What is a blood blister on the tongue?
What does it look like?
It is an accumulation of coagulated blood in an organic cavity under the mucous membrane
A blood blister is also called a hematoma, blood blister, or lump.
It is an accumulation of coagulated blood in an organic cavity under the mucous membrane.
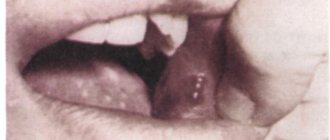
On the tongue, a hematoma looks like a swelling, the color of the tongue changes and becomes bluish, and swelling appears.
The patient feels pain and discomfort while eating and talking.
In addition, pinpoint hemorrhages are often observed on the mucous membrane.
The appearance of bloody bumps is a kind of hemorrhage that occurs as a result of injury to the capillaries and thin vessels of the oral mucosa.
Inside the bladder there may be a clear serous fluid without blood impurities, which indicates that the vessels are not intact and have not been damaged. Such hematomas are superficial in nature and the healing process occurs very quickly.
If a hematoma on the tongue contains blood inside, then the injury is deep and its healing period will be much longer until the blood resolves.
How does a blood blister form?
At the moment of microtrauma, harmful microorganisms begin to attack the damaged area
Bloody blisters in the mouth often do not pose a serious threat to human health.
They arise as a result of mechanical damage to the mucosa.
At the moment of microtrauma, harmful microorganisms begin to attack the damaged area.
To destroy them in the body, immune forces begin to activate.
Leukocytes and monocytes, macrophages are immediately sent to the injured area, which suppress the vital activity of microbes and eliminate them.
Important! Considering that a blood lump in the mouth is only part of the body’s defense reaction, it goes away quite independently after 7 days. If this does not happen, then it is recommended to visit a qualified specialist who can establish the correct diagnosis and prescribe the appropriate treatment regimen. This measure is necessary to exclude serious diseases in the body and neoplasms.
The level of health of the body is assessed according to the general condition and integrity of the oral mucosa, and only upon examination can a final diagnosis be made.
Since the clinical manifestations of many pathological conditions, including infectious, chronic, bacterial, occur along with a change in the color and integrity of the oral mucosa (tongue, gums). Here it is important to identify the true cause of the blood ball.
Localization
Appearing hematomas indicate microtrauma that has occurred.
Blood blisters are distinguished by their location. They can be on the surface of the tongue, under it and on the cheeks.
The appearance of hematomas indicates that microtrauma has occurred or the presence of a serious pathological condition.
A large number of blisters on the oral mucosa, filled with blood, can form due to diseases of the gastrointestinal canal, dental problems, and disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system.
So, with stomatitis, blisters and ulcers appear on the mucous membrane of the cheeks, on the gums, and on the palate, as well as on the tongue.
With syphilis, blood bumps are located on the tip, back of the tongue or on its lateral surfaces. With tuberculosis, hematomas are localized on the tongue, lips, cheeks, gums, and palate.
Structure and purpose of the language organ
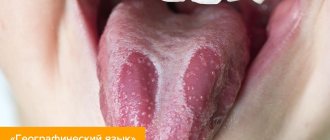
The tongue is a digestive organ. Essentially, this is a muscle that consists of striated tissue. It is covered with a protective layer - the mucous membrane. The anatomical structure of the organ includes two parts: the body and the root. The upper region is called the back, and under the organ is the frenulum. There are also terminal and longitudinal grooves - the first is located at the junction of the root and the body, and the second divides the organ vertically.
On a note! On the surface of the tongue there are many papillae, which contain taste buds. For example, those responsible for recognizing sweet taste are located on the tip, and salty taste is located on the sides. On the side, closer to the root, there are receptors that react to sour things, but the base of the organ is susceptible to bitter tastes.
The tongue not only allows us to enjoy the taste of our favorite treats, but also takes a very direct part in the conversational function. It also helps us chew food and is responsible for the production of salivary fluid, which, in turn, helps break down food particles and therefore participates in digestion.
Causes
Among the factors that provoke various external damage to the oral mucosa are:
Mechanical
Injury to the surface of the tongue is caused by all piercing and cutting objects that cause direct and instantly noticeable harm.
