Causes of caries
Caries occurs “thanks” to microorganisms living in the thickness of dental plaque. These bacteria - primarily streptococci, lactobacilli and actinomycetes - process food debris that remains on the teeth and produce acids that corrode the tooth enamel, leaching calcium from it. The tooth enamel begins to deteriorate.
The activity of bacteria varies from person to person: it is higher if a person brushes their teeth irregularly or not thoroughly enough, since soft interdental plaque is an excellent nutrient medium for them.
Stay vigilant
If you find plaque forming on your child’s teeth that you are unable to remove on your own, as well as brown or white spots, this indicates that the child urgently needs to be shown to a pediatric dentist. If the baby complains of discomfort that occurs when eating hot or cold food, this indicates the spread of caries into the deeper layers of the tooth. Parents should never ignore such complaints. It happens that a small child is not able to clearly communicate what is bothering him, so if he refuses food or a certain type of food, and also chews on one side, this may indicate toothache.
Possible causes of caries in children
- Poor dental hygiene.
- Poor nutrition. Bacteria multiply more actively in the mouth of people who prefer foods with a high content of easily digestible carbohydrates and sugars.
- Insufficient production of saliva, its increased viscosity.
- Lack of solid foods in the diet, which helps remove soft plaque.
- Lack of calcium and phosphorus in food.
- Lack of fluoride in water (below 1.5 mg/l).
- Crowding of teeth, since it is impossible to clean plaque from the interdental space in this case.
- Some diseases predispose to increased activity of the carious process: diabetes mellitus, thyroid disease.
Proper nutrition
One of the preventive measures for dental diseases is a balanced diet - one in which the daily diet contains proteins, carbohydrates, fats, minerals and vitamins that are necessary for the formation and proper growth of dental tissues. In infants, this is breastfeeding. Older children need to include in their diet all the necessary types of complementary foods that are recommended for this age. Additional sources of fluoride can also be water and fluoridated salt; their use does not require special indications. The main sources of calcium are fermented milk products (cottage cheese, milk, cheese, etc.), buckwheat, gooseberries, potatoes, peas, oats, mineral water (some of its types).
Clinical picture of caries
The first stage of the carious process
Caries occurs in the spot stage and in the superficial layers of enamel. Then we observe a stain on the surface of the tooth, which gradually becomes more dull, rough and porous.
The second stage of the carious process
If the enamel is chipped and a defect is formed, the tooth becomes more sensitive to irritants. Transient pain appears after eating cold, sweet and sour foods.
The third stage of the carious process
A carious cavity in dentin (tooth tissue located under the enamel). In this case, toothache appears depending on the situation, for example, when chewing on a diseased tooth or when there is a sudden change in the temperature of food, air, or when food gets into the cavity of a damaged tooth.
The fourth stage of the carious process
With further destruction, a deep carious cavity appears in the tooth, which gradually increases in size, so that eventually the tooth is destroyed and the pain appears spontaneous and constant. At this stage, an urgent visit to the dentist is necessary, as this indicates damage to the nerve of the tooth. In this case, it is not always possible to save the tooth.
Meet our tooth fairies and find out prices
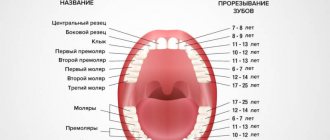
Stages of caries
There are 4 stages of caries in primary teeth.
Elementary
– the stage of a carious stain is characterized by softening and demineralization of the enamel. The tooth surface loses its uniformity and becomes rough with white or light brown inclusions. At this stage, caries is asymptomatic.
Surface
– the destruction of the outer shell of the tooth continues, the shade of the enamel deteriorates, the nerve begins to react to temperature stimuli, sweet foods and drinks.
Average
– bacteria penetrate into the inner layers of the tooth, and the upper layers of dentin begin to deteriorate. At this stage, the carious cavity is clearly visible. Sensitivity to hot, cold and sweets increases.
Deep
– the infection spreads and affects an increasing proportion of dentin. At this stage of the disease, the risk of complications increases, including tooth loss.
