Author: Brodsky Sergey Evgenievich Chief physician of the clinic, candidate of medical sciences in the specialties: dentistry and medical microbiology Pain and pathology in the temporomandibular joint have many clinical manifestations and, accordingly, names (Casten syndrome, myofascial syndrome, arthrosis-arthritis of the jaw joints, chronic subluxation of the lower jaw, dysfunction of the TMJ or temporomandibular joint, etc.). Musculo-articular and pain dysfunction of the TMJ has a code according to ICD-10 and belongs to block K00-K14, subparagraph K07.6. Modern gnathological treatment and clinical protocol of this multifactorial disease may require the involvement of several specialists, gnathologist, osteopath, neurologist, physiotherapist, maxillofacial surgeon, orthodontist, dental orthopedist-prosthetist. Where and how to diagnose and properly treat temporomandibular joint dysfunction (TMJ) in Moscow?
- Causes of TMJ dysfunction
- Symptoms and prevention of TMJ dysfunction
- Treatment of TMJ dysfunction
- Center for the treatment of TMJ dysfunction in Moscow
- Cost of treatment for TMJ dysfunction
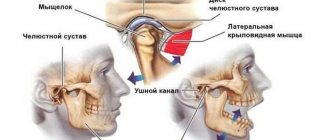
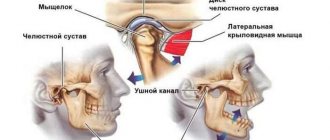
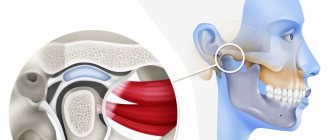
Structure and function of the mandibular joint
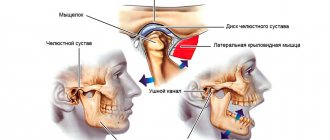
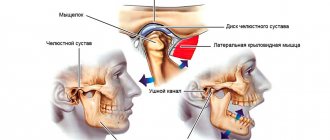
In order to better understand what causes pain and muscle dysfunction of the right and left TMJ joint, it is necessary to understand what it is - the temporomandibular joint, its structure and function.
Mandibular joint (TMJ), photo
In the broadest sense, the structure of the mandibular joint has the following elements and features:
- This is a double, in other words, paired (left and right), combined joint (the only one of its kind in humans).
- The jaw joint belongs to the category of complex joints in the human body, with maximum freedom of movement in different directions. It is divided into two floors (divisions): the upper floor is above the jaw disc, the lower floor is under the disc. The joint is covered by an articular capsule.
- Both joints of the lower jaw normally synchronously reproduce movements in 3 planes:
- horizontal: left - right
- vertical: up-down
- sagittal: back - forward (from back to stomach)
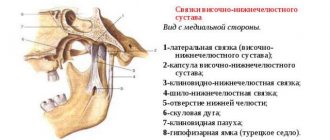
- Between the articular head of the lower jaw and the articular cavity of the skull there is a jaw disc, which covers the middle part of the articular head and serves to soften and absorb pressure in the joint.
- The articular mandibular disc is connected to the internal capsular ligaments, which regulate the movement of the disc forward, backward, left and right. The external ligaments of the joint determine the boundaries of the displacement of the lower jaw, together with the group of masticatory muscles.
- All articular surfaces are covered with cartilage, which secretes synovial fluid to lubricate the jaw joint and improve the sliding of the articular head in the joint.
Development factors
In infectious arthritis, pathogens affect the joint in several ways:
- contact (for otitis, osteomyelitis, furunculosis of the external organs of hearing, etc.);
- direct (infection enters the joint due to puncture of the TMJ, fracture of the movable jaw, injury, etc.);
- hematogenous (for sore throat, tuberculosis, measles, diphtheria and other infectious diseases).
The reactive form of arthritis is observed with chlamydia, rubella, viral hepatitis and other infections. Rheumatoid arthritis can spread to other joints. An acute traumatic form of pathology can develop due to mechanical damage to the joints.
Causes of TMJ dysfunction
Conventionally, we can distinguish 3 main reasons for the development and etiology of the clinic of TMJ jaw joint dysfunction:
- Imbalance and disruption of the nervous coordination of the jaw muscles that raise and lower the lower jaw. Most often, the tone and tension of the muscle fibers in the right and left masticatory muscles are first disturbed, and then their imbalance occurs, irritation of the bilaminar zone and pain when chewing and swallowing.
