Dentistry deals not only with teeth, but also with gums. If unpleasant and painful symptoms appear in the oral cavity, we recommend that you sign up for a consultation - it is better to find out from the doctor that there is nothing wrong, carry out a preventive procedure and get advice on home hygiene. For example, a phenomenon such as a hard lump on the gum may not cause discomfort at first, but can later become a serious problem. To avoid having to be treated and operated on, talk to your doctor as soon as you notice something unusual in your mouth or your sensations.
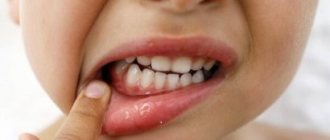
What does a white bump on your gum mean? That there is an infection or injury. This already gives reason to think about treatment. Next, we will talk about the causes of lumps in adults and young patients.
The main advice that can help anyone with any dental problem: do not be afraid or embarrassed by the doctor. At an early stage, all diseases can be eliminated much faster than later, when the process develops and penetrates into the deep tissues of the gum or tooth.
Content:
- Reasons for the formation of lumps on the gums
- Infections that cause bumps on the gums
- Bumps in the mouth of a non-infectious nature
- Lump at the base of the tooth after installing a permanent crown
- How do doctors treat a lump on the gum?
A change in the structure and shade of the oral mucosa is a reason to visit the dentist.
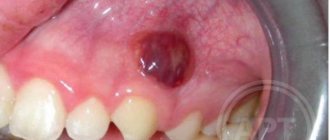
If a lump appears above the tooth - whether it hurts or not - it means there is some kind of problem. Such neoplasms do not just arise. This symptom may indicate various diseases. Most likely, the inflammatory process occurs in the gums, but without a preliminary diagnostic examination, the presence of systemic pathologies that manifest themselves in this way cannot be ruled out.
Use of folk remedies
Folk remedies for a lump on the gum should not act as an independent treatment. They will help reduce the intensity of some symptoms of inflammation, but are not able to eliminate the cause that provoked suppuration .
Home treatment methods are recommended for use when it is not possible to visit a doctor or as a therapy that complements the main treatment.
The most accessible effective method is a solution prepared from equal parts of soda and salt , which is used to rinse the mouth. Soda disinfects the mouth, and salt draws out purulent contents well.
In addition to this remedy, other, no less effective options are used:
- alcohol tincture based on horseradish and vodka . To prepare it, horseradish must be grated, poured with vodka and left for 3 days in a shaded place. The tincture is used diluted with water in a 1:1 ratio to rinse the mouth up to 4 times a day;
- tincture of 500 ml of vodka and 4 medium heads of garlic .
Leave the mixture for at least 5 days, after which it is used for rinsing every four hours. The product is not recommended for use in its pure form, or for more than 3 days, as it can negatively affect the microflora of the oral cavity; - Kalanchoe juice .
This plant relieves inflammation, promotes healing of the mucous membrane and strengthens the enamel. The juice is used to treat soft tissues of the oral cavity. To do this, the leaf is crushed and squeezed through a bandage. Treatment with juice can be replaced by chewing a Kalanchoe leaf, with preliminary removal of the film; - rinsing with decoctions prepared from medicinal plants .
A collection that includes chamomile, calendula, and sage is well suited for this. For the decoction, take a spoonful of each plant and pour in 1 liter of boiling water. After infusion for 30 minutes, the decoction is used for rinsing or mouth baths. When rinsing, you must ensure that the liquid is lukewarm, since too hot a decoction will provoke even greater suppuration.
The growth of a lump on the gum, in most cases, signals the development of serious inflammation, requiring a qualified examination and special treatment. Even a slight delay can lead to the development of complications that pose a danger to a person’s overall health.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Tags: gums, tooth cyst
Did you like the article? stay tuned
Previous article
Toothbrush holder: types, features, prices
Next article
Causes of blood taste in mouth
Reasons for the formation of lumps on the gums
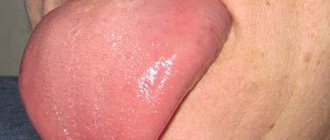
When speaking about a lump under a tooth, dentists mean a dense, white or red growth. There may be purulent masses inside it. The disorder is usually caused by damage to periodontal tissues. What led to its occurrence remains to be determined by the dentist.
