Necrotizing ulcerative stomatitis is a dental disease in which the oral mucosa becomes inflamed. This problem can be called differently, for example, ulcerative gingivitis, ulcerative stomatitis, ulcerative-necrotic stomatitis of Venson (Vincent), etc. The disease, as a rule, develops dynamically in children under 3 years of age, but is often diagnosed in adults. The disease is not a death sentence; with proper and comprehensive treatment, it is possible to relieve acute symptoms and consolidate the results, excluding relapses.
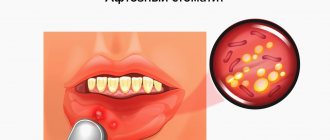
What does aphthous stomatitis look like?
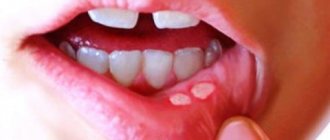
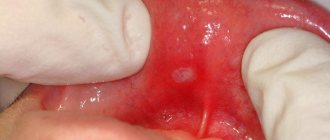
Aphthae occur on the inside of the cheeks or lips, under the tongue, at the base of the gums, or on the soft palate.
https://img.medscapestatic.com/pi/meds/ckb/75/43075.jpg
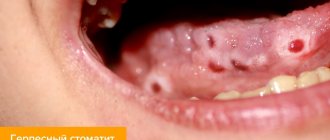
They can be confused with manifestations of herpetic infection , but the latter usually appears at the red border of the lips, rarely in the oral cavity - usually on the gums or hard palate.
Aphthae first look like red bumps (papules), which then quickly turn into ulcers, surrounded by a red rim and covered with a gray-yellow coating (exudate). 1-2 days before the appearance of aphtha, there may be a local burning sensation of the mucous membrane.
Sometimes the child or family members notice what often triggers the appearance of aphthae. Journaling can help with this.
According to American data, about 20% of the population suffered from recurrent aphthous stomatitis at one time or another in their lives.
Most often children suffer and usually these are minor canker sores.
The peak incidence of aphthae is 1-19 years.
Main symptoms of stomatitis
Stomatitis often appears in young children; more serious forms of the disease can occur in adulthood. There can be many causes of stomatitis. This includes poor nutrition, a complication from other diseases, metabolic disorders, and it can also be infectious. It often occurs against a background of reduced immunity.
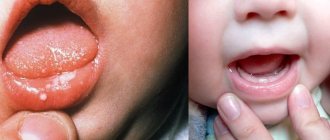
Stomatitis can manifest itself in different ways. For example, a child changes his behavior. Irritated and capricious, seemingly for no reason. Parents need to be attentive to their child’s complaints. As a rule, with stomatitis, it is painful for children to eat, and sleep is often disturbed. Body temperature rises. Photos of the external manifestations of stomatitis can be viewed in this article.
Stomach upsets, such as bloating and diarrhea, also occur. This is a clear sign that you need to pay attention to the child's health. If stomatitis occurs not for the first time, then parents should be wary.
Typically, this occurs due to the child's weak immune system. Vitamin deficiency also affects the recurrence of the disease. In this case, you need to carefully monitor your diet and take appropriate measures for treatment.
Types of aft.
Small aphthae is the most common type of aphthae (80-85%). Their size ranges from 1 to 10 mm. Ulcers can appear singly or several at a time (up to five).
Usually heal in 7-10 days.
Large aphthae (10-15%) - more than 10 mm in diameter, can even be up to 3 cm, deeper, take longer to heal (10-30 days).
They may leave scars behind. Very rare in children.
Herpetiform aphthae (5-10%) are small, from 1 to 3 mm, located in groups like herpetic vesicles. They heal quickly, within 10 days. They are not typical for children; they usually occur in the elderly.
The rest of the oral cavity looks normal - there is no inflammation of the gums, redness of the tonsils and pharynx, enlarged and painful cervical lymph nodes.
There is no fever or other general manifestations.
Aphthae in children is manifested primarily by refusal to eat and drink due to pain in the mouth.
