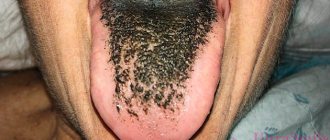
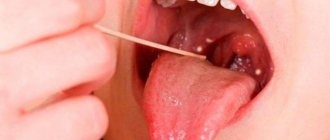
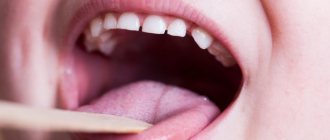
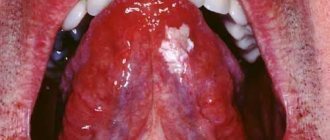
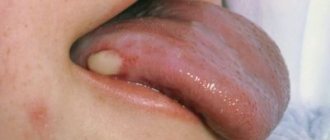
We are used to the fact that we need to go to the dentist if we have problems with our teeth or gums. What to do if you have inflammation of the tongue or glossitis? Dentists identify more than 10 types and subtypes of infection. The infection can be caused by both fungus and bacteria. Viral infection is less common. Inflammation can be caused by a lack of certain vitamins and minerals, or hormonal changes. There are many reasons for the disease, so it is important to identify what exactly caused the inflammatory process.
Causes of glossitis
- improper oral hygiene;
- bacterial infection;
- fungal infection;
- heavy metal poisoning;
- bad habits (smoking, alcoholism);
- congenital pathologies of the tongue (folded tongue);
- allergic reaction;
- tongue injury (often caused by malocclusion);
- oral infections;
- lack of iron in the body;
- burn of the mucous membrane (hot food or drinks);
- infectious diseases (AIDS, tuberculosis, scarlet fever, measles).
Signs of teething
There are several of them, let’s get acquainted with the features of each of them.
Baby teething
Anxiety, crying
The first sign that is difficult to ignore is the child’s anxiety . The baby is capricious and often cries, and may refuse food, water, or bottles. Behavior is often observed when the child takes the breast, begins to suck, but immediately releases it and begins to cry. This is explained by the fact that the gums are very sensitive and painful during the teething period; the baby is bothered by unpleasant sensations, but he does not know how to cope with them.
The baby is crying
It is not uncommon for a child to bite the breast with his gums during feeding. The baby just wants to get rid of the itching, which is why he clenches his jaw when any objects get on his gums.
It is worth sounding the alarm if the child does not eat for two days and no longer. And one or two missed feedings a day are not a cause for concern.
Drooling
The second sign is increased salivation . Pay attention to the child, if he puts everything into his mouth, the saliva is thin and abundant, perhaps the first tooth will appear soon. However, this sign does not always accompany teething. It happens that the baby drools like a river, but there are no teeth. Therefore, it is better to focus on other signs or their combination.
Baby's drooling
Increased salivation can cause irritation on the chin and around the lips.
Diarrhea
The third sign is stool disorder . Pediatricians recommend introducing the first complementary foods at 4 months. And if the period of introducing complementary foods coincides with teething, the first thought of parents is food poisoning of the child. Excessive diarrhea in children during teething is also very similar to intestinal upset caused by harmful infections. You should panic only if diarrhea occurs more than three times a day and for longer than 3-7 days in a row.
Diarrhea in infants
On a note! Pay attention to your baby's stool. If there are traces of blood in it, it is important to consult a doctor immediately.
The cause of diarrhea in infants associated with teething is a decrease in the level of functioning of the immune system. The gums begin to itch, and to relieve the itching, the baby puts his own fingers, clothes, mother’s hair, and toys into his mouth. On the surface of all these objects there are invariably microbes that penetrate the child’s body, develop, and as a result, dysfunction of the entire gastrointestinal tract is observed. Diarrhea is an indicator that the baby’s immune system simply cannot cope with the infection in the intestines. But the body quickly adapts, and the diarrhea goes away without a trace.
- Symptoms of teething in infants: how to recognize and respond correctly
You can distinguish teething from an intestinal infection as follows:
- calm the child down, create a cozy atmosphere for him;
- Place the baby on a changing table or other hard surface;
- Feel the baby's belly and observe the reaction. If the baby is calm during palpation, there is no reason for concern. If the stomach is hard, and the slightest touch causes the child to become hysterical, you should immediately seek medical help. institution.
A child's stomach is felt
On a note! Diarrhea may be accompanied by excessive regurgitation or vomiting. This is normal during teething.
