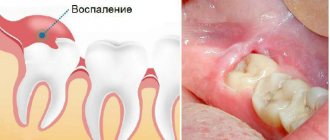
The wisdom tooth is one of the most difficult teeth to treat and remove. The reasons lie in the unpredictability of this tooth, namely: the number of roots, canals, their shape, the tooth is often not fully erupted, covered with a mucous membrane, sometimes even with bone. Also, all manipulations with this tooth are complicated by its localization and very limited access. In addition, many patients experience problems with wide mouth opening.
All this makes the removal process very difficult and traumatic, so after removing a wisdom tooth, a swollen cheek and pain are normal, and you should not be afraid of them. To help your body cope with symptoms and speed up healing, you need to follow your doctor's orders and follow simple symptoms management tips.
What to do after wisdom tooth removal
On this day, it is better to go home and relax: sleep, read a book, watch your favorite show or movie. It is not recommended to move a lot and intensively, or engage in physical labor.
Starting from the second day, it is necessary to rinse your mouth with antiseptics and take antibiotic medications to prevent the development of infectious and inflammatory diseases. The doctor decides which antibiotics to take after wisdom tooth removal. If there are no recommendations, then you can choose any medications with a wide spectrum of action.
Intense rinsing is not recommended, licking the blood clot is strictly prohibited, otherwise this will lead to the effect of a dry socket. A plug of clotted blood protects the resulting cavity and jaw bones from food particles and bacteria getting inside.
Do not consume hot or too cold foods, drinks, or overheat the body. Visiting the beach, baths, saunas is prohibited.
Smokers will have to give up cigarettes for 2, 3 days, or better yet for a week. Nicotine does not allow the wound to heal quickly, as it constricts blood vessels. Tissues are poorly saturated with oxygen and nutrients, and are more easily susceptible to infection.
A repeated visit to the doctor is necessary, even if the stitches do not need to be removed. The doctor will examine the wound, be able to identify complications in time and prescribe the correct treatment. You should not wait until the date of re-appointment if there is severe, ongoing pain, or the appearance of pus in the socket.
In what cases can swelling of the cheek be normal?
Please note that swelling of the cheek may appear not only immediately after tooth extraction (or the next morning), but only a few days later. The last scenario will definitely indicate the development of inflammation. Therefore, the norm may be the occurrence of swelling of the cheek or gums - in the first hours after removal, or the next morning. When it might be normal:
- After a complex tooth extraction – in this case, tooth extraction is often accompanied by incisions in the gums, cutting out bone tissue with a drill, and dislocation of tooth roots with special elevators. All this leads to significant trauma to bone tissue, as well as soft gum tissue. And therefore, it is quite natural that after a complex extraction you may experience swelling, and this happens especially often when it comes to the complex removal of wisdom teeth.
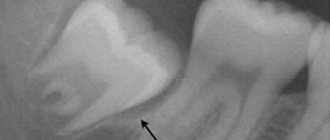
What does a complex wisdom tooth extraction look like?Moreover, if your cheek is swollen after the removal of the 8th tooth, then the appearance of swelling of the surrounding soft tissues can gradually lead not only to facial asymmetry, but also to temporary difficulty opening the mouth, as well as painful swallowing. Therefore, according to the rules, after a complex tooth extraction, the doctor is always obliged to schedule the patient for a second examination (the very next day) so as not to miss the development of inflammatory complications.
- After the removal of wisdom teeth , swelling can appear not only after a complex wisdom tooth removal, but also if the removal of the 8th tooth was relatively simple. The fact is that with a small length of the body of the lower jaw, with a small size of the upper jaw, the wisdom teeth may be partially located in the depths of the soft tissues (moving soft tissues of the oral cavity). Such a tooth can be removed easily, but with such localization of 8 teeth, swelling of the soft tissues can easily occur.
- When a tooth was removed due to inflammation - if the tooth was removed due to purulent inflammation (i.e. at the time of removal you could have symptoms such as swelling of the gums, pain when biting the tooth, the presence of a fistula on the gum with purulent discharge).