The reasons for the recurrence of aphthae are not completely clear; the most popular theory is related to errors in the immune system.
Doctors most often do not find a specific cause of the failure; most likely it is a combination of several factors.
But doctors still have assumptions about some factors.
Types of inflammatory processes
Gingivitis
Inflammation of the gums at the initial stage, that is, not yet spreading to the bone tissue, is called gingivitis.
Treatment of gingivitis in children follows the same principle as in adults, with the only difference being that children are prescribed more gentle medications. When starting the procedure, the hygienist performs professional cleaning, removing plaque and stone, after which he teaches the little patient proper hygiene techniques. Helps you navigate the selection of toothpaste and brush.
Periodontitis
Inflammation of the gums and periodontal tissues - periodontitis - is an advanced stage of gum disease. If left untreated, its progression may result in one or more teeth having to be removed.
Treatment includes occupational hygiene and physical therapy. If the process is advanced, surgical intervention may be required.
Periodontal disease in children
The defeat of all periodontal tissues, in this case, is called childhood periodontal disease. This degree is quite rare. Progression can be triggered by weakened immunity and vitamin deficiency.
An effective option in this case is surgical intervention, as well as strengthening the general condition of the body.
Stomatitis in children
Infectious inflammation of the mucous membrane of the gums, or stomatitis, is characterized by increased sensitivity and discomfort while eating. Therefore, you should show it to a dentist as soon as possible. A dental clinic specialist will examine the baby and prescribe appropriate procedures.
What predisposes to recurrent oral aphthae?
Perhaps the microflora of the oral cavity, herpes group viruses, and maybe Helicobacter pylori, a microorganism that causes stomach and duodenal ulcers, play some role.
Also influence:
- injuries to the oral mucosa
- stress
- deficiency of vitamins B12, B1
- vitamin D deficiency
- zinc deficiency
- poor oral hygiene
- nitrates in drinking water
- Sodium lauryl sulfate is a very popular surfactant in the industry, which is often added to toothpastes for better cleaning and foaming effect.
- food allergies (eg, cow's milk protein) or food hypersensitivity (cinnamon, coffee, chocolate, cheese, figs, pineapple, citrus fruits, some spices)
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
It is very important to understand: recurrent aphthae is an independent disease (most often this happens) or a manifestation of some systemic disease.
The latter option is rare, but the doctor should always keep in mind the possibility of this situation.
Diagnosis of gum disease in children
A routine oral examination should be performed by a pediatric dentist every six months. And as necessary, if a small patient exhibits any deviations in the development of teeth or symptoms of disease of the oral mucosa. Since it is advisable to diagnose the inflammatory process at the earliest stage.
If redness, swelling and bleeding are detected, the cause of which is an excessive amount of soft plaque or food debris on the teeth, the dentist will make a diagnosis and prescribe procedures.
If a bacterial infection is suspected, a clinic specialist can take biomaterial from the inflamed areas of the gums for clinical tests. Based on the results of the analysis, the specialist prescribes a treatment plan and the date of the next appointment to ensure the final recovery of the little patient.
What systemic diseases can manifest as aphthae?
- Reiter's syndrome
- Behçet's disease
- AIDS
- cyclic neutropenia
- PFAPA syndrome
The gastroenterologist is especially interested in the connection between recurrent ulcers and specialized systemic diseases.
Celiac disease is found in 5% , and for a long time canker sores may be the only manifestation of a reaction to gluten.
Let me remind you that the estimated prevalence of celiac disease in the general population is about 1%.
Enamel defects and aphthous stomatitis in celiac and healthy subjects: Systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled studies
Other important conditions that manifest as canker sores are inflammatory bowel diseases: Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.
Extraintestinal Manifestations of Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Prevalence, Presentation, and Anti-TNF Treatment
Diagnosis of stomatitis
An experienced specialist can determine this pathology visually. This can be done due to the manifestation of symptoms of the disease such as redness of the mouth, inflammation and swelling.
And, of course, it’s hard not to notice the white ulcers with a red border. Their size and quantity are different.