For example, dishes with bones cause damage to the oral mucosa during consumption. It is not the amount of food eaten that matters here, but the receipt of microtraumas that violate the integrity of the surface of the tongue.
Blood blisters that form due to mechanical action do not pose any threat to human health. To speed up the process of resorption of seals on the tongue, under it, it is recommended to rinse the mouth more often after eating.
Chemical
The duration of wound healing from thermal exposure directly depends on the depth of the lesion; they heal for quite a long time
When eating salty or sour food in the mouth, small lesions in the form of ulcers appear almost instantly on the mucous membrane of the tongue.
This reaction is observed among most fans of oriental cuisine, where hot seasonings are used.
Thermal
Such damage includes microtraumas resulting from drinking too hot tea or coffee.
The duration of wound healing from thermal exposure directly depends on the depth of the lesion; they take quite a long time to heal.
Depending on the degree of damage, sensations change:
- In the first degree, the burn occurs only on the outer layer of the tongue. A person experiences pain, the color of the tongue changes to red and after some time begins to swell. Rinsing the mouth with antiseptic solutions will help speed up the healing process.
- In the second degree , the sensations become more painful, since not only the outer but also the inner layer of the tongue is affected. The formation of blood blisters, swelling of the tongue and its redness are also observed. In this case, it is recommended to seek medical help as soon as possible so that the doctor removes the lump, washes the affected area and treats it with an antiseptic.
- In the third degree, the burn penetrates deep into the tongue, the burned surface becomes black. The patient complains of a feeling of numbness of the tongue and severe pain. The help of a doctor is mandatory here, otherwise there is a high probability of death.
Dangerous symptoms
Typically, cracks in the tongue do not cause any discomfort; their appearance is often discovered at a doctor’s appointment. But this is not always the case. Sometimes unpleasant symptoms may appear that indicate health problems:
- pain;
- burning, change in taste;
- itching or swelling;
- pain when chewing, problems with speech;
- temperature increase.
If cracks appear on the tongue, there are several of the listed symptoms, then perhaps the cause is an inflammatory process in the oral cavity - glossitis. If the tongue becomes covered with cracks and ulcers, the cause is ENT diseases (tonsillitis, pharyngitis). In any case, professional treatment is necessary.
Diseases accompanied by a blood bubble on the tongue
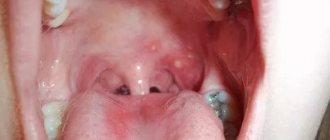
Stomatitis
With various types of this pathological condition of the oral cavity, blood sacs can also form on the inside of the cheeks, on the gums, palate, and tongue. Stomatitis is caused by pathogenic microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, fungi), a weakened immune system and injury.
Often this disease is of herpetic nature. Associated symptoms are swelling of the tongue, the presence of a yellow-white coating on it, wounds that cause severe pain and discomfort while eating and speaking.
If the disease is caused by the herpes virus, then it is accompanied by the presence of a large number of blisters on the surface of the tongue, which after some time combine into one blister.
When it bursts, erosion forms in its place. In addition to these manifestations, body temperature may rise, weakness, malaise, and loss of appetite may appear.
Syphilis
In this pathological condition, a characteristic feature is the presence of syphilitic chancre on the surface of the tongue; they are an ulcer or erosion that has a round shape.
The edges of the chancre are uniform, smooth, and the bottom is hard, from which liquid flows out when pressed.
Their sizes can vary from 1 mm to 2 cm.
There are ulcers on the tip, back of the tongue or on its lateral surfaces. The person does not feel pain or discomfort.
2-3 weeks after the occurrence of such ulcers, an increase in regional lymph nodes occurs.
Cancer
This disease, which has an ulcerative form, occurs with the formation of wounds on the tongue with a black bottom, which have unclear edges and blood oozes from them. The location is the edges of the tongue and its tip.
Obvious signs of this disease are pain, discomfort in the oral cavity, a putrid odor, swelling of the face and neck, difficulty swallowing, talking, and chewing.
Tuberculosis
After Mycobacterium tuberculosis enters the human body through the mucous membrane, ulcers appear at the site of the lesion. They can form on the tongue, lips, gums, cheeks, and palate. Externally, the ulcer looks like a pink crack, covered with a white-yellow coating, its edges are soft and scalloped.
