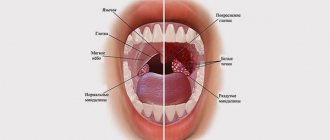
The oral mucosa in a child is normally light pink. There should be no visible changes on the surface of the gums. Only during the period of eruption of the lower incisors, tubercles with weak signs of the inflammatory process form on the upper part of the periodontium.
In other cases, the baby should be shown to a pediatric dentist, who can identify the cause of the lump on the gum.
Causes of white spots and spots on gums in infants and older children
Most young and older children have weak immune systems. Poor dental care, poor nutrition and vitamin deficiency can cause the formation of a white pimple on a child’s gum. The main factors that provoke unpleasant changes in the oral cavity include:
- plaque formation in the mouth due to poor oral hygiene;
- lack of Ca in the baby’s body;
- neonatal teeth that erupted ahead of schedule;
- infectious diseases of the oral cavity;
- gum injuries after mechanical, thermal or chemical damage;
- HIV transmitted from mother to baby through breastfeeding;
- endocrine disorders, including diabetes.
Harmless white pimples
Some forms of white spots on the gums of a baby are not dangerous to the child’s health and do not require prompt treatment. In such cases, the child is not anxious and has no complaints about the condition of the oral cavity.
Bon's knots
Bohn's nodules are whitish cysts of the oral mucosa up to 3 mm in size. In appearance, the whitish spots are similar to Epstein pearls. Spots on the baby’s gums are found at the site of the suture of the hard palate and the crest of the alveolar processes.
Pearls on the gums consist of dead epithelial cells and are benign in nature. As a rule, pearls on a child’s gums disappear by the 3rd month of life.
Epstein's nodules
A white pimple on the gum of a baby, resembling a pearl, may appear due to a decrease in the body's reactivity and disappear after the immune system improves. No special treatment aimed at eliminating the nodule is required. Pearls on the gums dissolve on their own by 6–8 months. baby.
Neonatal teeth
In rare cases, growths resembling teeth are found on the gums of a baby. Neonatal teeth affect the lower incisors and are almost always a normal addition to the primary dentition.
The reasons for this unusual phenomenon may be:
- poor maternal nutrition during pregnancy;
- intoxication of the fetus due to previous infectious diseases of the pregnant woman;
- smoking and alcohol abuse during pregnancy;
- pathologies of the development of the maxillofacial system in a baby.
Since neonatal teeth are in some cases a sign of serious syndromes, a complete examination of the infant is necessary for the early detection of serious diseases.
White spot as a sign of tooth eruption
White spots on a child's gums may indicate the eruption of baby teeth. The timing of the eruption of the first incisors falls on 6 and 12 months. baby's life. As a rule, at this time the child is restless, his appetite worsens and profuse salivation appears. Against this background, the following are often observed: fever, runny nose and gastrointestinal upset.
Gums before tooth eruption
To alleviate the baby’s condition, special toys have been created that, when chewed, reduce unpleasant symptoms at the site of tooth eruption.
Symptom of hormonal crisis
White pimples on a baby's gums can signal a hormonal crisis. This condition is the result of the child’s adaptation to conditions different from those in the womb. As a rule, white pimples appear on the gums in the first days after birth. The symptom of a hormonal crisis is associated with the accumulation of the female sex hormone – estrogen – in the child’s body. Biological substances enter the baby’s bloodstream from the mother in the last months of pregnancy.
White spot as a sign of tooth eruption
While most babies have their first teeth only at six months, some babies begin teething in the first weeks after birth or even before birth. In the first case, such teeth are called neonatal, in the second - natal. When a baby teethes, you can see a white spot on the surface of his gums.
If you are teething early, you should definitely contact a pediatric dentist. Neonatal teeth can be much weaker because their enamel is not fully formed. Sometimes dentists recommend removing such dental units. But in the absence of pathological signs, only regular monitoring of the baby’s oral health is required.
Dangerous white spots
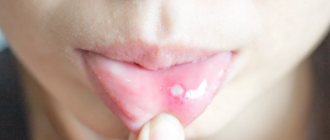
White spots on a child's gums are not always favorable. Blisters and spots are caused by bacterial, viral and fungal infections. Dental diseases cause discomfort to the baby and lead to the development of severe complications. In the photo below you can see examples of rashes that indicate a serious problem.
