Inflammation of the gastric mucosa caused by poor diet, negative effects of bacteria, and alcohol abuse is called gastritis. Types of gastritis are manifested by various symptoms, one of which is plaque on the tongue. This symptom may belong not only to gastritis, but also to other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and other organs.
These can be liver pathologies, dehydration, side effects of medications, as well as intoxication and dyes from food products. In order to correctly diagnose the plaque that appears on the tongue during gastritis, you need to become familiar with the features of this symptom.
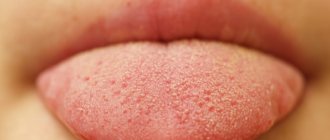
What does a healthy tongue look like?
The tongue is pale pink - absolutely healthy.
Diagnosis by the appearance of the tongue was mastered by ancient healers, who believed that a disease could not be considered cured until the patient’s tongue regained its previous appearance. The tongue of an absolutely healthy person has the following signs:
- Pale pink color;
- Small taste buds without pronounced features;
- No bad breath;
- Be moderately moist;
- The presence of a small amount of translucent bright pink coating is allowed;
- There is no unpleasant odor.
If you deviate from these signs, you should consult a general practitioner or gastroenterologist and undergo the examination prescribed by him.
Signs of deviations from the normal state of the tongue
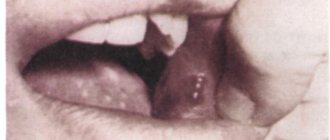
It is quite possible that, once you look at your tongue, you will see a rather unsightly picture. Symptoms of deviation from the norm:
- A coating of various colors, thicknesses, and with different locations of spots appears on the back of the tongue;
- The sides of the tongue are bright red;
- The taste buds look uneven, some of them increase in size and begin to disturb with unpleasant sensations, taste sensations change, their intensity weakens;
- The oral cavity becomes unusually dry;
- In some cases, the appearance of pain and burning is diagnosed;
- There is an unpleasant odor from the mouth;
- After cleaning the tongue, the plaque appears again after a short time.
In the plaque that appears on the tongue, laboratory testing can reveal leukocytes, pathogenic microflora, and exfoliated epithelial cells.
This video will tell you about plaque on the tongue due to gastritis:
Causes
If we exclude everyday causes associated with mechanical damage to the mucous membrane of the tongue, swelling is almost always a symptom of other diseases. Therefore, you cannot delay visiting a doctor. The most common reasons are:
- Allergic reaction. Swelling can be caused by taking medications or foods that cause allergies. Typically, patients prone to allergies are aware of their problem. If you suspect allergic edema, you should consult a doctor. A severe allergic reaction can cause angioedema or angioedema. This condition develops rapidly, quickly spreading to the lips, cheeks, and larynx. The patient finds it difficult to breathe. In the most severe cases, angioedema can be fatal.
- Mononucleosis. A disease characterized by inflammation of the throat. Swelling of the tongue with mononucleosis is one of the accompanying symptoms.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Edema develops against the background of colitis, enterocolitis, peptic ulcer, gastritis and other diseases. This reason is one of the most common.
- Hormonal disorders. For many diseases associated with hormonal imbalances, a swollen tongue is one of the symptoms.
Swelling of the tongue is not always a symptom of other diseases. Swelling often appears for everyday reasons:
- Bite.
- Burn.
- Mechanical damage (dentures, braces, poor-quality fillings, piercings, etc.).
Diagnosis of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract by language
The tongue will tell you about gastrointestinal diseases.
Modern gastroenterology does not specialize in diagnosis based on the appearance of the tongue. However, an attentive person suffering from such pathologies can distinguish the symptoms of gastrointestinal diseases:
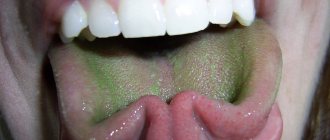
- Acute gastritis - a viscous, dense coating of white-gray color is visible on the entire surface of the tongue, with the exception of the tip and side parts. The mouth feels dry and has an unpleasant acidic taste. Perhaps, instead of dryness, increased salivation will appear. In acute gastritis, similar symptoms include heartburn and sour belching, cutting pain in the epigastric region 1-2 hours after eating, weakness, headaches, diarrhea, heaviness in the stomach. With inadequate treatment, acute gastritis becomes chronic.
- Chronic gastritis - light deposits on the tongue are replaced by occasional dark gray deposits. To the previous symptoms are added such characteristic signs of chronic gastritis as astheno-neurotic syndrome, constant irritation, aching pain that intensifies some time after eating. About 40% of all cases of acute gastritis become chronic. This condition is fraught with the spread of the process to the duodenum and the development of gastroduodenitis.
- A stomach ulcer in combination with gastritis affects the condition and appearance of the tongue - its surface becomes bright red, with gray spots of dense plaque that are difficult to clean. This picture is complemented by signs of stomatitis and cyanosis. The patient feels a burning sensation and the production of saliva increases.
- Oncological damage to the gastrointestinal tract, as well as the presence of internal circulation, is reflected in the condition of the tongue by the appearance of evenly spaced white plaque of increased viscosity, excessive saliva production, and a burning sensation in the oral cavity.
