Plaque on the tongue of fungal origin - why candidiasis appears and methods of combating it
Fungus on the tongue is not such a rare phenomenon, and the development of such a pathological condition is provoked by yeast fungi of the genus Candida. They are present in the body of any person and do not harm him until a certain point. But as soon as the immune system weakens and fails, the fungus will immediately begin to multiply and ultimately can lead to the development of candidiasis (thrush). Today we’ll talk about what a fungal infection of the tongue is, what symptoms are typical for it, and what treatment methods are used today to get rid of this unpleasant disease.
Candida - what is it?
Candida is a single-celled fungus with over 150 different species. Moreover, only 20 of its varieties are capable of provoking the development of pathological conditions in humans. When penetrating into the oral cavity, yeast fungi can spread to the tonsils, in the presence of carious cavities, penetrate into the dentin, and affect various areas of the mucous membrane.
Candida differs from other types of fungi in that it is not capable of forming mycelium or mycelium. They grow from special bags that are located in cells. Seeping into the tissues of the mucous membrane of the mouth and throat, they quickly destroy it. The enzyme they secrete promotes rapid cell breakdown. As a result, a person experiences soreness, dryness and tingling in the mouth, namely on the tongue.
Symptoms
Oral fungus has a pathological effect, which consists of damage to the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, on the red border of the lips (otherwise called cheilitis) and in the corners of the mouth. Damage to the mucous membranes in the mouth when the patient is in a weakened condition or after long-term antibiotic therapy can lead to acute catarrhal stomatitis .
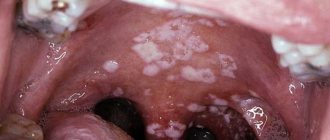
Pathology usually manifests itself in the form of a hyperemic or even bluish surface of the mucous membranes and the formation of single white plaques. They look like they are glued on. The fungus in the mouth, the photo of which is presented below, initiates chronic atrophic changes in the structure of the epithelium.
Fungus in the mouth
In addition, in addition to white plaque, crusts and redness, white papules, unpleasant local symptoms may occur in the form of itching, changes in taste, pain and burning.
Causes of pathology
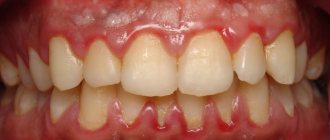
Candida are natural inhabitants of the human body, but under normal conditions they do not manifest themselves in any way. A provoking factor may be a malfunction of internal systems and organs, which leads to a deterioration of the immune system. The active reproduction of these microorganisms becomes a consequence of a chemical imbalance in the body, and as a result, a disease such as candidiasis develops, better known as thrush. The manifestations of this pathological condition are difficult to miss - the tongue becomes covered with a characteristic coating, and an unpleasant burning and tingling sensation is felt in the mouth. To understand what the tongue looks like, take a look at the photo below.
This is what a fungal infection on the tongue looks like
There is a whole list of possible reasons that can provoke unnaturally active proliferation of yeast fungi in the oral cavity:
- deterioration of immunity,
- hormonal imbalances, especially common in pregnant women,
- diabetes, tuberculosis, gastrointestinal problems, HIV infection,
- taking certain medications, including corticosteroids,
- long-term antibiotic therapy,
- deficiency of vitamins B, C, PP,
- dysbacteriosis,
- nicotine addiction, excessive alcohol consumption, drug use,
- radiation as part of the treatment of cancer,
- taking hormonal contraceptives,
- the presence of microtraumas on the mucous membrane or directly on the teeth.
Fungus on the root, back, sides or under the tongue may appear as a result of contact with a disease carrier. For example, a child may receive it from the mother during childbirth. In addition, you can become infected through kissing, sexual intercourse, or sharing personal hygiene items.