As for special, narrowly targeted tests for diagnosing stomatitis, they do not exist in modern medicine.
However, before prescribing a medicine to a person with such a clinical picture, it is necessary to determine the type of bacteria/fungus that provoked it.
This is possible by taking a swab from the patient's mouth. The smear is sent to a laboratory where specialists study it.
Only after this the doctor determines the treatment strategy.
Which doctor should I go to?
If signs of the disease are detected, you should visit a dentist who will conduct the necessary examination. If symptoms of related diseases are identified, you may need to consult a dermatologist, venereologist, therapist, immunologist or pediatrician.
What can help in finding the cause of aphthae?
A conversation sometimes helps to find out whether relatives have important diseases with a family predisposition - celiac disease, Crohn's disease, lupus erythematosus.
During the examination, the doctor can evaluate the general manifestations of the disease (not typical with ordinary recurrent aphthous stomatitis) and check for the presence of ulcers outside the oral cavity.
The simplest laboratory examination is carried out - this is most often enough.
A general blood test may show anemia due to deficiency of iron, folic acid, and vitamin B12.
The level of neutrophils is also assessed - their decrease may be a sign of the rare systemic disease cyclic neutropenia
A high ESR may be a sign of Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.
Serum iron levels may be reduced in up to 20% of recurrent canker sores.
Causes of gum inflammation in children
- Skipping or poor quality teeth brushing;
- Sucking dirty objects;
- Errors when installing seals;
- Pathologies of the dentition;
- Carious cavities with sharp edges;
- Bite correction;
- Breathing through the mouth;
- Abnormal structure of the oral cavity organs (attachment of the frenulum of the tongue and lips);
- Problems with the functioning of the cardiovascular system;
- Disruption of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Infectious diseases (ARVI, influenza);
- Hormonal abnormalities;
- Hereditary anomalies.
Treatment of aphthous stomatitis.
There is no radical and quick treatment.
The main task of the doctor is to fight the pain caused by aphthae. This is especially important for young children, who may refuse to eat or drink due to pain and become easily dehydrated.
For this purpose, local painkillers and drugs are used that form protective films on the aphthae.
The second goal is to speed up healing.
The most popular drugs for healing are anti-inflammatory corticosteroids for aphthae, in rare, especially severe situations - even orally for a short course (prednisolone tablets).
The third task is to avoid or at least reduce the frequency of recurrent aphthae.
For some people, regular intake of vitamins (especially B12), zinc, and iron helps.
Avoiding oral hygiene products containing lauryl sulfate may be helpful.
Together with your dental hygienist, you can consider ways to improve your oral hygiene.
A gluten-free diet will help with celiac disease.
How to treat ulcerative stomatitis?
Effective treatment of Vincent's ulcerative stomatitis should be comprehensive:
- Anesthesia – performed to relieve acute pain. Experts recommend applying compresses with pain-relieving solutions.
- Removing rashes. This should only be done by a doctor. First, compresses with a softening composition are applied to the ulcers, after which the crusts are gradually cleared from the surface of the mucosa, treating with hydrogen peroxide, potassium permanganate, chlorhexidine, etc.
- General treatment. It involves taking antihistamines that relieve general tissue irritation and the inflammatory process. For severe manifestations and complex symptoms, antibiotic therapy is prescribed. It is also recommended to take a course of vitamin therapy.
- Sanitation of the oral cavity. Effective treatment of caries, removal of pathological teeth. For wound healing, treatment with keratoplasty preparations, gels and ointments is recommended.
It is important! The disease cannot be treated at home! The maximum you can do on your own is to rinse your mouth with a decoction of chamomile or calendula, but strictly after professional dental care.
Conclusions:
Aphthae in the mouth recur at some point in life in almost 20% of all people, most often in the second decade of life.
It is difficult to establish a clear and unambiguous reason.
If recurrent aphthae occurs, the pediatrician, physician, or dentist should consider the possibility that rare aphthae are a manifestation of a serious systemic disease.