Diagnosis of caries in children
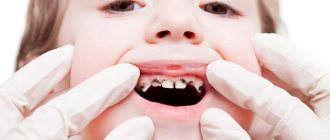
How to recognize caries in a child? A parent cannot always do this, since caries in children becomes noticeable only when there is already a hole in the tooth. Often a child is brought to the dentist “just to check his teeth,” and the doctor finds several caries after examining him with instruments.
The usual methods for diagnosing caries are inspection and probing. As a rule, this is enough to determine the presence of caries. The depth of the lesion can be assessed based on the child’s complaints and by x-ray examination.
Deep caries in a child is visible to the naked eye. At the same time, deep carious lesions on a tooth will almost always require x-rays so that the doctor can understand how far the carious process has gone, whether it is possible to save the tooth or whether removal is necessary.
How to prepare a child for treatment?
Children intuitively feel the fear of adults and begin to be afraid of dentists even before their first glance at the dental chair. In order for the treatment of caries in a baby under 3 years old to go as smoothly as possible, it is necessary to prepare him for a visit to the doctor in advance.
- Find a trusted, good dentist who can establish contact with your child.
- Take your child for preventive examinations to the dentist, do not wait until the tooth hurts. Believe me, pain will greatly increase children's fear.
- Be calm at your doctor's appointment. Remember, all the fears of the parents are transmitted to the baby. There is no need to tell the child “don’t be afraid”, “it won’t hurt”, “like a mosquito will bite” even before he approaches the doctor.
- If your baby is already playing on his own, rehearse your visit to the dentist at home. Treat caries for a bear, bunny, or cat. Let your child get used to the atmosphere of the dental office a little.
- Tell your child that everyone goes to the dentist - mom, dad, and grandparents. And, most importantly, emphasize that visits to the doctor bring joy and relief to everyone.
- Choose a time to visit the doctor when your child is alert and cheerful. Believe me, the baby will not be happy to be in the doctor’s chair during the daytime nap or in the evening when he is already tired. By the way, during the visit the baby should be well-fed.
- If you nevertheless went to the dentist for the first time because of a toothache, convince your child that the doctor will definitely help him. Remember, the baby is already very scared, so there is no need to use the words “drill” or “acute pain”. Better tell a story about how a good doctor will save a child from carious monsters, and his teeth will become white and healthy.
We hope our tips for treating caries in children under 3 years of age will be useful to you. Teach your child not to be afraid of dentists and to take care of their teeth. May you and your children always have beautiful snow-white smiles.
And in order for a child to love brushing his teeth from a very early age, it is important to choose a tasty, high-quality toothpaste for him. ASEPTA baby toothpaste gel-paste is created specifically for children aged 0 to 3 years. The soft, sweet gel carefully cares for the child’s teeth and gums without damaging them, and the natural components of the paste provide protection against caries and inflammatory processes in the oral cavity.
The paste does not contain abrasives, fluorine, parabens, or sodium lauryl sulfate, so it is absolutely safe for crumbs. And the bright taste of “tutti-fruiti” will make brushing your teeth very pleasant for your baby.
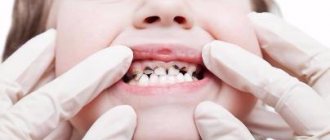
Caries of primary teeth in children
Caries in young children can occur immediately after the first teeth erupt. There are many reasons: the course of pregnancy, illnesses in the first years of life, the rules and regimen of feeding, and the nature and composition of early complementary foods.
Bottle or “circular” (circular) caries in children affects the necks of the upper incisors and canines, since in these areas the enamel is usually the least durable.
Caries of primary teeth in children at the initial stage manifests itself in the form of a chalky or white spot on the tooth. If you visit the dentist frequently, such caries can be stabilized. However, the enamel of baby teeth with stains can be damaged and destroyed very quickly. First, the stain becomes grayish or brownish, then softens and falls off, and after 2-3 months the carious process already damages the dentin. A cavity forms on the tooth - a clearly visible dark depression. If you see a cavity with a pigmented bottom (“hollow”) on a child’s tooth, do not put off going to the dentist, since at this stage the tooth already needs surgical and restorative treatment.
Do they give anesthesia to children?
Many parents are concerned about how to painlessly treat teeth in children under 5 years old.