Pathogenesis
Yeast fungi in the human body are considered to be opportunistic microflora . They may be present in the microflora, and if the immune system is strong, then the fungal infection does not cause diseases, for example, urogenital, respiratory, skin, or, as in this case, the mucous membranes of the oral cavity. Normally, in almost 70% of the population, yeast fungi are present in the resident microflora; they are inactive and do not cause candida or other fungal diseases. Reproduction usually occurs by budding and spores. Proliferation occurs not due to the departure of daughter cells from the mother cells, but through elongation and formation of a pseudomycellar tree. As a result of vital activity, toxic substances are released that weaken the human immune system.
Model of a fungus cell of the genus Candida
alcohol and drug abuse, oncology, and the use of contraceptives contribute to imbalance of the oral microflora and excessive proliferation of opportunistic fungi . Fungus in the mouth is most often a superficial disease that affects the mucous surface of the cheeks, the corners and borders of the lips, the back of the tongue, the palate, etc., but with significant spread and penetration into the bloodstream it can cause systemic chronic and generalized disorders.
In neutropenic or severely ill patients, candidal fungal infection can enter the bloodstream, where it causes widespread visceral dissemination. Generalized mycosis can lead to candida sepsis and even death.
How to recognize a fungus - symptoms of the disease
Currently, experts identify several of the most common types of fungal infections of the tongue, each of which is characterized by its own symptoms. Let's take a closer look at these types:
- pseudomembranous, acute form: most often affects newborns and adults with seriously compromised immunity. A whitish coating appears on all surfaces of the oral cavity, including the cheeks, gums and throat; visually it resembles traces of cottage cheese or milk,
- pseudomembranous chronic: develops in patients with AIDS, as well as against the background of infections that have developed resistance to antibiotics. The symptoms are similar to those described above, the person may also experience pain when swallowing,
- atrophic, acute form: usually develops after prolonged use of antibiotics, often found in diabetics. In this case, swelling of the tongue is observed, the mucous membrane becomes covered with cheesy discharge, the person feels an unpleasant burning sensation, and the corners of the lips dry out and become covered with small cracks,
- atrophic chronic: as practice shows, this form is usually encountered by people with dental prosthetic devices. Active reproduction of microorganisms often begins under the palatal covering of the structure, and a distinctive symptom is the fact that the tongue acquires a rich red tint,
- erythematous: a chronic form, which is characterized by inflammation of the entire oral mucosa, including the throat, as well as the formation of a whitish coating,
- hyperplastic: accompanied by the formation of a dense coating in the form of plaques, but in this case it is not white, but practically merges with the natural shade of the tongue. Slight redness may be detected along the edges.
How to treat the pathology is determined by the attending physician, and before prescribing therapy, he needs to find out what specific form of pathology he is dealing with. To do this, the specialist conducts a visual examination and sends the patient for tests.
Classification
Mycoses are divided depending on the form of the course - mild and severe, acute and chronic; according to the type of changes, they can be acute pseudomembranous candidiasis (thrush), acute atrophic candidiasis , chronic hyperplastic candidiasis , candida-associated periodontitis , ulcerative-erosive stomatitis .
The localization of fungi can be on the tongue, on the cheeks, on the lips, in carious cavities and root canals, on the tonsils, in the corners of the mouth, or affecting the entire surface area of the oral cavity.
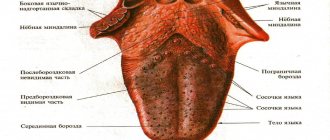
Fungus on tongue
The pathological effect of various infectious agents on the tissues of the tongue causes glossitis . One of the manifestations of glossitis may be the loss of the ability to determine tastes. Significant contamination also leads to the formation of ulcers, the sensation of blood in the mouth, and spread to the tonsils and pharynx.
Different types of candidiasis on the tongue
Fungus on the tongue, photos of various types of damage to the epithelial layer (atrophic, hyperplastic, all-membranous and thrush), clearly demonstrates how varied the symptoms of glossitis can be. At the first signs, you should contact your dentist for a consultation.
Fungus on lips
The course of mycoses on the lips is usually chronic and most often manifests itself in redness. Unpleasant symptoms can occur even in people with fairly strong immunity, but more often in patients with diabetes , tuberculosis or AIDS .
