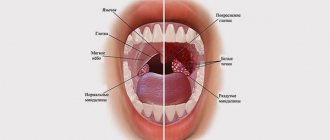
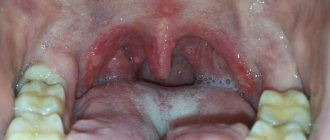
The disease can affect not only the pharynx. This tumor can occur in other parts of the human body or in the liver. It is important that such tumors, which form against the background of changes in the vascular walls, do not develop into malignant ones. Therefore, usually a trip to the doctor reveals the problem; all that remains is to treat it correctly.
Throat angioma, which appears from blood vessels, has a red-blue or purple hue. The tumor arising from the lymphatic vessels is pale yellow. The color in this case is due to the lymph filling the neoplasm.
So what is angioma in the pharynx? How does the disease manifest itself? Is this condition dangerous for humans and how to treat it correctly? Let's find out!
Probable Causes
Red spots in the throat are the main sign of the occurrence of pathological processes in the mucous membrane of the airways. The following factors can trigger their development:
- dry air;
- inhalation of volatile chemicals;
- hypothermia;
- vitamin deficiency;
- allergic reactions;
- decreased body reactivity;
- infectious diseases;
- disruptions in the gastrointestinal tract;
- endocrine disorders;
- bad habits.
The cause of the appearance of red spots on the throat and palate can be identified by their location, number and accompanying manifestations.
Most often, the causes of the occurrence lie in the development of bacterial and viral infections. However, in order to make sure that such suspicions are correct, you need to seek help from a doctor.
Causes
Most doctors are inclined to believe that the disease is mainly congenital in nature. Despite the fact that the first signs of the disease can appear at a fairly mature age. Most often, the catalysts for the appearance of a tumor are weakened immunity and periods of exacerbation of chronic diseases.
Injuries to the nasopharynx, liver disease, cancer, hormonal changes, and stress can also cause the formation of angioma.
But the main reason remains the disruption of the pregnancy of the expectant mother, associated with a lack of folic acid, emotional shocks and experiences during the period of bearing a child, as well as illnesses suffered by the woman during this period.
Pediatric infectious diseases
Many infectious diseases that manifest as a rash on the palate are known as “childhood” diseases. But this does not mean that adults are not susceptible to infection. Having suffered from such diseases once, a person receives lifelong immunity. But if you do not get the same chickenpox in childhood, there is a risk of contracting this infection in adulthood.
Rubella
With rubella, red spots may first appear on the child's palate, and only then on the face and body. Rubella usually resolves easily and without complications in childhood, with the exception of infants up to one year old. These babies endure the disease very hard, so scarlet specks in the mouth, which quickly merge into specks, should alert parents: this may be the first symptom of rubella. This disease is also dangerous for adults who did not have it in childhood, especially for pregnant women.
Measles
As with rubella, with measles a rash in the mouth may appear earlier than on the body - sometimes within a day or two. But the nature of the rash is very different: with measles, the rash looks like dots of white or pale gray color, reminiscent of semolina. Their accumulations on the upper palate, tonsils and back of the throat are surrounded by a pinkish border, this phenomenon is called Belsky-Filatov syndrome.
Chicken pox
With chickenpox, a red rash in the mouth should alert you, as it indicates a complicated course of the disease. Bubbles filled with liquid can shed the gums, tongue, inner surfaces of the baby’s lips and cheeks, and are often found at the top - on the hard and soft palate. Breaking through, they form ulcerations in the oral cavity.
Scarlet fever
With scarlet fever, a small red rash covering the child's body may also appear on the upper palate. The mucous membranes of the pharynx with scarlet fever are bright red, the regional lymph nodes and tonsils are enlarged, the tongue becomes crimson in color and is covered with a white coating - see photo.
Speckled rashes are usually accompanied by a very high fever and vomiting, and in severe forms of the disease - convulsions and clouding of consciousness.
- Causes of rashes in children
Roseola
Since the disease begins with a high fever, and after a couple of days, when the temperature subsides, a rash appears, roseola is often mistaken for ARVI and an associated allergy to medications. Small red spots and blisters in the throat and palate precede the appearance of similar rashes on the body. Their presence is accompanied by redness of the pharynx and pain when swallowing.
The difference between a rash in the mouth and on the body with roseola and any other is that it disappears when pressed.
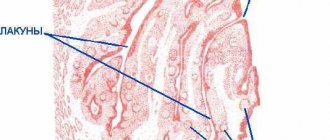
Types of throat angioma
Otorhinolaryngologists distinguish two types of such neoplasms depending on the vessels where the throat angioma forms:
- hemangioma;
- lymphangioma
Make an appointment right now!
Call us by phone or use the feedback form
Sign up
If the tumor grows from blood vessels, it is called a hemangioma. Hemangiomas, in turn, are divided into simple (capillary), cavernous (cavernous) and branched.
All these types of hemangiomas differ in appearance from each other. Capillary ones look like red-blue spots filled with blood. Cavernoses look like nodular new growths of a blue hue. Branched ones look like bubbles consisting of pulsating vessels.
Lymphangiomas also have their own classification. They are divided into simple, cavernous and cystic. As with simple hemangiomas, simple lymphangiomas are composed of capillaries, but these capillaries are filled with lymph. Cavernous formations have several cavities, like a sponge, where each of the cavities is filled with lymph. Cystic, as the name suggests, is one cyst or several cysts fused together.
Laryngeal angioma may not manifest itself for a long time, remain dormant and appear, for example, already in adulthood.