The described “growths” are of two types:
- infectious;
- non-infectious.
In the first case, they arise due to the abnormal activity of pathogenic microorganisms, in the second they are associated with mechanical damage to tissues, chemical burns and other unfavorable external factors.
More often than not, a lump on the gum forms precisely because of an advanced infectious process , but this does not mean that doctors can use standard schemes in their work. First, the doctor studies the features of clinical symptoms and draws up a detailed medical history, then carries out the necessary treatment measures and selects medications that will definitely help.
Clinical picture
Features of the manifestation of the clinical picture will depend on the root cause of the pathology and the age of the patient.
In an adult
In adults, the cause of lump growth is most often infectious diseases, which are characterized by the following forms of manifestation:
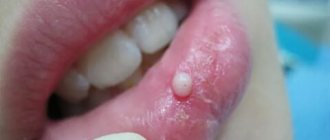
Fistula
Formed as a result of inflammation of dental or periodontal tissues. A fistula is a formation that rises above the level of healthy gums, with a diameter of 3 to 5 mm .
In the center of the elevation there is a white dot , which defines a channel for the release of pus from the source of inflammation. The gums in the area of elevation are hyperemic and painful.
As a rule, the formation of a fistula signals the growth of an infectious process. To ensure the outflow of exudate, you need to visit a dentist, who will open the lump and put drainage into its cavity.
After the outflow of all contents, treatment is carried out to relieve inflammation and the source of infection. Even with regular release of pus without concomitant therapy, the inflammatory process is not eliminated and can take a chronic form.
More details about the fistula in the following video:
What are the types of non-carious lesions on human teeth?
Let's discuss topical anesthesia in dentistry here.
The price of a filling for a front tooth https://www.vash-dentist.ru/lechenie/zubyi/plombyi/iz-chego-skladyivayutsya-tsenyi.html is announced at the link.
Periodontitis
It is characterized by the appearance of a dense, voluminous lump about 1 cm in diameter . The formation is characterized by slight pain that occurs upon palpation of the gums. The cause of periodontitis is teeth affected by caries with inflamed canals and pulpitis, which contribute to the accumulation of bacteria at the base of the root apex.
Gradually, a granuloma forms at the site of accumulation , and without subsequent treatment it degenerates into a cyst . Treatment options for the pathology will depend on the degree of neglect of the process.
In case of minor inflammation, carious tissue is removed, the canals are cleaned, and a medicinal preparation is placed in the tooth cavity, which is covered with a temporary filling. After the inflammation is removed, the tooth is once again cleaned of pathological tissues and filled, completely restoring the coronal part.
Periostitis
It is a complication of periodontitis, in which the infection affects the bone tissue of the jaw. Periostitis is manifested by the growth of lumps on the gums, swelling and redness of the periodontium. In the area of inflammation, constant acute pain occurs, which intensifies as the formation grows .
At the same time, a person experiences an increase in lymph nodes and body temperature. By the deterioration of the general condition one can judge the severity of the pathology.
Treatment of pathology begins with cleaning the canals into which the medicine is placed. After the inflammation is relieved, the medicine is removed, and a new medicine is placed in its place and covered with a temporary filling.
Treatment lasts about 2 months. Only after the source of infection and the consequences of inflammation have been eliminated, the tooth is filled with a permanent composite.
After tooth extraction
The cause of the development of a lump in this case may be a hematoma or inflammation . A hematoma is formed due to damage to blood vessels, which is not uncommon during the process of tooth extraction.
During the normal course of the process, the hematoma does not cause discomfort and resolves after some time. Its soreness and change in color may signal the onset of inflammation.
Also, inflammation can occur without a hematoma, as a result of a blood clot breaking off and bacteria entering the hole. Pain that increases every day after tooth extraction is an indicator of developing inflammation.
If the pain is accompanied by redness of the gums, severe swelling and bleeding, then you need to quickly contact a dentist who will carry out the necessary therapeutic procedures.
Cyst
The reason for its development is advanced periostitis. In this case, a voluminous lump with a diameter of 1 cm appears on the gum , which has a dense structure . The lump can cover both the area of the affected and adjacent tooth.
Soreness and hyperemia are not observed, but there is a constant putrid odor from the mouth. If a cyst is detected in a multi-rooted tooth, partial root resection is performed while preserving other roots and neurovascular bundles.