- Chronic stress, over a long period of time (from a year or more), caused by a disorder of the central nervous system and higher nervous activity.
- Malocclusion and occlusion (closing) of teeth, coupled with non-standard sizes and position of the jaws relative to each other and the base of the skull.
As a rule, all of the above factors, to a greater or lesser extent, occur if a diagnosis of TMJ dysfunction syndrome is made. Reviews from patients and a forum on the Internet confirm this.
A hereditary predisposition to dysfunction of the jaw joints has been proven, with genetic anomalies associated with malocclusion, especially with micrognathia and macrognathia of the lower or upper jaw.
Classification
TMJ arthritis can be:
- Spicy;
- Chronic;
- Bilateral;
- Unilateral;
- Infectious;
- Rheumatoid;
- Purulent;
- Deforming osteoarthritis;
Infection may result from direct spread or hematogenous spread. The area becomes inflamed, movement is limited, and pain appears. Bone destruction may be diagnosed. Acute traumatic arthritis can sometimes be associated with severe removal of the masticatory organ. Creaking and stiffness can occur in old age when bones rub against each other. Common manifestations of rheumatism are pain, swelling, and limited movement. Secondary degenerative pathology most often develops after injury. The patient has difficulty opening his mouth, and the pain is usually one-sided. The disease code according to ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases) is K07.6.
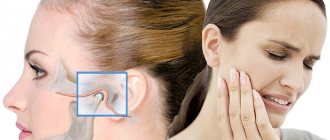
Symptoms and prevention of TMJ dysfunction
At the PartnerMed dental clinic, diagnosis of TMJ dysfunction is carried out by a gnathologist. He also draws up a treatment plan. When making a diagnosis, the following symptoms are taken into account:
- Pain in the jaw joints
- As a rule, with TMJ dysfunction, chronic pain occurs in the temporal, trapezius, chewing and a number of other muscles. Dull or aching dental, eye, headache and facial pain appears, and trigeminal neuralgia syndrome may develop, which forces differential diagnosis with arthritis and osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, as well as otitis media.
- Difficulty opening the mouth
- There is a kind of blocking of movements or jamming in the TMJ. In order to open your mouth, you must first move your jaw slightly to the left, right, forward or backward.
- Clicking in the jaw
- At the moment of opening the mouth, chewing and yawning, clicks and crunching occur in the TMJ joint. Other noises are also possible in the form of grinding, popping, sometimes loud enough to be heard by strangers.
In addition, depending on the dominance of various causes during the development of the disease, there may be difficulties in swallowing food, pain in the tongue, ringing and noise in the ears, dry mouth, changes in the sensitivity of the lips, palate and other pathological manifestations.
In order to make a complete and final diagnosis of TMJ dysfunction, the following clinical examinations are carried out as prescribed by a gnathologist:
- CT and MRI of joints (it is most advisable to do a dynamic MRI of the TMJ)
- Blood tests, including rheumatoid factor, allergy status, extended immunogram
- Consultation with a gnathologist and an osteopathic dentist (or an osteopath working together with a dentist)
- Functional diagnostics of dentition (taking into account lateral and frontal separation of teeth)
- Diagnostics of tooth models in an articulator
- MPI analysis (finding the correct position of the lower jaw)
- Electromyography
- Electronic axiography and condylography
Request a call back or dial our number!
+7
This phone call does not obligate you to anything. Just give us a chance and we will help you!
Proper prevention of TMJ jaw joint dysfunction requires timely getting rid of bad habits, chewing gum, and frequent consumption of very hard foods, such as chewing dried squid and fish with beer. When engaging in professional sports such as boxing, wrestling, and mixfight, be sure to use protective equipment, helmets, and protective mouthguards. It is necessary to regularly consult a gnathologist for the treatment of bruxism, jaw clicking and other gnathological diseases.
TMJ dysfunction, photo
Treatment of TMJ dysfunction
Effective and modern methods of treating TMJ dysfunction involve an interdisciplinary approach. This means that medications, speech limitation, physiotherapy, osteopathy, exercise therapy, myogymnastics, splints and distraction mouthguards for the lower jaw, orthopedic and orthodontic structures are selected by a single team consisting of doctors of different specialties, gnathologists, osteopaths, neurologists, psychologists, orthodontists and others specialists. Methods and methods for treating TMJ dysfunction in Moscow, St. Petersburg and other large Russian cities are not fundamentally different from each other and have a common algorithm.