Fungus on lips
Other symptoms may include slight swelling of the lips, burning, peeling, and a white coating as in the photo of fungus on the lips. The existing crusts are grayish in color, have raised edges and a tightly attached center, and differ in size. If you try to tear off the crust, a bleeding wound will open. In general, the pathology causes discomfort and pain.
The mucous surface of the inner part and red furrow of the lips may become thin, cracked, and tense. This is a fairly rare separate disease, also called cheilitis .
Age factors of distribution
Candidiasis on the tongue most often occurs in newborns. Moreover, treating a disease in a child is much simpler and faster than in an adult patient. The younger he is, the easier the disease is to treat.
Most common in childhood
“My daughter, when she was not yet a year old, was diagnosed with candidiasis. I noticed a white coating on my tongue, at first I thought it was a nutritional mixture. I tried to wash it off with water, but nothing happened. The doctor said that there was nothing wrong with it; fungus in the mouth is often found in infants. We were prescribed Fluconozol and a general strengthening multivitamin complex. The plaque disappeared quite quickly, literally within a week, and did not appear again.”
Karina88, Moscow, from correspondence on the woman.ru forum
Quite often, older people have to deal with candidiasis. According to statistics, about 10% of people over 60 years old experience this unpleasant disease1. This trend is primarily associated with wearing prosthetic structures in old age, which often create ideal conditions for the rapid spread of fungus.
How it manifests itself
The disease is easily diagnosed, since its symptoms are clear and speak for themselves. Symptoms are the same in adults and children. The pathology develops according to the principle of dermatitis. The skin becomes inflamed, red, and mucous membranes swell. As the number of fungi increases, sores form. They are painful, covered with a white or yellowish coating. When trying to remove the latter, blood begins to flow.
Subjectively, the patient complains of:
- itching/burning on the affected areas of the tongue;
- pain when eating solid foods;
- bad breath;
- discomfort during a conversation.
Plaque found on mucous membranes consists of dead epithelial cells, fibrin, bacteria, and food microparticles. It can be located in small isolated areas or merge into volumetric circles. If measures are not taken in time to eliminate this symptom, the infection will spread to the throat and then to the internal organs.
The danger lies in the fact that candida multiplies very actively. They are able to penetrate into the deep layers of the mucous membranes of the mouth. Then the disease is difficult to treat, and the likelihood of relapse remains high.
As for the painful sensations that appear while eating, they are associated with severe tissue inflammation. The latter turn red and bleed. Any mechanical impact aggravates the situation.
If pain occurs when swallowing, it means that candidiasis has spread to the pharynx. A feeling of a lump in the throat indicates the appearance of voluminous film growths. This should not be allowed. The sooner treatment is started, the lower the risk of unwanted complications.
Other symptoms of candidiasis on the tongue
Other signs indicating the disease include:
- weakness, lethargy;
- increased body temperature;
- proliferation and enlargement of the papillae on the surface of the tongue;
- deterioration of taste or loss of the ability to recognize tastes;
- tissue swelling;
- decreased tongue mobility.
If these symptoms appear, you must make an appointment at a dental clinic.
How to deal with the disease - treatment methods
General and local remedies will help cure candidiasis. However, only a doctor can select the appropriate set of medications after diagnosing and identifying the causes of the disease. So, how to get rid of fungus on the tongue? Common treatment methods are discussed below.
General agents
To quickly and reliably remove manifestations of infection in the mouth, drugs are usually prescribed that affect not only the affected area, but the body as a whole, helping to remove infection from the blood. In such situations, antibiotics are often prescribed - Levorin and Nystatin tablets. Already on the fifth day after the start of treatment, the symptoms begin to subside, and a clear decrease in plaque can be noticed.
Medicines will relieve symptoms on the 5th day
In advanced stages, the doctor may suggest Amphotericin (intravenously administered) or a course using Amphoglucamine in tablet form. Additionally, multivitamin complexes and calcium gluconate are prescribed to strengthen the immune system.