If a cyst is diagnosed in a single-rooted tooth, the only treatment option is its removal.
Fibropapilloma
It is a small, slowly growing formation on the gum , benign in nature. It occurs due to the proliferation of periodontal tissue cells.
The tumor is painless on palpation and acts only as an aesthetic defect. To eliminate this problem, surgical intervention is used.
How dangerous is a dental x-ray in the first weeks of pregnancy for a child?
Read the link https://www.vash-dentist.ru/lechenie/zubyi/infiltratsionnaya-anesteziya-v-stomatologii-chto-eto-i-kak-provoditsya.html about the technique of infiltration anesthesia in dentistry.
What is dental physiotherapy here is a description
The child has
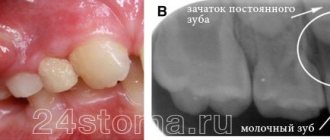
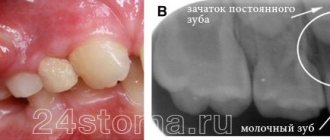
White bumps on the gums in childhood can appear during the eruption of temporary or permanent teeth, and can also act as complications of dental diseases. In each case, they have different causes and a specific clinical picture:
hard lump
Occurs during the period of eruption of units at the site of the future tooth. In this case, there is slight swelling of the gums and pain , which prevents the child from chewing food normally.
As a rule, teething occurs within a few days and the accompanying symptoms disappear. In isolated cases, an additional hematoma may form at the site of the bump.
To reduce pain and relieve inflammation of the gums, it is recommended to treat them with special gels or ointments for children. For example, Dentinox or Kalgel.
If the lump has formed next to the milk unit, then this indicates the growth of a permanent tooth. If the lump increases significantly and the tooth does not fall out for a long time, you should consult a dentist.
Purulent lump
The appearance of a lump of this nature requires immediate attention to the dentist, as it indicates the development of a serious inflammatory process , which not only affects the tissues of the oral cavity and jaw, but can spread to other organs. The growth of a tumor near a baby tooth will lead to its removal.
An abscess on a permanent tooth is treated by preparing the tooth and canals from tissues affected by caries. The medicine is placed into the cleaned cavity and covered with a temporary composite. After the inflammation has been eliminated, the tooth is restored with permanent filling material.
Infections that cause bumps on the gums
Among the infectious diseases that contribute to the appearance of unusual gum growths:
- Periostitis. Inflammation of the periosteum of an acute or chronic nature. In advanced cases, it causes symptoms of general intoxication. The patient complains of a painful lump. It can either increase or decrease in size. Often there is pus inside it. Treatment consists of anti-inflammatory therapy, opening and draining the abscess. At the doctor's discretion, root canal treatment may be performed.
- Granulomatous periodontitis. Most often, this pathology is asymptomatic and is discovered accidentally during an x-ray for another disease. If the cyst is not localized in the area of the apex of the tooth, but is strongly displaced to the side (this is quite rare), a resemblance to a tumor can be observed.
- Radicular cyst. In advanced cases, its walls become inflamed. Then the infected contents of the tumor turn into pus. The necrotic masses are trying to find a way out. A lump appears, from which a foul-smelling liquid is released. During an in-person examination, hyperthermia and tenderness of the surrounding tissues are recorded. The situation may be complicated by symptoms of general intoxication: chills, fever, severe weakness.
- Gingivitis. Inflammatory gum disease. They bleed and become inflamed. Deformation of the gingival margin may occur. Sometimes the inflammation becomes so severe that small benign tumors appear.
- Periodontitis. A condition in which the tissues responsible for holding the tooth in its socket weaken. As a result, the unit becomes mobile. Deep “pockets” form at its base. If food residues accumulate in them, the situation is aggravated by the formation of small round seals.
Bumps in the mouth of a non-infectious nature
If we talk about dental “growths” of non-infectious origin, then we need to mention:
- Epulis. Tumor-like formation of a productive nature. It appears due to the negative influence of local irritating factors. It is caused by injuries, incorrectly installed prosthetic structures, the habit of constantly gnawing hard objects, and malocclusion. Externally, epulis is very similar to tumors caused by gingivitis. To make a correct diagnosis, dentists take x-rays and conduct a histological examination. When treating pathology, the negative influence of the provoking factor is first eliminated. After this, the oral cavity is sanitized. In some cases, it is necessary to excise the neoplasm within healthy tissue along with the periosteum.