According to the rules, in this case, after removal, the doctor must wash the wound with an antiseptic, put medicine (Alvogel) into the hole of the extracted tooth, and also prescribe antibiotics to prevent suppuration of the blood clot in the hole. The development of soft tissue edema in this case is due to the fact that any surgical operation on inflamed tissues always leads to more pronounced edema. Those. in this case, swelling will not necessarily indicate the development of a complication. But on the other hand (even with prophylactic antibiotics) increasing swelling of the cheek may also indicate a complication that requires a visit to the doctor. - If you have had a gum incision made – if the tooth was removed due to pain and inflammation, then an inflammatory infiltrate (slight swelling) could be present on the gum or in the area of the transitional fold. Making an incision in this case has the purpose of 1) releasing pus if a purulent abscess has already formed, 2) preventing the formation of an abscess after tooth extraction. An incision is made in the center of the infiltrate; usually a thin rubber drainage is inserted inside it.
Making an incision in the area of the transitional fold (i.e., where the gum meets the cheek) can always lead to the appearance or increase of existing swelling of the cheek. According to the rules, if a doctor opens an abscess along a transitional fold, the patient should always be scheduled for a re-examination the next day. If the infiltrate was opened, but no pus was obtained, then in the absence of complaints from the patient, the latter is sometimes recommended to independently remove the drainage from the wound after a few days (24stoma.ru).Opening an abscess along the transitional fold -
- Complaints that the cheek is swollen after tooth extraction occur very often in certain groups of patients. For example, hypertensive patients, as well as people with a significant amount of subcutaneous fat on the face, are predisposed to the appearance of edema after tooth extraction. In these patients, swelling of the cheek may appear after a simple simple removal.
What symptoms in this case will indicate the absence of inflammatory complications -
As we said above: swelling after tooth extraction usually appears either within a few hours after the intervention, or the next morning. Accordingly, only over the next day will it be possible to draw timid conclusions about whether there is a reason to worry or whether you need to urgently run to the doctor for a second examination. Let's look at the signs that indicate that the development of edema does not require urgent intervention -
- The swelling that appears is not too pronounced and does not tend to increase. The latter means that the swelling that occurs the next morning after tooth extraction should not increase further in the evening. But if the swelling tends to further increase, this is a bad prognastic sign. Also not a very good sign is hardening of soft tissues, i.e. Normally, edematous tissue should be soft, but if tissue compaction (infiltrate) appears in the center of the edema, then this is a sign of suppuration.
- If you do not have a fever, especially an increasing one - if you did not have an elevated temperature at the time of tooth extraction, then normally it should not be elevated the day after the extraction.
At the same time, a slight temperature of up to 37.5 in the evening on the day of removal (after a complex removal or removal due to inflammation) is considered normal. If you had a high temperature before removal, then from the next day it should begin to decrease progressively. If an elevated temperature after tooth extraction appears only the next day or even later, this most likely indicates the development of complications and requires immediate consultation with a doctor.
- If you do not have severe pain, especially increasing pain, after a simple removal you may feel pain for only 1 day, after a complex removal it is normal for only a few days. The appearance of severe pain and prolonged pain for 4-7 days only indicate that the removal is excessively traumatic, and this is a question for the doctor’s skills. In any case, normally the pain should progressively decrease every day, but if the pain does not decrease or occurs, this is a symptom of the development of complications.
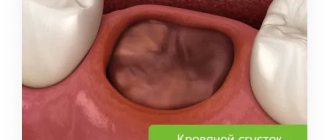
- The hole must be closed with a dense blood clot - after removal, the hole is filled with blood, which immediately coagulates, forming a blood clot in the hole of the extracted tooth. In some cases, the clot may not form, or it may fall out due to the patient rinsing the mouth too much. The absence of a blood clot in the socket will inevitably lead to the development of alveolitis (inflammation of the socket of an extracted tooth).
A fresh clot normally has a dark burgundy color, but after some time a whitish or grayish-yellow fibrinous coating will appear on its surface (this is normal and does not indicate inflammation). The clot should be dense, without an unpleasant odor. Pay attention to how the blood clot should look on the day of removal and a few days after (Fig. 6-7).What should a blood clot normally look like?