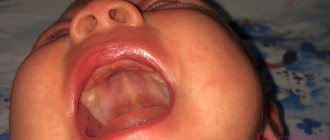
Stomatitis
There are several forms of stomatitis, but oral candidiasis occurs most often in newborns under 1 year of age. The causative agent of the disease is a yeast-like fungus of the genus Candida. The microorganism is also found on healthy gums, but in small quantities it does not cause unpleasant symptoms.
Active reproduction of the causative agent of candidal stomatitis is caused by:
- long-term use of antibiotics;
- poor oral hygiene;
- decreased local and general immunity of the newborn;
- candidiasis of the mother's genital organs, transmitted to the child during labor.
Spots and white spots on the gums of infants cause burning and pain during breastfeeding. The child's salivation increases, it hurts him to swallow and make sounds. To eliminate unpleasant symptoms and prevent complications, timely treatment of a dental infection is necessary.
Herpes
Due to the mother’s weak immunity and viral diseases during pregnancy, the baby becomes ill with the herpes virus. The causative agent of pimples on the gums is the herpes simplex virus.
Symptoms of infection include:
- many white balls on the gums, surrounded by hyperemic tissue;
- increase in body temperature up to 38 degrees;
- burning in areas of rash;
- anxiety and insomnia;
- loss of appetite.
Inside the bubbles there is a cloudy liquid, after removal of which ulcers and wounds form at the site of the lesion. The disease requires local and general treatment.
Wen
White bumps on a child’s gums indicate the presence of a benign tumor. Wen, or lipoma, develops from the submucosal layer and does not pose a danger to the baby’s health.
If the tumors are large in size, they are removed surgically.
If white balls containing liquid are frequently injured, a secondary infection may occur, so the formation of a wen is a good reason to consult a dentist.
Cyst or fistula on the gum
A white pimple on the gum, filled with purulent contents, forms after the eruption of one or more teeth. A cyst on the gum is a rounded small growth up to 2 cm in size. The inside of the pimple is lined with epithelium, and the outer shell is formed by connective tissue.
The reason for the formation of the growth is a bacterial infection that got under the gum due to poor oral hygiene.
A child’s complaints may indicate the following conditions:
- pain while eating and talking;
- sensation of a foreign object in the mouth;
- difficulty opening the mouth (if a white lump is localized near the chewing teeth);
- increase in body temperature;
- drowsiness and apathy;
- enlargement of regional lymph nodes.
Due to the seriousness of the complications, purulent inflammation of the gums must be treated immediately after they appear. In this case, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory therapy is prescribed.
Gum burn
Exposure to high temperatures and harsh chemicals can lead to the formation of pimples and blisters on the oral mucosa. After contact with the irritant, a strong burning sensation is felt on the gum.
Externally, all signs of a gum burn are determined: hyperemia, bleeding, swelling and the release of fluid from neoplasms. With the right treatment, you can get rid of the lesions in 10–14 days.
White spots in the baby's mouth as an alarming symptom
White spots in a baby's mouth can appear for serious reasons. Sometimes they occur against the background of other unpleasant symptoms and, without proper treatment, lead to the development of dangerous complications.
| Probable diagnosis, photo | Causes | Associated symptoms |
| Candidiasis | Fungal infection | Sores covered with a white cheesy coating on the gums of the baby, a sour smell from the mouth, fever, anxiety due to pain and itching. |
| Bacterial stomatitis | Bacterial infection | Pimples on the gums, tongue and inner surface of the cheeks, heavy plaque in the mouth, fever, anxiety. |
| Viral stomatitis | Viral (herpetic) infection | The symptoms are similar to those of bacterial stomatitis. Spots on the gums and tongue of a newborn look like small watery blisters. |
| Non-infectious stomatitis | Anemia, vitamin deficiency, stress after weaning | Symptoms depend on the specific cause of spots on the gums. Pale skin, restlessness, slow growth, and weight gain may occur. |
| Cyst | Accumulation of pus in the gum due to the development of a bacterial infection at the root of the tooth | The appearance of fistulas through which pus comes out. |
| Benign or malignant formations | Changes at the cellular level | The appearance of balls that can increase in size and quantity. |
Dr. Komarovsky about the types, symptoms and methods of treating stomatitis in infants:
How to recognize pathology
Every mother needs to know what signs indicate serious pathology in the oral cavity.