In such situations, the gastroenterologist must exclude celiac disease, Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.
5, total, today
Bleeding stomatitis: how to treat?
Is it possible to cure bleeding gums and stomatitis at the same time? Because the methods of treating stomatitis and gingivitis are identical, they can be combined. As soon as the doctor establishes the causes of stomatitis on the gums, the form, then gingivitis should be treated in parallel.
The following methods are excellent for treating stomatitis:
- Rinse with antiseptic, effective anti-inflammatory drugs
- It is imperative to perform antifungal and antibacterial treatment of the mouth
- The use of hemostatic drugs, astringents
- You can get rid of unpleasant odors using special products using lemon balm, mint and lime.
- It is imperative to get rid of plaque, dangerous tartar, which only aggravates the course of the disease.
- Elimination of traumatic factors
- Relief from pain using lidocaine
Drugs that relieve stomatitis and associated bleeding
You can choose an effective remedy for a disease, but it is important to know what properties it has. So, to get rid of bleeding, you should choose drugs that solve a complex of problems at once, and not just one. Thus, the remedy must have a complex effect to treat related problems.
Recent innovative advances have shown that the best remedy for bleeding is phytotherapeutic agents designed for a long service life. And it is important that addiction is not provoked.
Experts noted that the best remedy for the disease is the rinse drug Stomatofit , its analogue Stomatofit A. The drugs were created using the latest innovative achievements with the participation of Polish pharmacists. The product is created from 7 healing and miraculous plants.
It is adjusted in accordance with the nature and level of gum damage. Bleeding is treated with antiseptics and herbal decoctions, which help reduce inflammation and heal the mucous membrane faster. To get test results, the doctor needs to prescribe symptomatic therapy.
If it is not possible to eat as before, then you need to start using local anesthetics. Such drugs are used immediately before eating. The best, proven drugs include:
- Benzocaine - anesthetic effect
- Chlorhexidine – gives an antiseptic effect
- Lidochlor, lidocaine
If we talk about products of natural origin, then you need to opt for chamomile, sage, and calendula.
Make it a habit to rinse your mouth with these herbs every 2 hours. If possible, then in the first days, preferably more often. If we talk about children, then they should take a soda solution.
Ointments and gels
Dental ointments and gels are used after preliminary rinsing 2-4 times a day, depending on the severity of the lesion.
Products with anti-inflammatory and restorative effects are used:
- Metrogil Denta;
- Solcoseryl;
- Dental;
- Holisal;
- Asepta;
- Gengigel;
- Actovegin.
Compresses
One of the treatment methods that destroy bacteria at the cellular level is the use of immunomodulatory drugs. The most effective means are Viferon, Interferon, Lafarobin.
Iodinol, or “blue iodine,” works well for treating the oral cavity with stomatitis on the gums.
Some experts advise using brilliant green. This is a rather painful method, but it will get rid of rashes in 1-2 applications.
To treat rashes in a child, brilliant green should be mixed with honey in a 1:1 ratio, then moisten a cotton swab and apply it to the ulcer. If there are a lot of rashes, you can lubricate the surface completely.
Rinse
Rinsing with antiseptic solutions is carried out 3-4 times a day after meals until the signs of the disease completely disappear.
The use of drugs with antiseptic properties is recommended:
- Chlorhexidine;
- Miramistin;
- Furacilin;
- Chlorophyllipt;
- Hydrogen peroxide;
- soda solution;
- potassium permanganate solution.
Nutrition and other factors
Child nutrition becomes a big problem. This process is accompanied by unpleasant and painful sensations. These can be reduced by using painkillers prescribed by your doctor.
As for the food itself, you can give your child dairy products. They should be low-fat. This is due to the fact that fat may not be absorbed and cause digestive problems. You can give your child soft-boiled eggs, omelettes, and liquid porridge. Decoctions of vegetables and fruits are also good.
It will be useful to include various soups and purees in your diet. If fish and meat are present in the diet, they should be well boiled and ground.
What should be excluded?