Non-invasive methods are absolutely painless. If a cavity needs to be prepared, anesthesia may be required. Children most often undergo two-stage anesthesia. First, the gum area is treated with an anesthetic gel, which numbs the injection site, and then an anesthetic injection is given.
In some cases, it is advisable to use sedation - when the child is introduced into a relaxed state of half-asleep using a special gas. Choosing the optimal method of pain relief and treatment is the responsibility of the dentist.
Caries of permanent teeth in children
Newly erupted teeth have lower mineralization, which is finally completed only by 4-5 years after eruption. Young permanent teeth are especially vulnerable in the first year of development. The enamel on them is easily permeable to caries bacteria, so a junior schoolchild should be helped to brush his teeth and be sure to consult with a dentist about the need to seal the fissures and make a protective coating for the enamel.
Meet our tooth fairies and check prices.
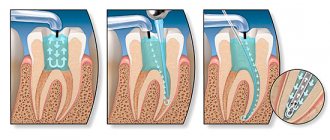
Other important features of the treatment of pulpitis in permanent teeth for children under 14 years of age:
In order for the treatment of pulpitis to be successful and the patient to have no relapses or complications, it is necessary to:
- Strictly maintain sterility to avoid infection during treatment.
- Use a rubber dam to isolate the patient’s oral cavity from the manipulation field.
- Carry out a thorough filling of the canals - the voids left in them will provoke the re-development of inflammation.
- Monitor the quality of canal filling after treatment using repeated x-ray diagnostics.
- Do not forget that not only adults, but also children need high-quality fillings and dental restoration, and, sometimes, even prosthetics with ceramic inlays.
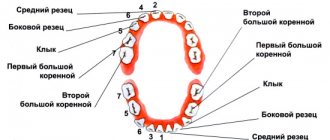
Types of caries
According to the place of manifestation
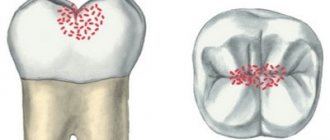
- Fissure caries affects the grooves and grooves on the surface of the chewing teeth - fissures. Food debris accumulates inside the fissures, which means bacteria that cause caries.
- Approximal (interdental) caries occurs between adjacent teeth, especially often when teeth are crowded. It is very difficult to clean out food debris from the interdental spaces, so plaque often accumulates there.
- Cervical caries destroys the enamel next to the gum, since it is in this place that it has lower mineralization and minimal thickness.
- Root caries characterizes the destruction of the tooth root under the gum. To diagnose root caries, additional methods are needed, since it is difficult to detect visually. In children, it occurs when there is severe destruction of baby teeth.
According to the speed of development
- Compensated caries proceeds slowly; many months can pass from the spot stage to the development of deep caries. In some cases, the process may even be reversible, but only by restoring the mineralization of the enamel in a tooth with caries in the stain stage.
- Decompensated caries develops quickly and on several teeth at the same time; sometimes from the stain stage to deep caries it can take less than 2-3 months. Numerous foci of carious lesions, increased sensitivity of teeth to irritants, deterioration of the enamel structure are signs of decompensated caries.
Treatment of caries in early childhood
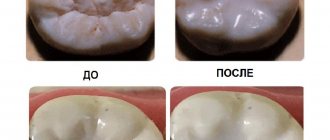
- Fluoridation. The second name of this method is remineralization. This is the saturation of the affected areas of enamel with minerals, its restoration. The tooth surface is treated with a special composition containing calcium, phosphorus, fluorine and other elements. The effect of this treatment lasts for about six months. Fluoridation is indicated for children from 6 years of age.
- Silvering. This method is outdated, but is still sometimes used. The surface of the tooth is coated with a 30% solution of silver nitrate, which destroys bacteria that cause caries. The procedure is absolutely painless. But after it the teeth become black, which can cause complexes in the child.
- Infiltration. A special gel is applied to the affected area of the tooth, which softens the tissue. Afterwards they are washed with an abrasive mixture. The area is then dried and covered with Icon Liquid Filling. The material hardens under a curing lamp.
- Ozone therapy. Ozone under pressure in a gaseous state is applied to the area of the tooth affected by caries. This does not cause any pain. The duration of the procedure is 10-20 seconds. Ozone destroys bacteria that cause tooth decay. After ozone therapy, tooth decay stops.
