists.
The reason is simple.
Many pathogens of STDs, in addition to the genitals, feel very good in the oral cavity or on the epithelium of the ENT organs.
Who needs a mouth swab and when, how and where it is done - we will tell you below.
What is it and why?
The oral cavity of every person is very densely populated with microorganisms.
Most of them are harmless saprophytes, among which there are cocci and bacilli.
There are even non-pathogenic spirochetes.
Our body has learned to coexist safely with them, and we simply do not notice them.
But such prosperity does not always happen.
Problems arise when foreign microorganisms enter the oral cavity.
For example, pathogens of sexually transmitted infections that thrive on the mucous membranes of the mouth and genitals.
The list of microbes that are capable of such a change in habitat is quite wide:
- Trichomonas
- treponema pallidum
- human papillomaviruses (HPV)
- herpetic group viruses
- gonococci
- chlamydia
In principle, this list can include almost all STD pathogens.
A smear helps to identify them in the mouth.
How the research works
To take a throat swab, the patient must open his mouth wide and tilt his head back. The patient's tongue is pressed against the lower jaw with a spatula, and the specialist runs a special sterile cotton swab along the exposed surface of the pharynx. The procedure is painless and does not cause discomfort to the patient.
With a developed gag reflex, gagging may be disturbing. However, a short duration of the procedure and fasting the day before will help ensure the comfort of the procedure.
After collection, a cotton swab with a holder is placed in a sterile container in which special conditions are created for bacteria to ensure their viability. This is necessary to ensure that the microorganisms remain active until the samples are sent to the laboratory for analysis. Here, all the collected material will be placed in certain nutrient media and, based on their growth, it will be possible to draw conclusions about what disease needs to be treated in the patient.
Diagnostic value of mouth swab
At its core, it is completely, 100% analogous to a urogenital smear.
The only difference is where the diagnostic material is taken from.
A mouth smear helps determine the spectrum of oral microflora in the person being examined, regardless of gender.
This method refers to laboratory-instrumental techniques and performs one task: obtaining diagnostic material for a detailed study of microflora.
Samples obtained using a mouth swab are examined in different ways:
- microscopy of native material and fixed, stained smear
- bacteriological examination (culture)
- immunological studies
- molecular genetic
The main thing is to correctly and accurately collect diagnostic samples.
But before you collect them, you need to determine who needs it.
Laboratory at home, how to collect material at home?
Cotton swabs for collecting materials.
Various situations happen in life. There are times when it is not possible to take the child to the laboratory or come independently. What to do in this case? Is it possible to collect material for research on your own? Conducting a fence at home is not difficult. To do this you will need:
- Non-sterile gloves – 1 pair
- Cotton wool or cotton swab – 1 pc.
- Sterile container
How to make a fence:
- Prepare container
- Wear gloves
- Apply a cotton swab several times in the anal area
- Place the stick in the container, close the lid tightly and deliver it to the laboratory.
Remember! Biological material is not stored even in the cold. Therefore, you need to take him to the clinic as quickly as possible! While you're getting dressed and getting ready, put a sample in the refrigerator!
Indications for performing an oral smear
The reasons for conducting such a study differ for doctors of different specialties.
As for venereology, here are the main symptoms for which dermatovenerologists take a swab from the mouth:
- burning and pain in the mouth
- painful rash on the mucous membranes of the mouth and cheeks
- enlarged tonsils without pronounced clinical signs
- complaints of a sore throat for a long time
- the appearance of painless lumps and wounds in the mouth, on and under the tongue
- unpleasant odor with the exception of dental caries
- sour taste, foamy saliva
In principle, everything is decided individually each time.
We have listed only a few signs that indicate the main STDs characteristic of lesions in the oral cavity.
4. Results of throat culture for microflora
Culture results will be ready within 1-2 days, in some cases testing is carried out within a week.
There is also a rapid test for streptococci.
The results of such a test for streptococcus will be ready in 10-15 minutes. This test is only for bacterial infections caused by streptococcal bacteria.
A rapid test for streptococcus can show two results:
- Negative test results for streptococcus.
Streptococcal bacteria were not detected. Microflora culture may be recommended. - Positive test results for streptococcus.
Streptococcal bacteria were detected. This means you have strep throat (strep throat). You must start taking antibiotics immediately.
Throat culture for microflora can also be negative or positive:
- Negative culture results for microflora. There are no bacterial or fungal infections and their growth is not observed. Negative results may mean that your infection is caused by a virus rather than bacteria or fungus. Throat infections can be caused by different viruses - enteroviruses, Epstein-Barr virus, herpes simplex virus, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV).
- Positive results of throat culture for microflora. Bacterial growth is observed. Examples of bacterial throat infections are strep throat, diphtheria (diphtheria corynebacterium), and whooping cough (whooping cough). Fungal growth is observed. The most common fungal infection in the throat is oral candidiasis, which is caused by yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida.
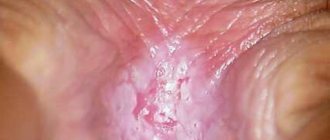
Typical signs of oral STDs
It often happens that people come to dermatovenerologists from dentists or laryngologists.
After the treatment from these doctors turned out to be ineffective.
Or after the patient has had a mouth smear examined for microflora.
And they found sexually transmitted infections in the material.
How they get there is sometimes quite difficult to figure out.
The most common method is oral sex.
It is also necessary to remember that more than 200 thousand germs are transmitted with a deep kiss.
And, if your partner had herpetic rashes in the mouth, infection cannot be avoided.
The same applies to atypical forms of primary syphilis, gonorrhea and other STDs.
Gonorrhea is transmitted through oral sex.
It manifests itself as a sore throat, hoarseness and other symptoms of a prolonged cold.