It is also important not to give your child very cold or hot food. It should be warm to reduce discomfort. It is imperative to remove salty and sour foods. Spicy foods are also excluded.
You also need to reduce the amount of sweets. This will speed up the healing process and help the medications work properly. You should not feed your baby more than four times a day. Eating in between is excluded.
This is interesting: What to do if a child has herpes in his mouth
The general recommendation would be to structure the diet in such a way as to reduce the impact on the oral mucosa and not injure it further. Honey is also excluded.
Doctors say that it can provoke the appearance of a fungus, which leads to the onset of the disease. It’s also a good idea to give your child juices and rosehip infusion.
It is important to note that citrus juices can negatively affect the healing process. Therefore, the best solution would be carrot juice. Decoctions of sage, chamomile, oak bark, calendula and eucalyptus will be useful. It is also important to drink plenty of water. It should be warm. Rinsing your mouth also helps.
How else can you speed up the healing process?
To prevent the disease from progressing, the child must remain at home. Therefore, parents need to make sure that he does not go to school or kindergarten.
You need to provide him with a separate towel and dishes. The room in which the child is located must be frequently ventilated and wet cleaned.
If a child has stomatitis on the gum, then the teeth should be brushed with a synthetic brush. This will reduce the traumatic effect on the gums and oral cavity in general. Under no circumstances should this be done with someone else’s brush, because the likelihood of spreading the disease is high.
Folk remedies
To get rid of the disease at home, remedies are used to relieve pain and reduce inflammation. They are used in addition to the main therapy.
The following remedies will help relieve symptoms:
- Freshly squeezed carrot or cabbage juice has regenerating and healing properties. In addition, they strengthen overall immunity.
- Applications made from finely grated potatoes mixed with olive oil.
- Cinquefoil erect root, bergenia and several clove buds are ground in a coffee grinder and mixed with tooth powder. The composition is applied to the gums twice a day using a toothbrush. The course of treatment is 10 days.
- Melt 75 grams of beeswax in a water bath, mix with two tablespoons of honey and a few drops of mint oil. After cooling, form small balls that should be chewed throughout the day.
- Dissolve a pin-head piece of mummy in a glass of warm boiled water and use for rinsing in the morning and evening.
Is stomatitis contagious?
Whether stomatitis is transmitted or not is a question that worries many. Ulcers are not contagious if they are the result of:
– mechanical injuries;
– allergies;
- during intoxication.
If the cause of stomatitis is an infection, then the disease can spread to other people. These types include fungal, herpetic, and infectious stomatitis.
Causes
The causes of stomatitis in the mouth in adults are of the following types:
- Due to non-compliance with the rules of oral hygiene or improper care of it - rotting of food waste residues in damaged teeth or in gaps with an abnormal structure of the dentition, mechanical impact on the epithelium with a hard brush or rapid movements and strong pressure while brushing the teeth.
- Due to sudden and systematic changes in temperature in the oral cavity.
- Chemical exposure - brushing teeth with toothpastes that contain sodium lauryl sulfate or contain a lot of fluoride; sharp contrast between alkaline and acidic foods. For example, eat boiled meat with a sour apple or fresh wild berries after flour.
- Increased acidity in the mouth;
- Infectious agents: bacteria – cocci; viruses – herpes, ARVI, influenza; pathogenic microflora in the gastrointestinal tract - dysbacteriosis (not so much the microorganisms themselves, but putrefactive and or inflammatory processes due to their vital activity).
- Non-infectious pathogens - pneumococci, fungi except candida. Candida is classified as both infectious and non-infectious, depending on the quantity and location.
- Pathology with concomitant diseases: with diabetes, as a complication of periodontitis, other diseases whose symptoms are inflammatory processes in the body.
Immune nature:
- Autoimmune diseases - when antibodies attack healthy cells;
- Arthritis;
- HIV - in late stages or during exacerbations, or during manifestations of other diseases due to reduced immunity by the immunodeficiency virus.
- Taking medications or folk remedies that interfere with salivation or failure to replenish the body with fluid in a timely manner after taking them.