If a suspicious dot or stripe appears on the gum and the baby’s health worsens, you should immediately contact a pediatric dentist or pediatrician.
Doctors make a diagnosis based on the results of a diagnostic examination, after which they prescribe further treatment at home. If all treatment recommendations are followed, a favorable prognosis is expected.
A white dot on a child’s gum as a harmless symptom
If any changes appear in the baby’s oral cavity, you should contact your pediatric dentist. At a doctor's appointment, you can be relieved to learn that white spots in your baby's mouth are a completely safe phenomenon. Possible diagnoses may include:
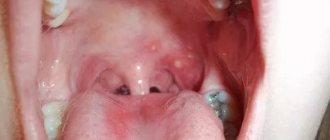
- Bohn's nodules are white formations that often appear on the gums of newborns. In fact, they are cysts, but they do not pose a danger to the child and will go away on their own over time. Sometimes parents mistake them for teething.
- Epstein's pearls are spots similar to Bohn's nodes, but localized on the palate. Pearl mussel also does not require treatment and goes away on its own.
Pictured are Bon's knots
Pictured are Epstein's pearls
White spots in the mouth may be the remains of food that the baby ate or regurgitated. But they are washed off with saliva within a short time. If plaque remains in the mouth for a long time, you should consult a dentist.
Treatment of white spots and dots on the gums of a baby
Treatment of a pimple on the gum is complex and depends on the diagnosis:
- Accumulated plaque from the surfaces of teeth and gums should be removed using a clean cloth soaked in chamomile infusion. A hygiene procedure is carried out after each feeding.
- For a fungal infection, antifungal agents are prescribed, for a viral infection, antiviral agents, and for a bacterial infection, antibiotics. Medicines and their dosage are prescribed by a doctor.
- For rapid wound healing, vitamins A and E should be applied.
- In case of heat and high temperature, children are given antipyretics. To relieve intoxication, drinking plenty of fluids is also recommended.
- If large lumps form, surgical treatment is prescribed.
- To strengthen the immune system, vitamin and mineral complexes should be added to food (from the age of 3 years).
It must be remembered that a child’s body is not able to fight the disease on its own, therefore, in order to destroy the causative agent of the infection and quickly heal wounds, it is necessary to consult a doctor as soon as possible after discovering a pimple on the gum.
Prevention of formations
Prevention of white and yellow spots on the gums includes several rules:
- Eliminate foods that are harmful to the baby from the mother’s diet.
- After feeding the child, carefully remove food debris and bacterial plaque from the surfaces of the teeth.
- After the first tooth erupts, hygienic cleaning is carried out using small rubber brushes.
- For early detection of tumors, examine the baby’s oral cavity daily.
- Every six months, take your child to the pediatrician and dentist for preventive purposes.
You should not panic if a pimple forms on a baby’s gum, since this problem does not always indicate the development of pathology. But if the mucous membrane is red, swollen and covered with plaque, it is not recommended to postpone a visit to the doctor for a long time.
Bibliography
- Ivanova E.N. [and others] – Diseases of the oral mucosa – Rostov n/D.: Phoenix, 2007.
- Murovyannikova Zh.G. – Dental diseases and their prevention, Rostov n/a: Phoenix, 2011.
- Khomenko L.A. – Therapeutic dentistry of children – Kyiv: Medical literature, 2002.
- Vinogradova T.F., Maksimova O.P., Melnichenko E.M. — Diseases of periodontal and oral mucosa in children, M., 1983.
- Angus C. Cameron - Handbook of Pediatric Dentistry - Mosby - 2008.
- Pediatric therapeutic dentistry: textbook, ed. L. P. Kiselnikova, M.: Litterra, 2009.
- Kuzmina E.M. et al. — Prevention of dental diseases in pregnant women and young children, M., MMSI. 1999.
Find a clinic