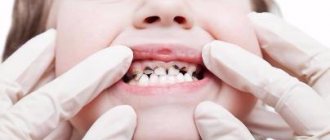
Tooth enamel is the hardest tissue in the human body. Up to 90% of calcium reserves are concentrated here. However, cosmetic dentistry regularly deals with defects in this tissue. The fact is that hardness and ductility are different things. With impressive hardness levels, enamel is a fragile material that easily chips and cracks.
The situation gets worse if the enamel is weak. Temperature changes, chronic diseases, blows - and then the tooth breaks off. The situation is unpleasant, and in the long term it is also fraught with caries. Through the crack, bacteria penetrate directly into the tooth, to the pulp, which means that caries will quickly develop into pulpitis. In general, a chipped tooth is a reason to see a doctor, and quickly.
So, what to do if a tooth chips?
- Rinse your mouth with any suitable antiseptic or water to protect the tooth from bacteria and food debris.
- If there is bleeding, apply a tampon with hydrogen peroxide or a hemostatic sponge.
- Apply cold externally to prevent swelling from developing.
- If the pain is very severe, take a pain reliever.
- If a tooth chips on the street, try to rinse your mouth with drinking water (mineral water is also suitable, but not sugary drinks). Other measures can be postponed to your home or the nearest pharmacy.
After that, call your dentist. There is no point in going to emergency rooms - they will simply pull out the affected tooth, especially if a child’s baby tooth has chipped off. You need to eliminate the defect without unnecessary sacrifices.
Fortunately, there are ways to quickly restore a tooth, even if it is severely damaged. There is a whole direction - aesthetic restoration of teeth, it deals with both acquired and congenital defects. Today, restorative dentists work wonders to transform small and uneven teeth into a Hollywood smile. This direction is developed both in pediatric and adult dentistry.
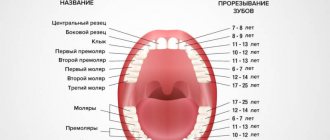
Why a baby tooth may break off - possible reasons
Before we get into what to do if a baby tooth chips, it's worth considering the potential causes of the injury. For example, in children under 2 years of age, the most common traumatic factor is careless handling of toys when trying to “taste” them. An equally risky period is learning to eat independently using cutlery. The baby can easily miscalculate the force and accidentally hit the crown on a spoon or the edge of a cup.
The cause of the breakdown may be careless handling of hard objects.
If a tooth breaks off in a child aged 5 years or older, this is usually preceded by a fall or blow, again received during play or active activities. Dietary habits also play an important role. For example, if a child is used to chewing icicles, does not carefully bite off solid foods, and often eats crackers and chips, the risk of injury in his case will be much higher.
Certain circumstances also create suitable conditions for injury:
- carious processes - lead to the appearance of a cavity that rapidly grows, as a result of which the enamel weakens and quickly collapses,
- hypoplasia and other non-carious lesions - fragmentary or even complete (aplasia) absence of enamel, its obvious underdevelopment,
- malocclusion - uneven distribution of the chewing load leads to constant excessive impact on individual elements, as a result of which they are destroyed over time,
- abnormal position of the teeth - the presence in a row of strongly curved elements protruding beyond the alveolar arch, more susceptible to injury.
Caries of baby teeth can also cause breakage.
One cannot ignore such a fairly common phenomenon as bruxism. Children with this diagnosis involuntarily clench their jaws and grind their teeth during sleep. As a result, the enamel quickly wears off and becomes sensitive - hyperesthesia develops. Thus, bruxism creates optimal conditions for the appearance of chips and cracks.
Obviously, the weaker and thinner the enamel, the higher the likelihood of damage occurring on it. If we consider the problem from this perspective, then many endocrine disorders, acute deficiency of calcium and other important minerals in the body, and congenital anomalies also lead to the depletion of the external protective layer.
Classification of chips and associated symptoms
Dental experts classify chips according to severity. So, a chip of enamel is a minor damage that affects only the top layer. The patient may not experience any pain or discomfort at all.
A chip of enamel is a minor damage
Sometimes the injury affects the dentin, and under it there is a pulp chamber with a bundle of blood vessels and nerve endings. If the damage also affects the pulp, the child will feel severe piercing pain. In such a situation, emergency medical attention is required.
The photo shows teeth with dentin and pulp trauma
A root fracture is a serious injury that can result from a strong blow or fall. The crown breaks, but the root remains inside. With such damage, there is a serious risk of injury to the rudiments of permanent incisors and canines. In all of the above cases, you need the advice and help of a specialist. In this case, the method of treatment and restoration will directly depend on the degree of damage to the visible part and internal structures of the tooth.
Fracture – serious injury to a tooth
The following symptoms often indicate injury - pay attention to them:
- there are complaints of increased sensitivity or the child makes it clear by his behavior that he is experiencing discomfort. He may refuse hot and cold foods, avoid sweets and sour foods, try to chew on one side,
- if the damage reaches the pulp, severe piercing pain occurs,
- discomfort may intensify at night, and this also indicates injury to the pulp,
- Many children acquire the habit of “searching” with their tongue behind their cheek, as if there was something in the mouth.
Severe pain may indicate damage to the pulp.
If you notice one or more of the symptoms described above in a child, ask him, find out if his teeth are bothering him. And be sure to show your baby to a specialist.
