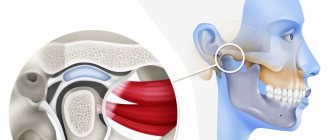
Causes
Clicking in the ears, not associated with swallowing, occurs when the muscles of the hearing aid contract. This occurs with muscle spasm, as well as due to swelling of the auditory tube. Swelling accompanies infectious diseases of the ENT organs (otitis of a bacterial or fungal nature, sinusitis, pharyngitis), Meniere's disease (fluid accumulation in the inner ear), habitual dislocation of the jaw. With arthritis and arthrosis of the jaw joints, patients are bothered by crunching and clicking noises due to damage to the cartilage tissue. Ear plugs lead to pronounced clicking sounds when swallowing, as the patency of the auditory tube is impaired.
Monotonous tinnitus occurs with high blood pressure. The cause may be not only chronic hypertension, but also stress, heat stroke and intoxication. Complex noises that are auditory hallucinations are often a sign of mental illness. In any case, no matter what reason the patient suspects, self-medication is not worth it. A timely visit to an otolaryngologist for diagnosis and treatment is the best solution if noise or clicking occurs.
Why does it crunch?
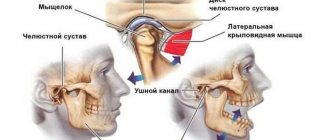
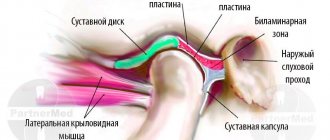
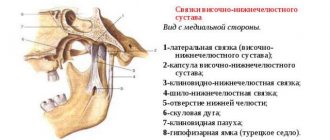
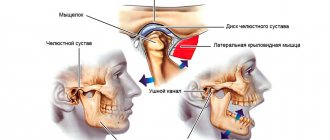
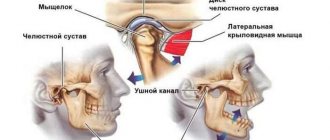
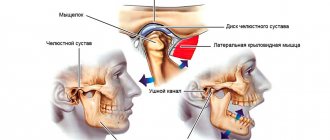
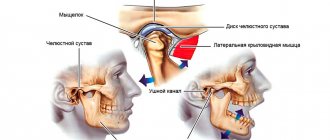
To begin with, it should be said that it is not the jaw itself that crunches, as many believe, but the temporomandibular joint (TMJ).
Here are the reasons that can lead to this problem:
- Neurosis that causes night grinding of teeth;
- Joint injury, for example, dislocation when biting off a large piece;
- Lack of teeth (the tooth was removed, but prosthetics are being delayed);
- A filling that was incorrectly polished by the dentist;
- Malocclusion since childhood
- This is a natural disorder - the ligaments stretch very easily, which can lead to crunching.
Symptoms
If clicks in the ears are associated with swelling of the inner ear, then the ENT doctor will be able to objectively record them during the initial examination. Patients with inflammatory diseases of the ENT organs are also concerned about fever, congestion and pain in the ears (usually “shooting”), and possible ear discharge. With lesions of the jaw joints, patients complain of pain when chewing and a feeling of dislocation, often accompanied by an increase in temperature.
With tinnitus, against the background of high blood pressure, patients complain of weakness, headache, nausea, spots before the eyes. The skin of these patients is hyperemic, and convulsions may occur. With heatstroke, your body temperature rises, your pulse becomes rapid and weak, and your breathing becomes faster. These conditions require emergency medical attention.
Common causes of clicking in the ear
If we consider possible pathologies, then first of all you should pay attention to the condition of the cervical spine. If you lead a sedentary lifestyle and engage in sedentary work, then there are likely structural changes that prevent normal head movements in full amplitude. The sound source may be located in the cervical spine, and to the ear it is perceived as if it is located inside the auricle. Such a symptom may indicate the presence of spondylosis, vertebral instability, spondyloarthrosis, or deformation of the ligamentous apparatus.
Common causes of a clicking ear also include the following:
- violation of physiological posture in the thoracic and cervical spine;
- vertebral displacement;
- disruption of the conductivity of the vascular bed in the cerebral vessels;
- arthrosis of the mandibular joint;
- change in bite;
- pathologies of the vertebrobasilar apparatus;
- damage to the eardrum and much more.