Often, stomatitis in adults occurs from a high temperature: 39.5 or higher, which lasts 5 days or more. After the temperature normalizes or drops to subfebrile levels, the disease goes away in 3-5 days, and in case of reduced immunity - 7-10 days.
Symptoms
Symptoms of stomatitis appear depending on the cause. In any case, the first signs are itching and redness of the affected area, the tongue feels uneven. Further, the manifestations are already different from each other.
- Virus - itching intensifies, redness spreads to new areas, rash.
- Bacterial nature - first a rash, then vesicular formations, then blisters, ulcers that become inflamed and or fester.
- Fungi - from the very beginning, a white coating and unbearable itching, accompanied by an unpleasant, sometimes putrid odor from the mouth.
- Increased sugar - the formation of wounds with the release of colorless liquid (ichor), a constant sweetish odor is emitted from the mouth.
- Allergies - a small rash with or without itching, headache, possible weakness, nausea, unfocused attention for a few seconds.
- A sharp increase in temperature to 39 and above, regardless of the time of day, the temperature is not brought down by antipyretics. The skin peels off.
- Immune diseases - the temperature does not rise or drops to 36 and below, weakness, nausea, short-term fainting is possible.
Important! If the symptoms of stomatitis last 5-7 days or longer and no treatment is carried out, the disease goes into an advanced form with possible complications in the form of periodontitis, ulcers in the oral cavity, the development of connective tissue cancer, meningitis, breakthrough of suppuration into the lymphatic system or entry into the blood vessels , and this is blood poisoning, which, if not treated promptly, can be fatal.
Treatment of stomatitis in adults
Treatment tactics are determined by the type of disease and what causes it. Dentospas doctors do not recommend treating this disease on your own. “Home” treatment will stop the acute course of the disease, but at the same time it will continue to develop, becoming chronic.
Before starting treatment, a diagnosis is performed. The doctor must determine what caused the inflammation and establish the type of disease. If inflammation is a secondary manifestation of other diseases or is provoked by drug therapy, you need to consult with your doctor to adjust the prescription. The treatment plan for stomatitis is formed depending on its type:
- herpetic. The inflammation is caused by the herpes virus, which cannot be cured. Stomatitis occurs during exacerbations, with weakened immunity, against the background of colds, etc. For prevention during remission, immunostimulants are used, during exacerbation - antiviral drugs and local remedies to relieve discomfort;
- candida. It is caused by the fungus Candida albicans. Multiple areas of inflammation form on the mucous membrane, which are covered with a white coating. During an exacerbation, the throat may hurt and there may be a burning sensation in the mucous membrane. Treatment of stomatitis should be accompanied by antimicrobial and antifungal therapy. The affected areas are treated with antifungal ointments and rinsed;
- aphthous. Accompanied by the formation of aphthae - round painful ulcers with redness around the edges. Often occurs against the background of systemic diseases, problems with the gastrointestinal tract, liver, and immune system. Antimicrobial therapy and antiseptics are used for treatment. To prevent relapses, oral sanitation is recommended;
- ulcerative It is provoked by smoking, poor oral hygiene, and frequent injuries to the mucous membrane. Requires mandatory treatment by a dentist (treatment of the affected area with antibacterial agents, prescription of antibiotics, in advanced cases - gum grafting, removal of dead tissue);
- bacterial. Often occurs in patients who use dentures but do not properly care for them. If microorganisms accumulate between the denture and the gum, inflammation occurs, which turns into stomatitis. During treatment, the prosthesis is cleaned and antibacterial treatment is performed. Replacement may be required if the prosthesis is poorly made. Additionally, the doctor prescribes anti-infective drugs and antiseptic rinses.
If you consult a dentist in a timely manner, stomatitis can be cured in 1-2 weeks. For this, 2-3 visits to the dentist are enough. Do not delay your visit to the dentist: without treatment, the course of the disease worsens, complications may occur (scarring of the mucous membrane, spread of infection, etc.).