Depending on the predominance of one or another etiological factor, emphasis may be placed to a greater or lesser extent on different methods of treating jaw joint dysfunction. However, the same algorithm and clinical protocols exist for the treatment of chronic TMJ dysfunction.
Standard treatment regimen for TMJ
- Relief of pain in the TMJ using a distraction cap and analgesics;
- Carrying out physiotherapy and drug complex therapy to relieve intra-articular inflammation;
- Normalization of masticatory muscle tone using splint therapy (and possibly Botox);
- Determination of the correct constructive occlusion of the oral cavity;
- Temporary prosthetics of the oral cavity using a silicone key for constructive occlusion;
- Final prosthetics with fixed dentures.
Treatment of TMJ, photo.
Center for the treatment of TMJ dysfunction in Moscow
Today, clinics and treatment centers for TMJ dysfunction in Moscow, various forums and patient reviews make it possible to determine the gold standard of effective treatment methods and related equipment that most effectively treats this disease.
The list of necessary diagnostic and treatment equipment used by leading specialized institutions, including the Partner Med clinic, includes:
- Articulators and facebows "Girbach"
- Axiograph "Gamma"
- "Mist Tens" device
- Computer electromyograph "Synapsis"
- Fox osteopathic apparatus
- Computer occlusion analyzers “T-scan”
and some other devices.
The course for the treatment of TMJ dysfunction at the Partner Med dental clinic lasts from 3 to 12 months, depending on the complexity and number of necessary diagnostic and treatment procedures in each specific clinical case.
Prevention
To minimize the risk of developing a pathological process, it is recommended to follow the following rules:
- promptly treat diseases in which the formation of purulent foci occurs;
- protect yourself from traumatic factors;
- avoid hypothermia;
- promptly treat nasopharyngeal pathologies;
- treat acute infectious processes;
- eliminate dental problems.
To prevent the pathological process from worsening, it is important to seek help from a medical facility as quickly as possible.
Advantages of the TMJ Treatment Center Partner-Med
Experience at least 5 years
Only doctors with 8-30 years of experience practice at the Partner-Med clinic
15 year labor guarantee
Only a qualified dentist gives an extended guarantee of up to 15 years on his work.
Study abroad
Our doctors annually improve their qualifications in specialized clinics in Europe.
Chief Physician, Dmitry Nikolaevich Salatsky
Sign up for a gnathological consultation
+7
Cost of treatment for TMJ dysfunction
Answering questions frequently asked by patients: “How much does treatment for TMJ dysfunction cost, with a discount, at a promotion? Where and how much cheaper are the prices for such turnkey treatment, in Moscow, St. Petersburg or other cities of Russia?”, it should be noted that the price of treatment for pathology and dysfunction of the TMJ jaw joints and the cost of its individual stages depends on the following points:
The cost of diagnosing TMJ dysfunction starts from 10,000 rubles and can reach 80,000 rubles or more. The price of treatment starts from 15,000 rubles and can reach 300,000 rubles or more.
- From the complexity of diagnosis and the number of medical procedures
- From the qualifications of gnathologists, orthodontists and other specialists
- From the pricing policy of each specific dental center
Just pick up the phone and call us!
8
We will definitely make you an offer that you cannot refuse!
Clinical picture
The development of osteoarthritis of the TMJ begins in patients with degeneration of intra-articular cartilage tissue. As the pathology becomes more complex, it spreads to bone tissue. Dystrophy leads to severe thinning of cartilage tissue and a decrease in its performance.
After complete destruction of cartilage, the disease spreads to hard tissues, which is due to their constant friction. As a rule, the destruction of soft and hard tissues is chronic. Pathological changes lead to increased mobility of the TMJ, and osteoarthritis becomes more pronounced.
General symptoms:
- uncharacteristic noises and crunching sounds;
- aching or dull pain, aggravated by jaw movements;
- decreased joint mobility;
- spread of pain to the peritemporal tissues;
- difficulty eating due to deformities of the affected joint;
- facial asymmetry associated with swelling and inflammation (observed in advanced cases).
Patients often do not realize the seriousness of the consequences, feeling minor discomfort in the TMJ area and consult a doctor with complaints of stiffness and severe pain. It is the lack of timely treatment that leads to the destruction of cartilage tissue.