After tooth extraction, the cheek is swollen: what to do in this way, let's summarize... if the resulting swelling of the cheek is 1) soft to the touch and does not tend to increase and harden, 2) if there is no temperature, difficulty opening the mouth and painful swallowing, 3) if the hole is closed by a dense blood clot, 3) if there is no severe or constant aching pain in the area of the socket of the extracted tooth, then, in principle, we do not see any indication for an urgent visit to the dentist for a second examination.
How long does swelling last after tooth extraction?
There is no average answer to this question, because... much depends on the degree of trauma of the removal and the characteristics of the body. In some patients, swelling of the cheek may last only a few days, while in others it can last for a week. The problem here is that after a traumatic extraction (especially with cutting out the roots with a drill), very often a sluggish inflammation can occur in the socket of the extracted tooth for a very long time.
In this case, there may be only slight discomfort or no pain at all, but the swelling in this case can last quite a long time. Therefore, after a complex extraction, it is always worth going to the doctor for a second examination to see if the socket of the extracted tooth and the blood clot in it are normal. By the way, you can also make the swelling go away faster.
How to relieve swelling after tooth extraction -
So, if the appearance of edema is associated with traumatic removal or making an incision along the transitional fold, we can significantly increase the rate of its reduction. This can be done at home using compresses with a dimexide solution (diluted 1:4 or 1:5, i.e. to obtain a 20 or 25% concentration). Dimexide is diluted with lukewarm boiled water.
A gauze bandage is soaked in the diluted solution and applied to the site of swelling for 20 minutes. A layer of cling film is placed over the gauze bandage, and then secured to the head with a bandage. The procedure can be done 1-2 times a day, the duration of the procedure is 20 minutes. An important point - in this case, you cannot place a thick cloth or towel on top of the cling film (this is usually done to make a thermal compress). If there is inflammation, a heat compress can be harmful.
If your temperature rises after wisdom tooth removal
The symptom may occur immediately after extirpation. This is due to the action of the immune system in response to tissue injury and invasion of foreign elements into the body.
Doctors recommend taking antipyretics and using cold compresses to remove heat locally.
If the patient then develops a fever several days after extirpation, this may indicate the presence of an inflammatory process. The most common is alveolitis. It is accompanied by acute pain, which can radiate to the throat, temple, ear, depending on where the hole is located. If, when you probe the hole with your tongue, you feel an empty cavity, then you need to urgently go to the dental clinic where the surgery was performed.
Folk remedies
Let's look at useful rinse recipes that are used to treat gingivitis and alveolitis after tooth extraction.
One tablespoon of dry crushed chamomile (sage, calendula) should be steamed with 250 ml of boiling water. The mixture should be left for an hour, wrapped in a towel, then filtered and used for rinsing. It is recommended to rinse your mouth every 2-3 hours.
The following healing recipes will help relieve inflammation and relieve discomfort:
- Mix 20 drops each of tea tree oil, cloves and liquid vitamins A and E, add a pinch of cayenne pepper. Moisten a cotton swab with the resulting medicine and apply it to the painful area.
- Wet baking soda with water to form a paste and apply it to the inflamed area.
ASEPTA gel with propolis will help you quickly cope with gum inflammation. This unique product containing the waste product of bees relieves inflammation of the gums by 31%, has anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial effects against gram-positive bacteria, as well as antipruritic and analgesic effects (reduces the pain of affected tissues), accelerates the process of regeneration and epithelization of wound surfaces, stimulates metabolic processes.
We hope that our recommendations for the treatment of gum inflammation after tooth extraction will be for informational purposes only. Treat yourself carefully and remember: at the first symptoms - acute pain in the gums, sudden changes in temperature, severe swelling of the gums, discharge of purulent exudate - consult a doctor as soon as possible. A lesion can be disastrous, so take care of yourself after surgery.