- Filling. The installation of fillings on baby teeth begins with the removal of dead tissue from the cavity. This is done with hand tools or a drill. The cavity is disinfected with a special composition and hermetically sealed. Upon completion, the surface of the filling is ground.
The filling material should be no harder than enamel. Otherwise, protrusions will form along the edges. Therefore, glass ionomer cements are used for children. They wear evenly and naturally together into enamel.
Some clinics use colored fillings for fillings. They are made from compomer and have no side effects.
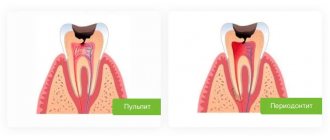
Complications of caries in children: pulpitis and periodontitis
Pulpitis is an inflammation of the neurovascular bundle of a tooth (where its nerve endings and blood vessels are located). Pulpitis can develop from caries very quickly - within 3-4 months. Up to three years of age, pulpitis of primary teeth in children usually develops on the front teeth, after three years - on the chewing teeth. In acute pulpitis, the pain in the tooth is very severe, the temperature may rise, and the child refuses to eat.
Chronic pulpitis in children can occur asymptomatically or be similar in symptoms to deep caries. Such pulpitis develops under fillings or in teeth with advanced caries. If a child of any age develops pulpitis, he must be treated immediately, since pulpitis, in turn, is fraught with serious complications.
Periodontitis is an inflammation of the tissues located near the root of the tooth. Acute periodontitis in children develops quickly and leads to severe pain in the affected area, especially when pressing or touching hot food. The general condition deteriorates sharply, the body temperature can rise to 39 degrees, the child cannot eat. Chronic periodontitis in children can develop slowly and is characterized by mild pain when pressing on the tooth or chewing on the affected side. The mucous membrane next to the tooth swells and becomes bright red.
Complications of childhood caries
It is important to treat baby teeth. After all, deep caries can penetrate the tissue so much that it damages the permanent dentition. In addition, the condition of temporary teeth subsequently affects the child’s bite. Removal leads to abnormal growth of the jaw. As a result, permanent teeth may appear out of place. Because of this, the child will have to wear braces.
Deep caries leads to inflammation of the pulp, periodontitis, and the formation of basal cysts. Treating these problems is very difficult and painful. It requires root canal filling.
If periodontitis starts, it can cause an abscess and even osteomyelitis. This is already dangerous for the child's life.
Treatment of caries of primary teeth in children
Preservation of primary teeth is very important for the growth of the facial skeleton and for the subsequent development and correctness of permanent teeth. If baby teeth have to be removed, chewing food, diction, and the development of the rudiments of permanent teeth suffer. Therefore, treatment of caries in children must begin in a timely manner. Treatment methods for caries in children may vary depending on the stage of the process and the age of the child.
Fluoridation and mineralization
We have already written above that in order to treat caries at the stain stage, it is sometimes sufficient to remove the stain and ensure the restoration of the enamel composition. For this purpose, there are solutions, gels and resins containing calcium and fluorine. Remineralization of enamel is also a good prevention of caries.
Fissure sealing
This procedure is recommended to prevent the development of fissure caries on primary and permanent chewing teeth. The dentist cleans the fissures and seals them with a special liquid sealant that penetrates the enamel fissures and then hardens under the influence of special light. A sealant containing fluoride or calcium fills the recesses of the tooth surface and protects this surface from damage for several years, creating a mechanical obstacle to the penetration of plaque and microorganisms into these physiological recesses of the tooth.
Sealing
The traditional technology for treating medium and deep dental caries in children is filling. Under local anesthesia, the dentist opens the cavity and cleans it. If a child’s caries is not very deep, sometimes you can do without a bur, using only hand tools. The dentist then places a filling.
Meet our tooth fairies and check prices.
Treatment of caries in a child under anesthesia
Sometimes we suggest parents treat their child’s teeth under general anesthesia, in medicated sleep. If the child is small and cannot sit with his mouth open, if several teeth need to be treated at once, if we are talking about a special child, then treatment in medicinal sleep will be the only opportunity to provide him with full dental care.
We also have a video in which we filmed the treatment process in medicated sleep. Look