Predicting and assessing the risk of dental caries in children is a pressing problem in modern pediatric dentistry throughout the world, including in Ukraine. At the same time, preference is given to the most accessible and simple method - assessing the intensity of dental caries using the CPU index. Indices of caries intensity (KP, KPU, KPU+KP) or “carious history” at the time of a child’s dental examination are predictors of the risk of developing dental caries.
According to the literature data [2, 4, 9] and the results of our research [8, 12], many children have fairly high rates of caries intensity, significantly exceeding the average, and are characterized by the third degree of caries activity according to T.F. Vinogradova modified by N.I. Smolyar, N.L. Chukhrai [3, 7]. A detailed analysis of epidemiological indicators indicates that there is often an uneven distribution of dental caries: in some of the examined children the CP index is quite high, in others its minimum value or intact teeth were determined. This difference in the intensity of caries determines a different approach to prevention [13].
Developed in 2000 by Swedish scientists (M. Nishi, D. Bratthall, 2000, 2002), a new index of the highest intensity of caries (NIC) - Significant Index of Caries (SIC) - made it possible to identify among the examined groups of children with the highest values of CSI [1 , 15, 19]. The use of the NIC index solves the problem in the case of uneven distribution of dental caries among those examined.
WHO has officially adopted this technique and implemented it in various centers that collaborate with WHO. Similar studies have been carried out in many countries [6, 10, 14, 16-18, 20]. Unfortunately, this index has not yet become widespread in dental science in Ukraine.
The purpose of the study is to evaluate the NIC index in children of different age groups and compare the NIC indicators with the KPU index.
Stages of caries development
The caries process develops sequentially in several stages:
Initial stage or caries in the white spot stage
Caries of primary teeth often begins with the appearance of white spots on the enamel. Over time, they may increase in size and change color to brown.
Superficial caries
At this stage of dental caries, the damage to the enamel is minor, but the tooth already reacts with aching pain to warm and hot food.
Average caries
A child can feel a carious cavity at the site of enamel destruction with his tongue, and parents and a doctor can see it with the naked eye. Pain when food gets on the tooth, as well as when eating hot and cold foods and drinks, increases.
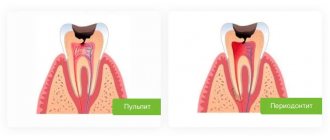
Deep caries
The last stage, when not only the enamel is affected, but also the dental tissue. In the absence of treatment, inflammation of the pulp develops - pulpitis.
What types of caries are there?
fissure
caries - damage to the enamel affects special depressions on the chewing surface of the tooth - fissures.
Cervical
caries occurs in the area between the gum and the neck of the tooth, forming a kind of yellow or brown rim on the enamel.
Tooth root caries in children develops quite quickly in the absence of timely treatment of the initial forms of the disease.
Interdental
caries occurs between the lateral surfaces of adjacent teeth.
WHO (World Health Organization) offers the following classification of caries:
- enamel caries - superficial caries
- Dentin caries - spread of the inflammatory process under the enamel
- cement caries - damage to the root region of the tooth
In children, a separate classification is used - “according to Vinogradova”, on the basis of which the activity of the carious process is determined.
There is another children's classification that determines the activity of dental caries according to T.F. Vinogradova.
Based on an analysis of the number of carious teeth, the degree of their damage and the speed of development of the pathological process, Vinogradova identified three degrees of caries activity.
Compensated
This form of caries occurs in approximately half of children. The pathological process develops slowly; upon examination, isolated lesions of the teeth are detected. The enamel has a healthy shine. It is recommended for such children to visit the dentist once a year.
Subcompensated
The enamel is still shiny, but has some dull areas. As a rule, caries spreads horizontally; deep damage to the teeth is not observed.
The subcompensated form does not cause discomfort or complaints in children, but requires observation by a dentist with examinations at least once every 6 months.
Decompensated
The rarest and most severe form of caries with a high rate of development and serious complications in the form of pulpitis and periodontitis. The enamel is matte and rough, and the fissures are brown. Most often, when opening such a tooth, a carious cavity is discovered.
In case of decompensated form, the child is recommended to undergo preventive examinations at the dentist every 4 months.