Sources:
- Clinical and laboratory assessment of the influence of domestic therapeutic and prophylactic toothpaste based on plant extracts on the condition of the oral cavity in patients with simple marginal gingivitis. Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Elovikova T.M.1, Candidate of Chemical Sciences, Associate Professor Ermishina E.Yu. 2, Doctor of Technical Sciences Associate Professor Belokonova N.A. 2 Department of Therapeutic Dentistry USMU1, Department of General Chemistry USMU2
- Clinical studies of antisensitive toothpaste “Asepta Sensitive” (A.A. Leontyev, O.V. Kalinina, S.B. Ulitovsky) A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist O.V. KALININA, dentist S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry, St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova
- Comparative clinical evaluation of the effectiveness of treatment of traumatic lesions of the oral mucosa IORDANISHVILI A.K. *,** Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, Professor of the Department *Department of Orthopedic Dentistry of the Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Education “North-Western State Medical University named after. I.I. Mechnikov" of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation (rector - Doctor of Medical Sciences Sayganov S.A.); **Department of Maxillofacial Surgery and Surgical Dentistry of the Federal State Budgetary Military Educational Institution of Higher Education “Military Medical Academy named after S.M. Kirov" of the Ministry of Defense of the Russian Federation (chief - Corresponding Member of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Professor A.Ya. Fisun).
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
- Report on clinical trials of anti-inflammatory balm for gums "Asepta" adhesive, St. Petersburg State Medical University, 2007
- Report on determining/confirming the preventive properties of commercially produced personal oral hygiene products: Asepta toothpaste used in combination with Asepta mouthwash and Asepta gum balm Head. Department of PFS Doctor of Medical Sciences Professor S.B. Ulitovsky St. Petersburg State Medical University named after Academician I.P. Pavlova. Faculty of Dentistry. Department of Preventive Dentistry.
How to relieve pain after wisdom tooth removal
The doctor prescribes drugs for pain relief to the patient. If there is no list, but the pain is severe, then you can buy Tempalgin, Baralgin, Ketanov and similar medications. Medicines must be taken according to instructions. If you take too many tablets, it will lead to side effects. One tablet is usually enough to stop an attack. Take three times a day.
In addition to medications, pain can be reduced with cold. A cold compress is applied to the cheek for 15 to 30 minutes up to four times a day. You can use pieces of ice or frozen food from the freezer. They are placed in a plastic bag and a towel, and then applied to the sore spot.
What does flux look like?
It is of infectious origin, the process occurs against the background of inflammation of the body of the jaw or in the periosteum. Flux is formed not only after dental surgery, but also after furunculosis or tonsillitis. If the cheek and gums are swollen, there is throbbing or mild pain, in advanced stages pus may appear and the temperature may rise. On the upper jaw, the flux covers the lip, cheek, gum and nasolabial area. In addition to the face, the infection often spreads to the neck.
Anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs are used for treatment. After using topical medications, you should not eat or drink liquids for 2 hours.
What can you eat after wisdom tooth removal?
It is forbidden to put anything in your mouth for two hours after extraction. During this time, a plug of condensed blood is formed and fixed on the socket, which is necessary to protect against the entry of various elements, including pathogens. If you are very thirsty, you can do this through a straw or in small sips.
On the first day, you can drink non-hot drinks and eat liquid porridge, yogurt, and soups. Over the next few days, you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- food must be at a comfortable temperature; hot and too cold food is prohibited, including drinks;
- it is necessary to exclude solid foods that can injure the gums;
- You need to chew food on the side that has not undergone surgery;
- After each dose, you need to rinse your mouth with a warm saline solution;
- If your immune system is weakened, you can take additional multivitamins.
It is better to refuse or limit sweet, spicy foods, alcohol, and carbonated drinks.
Complications of edema and methods of dealing with them
Often, swelling is accompanied by one or more complications from the list below:
- bleeding. A little bleeding is normal. If there is more blood, the wound can be pressed with a gauze pad moistened with an antiseptic (for example, Chlorhexidine). If bleeding does not go away for more than 2 days, you should not delay visiting a doctor;
- numbness. After any dental procedure, the area around the mouth may lose sensation. There is nothing wrong with this if the side effect goes away within 12 hours;
- the occurrence of pain, which is acceptable even after surgery. The main rule is that pain should decrease within a couple of days. In some cases, the pain can be so severe that a person cannot chew food (the condition should last no more than 5 days). To alleviate this condition, you can take painkillers (for example, paracetamol);
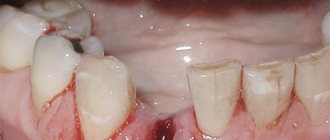
- the occurrence of a dry socket after surgery (especially important for smokers). In this case, a blood clot, without which the healing process is impossible, does not form. The condition is often accompanied by a feeling of pain and an unpleasant taste in the mouth. The most effective way to combat it is to wash the wound several times a day, followed by applying an antiseptic bandage.