Syphilis is the same.
Characteristic signs are painless lumps and reddish ulcers on the tongue and red border of the lips.
May occur as chronic flaccid tonsillitis.
Trichomonas, chlamydia and mycoplasma when localized in the mouth do not cause specific symptoms.
They can be suspected only by a lingering cough or tonsillitis.
The patient's general well-being does not deteriorate.
Herpes is easy to detect: pain and burning, rashes on the mucous membranes, transforming into erosions.
Relapses up to 5-6 times a year.
Against the background of immunodeficiency, constant persistence of rashes in the mouth is possible.
Human papillomavirus lesions are painless and usually have the appearance of genital warts.
Having reached large sizes, they can make swallowing and speech difficult.
Infection through domestic means cannot be ruled out.
All infections can be transmitted through a toothbrush.
Because of this, children whose parents suffer from the oral form of one or another sexually transmitted infection often suffer.
Another reason for taking a swab from the mouth is the need to assess the prevalence of STDs when examining a patient with established damage to the reproductive organs.
How to avoid re-infection
Doctors' recommendations are simple and concise. The following rules will help you avoid relapse:
- Maintaining personal hygiene rules
- Complete the course of treatment with prescribed medications
- Do not self-medicate or self-diagnose
- Do not try untested methods on yourself
- Be periodically tested for enterobiasis
- If you suspect a relapse, consult a doctor
If the test result is positive, then do not be upset. Getting rid of parasites is not difficult. It is enough to carry out an appropriate course of treatment.
Treatment of tongue candidiasis
The treatment regimen is selected taking into account the factor that provoked the development of the disease. The main goal of therapy is not just to destroy pathogenic flora, but also to strengthen the immune system and improve the functioning of the stomach and intestines. If this is not done, the likelihood of relapse will remain high.
If the disease is caused by long-term antibiotic therapy, taking hormones or steroids, as is most often the case, you need to reduce the dosage of drugs from these groups and at the same time start using antifungal tablets. B vitamins and immunomodulators have an excellent effect on the body during the treatment of tongue candidiasis.
Medicines used for candidiasis
It is impossible to get rid of fungi of the genus Candida that have multiplied on the mucous membranes of the tongue without medications. Medicines should:
- relieve inflammation;
- activate regeneration processes;
- reduce pain;
- destroy fungi;
- heal ulcers;
- reduce swelling.
For this purpose, dentists prescribe the following pharmacological groups:
- Antifungal. They act by destroying the cell membranes of the pathogen. They are manufactured in the form of tablets and capsules for oral administration.
- Antiseptics for mouth rinsing. They destroy viruses, fungi, bacteria, and create conditions for the restoration of healthy microflora.
- Gels and ointments with antifungal activity. Used strictly locally. They treat the surface of the entire tongue. They help remove swelling, minimize itching and burning. Excellent healing of existing wounds.
- Antiseptics in the form of aerosols. Very convenient to use. Suitable for use in public places. Characterized by a wide spectrum of action.
When treating candidiasis in the tongue, it is important to use exactly the drugs prescribed by the doctor. There is no need to exceed their dosage, as this may cause the opposite effect.
Traditional methods of combating oral candidiasis
If you really want to supplement drug therapy with herbal remedies, it is permissible to use:
- decoctions of anti-inflammatory herbs;
- alcohol tincture of propolis;
- soda solution.
These products should be used while rinsing the mouth.
What exactly is determined during the analysis process?
A comprehensive study of the bacterial microflora of the vagina is carried out using real-time PCR (real-time PCR). The composition and ratio of normal, opportunistic microflora is determined and NCMT - pathogens of sexually transmitted infections (N- gonococcus, C- chlamydia, M- mycoplasma genitalium, T- trichomonas) are identified.
The following microorganisms are detected:
STI pathogens: Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Chlamydia trachomatis, Mycoplasma genitalium, Trichomonas vaginalis.
Normal and opportunistic flora: bacterial DNA, Lactobacillus spp., Gardnerella vaginalis, Atopobium vaginae, Enterobacteriaceae, Staphylococcus spp., Streptococcus spp., Ureaplasma parvum, Ureaplasma urealyticum, Mycoplasma hominis, Candida albicans, DNA Candida glabrata, Candida krusei, Candida paraps./ tropicalis.
Content:
- Features of the disease
- Causes of yeast glossitis
- How it manifests itself 3.1. Other symptoms of candidiasis on the tongue
- Treatment of tongue candidiasis 4.1. Medicines used for candidiasis 4.2. Traditional methods of combating oral candidiasis
- How to eat during treatment
- How to avoid getting sick
For the full functioning of all parts of the gastrointestinal tract, various fungi and bacteria must be present in the body.
They are called opportunistic pathogens. If their quantity corresponds to the norm, the person feels well and does not experience unpleasant symptoms of the disease. But under the influence of negative external or internal factors, bacteria and fungi can begin to actively multiply. Then their activity becomes abnormal - a disease of the oral cavity or stomach or intestines is diagnosed. It is in this scenario that candidiasis develops on the tongue, throat and cheeks. Let's look at how to treat it and what measures to take to avoid relapse after recovery.
References
- Khaitovich, A.B., Voevodkina, A.Yu. Microbiome and its impact on human health. Crimean Journal of Experimental and Clinical Medicine, 2022. - No. 1. - P. 61-70.
- Krasnova, E.I., Khokhlova, N.I., Evstropov, A.N. and others. Streptococcal infection of the oropharynx: approaches to diagnosis and treatment. Infectious diseases, 2015. - No. 4. - P. 30-36.
- Li, N., Ma, W., Pang, M. et al. The commensal microbiota and viral infection: a comprehensive review. Frontiers in immunology, 2019. - Vol. 10.