If you try to remove the plaque, its granular bottom begins to bleed. In most cases, yellow-red bumps form around the affected area.
With tuberculous ulcers, pain, discomfort in the oral cavity, and difficulty eating and speaking are noted.
The healing process of wounds occurs quite slowly. When palpated, regional lymph nodes cause severe pain and are enlarged.
Necrotizing periadenitis
With this disease, there is increased salivation, bleeding, and foul odor from the mouth.
In a recurrent condition, the ulcers are localized on the side; they affect not only the tongue, but the lips and cheeks.
Before they form, the mucous membrane thickens, the edges at the site of the lesion rise.
Inside the ulcers there is an inflammatory infiltrate, which contains blood, lymph, and cellular accumulations.
With this disease, there is increased salivation, bleeding, and bad odor from the mouth.
In advanced forms, the ulcers deepen and fill with purulent contents, which provokes increased body temperature, a feeling of weakness and poor health.
They are very painful and very difficult to cure. This period can last several months. Treatment here must have a comprehensive approach.
Afty Bednary
This pathological condition most often affects small patients under 1 year of age who are bottle-fed or breast-fed. Aphthae can form due to excessive pressure on the nipple or when using an uncomfortable bottle.
After some time, they turn into ulcers covered with a gray-yellow coating, which is quite problematic to remove. The inflammatory process occurs with a change in color, the aphtha has a red color and swelling appears around it.
Given the severe pain that is characteristic of such ulcers, the child refuses food and begins to be capricious, which is easy to notice. Aphthae can also appear on the tongue, cheeks, and gums in older children as a result of constant sucking of hands, fingers, and toys.
Endocrine pathologies
If there is an acute shortage of nicotinic acid, then there is an increase in the size of the tongue, a dense coating on it, and the presence of furrows.
In diabetes mellitus, due to trophic changes in the tongue, decubital wounds appear, filled with a dense infiltrate in the center.
They heal very slowly and cause a person a lot of unpleasant sensations. The tongue becomes red and swells.
Gastrointestinal diseases
Blood blisters on the tongue, under it, are formed due to disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Thus, ulcerative glossitis can develop with enterocolitis and hypoacid gastritis.
Worm infestation
Ulcers with a white-yellow coating, hyperemia of the tongue, its swelling, severe pain, increased salivation, bad breath may indicate the presence of parasites in the human body.
Hypovitaminosis/vitaminosis
With a lack of vitamin A, a person complains of a feeling of dryness in the mouth, which leads to the formation of cracks and ulcers on the surface of the tongue.
If there is an acute shortage of nicotinic acid, then an increase in the size of the tongue, a dense coating on it, and the presence of furrows are observed.
When removing plaque, irritation of the mucous membrane occurs, which causes discomfort and pain in the affected area. In case of vitamin C deficiency, blood vessels become fragile and blisters form when they rupture.
The papillae may atrophy, the tongue acquires a folded structure, and ulcers appear on its surface. Such manifestations on the tongue are characteristic of a lack of vitamin B6.
Is it worth treating glossitis with folk remedies?
If you have a question: how to cure glossitis, don’t waste time looking for folk remedies! If you notice characteristic symptoms that do not go away for more than a day, you need to seek help from a specialist. Treatment of glossitis should be carried out only by a dentist, who will determine the cause of the changes in the oral cavity, carry out all the necessary therapeutic and diagnostic procedures, prescribe a set of therapeutic measures that the patient can perform at home, and also monitor the entire treatment process, making changes to it as needed. necessary adjustments. Moscow dental clinics are presented in the “Search” section on our website.
Glossitis, like other periodontal diseases, is fraught with many complications, so treatment with folk remedies can only serve as an aid in complex therapy.
In order not to come face to face with glossitis, it is enough to brush your teeth regularly, including brushing your tongue, and do not skip preventive examinations at the dentist. In addition, doctors recommend avoiding excessive consumption of spicy foods and spices, limiting the intake of alcoholic beverages and smoking. Remember, disease is easier to prevent than to treat.
How to treat a blood bladder?