Local remedies
Topical medications help relieve visible manifestations of the disease in localized areas. They help relieve redness, eliminate discomfort in the oral cavity, restore the integrity of the mucous membrane and stop the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms. Often, treatment of the affected areas with Fukortsin and brilliant green is prescribed, or Lizak or Lysozyme are suckable tablets. If pathological processes have affected the lips, levorin or nystatin ointment is recommended.
Important! You can start taking pills and using external products only with the permission of your doctor. Self-medication is strictly prohibited - otherwise, you can cause a sharp deterioration in the condition. The same applies to the use of folk remedies - only after agreement with a specialist.
You will also need to undergo complete sanitation of the oral cavity, which will stop the spread of infection and prevent it from “spreading” to new, untouched tissues.
What is recommended to rinse your mouth with?
As part of the treatment, various rinses are recommended. As a rule, specialists prescribe solutions for disinfection; they help remove plaque, remove secretions from other areas of the mucous membrane, suppress inflammation, and also heal microtraumas on soft tissues. In such situations, a 2% solution of regular baking soda or a mixture of iodinol and water is often used. It is recommended to repeat rinsing every couple of hours, as well as after waking up and before going to bed. On average, the course lasts about 2 weeks. However, therapy should never be started without the consent of a specialist. Before performing the first procedure, consult your doctor.
Rinsing is prescribed by the attending physician
Tests and diagnostics
To confirm the diagnosis, microscopic examination of crusts and other biological tissues, fluids or scrapings is carried out, depending on the location of the pathology. As a result, fungal mycelium is detected. It is quite important to identify the causative microorganism (PCR diagnostics, ELISA, cultural inoculation with quantitative monitoring can be used for this), since various types of fungi can exhibit resistance to antifungal drugs.
Additional studies include checking for gastrointestinal pathologies, diabetes mellitus and leukemia .
Carry out differential diagnosis:
- with eczema - characterized by the formation of weeping surfaces after the opening of the blisters, redness and swelling are more pronounced;
- with leukoplakia , manifested by the development of plaques and opacities of areas of the epithelium;
- with allergic, streptococcal stomatitis, cheilitis and other similar lesions of a different nature.
Diet for candidiasis on the tongue
Compliance with certain dietary restrictions is an important point in treatment. For example, experts strongly recommend avoiding products with yeast. Too spicy and sour foods provoke irritation of the oral mucosa, which can cause an unpleasant tingling sensation and even pain. During recovery, doctors advise eating mainly liquid and warm food. In this case, spices and acid-containing foods will have to be excluded for a while.
You need to return to your usual diet gradually. For three months you will have to give up sweet and fatty foods, carbonated water, mushrooms, as well as confectionery and alcoholic drinks.
Diet for fungus in the mouth
Antifungal Diet
- Efficacy: no data
- Terms: 3-6 months
- Cost of products: 1500-1600 rubles. in Week
In addition to complex antifungal treatment, patients are strongly recommended to follow a strict diet consisting of foods without vinegar, sugar, yeast and alcohol. in vitamins and strengthening the immune system is also recommended The menu should include bananas, onions, garlic, asparagus, chicory, olive oil, seafood, legumes, and buckwheat.
Preventive measures
After recovery, it is important to take care of preventing relapses. To do this, you need to maintain oral hygiene, brush your teeth at least twice a day with a brush and paste, use special floss to clean the interdental spaces and rinse your mouth with water every time after eating. These are basic rules, the observance of which will significantly reduce the risk of recurrence of candidiasis symptoms. Also, do not forget to renew your toothbrush every 4 months and visit your dentist every six months for preventive examinations. In order to maintain the body's immune strength, doctors advise taking vitamin complexes from time to time, eating more vegetables and fruits, leading a more active lifestyle, and also spending more time in the fresh air.
- Statistics from WHO - World Health Organization.