Associated symptoms will help determine the suspected cause. In particular, if there is pain in the corners of the jaw, convulsions of the facial muscles appear, then trigeminal neuritis is possible - a very difficult disease to treat. Dizziness, headaches, general weakness and constant fatigue can be a consequence of cervical osteochondrosis or vertebral artery syndrome. With a curvature of the spine, you may feel excessive tension in the muscles of the back and neck on one side.
You can find out the exact reason for the clicking in your ear when you visit a specialist at our clinic. If necessary, additional diagnostic examinations will be carried out. After an accurate diagnosis has been established, effective treatment using manual therapy methods will be offered.
Diagnostics
It is necessary to conduct a general and biochemical blood test to determine the presence of infection, a microbiological analysis of a smear from the ear and nasopharynx. An ENT doctor examines the level of hearing and the patency of the auditory tube. X-rays and MRIs can determine the presence of inflammatory diseases, lesions of joint tissue or neoplasms; An ultrasound is performed to determine the condition of the hearing organs. In case of hypertension, blood pressure and ECG measurements are required. In the absence of physiological changes leading to tinnitus, consultation with a psychotherapist is necessary.
How will we treat?
If suddenly the pain is very severe, you need to resort to first aid:
- apply hot and moist heat to the sore area, for example, a heating pad wrapped in a damp towel;
- cold - ice, also wrapped in a towel;
- take analgesics - spazmolgon, analgin, baralgin.
Anti-inflammatory drugs should not be taken, they can do a disservice - they will relieve pain, but will not help in treatment, in addition, they will also cause noise in the ear.
If the crunch in the jaw has been around for a long time and has already begun to irritate you, then first of all, you need to eliminate its cause. As a rule, in this case the prognosis is very favorable and the crunch is eliminated without problems in 90% of cases.
As for the remaining 10%, here the situation is more serious:
- irreversible change in the joint due to injury (blow to the jaw);
- rheumatism (sometimes leading to destruction of the TMJ).
If you have a broken bite, an incorrectly installed prosthesis or filling, contact your dentist or orthodontist. Sometimes it is necessary to take an x-ray of the diseased joint to exclude possible displacement of the articular head.
The main thing is that you should not prescribe treatment yourself, regardless of what caused the crunch. You will definitely need to do a general blood test to identify or rule out inflammation in the body.
If there are disturbances in the structure of the TMJ, you may have to undergo surgery to eliminate them. In particular, if the problem is an old injury. There are not as many specialists in carrying out such complex surgical interventions as we would like, but only they will help solve the problem once and for all. If the cause of the crunch is a dislocation or subluxation, then the joint can be realigned in an outpatient clinic.
In addition to the listed measures, other treatments are prescribed for jaw crunching:
- physiotherapy;
- acupuncture;
- installing a splint that will limit movement and relieve pain for a while.
Treatment
It is clear that due to various reasons for the appearance of noise, treatment methods can vary significantly in each case. If the clicking in the ears is caused by the presence of wax plug, it is removed in a hospital setting. In the presence of infection, complex antimicrobial therapy is carried out - antibacterial or antifungal drugs, antihistamines (Diazolin, Suprastin, Loratadine) and vasoconstrictors (Otrivin, Naphthyzin, Polydexa), non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Nurofen, Ibuprofen). In case of severe muscle spasm, muscle relaxants (Drotaverine, No-Shpa) are prescribed. For lesions of the jaw joints, it is recommended to take chondroprotectors (Glucosamine, Chondroitin).
The accumulation of fluid in the inner ear requires the prescription of antipsychotics (Aminazin, Triftazin) to normalize the functioning of the vestibular apparatus and diuretics (Diacarb, Veroshpiron) to reduce the level of edema. Pneumomassage of the eardrum, performed by an otolaryngologist, is also indicated. Tinnitus with hypertension requires treatment of the underlying disease. To normalize blood pressure, beta-blockers (Anaprilin, Metoprolol), sedatives (Persen, Novo-Passit), ACE inhibitors (Captopril, Lisinopril, Ceronapril), calcium blockers (Nifedipine, Manidipine), diuretics are prescribed.
If tinnitus reduces the patient’s quality of life, along with drug therapy, the use of psychological techniques may be recommended to reduce the severity of subjective perception of noise.