General therapy
Depending on the type of pathological condition that caused the appearance of a blood bubble in the mouth, treatment can be carried out with the following medications:
- In case of traumatic formations that go away on their own over time, the oral cavity is treated with antiseptic agents
For candidal stomatitis, antifungal drugs such as Levorin and Nystanin are effective.
- For diseases of viral etiology, the treatment regimen includes Viferon, Amoxicillin, Tsiprolet, Azithromycin.
- To combat gingivostomatitis, where it is expected to remove areas affected by necrosis, antiallergic medications, antibacterial agents, and vitamin complexes are used.
- In case of traumatic formations that go away on their own over time, the oral cavity is treated with antiseptic agents. If there is pain, the doctor may prescribe Cholisal, Ketoprofen, Voltaren, Lornoxicam, Kamistad.
- To eliminate tuberculosis, appropriate chemotherapy is prescribed, which includes Rifampicin, Ioniazid, Pyrazinamide.
Local therapy
To speed up the healing process, regularly rinse with antiseptic agents. Furacilin, Chlorhexidine, Stomatidine, Betadine, Miramistin, hydrogen peroxide solution, Iodoform, Chlorophyllipt show good results.
Treatment of the affected tongue with disinfectant solutions should be performed twice a day, at a minimum, but before that you must brush your teeth and remove any remaining food.
It is advisable to eat food after the procedures within 30-60 minutes, which will significantly increase their effectiveness.
Traditional methods
Aloe or Kalanchoe juice has a wound healing effect
To alleviate the condition, it is good to use healing decoctions based on chamomile, sage, yarrow, St. John's wort, and viburnum fruits.
They are prepared at the rate of 1 tbsp. herbal raw materials per 1 glass of water.
The mixture is brought to a boil and left for 2-3 hours to infuse. Before use you need to strain.
Aloe or Kalanchoe juice has a wound-healing effect.
Oil from sea buckthorn and rosehip also has the same property. They are applied directly to the affected area.
These agents accelerate the regeneration process, prevent the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms and anesthetize the lesion.
A solution prepared from salt (1 tsp), 3 drops of iodine and soda (1 tsp) is a universal remedy in the fight against inflammatory processes in the oral cavity.
These components are mixed in one glass of warm boiled water and used for lotions and rinses. It is also good to treat the affected areas with hydrogen peroxide.
Diagnosis and treatment
To diagnose glossitis in adults, the following basic methods are successfully used today.
- Examination
An experienced dentist in 95% of cases is able to diagnose glossitis based only on visual data. - RPR test
A special test that detects antibodies to the cardiolipin antigen. - Scraping
It is taken from the surface of the tongue to exclude syphilis, whose symptoms are similar to glossitis. - PCR
The most modern and accurate diagnostic method for identifying a wide range of infectious pathogens.
Treatment of glossitis depends on the form of the disease and analysis of concomitant diseases, but in any case it should be comprehensive:
- enhanced oral hygiene;
- general strengthening therapy aimed at increasing immunity;
- local treatment with antiseptics;
- strict diet;
- targeted medications (for example, for candidal glossitis - antifungal agents).
You can find out more about how to treat glossitis of the tongue in the article.
What not to do?
If you have blood blisters, you should not:
- Pierce and burst them yourself. This technique will only worsen the situation; as a result of additional injury, a fungal infection will join the existing problem, which will prolong the disease.
- Ignore the hematoma, lump, or clot that appears in the oral cavity. If there are any changes in the mucous membrane of the tongue, gums, palate, or cheeks, it is recommended to contact a qualified specialist who will identify the true cause of the disease and prescribe an appropriate treatment regimen.
Which doctor should I contact for help?
When a vessel on the tip of the tongue bleeds, you need to visit a doctor. Do not hesitate to visit a doctor if you have the following symptoms:
- Prolonged bleeding.
- The wounded area of the muscle organ was severely swollen.
- Painful sensations increase.
- A hematoma formed, pus, strong furrows and plaque appeared.
- There is a burning sensation when eating.
- Damage to the muscle due to penetrating damage to the organ.
These problems are aggravated by the entry of pathological microflora into the wound. The first thing you should do is see a dentist. In difficult cases, consultation with a therapist, ENT doctor, endocrinologist, gastroenterologist and other specialized specialists may be required.