Stomach ulcer
The symptoms of the disease and its nature are generally similar to the symptoms of gastritis, but its manifestations are more striking and persistent. Standard gastrointestinal pathologies can develop into a gastric ulcer due to increased stress, frequent and unnecessary medications, alcohol and tobacco abuse, or genetic predisposition.
Dental symptoms - swelling of the tongue, plaque on the oral mucosa, enlargement and increased sensitivity of the papillae of the tongue, increased temperature in the mouth, gingivitis and stomatitis
.
Treatment:
similar to the treatment of chronic gastritis or gastroduodenitis.
Differentiation of plaque in gastritis from other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
A thick, grayish coating is characteristic of dysentery.
It is important to suspect the onset of a dangerous disease in time. To take action and prevent complications from occurring. Differential diagnosis by tongue of gastritis from other diseases and conditions:
- A thick, grayish coating is characteristic of dysentery. In this case, the tongue looks cracked, and less saliva is produced than usual.
- Desquamative glossitis - this type of inflammation of the tongue is characterized by such symptoms as red spots of complete absence of epithelium or several altered taste buds on the tongue, covered with a white coating.
- Galvanic stomatitis is a form of inflammation of the tongue that arises as a result of a reaction to metal prostheses, manifested by spots in the form of pimples, and subsequently by the appearance of erosions against a background of white plaque.
- Infectious diseases - sore throat, scarlet fever, diphtheria, HIV infection can cause the appearance of a white coating on the tongue, but almost all of these infections are accompanied by high fever and skin rashes.
- Diseases of the heart and blood vessels - plaque is located on the anterior third of the tongue.
- Kidney disease - plaque on the tongue is localized at the back along the edges.
- Endocrine disorders - under the plaques of white plaque there are ulcers and erosions.
- Anemia is not a coating on the tongue, but blanching of the entire surface of the organ. Diseases of the respiratory system are often indicated by the localization of white plaque on the front and along the edges of the tongue.
- Diseases of the salivary glands - the appearance of a white coating is accompanied by the appearance of an unpleasant odor.
- Diseases of the liver and gall bladder - the color of the plaque is not white, but has a yellowish or brown tint. A white coating on the tongue can be caused by the consumption of dairy products, as well as the proliferation of bacteria and fungi in those who abuse sweets. Unlike plaque during gastritis, such layers are easily removed and do not form further.
What if it's a disease?
A strong coating on the tongue and bad breath are already a reason to be wary. An experienced doctor will determine which disease the plaque on the tongue is a sign of, comparing the degree of density of the deposit, color and location.
Glossitis
One of the typical diseases characterized by plaque on the tongue is glossitis - inflammation of the tongue caused by injury or of an infectious nature. With glossitis, red spots appear on the tongue, which is why the disease is sometimes called “geographic tongue.” Read more in the article.
Gastritis
If your mouth is sour and there is a coating on your tongue, this is a sign of inflammation of the gastric mucosa. Usually the plaque disappears if you follow a diet.
Thrush
With thrush, the plaque is located under the tongue. It is distributed unevenly and has the character of spots.
Chlamydia
With chlamydia, a sexually transmitted disease, a thick, sticky coating appears on the roof of the mouth and tongue as a result of a malfunction in the immune system after an attack by chlamydia.
Bronchitis and pneumonia
Plaque on the sides of the tongue will indicate an upper respiratory tract disease. In most cases, it is whitish and is easily removed by brushing your teeth and tongue, but also quickly returns to its original place.
Alcoholism
A coating on the tongue after alcohol abuse is common. People talk about this figuratively: “It’s like cats have shit in your mouth.” However, in chronic alcoholics, the dark brown coating never goes away and is localized at the root of the tongue.
Cancer
If the tongue is coated, one cannot say with certainty that a specific type of cancer is present. But it is precisely this symptom, coupled with a number of other characteristics, that indicates a complication of an oncological disease (for example, a malignant tumor in the lungs).
Plaque on the tongue of a pregnant woman, with rare exceptions, is not a sign of illness - it is the result of changes in hormonal levels.
Is plaque on the tongue dangerous - how to treat it
An ultrasound of the stomach will help clarify the diagnosis.
Plaque itself does not pose any threat to health. As soon as the underlying disease is cured, the condition of the tongue will return to normal.
As for gastritis, long-term treatment with careful adherence to the recommendations of a gastroenterologist will help relieve its symptoms.
Perhaps the doctor will conduct research aimed at clarifying the diagnosis: FGDS, ultrasound of the stomach, laboratory tests of blood and gastric juice. The following drugs will be prescribed as treatment:
- Antibiotics of 2-4 types, taken in combination:
- Pro- and prebiotics;
- Vitamins;
- Antacids;
- Proton pump blockers.
Patients with gastritis must follow a strict diet aimed at sparing the gastric mucosa and not provoking the release of excessive amounts of hydrochloric acid. With this treatment, not only the gastric mucosa, but also the condition of the tongue will definitely return to normal.