Other reasons
Rashes in the throat, if severe discomfort and pain occur, can signal a change in the morphological properties of soft tissues in the areas of their localization. Erythematous spots, which are localized on the soft palate, in some cases develop due to the occurrence of complex diseases:
- exudative erythema;
- staphylococcal infection;
- syphilis;
- Kawasaki syndrome;
- roseola;
- meningitis;
- typhus
Since the list of possible pathologies is very extensive, if red spots appear in the throat, a visit to the therapist cannot be postponed. The principles of therapy depend on the etiological causes of the development of the disease, the localization of pathological formations and accompanying clinical symptoms. As a rule, in order to eliminate infectious ENT diseases, antiviral and antibacterial drugs are used. Analgesics, antipyretics and antihistamines can also make the patient feel better and eliminate discomfort.
Some bacterial and viral infections cause rashes and spots on the mucous membrane of the throat. They are most often red in color, but can be of different sizes and shapes, and their localization also differs. They can be located in different places.
In some pathologies, red spots in the throat occur only in rare cases and are not important for diagnosis. They do not affect subsequent therapy of the underlying disease. Similar diseases include influenza and ARVI, in which red spots in the throat do not always appear and not in all patients.
However, there are situations when a doctor, looking at a rash in the throat, can make a diagnosis immediately, since in some cases characteristic spots become one of the main symptoms. Such pathologies include, for example, acute stomatitis and herpetic sore throat. It is very unpleasant to notice such a rash in the mouth, especially if red spots are found in the throat of a small child.
Symptoms
A small angioma does not cause the patient any discomfort. Only by growing and reaching large sizes does it make itself felt. At this time, the patient begins to feel a lump in his throat. The constant feeling of a foreign object in the throat causes discomfort. The patient has difficulty swallowing food or saliva.
Growing to the vocal cords, the tumor can cause a slight hoarseness in the voice.
An increase in the size of angioma is accompanied by:
- sore throat;
- cough;
- problems swallowing food;
- the presence of blood clots in saliva;
- pain in the throat area.
As a rule, the first “bells” appear at the age of twenty. A sign that makes it easy to identify an angioma is that when pressure is applied to the tumor, it disappears and then reappears.
Friends! Timely and correct treatment will ensure you a speedy recovery!
Hemangiomas usually reach large sizes. Injuring them can cause severe bleeding. Lymphangiomas do not grow to large sizes and cannot lead to bleeding.
Despite the fact that these neoplasms do not develop into malignant tumors, they cannot be left without attention and medical care. The symptoms expressed in the presence of angiomas adversely affect the patient’s quality of life, and the risk of bleeding threatens with more serious consequences. Therefore, it is important to pay great attention to your throat and, when the first signs of illness appear, seek medical help.
This pathology often occurs in pregnant women: neoplasms appear against the background of changes in hormonal levels and reduced immunity. The difficulty of therapy in this case lies in the inability to use the entire range of means to combat the tumor. But medicine knows of cases where after the birth of a baby the tumor disappeared by itself.
What causes the appearance of rashes
- viruses that cause diseases of the upper respiratory tract;
- influenza virus;
- Epstein-Barr virus (causative agent of mononucleosis);
- adenovirus;
- enterovirus HSV - 1 (virus that causes herpetic sore throat).
If infected with any of these viruses, the ciliated epithelium lining the upper respiratory tract is affected.
Of the bacterial microorganisms that can cause the symptom of “red throat,” the most common is streptococcus A (GAS). This is practically the only bacterium that can infect the throat. This is what causes streptococcal sore throat.
- Encyclopedia of rashes - 2
Principles of treatment
The disease does not require hospitalization. All events are held at home.
Scarlet fever in children: how to treat a contagious disease:
- antibiotics (penicillin group) for a course of 10 days;
- antitoxic serum;
- gargling with a solution of furatsilin, a decoction of chamomile, calendula, eucalyptus;
- in case of dehydration - intravenous infusion of saline preparations;
- symptomatic therapy – antipyretics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- gentle diet, bed rest.
The modern approach to the treatment of streptococcal infections guarantees a favorable outcome without serious consequences. Re-infection is diagnosed in 1-3% of patients.
Allergic reaction as a cause of rash without fever
The pathological reaction of the immune system is the result of exposure to external factors. The causes of an allergic reaction may be:
- rinses, toothpastes of bright color, with a pungent odor and taste;
- low-quality filling material or dental structures - braces, veneers;
- certain foods: citrus fruits, honey, nuts;
- low quality plastic toys that a small child puts in his mouth.
The allergic reaction occurs without fever. Rashes are observed not only on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, but also on the skin. A typical symptom is severe itching of the skin.
Treatment includes antiallergic drugs; local dosage forms are prescribed only in severe cases. These can be hormonal ointments that reduce itching and reduce redness on the skin. The main task is to eliminate contact with the allergen and prevent its re-entry.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis and treatment of this disease is carried out by an otolaryngologist. Small neoplasms are more often diagnosed during a routine examination of the pharynx, when the patient comes to be treated for tonsillitis, pharyngitis, or when diagnosing adenoids. It is not difficult for an experienced ENT doctor to identify a neoplasm by its characteristic color and appearance.
Large angiomas force patients to purposefully go to an ENT doctor, since unpleasant symptoms interfere with their usual way of life.
To confirm the diagnosis, the patient is sent to undergo pharyngoscopy, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT), X-ray examination, and stroboscopic examination of the larynx (examination of the vocal cords).
It is noteworthy that the collection of tumor tissue cells (biopsy) is not performed in this case, since such measures can provoke severe bleeding.
In some cases, a swab is taken from the throat to rule out the presence of foreign bodies, scleromas, or other cancers.