Classification according to the location of the outbreak
- Fissure caries
Fissures are called tubercles and depressions on the chewing part of the tooth. They are an ideal place for food debris to stick and bacteria to grow, so cavities are not uncommon there. Fissure caries is always located strictly in the central part of the tooth and never affects its neck and roots. Neglected cavities are usually very deep and painful. If there are no complications, the tooth is filled.
- Contact caries
If the teeth grow crowded, and it is not possible to regularly clean the interdental spaces with floss from stuck pieces of food, then contact caries develops. It got its name due to the fact that the lesion occurs on the proximal part of the tooth. These sides are where the teeth touch each other. The main symptom is the appearance of a dark carious cavity. During treatment, the doctor first restores the side wall and then fills the tooth.
- Cervical caries
The carious process affects the neck of the tooth, it is located near the gingival margin. Here the enamel-dentin layer is very thin, so tartar destroys its integrity in a short time. First, a characteristic white or dark spot appears in the lesion, then the tooth begins to react painfully to sour and sweet foods, as well as changes in temperature. Treatment of cervical caries cannot be delayed, because You can lose a tooth in a short time. Most often, cervical caries affects the front teeth.
- Circular caries
This is a form of cervical caries. They talk about it if the pathological process covers the diseased tooth in a dark ring. Circular caries mainly occurs on baby teeth or is an occupational disease in adults - for example, in musicians who play wind instruments.
Manifestations of caries in children
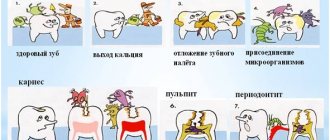
The appearance of light or dark spots on tooth enamel
The first sign of caries in children is white spots on the enamel, resulting from calcium loss. At this stage, treatment may be minimal; often the doctor prefers minimally invasive methods, for example the ICON technique. The dentist applies a special preparation to the affected tooth tissue, thereby blocking the proliferation of bacteria and the development of the infectious process - caries is “preserved.”
If the white areas darken, dentin, the deep tissue of the tooth, is involved in the pathological process.
Cavity formation
In a child, the caries process develops very quickly, and the next stage is the formation of cavities. Most often they are visible upon examination even with the naked eye, and the child complains of pain while eating.
Reaction to food temperature
With the further development of the carious process, the affected tooth begins to react to hot, cold and sweet foods and drinks.
Pain
Pain occurs while eating - when food gets on a carious tooth. If the infectious process has spread to the pulp, the child will complain of pain constantly. Often unpleasant sensations occur during night sleep.
5.Bad breath
Food particles accumulate in carious cavities, bacteria cause rotting, so parents often complain about bad breath.
How is blooming caries treated?
Treatment of decompensated forms of caries can be divided into three stages:
- removal of all tooth tissue affected by caries;
- removal of the nerve (if necessary);
- tooth restoration.
Since blooming caries causes severe pain, all stages of treatment are carried out under local anesthesia or general anesthesia (more often). This means that the procedures are painless for the patient. Modern anesthetics are absolutely safe and hypoallergenic, so this treatment is available even for pregnant women.
Removal of affected tissue is mainly carried out using a drill. But this is not the only possibility. There are also more modern methods: washing out with dental sandblasting, evaporation with a dental laser. Unfortunately, these modern methods do not yet have a good evidence base for their effectiveness for the treatment of serious carious lesions, and are not widely used in our country.
At the next stage of treatment (if necessary), the dental nerve is removed using special equipment. Then the dental canals are cleaned and filled.
Restoration is the last stage of treatment. Using filling materials, the dentist restores the original shape of the tooth.
Treatment of acute caries is a complex and lengthy process. Most often it takes place in two visits. During the first, the affected tissue is removed and medicinal treatment is carried out. During the second visit, the tooth is restored.
Determination of caries activity according to J. Nikiforuk (1986)
The method consists of determining individual caries prevalence by calculating CP and CP. Based on the degree of existing dental caries damage, predisposition to the disease is determined and further development of the carious process is predicted.
Methodology. During a dental examination, the individual intensity of dental caries is determined using the KP or KPU index. Then these individual indicators are compared with the KP or KPU indices from the tables developed by the author. They reflect the distribution of these indices for the population of different age groups consuming non-fluoridated water (Table 6). For example, having determined the average index of KPU = 1 in a 6-year-old child, it is a mistake to think that the intensity of caries in this group is low. It turns out that resistance to caries with such intensity indicators according to the KPU index is defined as average and requires the development of a special caries prevention program for this child.