Sensitivity and itching of gums
The fourth sign is swelling of the gums, redness, sensitivity, itching. If you notice that your four-month-old baby is teething, try to calm yourself down initially. You will in no way be able to influence the progress of teething, their sequence and speed, but you can provide the baby with moral support that is so important these days. There is no need to climb into the child’s mouth every minute, try to tap the gums with steel objects, you will only introduce more germs, scare the child, and his tense state will worsen.
The baby is cutting his first teeth
Very important! If the first tooth has already come out, and then the second one is emerging, do not try to relieve the itching of the gums by offering your child pieces of cookies, crackers, crusts of bread, any confectionery, apples or carrots. An accidentally bitten off piece of food can get into the baby's respiratory tract, which will have disastrous consequences.
You may notice small bumps on the gums or bruises. They will go away on their own; outside intervention is unnecessary.
Fever, cough
Table. How do you know if your baby has caught ARVI or is just teething?
| Signs | Teething | ARVI, infectious diseases |
| Increased body temperature | An increase to 37-38°C is considered normal, lasting no more than four days | Elevated body temperature of 37-40°C and above lasts more than four days |
| Heat | Absent | Usually present |
| Weakness | Absent | Occurs frequently |
| Cough | Rare, appears due to the fact that the baby chokes on a large amount of saliva without having time to swallow it | The cough is systematic, frequent, and may cause hoarseness. |
| Runny nose | It may be small if the child's saliva gets into the nasopharynx. Runny nose for no more than three days | Present abundantly, for a long time |
The child has a high temperature
Note! If your child constantly rubs their face and chin against the surface they are lying on, this may be a sign of ear inflammation. You need to see an otolaryngologist.
Video: Teething Symptoms
The most common types of glossitis
The most common occurrences in dental practice are:
- acute catarrhal glossitis;
- tongue abscess;
- desquamative glossitis.
Acute catarrhal glossitis is the most common type of inflammation. Inflammation can be caused by microbes or mechanical damage to the tongue. The predominant symptoms are pain, redness and swelling.
A tongue abscess is the appearance of an abscess in the tongue. The abscess can be superficial, under the mucous membrane, or maybe in the thickness of the tongue. Abscesses in the thickness of the tongue, in addition to pain in the tongue, can cause a disturbance in the general condition. A person develops a fever, a headache, and weakness. Most often occurs due to injury to the tongue.
Desquamative glossitis, also known as “geographic tongue,” most often appears in children. It appears in the form of various spots on the tongue, which look like a white coating, alternating with areas of pink mucous membrane. There are no changes other than appearance. Scientists have identified a clear reason for it. The main factors are believed to be bacteria, allergic reactions and hormonal imbalances.
External causes of the development of allergic dermatitis in children
The disease can be caused by one of the factors or a combination of several.
- Physical - friction or pressure on the skin of fabrics, leather products, high or low temperatures, humidity, electric current, ultraviolet or x-rays.
- Chemical - various acids and alkalis, substances included in creams and hygiene products, medicines, tobacco smoke.
- Biological - sap and pollen of plants, bites and secretions of insects and animals.
Of the plant agents, the most dangerous are the juice of celandine, hogweed, nettle, pollen of meadow and weeds.
In industrial cities in winter, there are widespread cases of contact dermatitis under the eyes and on the hands of children. Three factors are combined here: cold, chemical impurities in the air and touching the skin with wet mittens.
In infants, allergic inflammation can be caused by a combination of high humidity in diapers, fabric friction and the action of inappropriate cream.
A special type of contact dermatitis is phototoxic, when sunscreens degrade in sunlight and cause allergic damage to the epidermis.
Symptoms of glossitis
- increased salivation;
- swelling and redness;
- pain and burning when eating;
- plaque on the tongue in the form of spots;
- bad breath;
- papillomas or warts on the tongue;
- speech disorder;
- foreign body sensation.
Prevention of glossitis - high-quality oral hygiene and no bad habits. It is important to undergo timely preventive examinations and also eat well. All these factors actively contribute to the development of the disease and bring a number of problems.
Causes of tongue itching
In young children, itching of the tongue can be caused by food allergies . You should review the child's menu and exclude those foods that can provoke irritation of the organ. Against the background of an allergy, the tongue may not only itch, but also hurt, tingle and swell, and the stool may acquire a liquid consistency. With allergies, symptoms appear immediately upon contact with the allergen or after a short period of time.