The reception is conducted by specialists
Kirillov Evgeniy Sergeevich
Audiologist, otoneurologist
Cost of services
Initial consultation with an audiologist
1200₽
Repeated consultation with an audiologist
1000₽
Treatment methods at home
We are categorically against self-medication, but there are situations when the pain takes you by surprise and going to the dentist in the next 24 hours is not possible, then several procedures will help relieve your condition for a short time:
— Apply a moistened cool towel to the joint for 10-15 minutes, such a compress will help if there is inflammation in the joint
— A hot compress will help with arthrosis
— Rinsing with a decoction of sage or calendula to relieve inflammation and pain
What pathologies can we talk about?
From the list of diseases that can provoke the manifestation of constant creaking in the ear, we can highlight:
- inflammation of the maxillary and paranasal sinuses;
- nasopharyngitis;
- adenoiditis;
- violations of the anatomical integrity and deformation of the nasal septum;
- chronic and allergic rhinitis;
- polyps in the nasal cavity;
- tumors and cysts localized in the nasopharynx.
Creaking in the ear often occurs in patients experiencing nasal congestion. Often the symptom appears with a common cold. In this case, patients note a sharp disappearance of the crackling sound after the congestion is eliminated.
Attention! The problem of creaking in the ears may persist for several weeks after the doctor determines the fact of clinical recovery. In this case, the change is a residual phenomenon.
The main cause of creaking in the ear is associated with dysfunction of the auditory tube. A common cause of dysfunction of the auditory tube is often the patient's tendency to rhinitis of an allergic, bacterial or viral nature. In this case, the body loses the ability to naturally drain the auditory tube. The process often becomes chronic.
Our doctors
Gogolev Vasily Gennadievich
Doctor - otorhinolaryngologist
20 years of experience
Make an appointment
Zharova Galina Gennadievna
Doctor - otorhinolaryngologist, member of the European Society of Rhinologists, doctor of the highest category
40 years of experience
Make an appointment
Debryansky Vladimir Alekseevich
Doctor - otorhinolaryngologist, doctor of the highest category
34 years of experience
Make an appointment
Inflammation of the inner ear (labyrinthitis)
The labyrinth is an organ of hearing and balance, is richly innervated and includes auditory and kinetic receptors, so its inflammation causes:
- severe ear pain and headaches;
- a sharp decrease in hearing, the appearance of noise, crackling, squeaking in the ear;
- dizziness, nausea, loss of orientation in space, horizontal nystagmus.
Labyrinthitis occurs as a result of the penetration of infection in various ways from different parts and cavities of the body:
- from the middle ear with untreated or advanced otitis media;
- with infected meninges during meningitis;
- with blood for diseases such as syphilis, tuberculosis, herpes;
- damage to the temporal region, the organ of hearing with disruption of the integrity of cells and blood vessels.
The disease requires immediate medical attention.
Eustachite
Eustachitis is an inflammation of the canal connecting the middle ear to the nasopharynx. The degree of pain varies. Characteristic features are:
- feeling of stuffiness in the ear;
- noise and crackling in the ear, the patient hears his voice as too loud with a weakened perception of extraneous sounds;
- sensation of water pouring into the ear.
In the absence of timely treatment, eustachitis becomes chronic, causing chronic exudative otitis media.
Otitis externa
Most often, inflammation of the outer ear is bacterial in nature.
The causes of infection may be:
- trauma to the external auditory canal, for example, from a sharp or blunt object, or from a hearing aid;
- skin defects due to eczema, psoriasis, diabetes and other diseases;
- too thorough removal of earwax, which creates an acidic environment that prevents the growth of microbes;
- frequent entry of water into the outer ear (“swimmer’s disease”).
Symptoms of external otitis:
- acute ear pain, aggravated by pressing on the tragus or pulling the earlobe;
- possible itching and a feeling of “stuffiness” in the ear;
- discharge of a purulent or bloody nature, sometimes having an unpleasant odor;
- examination reveals swelling and hyperemia of the external auditory canal;
- possible hearing loss;
- enlargement and tenderness of the lymph nodes in the neck and behind the ear on the affected side.
The course of the disease may be complicated by a perforation of the eardrum, which cannot be determined without a visit to an ENT specialist.
External otitis of fungal origin is a common phenomenon, usually occurring in patients with low immune status or due to long-term use of antibacterial drops. It is characterized by severe itching, the formation of crusts, profuse thick discharge and the absence of a therapeutic effect from the use of antibiotics.
Separately, it is worth noting the localization of a boil on the skin of the external auditory canal or inflammation of the atheroma. The clinical picture is similar to otitis externa, but upon examination there is a more localized focus of inflammation with an opening from which pus and blood can be discharged.