Distribution of KP and KPU indices for different age groups J. Nikiforuk (1986)
Classification according to the size of the affected area
- Plural form
If acute caries affects more than 5-6 teeth at the same time, then this is called multiple caries. The main causes of such severe pathology are heart disease, kidney disease, respiratory disease and serious infections. In no case should you delay treatment of multiple caries, otherwise you may lose your entire dentition. The disease is equally common in children and adults.
- Single form
In this case, the carious process develops exclusively in one tooth and does not affect its neighbors. The course of the disease is usually very slow and almost imperceptible until it penetrates into the deep layers of dentin.
- Compensated form
This is a chronic caries that develops over years and hardly bothers a person. It causes the formation of many pigmented cavities in dentin.
- Decompensated form
The carious process progresses very quickly; very little time passes from the initial damage to the enamel to pulpitis. It is considered a very complex form of the disease.
Any type of caries, except for extremely advanced cases, is highly treatable. Its essence is to remove corroded tissue, restore the integrity of the walls, disinfect the cavity and fill the tooth. Unfortunately, if pulpitis or periodontitis (complicated caries) has been identified, then removal and further prosthetics may be necessary.
Determination of the caries activity index according to Vinogradova
The activity index is calculated based on indicators such as:
- KP.
- Kp+KPU.
- CPU.
KPU is the sum of teeth affected by caries (C), filled (P) and extracted teeth (U). The Kp index shows the sum of carious (K) and filled (P) teeth.
The use of indices is implemented in practice at different periods of bite formation:
- Temporary - Kp.
- Replaceable - KPU+KP.
- Permanent - KPU.
The index indicator varies depending on the degree of activity :
| First | up to 4 |
| Second | From 4 to 6 |
| Third | over 6 |
Topographic classification
Classification of caries by localization involves:
- Superficial - affects only the enamel, without affecting the dentin.
- Medium – destruction of enamel and dentin.
- Deep – damage to enamel, dentin and cement with involvement of the pulp in the inflammatory process.
These types of caries classification are the main ones, since they form the scheme and features of further treatment.
As for the classification of the stain stage (pronounced demineralization of the enamel), most dentists are inclined to believe that such manifestations are not yet caries, but already a pathology that requires taking appropriate measures. If you notice that any areas of your teeth differ in color from the main shade of the enamel, then you should definitely consult a dentist and rule out the possibility of demineralization. By the way, this process is easy to stop if everything is done on time.
According to WHO ICD 10
The international classification of caries is generally accepted and includes several categories:
- K 02.1 Dentin caries – the hard tissue of the tooth is affected, which precedes its destruction and increases the risk of chipping.
- By 02.0 Enamel caries are dark spots on the surface of the tooth that can be easily treated without serious health consequences.
- K 02.2 Cement caries - a pathological process affects the root of the tooth, which increases the likelihood of the need for its removal.
- By 02.3 Suspended caries - destruction stops on its own, which is influenced by changes in diet, avoidance of sweets and good oral hygiene.
- K 02.4 Odontoclasia (melanodontoclasia, childhood melanodentia) - pathology caused by demineralization and thinning of tooth tissue, which leads to the formation of a carious cavity.
- By 02.8 Other specified caries is a secondary disease that develops on a previously treated, filled and pulpless tooth.
- K 02.9 Unspecified dental caries - destruction of tissue at the junction with the filling or in the gum area.
Classification of carious cavities allows you to determine the desired treatment regimen, as well as formulate proper care for the entire oral cavity. First of all, attention is drawn to the reasons for the formation of a destructive process, without stopping which any treatment of caries will be meaningless.
The advantages and disadvantages of the WHO classification are as follows.
| Advantages | Flaws |
| Exclusion of the stage of a pigmented spot, which, according to its characteristics, is directly dentin caries | There is no clarification of symptoms when caries reoccurs on a previously treated tooth |
| Identification of cement caries, the treatment of which requires compliance with the preparation features | |
| Definition of suspended caries, when the pathological process has slowed down under the influence of various factors |
This classification of caries forms the basis of modern dentistry and is used in Russia, as it is considered to be the most refined and most expanded of all existing ones.