A rash may appear on the cheeks or throughout the body. With obstruction, breathing becomes difficult and swelling occurs. It should be remembered that allergies can be a consequence of problems in the gastrointestinal tract, especially if the temperature rises and diarrhea appears.
Food allergies
Candidiasis is manifested by the presence of a white coating on the mucous membranes of the mouth and tonsils, but the back of the tongue is clean. The child may experience a sour taste and pain when swallowing. Usually the fungus is contained in the baby’s body in a latent form and the catalyst for the disease can be a weakened immune system, injury to the mucous membrane of the mouth or tongue. When the tongue is cleaned, under the coating you can see an inflamed focus of infection of a bright scarlet color.
Candidiasis
The tonsils may also become covered with white dots due to chronic tonsillitis , but in this case the formations are sporadic and the oral cavity is clean. The resulting crusts must be carefully removed with a cotton swab or bandage, as this is nothing more than purulent discharge.
Worm infestation in a baby manifests itself in the mouth area, and not just in the anus area. Itching can be either constant or periodic. The tongue may not only itch, but sometimes there is a burning sensation.
In diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, itching is not accompanied by other visual changes in the oral cavity, except for a white coating along the entire base of the tongue. But the patient may be bothered by pain in the right hypochondrium and itchy skin.
In case of caries, the damaged tooth should be filled immediately, otherwise the location of the disease becomes a favorable environment for harmful bacteria to live.
Infectious diseases of a long course can also provoke the appearance of microbes in the pharynx, penetrating there through the nasal passages.
Treatment of glossitis
A specialist must make an accurate diagnosis and identify the cause of the disease. If you suspect that you have glossitis , and all symptoms indicate this, contact your dental clinic. This is the only way to create the right treatment plan and provide timely assistance. Quite often in such cases, doctors prescribe antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs and rinsing the mouth with special antiseptic solutions. In advanced stages, glossitis is treated surgically. Deep abscesses must be opened in the maxillofacial department. Under no circumstances should you take medications without a doctor’s recommendation.
You can cure glossitis, caries or any other diseases of the oral cavity right in your sleep. Family Dentistry Center "Medexpert" provides dental treatment under medicinal sedation. Thanks to this approach, the patient falls into a healthy sleep, ceases to feel pain and discomfort, while the vital functions of the body remain unchanged. Sedation is widely used in pediatric dentistry and even helps fight dental phobia. Dental treatment can be comfortable and painless - tested for yourself.
How to cope with unpleasant symptoms?
It is important to avoid consuming raw vegetables and fruits that cause reactions, especially during allergy season. This is due to the fact that for many people, oral allergy syndrome develops more often and is more difficult during the flowering season of certain plants. You can reduce cross-reaction with food by boiling or baking vegetables and fruits, since proteins that cause allergies are destroyed at high temperatures.
Symptoms of allergic rhinitis and oral allergy syndrome can be managed with antihistamines. However, when it comes to treating a child, the choice of medications must be approached with great caution. First generation antihistamines can cause severe sedation and impaired psychomotor activity.
Cross-reactions with other foods
Children with allergies to the following foods may react to other foods:
Cow's milk allergy: 90% also react to goat's milk and 40% to soy milk.
Egg: in 5% there is a reaction to chicken meat
Peanuts: In 5% of cases there is a reaction to other legumes (such as peas or beans). In 30% there is hypersensitivity to tree nuts.
Fish: in 10% a reaction to seafood is also observed.
Melon: 90% reacts to bananas and avocados
Ragweed pollen allergies can cause a cross-reaction with all melons, bananas and tomatoes.
Birch pollen allergies can cross-react with raw potatoes, carrots, celery and apples.
Grass pollen allergies may cross-react with tomatoes and kiwis.
Main causes of food allergies
8 foods cause 9 out of 10 food allergies.
In the first year of a child's life: cow's milk, soy milk and egg.
Older children: peanuts, tree nuts, fish, seafood and wheat.
Seafood includes shrimp, crab, lobster, clams, oysters and scallops.
Tree nuts include all nuts (such as almonds and cashews) except peanuts. Peanuts and tree nuts are the most common triggers for severe reactions.
Of children with a proven food allergy, 40% have severe reactions. The remaining 60% have a mild reaction.
Still have questions?
Get an online consultation from leading allergists in St. Petersburg!
A professional and experienced pediatrician will answer your questions.
Medical care for a child without leaving home at a convenient time.
sign up for a consultation
A Skype consultation lasts 45 minutes.