- Exostosis (osteophyte). A bone growth that causes the gum level to rise. Usually does not cause any discomfort. Appears after facial injuries or tooth extraction. Most often it is discovered by chance during a routine examination or during preparation for prosthetics. Therapy boils down to removing the bony protrusion and smoothing its surface.
- Hematoma. It looks like a ball filled with blood. Indicates that in a certain area the capillaries or vessels of the mucous membrane have been injured, but the damage is superficial. Hematomas appear due to chemical burns, thermal and mechanical injuries. It is important to differentiate such hemorrhages from hemangiomas and vascular tumors. The latter are very dangerous and require completely different treatment.
When to see a doctor?
Many patients do not make an appointment with the dentist if the growth on the gum does not hurt. It is important to know that some diseases are asymptomatic in the initial stages. Unpleasant sensations appear when nerve endings become inflamed.
It is necessary to contact specialists in the following cases:
- a soft growth or hard compaction has appeared on the gum;
- I am worried about acute pain that is not dulled by painkillers;
- discomfort occurs when chewing or closing the jaws;
- a very swollen cheek or lip.
Lump at the base of the tooth after installing a permanent crown
If the prosthetics are carried out correctly, the doctor did not make mistakes, no neoplasms should appear in the mouth. If, after the end of treatment, the gums swell and a painful blister forms on it, it means that something did not go according to plan.
Most likely, the doctor poorly prepared the unit for prosthetics. Depulpation must be carried out extremely carefully. There should be no air bubbles in the canals to be filled. Under no circumstances should you leave fragments of dental instruments in them. Poor depulpation creates conditions for the development of an infectious process and subsequent periodontitis.
It is also possible that the lump was formed due to shortcomings that were made at the time of fixation of the artificial unit. Then the glued structure begins to put pressure on the mucous membranes and rub the tissue. Abscesses, growths, and purulent lumps form. To eliminate these unpleasant symptoms, you need to adjust the shape of the prosthesis.
If the crown is installed correctly, it will never interfere. This needs to be understood. Only in the first hours after its fixation may an unusual sensation of a foreign body in the mouth persist. But then the person stops noticing the structure altogether.
How do doctors treat a lump on the gum?
The treatment regimen directly depends on the cause of the disorder. Therefore, the patient is first offered to undergo diagnostics. It includes:
- survey, inspection;
- performing radiography;
- taking a tissue sample (if necessary).
Based on the results obtained, the doctor decides on further procedures. It can be:
- drainage and washing of purulent neoplasm;
- root canal filling;
- removal of osteophyte;
- excision of a benign tumor;
- dental crown replacement;
- conducting pharmacological therapy.
It is important that the patient strictly follows all medical prescriptions. Then the likelihood of complications will be minimized, and the oral tissues will be restored in a short time.
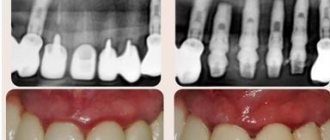
Diagnosis and treatment of gum formations
A gingival lump can be easily identified during a visual examination and instrumental examination. To clarify the diagnosis, an x-ray or biopsy may be indicated.
Treatment methods are determined by the root cause of the formation on the gums. First of all, you will need to limit the further development of the infection and eliminate pain.
Traditional treatment is as follows:
- fistula
– elimination of pus by rinsing (using Chlorhexidine, Miramistin, decoctions of medicinal herbs, saline solution);
- epulis
– surgical treatment (removal with a scalpel, cryodestruction or diathermocoagulation);
- periodontitis
– unsealing and cleaning of root canals, removal of accumulated pus, mouth baths made of soda solution or herbal decoctions;
- periostitis
– opening the tooth and placing special medications under a temporary filling (if there is no positive result, the diseased tooth must be removed);
- gingivitis
– cleaning of periodontal pockets, antibacterial and antiseptic treatment, removal of pathological formations.
Traditional medicine offers treatment with freshly squeezed juice of Kalanchoe leaves, used in the form of lotions. Another option is to chew the leaves, having previously cleared them of the film. A popular remedy for bumps in the mouth is rinsing with regular vodka.