Combined root and crown fracture with pulp exposure (E) (S02.54)
This type of injury has a high degree of complexity and is quite rare. As a result of its production, destruction of the crown and root into small fragments may be observed. The patient experiences bleeding in the pulp and periodontal areas, as well as in the fracture crevices. The severity and nature of the injury is determined using x-ray examination. The exact depth of the fracture can be determined after removing the broken tooth fragments. Treatment of combined fractures, affecting both the root and crown, usually involves tooth extraction.
When should you go to the dentist?
Immediately after receiving an injury, parents need to pull themselves together and try to calm the baby. The first thing you need to do is make a visual inspection, try to carefully clean the oral cavity from food debris, ask the child to rinse his mouth with boiled water at room temperature or a light antiseptic solution. To relieve the pain a little and reduce swelling, you can apply ice wrapped in several layers of napkins to the cheek on the side of the sore spot. If bleeding occurs, apply a piece of sterile bandage to the wound and immediately go to the doctor.
The first step is to ask your child to rinse his mouth.
What complications can there be?
If the chip is minor and does not cause discomfort, this does not mean that you can ignore it. Damage will lead to further destruction of hard tissues, and then dentin and pulp will be at risk. If the neurovascular bundle is damaged, the child will inevitably experience severe piercing pain, and further treatment may require removal of the nerve.
In addition, the presence of injured elements in the oral cavity creates favorable conditions for the proliferation of bacteria and infection of tissues. In addition to serious dental problems, this can lead to the development of diseases of the liver and kidneys, digestive and cardiovascular systems.
Treatment methods - what can be done in dentistry
Now let’s move on to the question of what to do if a child’s piece of a baby tooth breaks off. If this is a one-year-old baby, seek help from a specialist as soon as possible. The doctor will assess the severity of the injury and suggest the best solution to the problem. You may need to undergo x-ray diagnostics and additional examinations. At this stage of development of the body, it is important to make sure that the baby does not have systemic disorders that could lead to a deterioration in the condition of hard tissues and their destruction.
“Many thanks to the doctors of your clinic! My daughter is 4 and a half, she damaged her tooth while playing with other children. Your crown was completely restored for us, very quickly, efficiently and completely without stress for the child. Now she always goes to the dentist in a great mood! Everything is very professional and kind. Thank you for such a correct approach to working with children!”
Valentina V.D., fragment of a review on the website of one of the Moscow dental clinics
If we talk about older children, then if chips of enamel or dentin appear, the dentist can perform a composite build-up to hide the defect. If the cause was caries, the doctor will remove the affected tissue and put a filling. A restoration insert may be required to hide large chips. It looks like a large filling, but it is created from impressions in a separate laboratory. In order to strengthen and saturate the enamel with useful microelements, a course of fluoridation and remineralization is prescribed.
For minor defects, dental treatment is performed
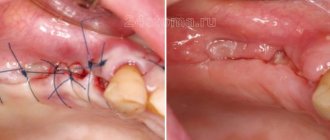
It’s another matter when the pulp or root is damaged during an injury. In the first case, the nerve is removed and the tooth is then restored using a pin. If the root is severely damaged, the tooth is completely removed. And if you wait even more than a year before changing the primary bite, the doctor is obliged to offer temporary prosthetics for this period. Otherwise, even one primary incisor or molar, removed ahead of schedule, can lead to displacement of the rows and curvature of the bite1.
The photo shows teeth after prosthetics
Trauma with root fracture (F) (S02.53)
Damage of this type is often combined with destruction of the alveolar bone and is considered a severe injury. The fracture can have different locations: in the middle part of the root, in the cervical or apical zone. Also, this type of injury is divided into longitudinal, oblique, combined or transverse, with and without increased mobility, with and without displacement of fragments. The doctor makes the final diagnosis based on the results of radiography. Depending on the direction, location and degree of the fracture, the following methods can be used to treat it:
- rigid wire splinting;
- filling of equine canals;
- endodontic intervention;
- surgical removal.
In case of pulp necrosis, death of the neurovascular bundle, or high mobility of fragments, the prognosis for tooth fusion is unfavorable. In other cases, with timely and high-quality treatment, there is a high probability of complete healing of the injury.
What experts advise for prevention
As in the case of any other pathological conditions, it is always better to prevent unpleasant consequences than to later engage in long and costly, and sometimes quite painful, treatment. To reduce the risk of damage and destruction of children's primary incisors and molars, it is necessary from an early age to teach the child to take a responsible approach to oral care, brush his teeth every morning and evening, and follow all basic hygiene rules.
It is worth keeping a close eye on your baby while he is playing. Try to exclude all traumatic factors. Later, if the child begins to engage in traumatic sports, he should be given an individual protective mouthguard - this service is provided by many modern dentists.
It is worth keeping a close eye on your baby while he is playing.
But finally, in no case should you ignore any pathological changes in the oral cavity, even if there are only temporary baby incisors and molars. If there is a clear malocclusion, orthodontic treatment should be started promptly. If caries and inflammatory processes develop, immediately show the child to a specialist. Parents need to remember that any advanced dental diseases can easily damage the buds of permanent teeth, which will inevitably affect their condition and health in the future.
1Eradze E.P., Osipov G.A. Modern methods of treating acute dental trauma in children, 2001.
What are the dangers of cracked teeth in children?
Even a superficial defect in tooth enamel can negatively affect the condition of the tooth. If you let the situation take its course, over time the cracks can lead to unpleasant consequences:
- development of caries, gingivitis, periodontitis due to the accumulation of plaque in the defect;
- chips of the enamel, which, in turn, injure the tongue and mucous membranes;
- penetration of infection into the pulp with the development of pulpitis and other emergency conditions;
- premature loss of a tooth unit.