How to rinse your mouth after wisdom tooth removal
The first few hours after extirpation, rinsing is strictly prohibited. This can lead to the natural plug being washed away, exposing the socket and bone. If bacteria penetrate inside, alveolitis or osteomyelitis will develop.
From the second day, carefully, not intensively, rinse your mouth with various antiseptics:
- chlorhexidine;
- miramestin;
- furatsilin;
- diluted potassium permanganate.
At home, you can prepare a solution with salt, soda, and add a few drops of iodine to the water. Herbal decoctions with sage, eucalyptus, chamomile, calendula, and oak bark perfectly relieve swelling and inflammation.
How to prevent complications?
To avoid swelling and subsequent treatment, it is recommended:
- Keep your head held high for at least 12 hours after surgery (or better yet, 24 hours). To do this, while lying down, you need to place several pillows under your head;
- do not touch the hole with your tongue or fingers;
- do not use warm compresses for 36 hours after surgery;
- do not smoke or drink alcohol for 72 hours after surgery.
Correct behavior after surgery is no less important than the procedure itself: if you adhere to the above rules, the swelling will go away either in the shortest possible time or will not occur at all.
How long does it take for gums to heal after wisdom tooth removal?
It is impossible to answer this question unambiguously, since the answer depends on the following factors:
- difficulties of extirpation - with a simple procedure, the tissues are minimally injured, which means the hole will heal within a few days; with incisions in the gums, the tissues heal for several weeks;
- age - faster for young people;
- the presence of complications, inflammatory processes that delay healing indefinitely until the infection is eliminated;
- compliance with doctor's instructions for the rehabilitation period;
- individual characteristics of the body.
When the tumor is predetermined
Everyone knows that you need to go to the dentist when a tooth just begins to bother you. But in real life this does not always happen. The result is tooth extraction as a last resort. And since treatment cannot be carried out, it means that there are serious problems in the oral cavity. Even when absolutely healthy tissues are damaged, for example by a cut or an injection, they swell. Moreover, a tumor occurs if the extracted tooth was adjacent to infections of the oral cavity or there are other dental problems.
Swelling after tooth extraction is inevitable if there are infectious processes in the oral cavity
By the way. The duration and intensity of swelling after extraction directly depends on factors such as the qualifications of the dental surgeon, the choice of anesthesia method, types of anesthesia, the complexity of the surgical operation, and the quality of the antiseptic used.
Table. Causes of soft tissue tumors
| Reason for swelling | Description |
| Alveolitis | A disease in which the socket of an extracted tooth becomes inflamed due to infection. It is not necessary that microbes are introduced into the socket due to non-compliance with the operation protocol (although such cases have occurred). Alveolitis after extraction often occurs against the background of existing inflammatory processes, the most common of which are periodontitis and stomatitis. After removal, the infection will spread and develop with renewed vigor. In addition to the inevitable swelling, the patient will feel severe pain and a bad smell will come from the mouth. |
| Difficult removal with incision of gum tissue | To remove a problematic tooth during an active purulent process, you must first release the pus. To free the gum tissue from the pus sac and remove the abscess, it is necessary to cut the gum. Only after this can the surgeon remove the tooth cleanly, along with the roots. Of course, additional trauma to the gum in the form of a cut increases the swelling that forms after extraction. |
| Traumatic extraction | Occurs when a dystopic (improperly located, growing at an angle, protruding from the dentition) tooth is subject to removal. To remove such a tooth, which is practically healthy, firmly embedded in the gingival tissue, and is subject to extraction only due to its dangerous location for other teeth or mucous membranes, significant efforts will be required. The gums swell very much when such a tooth is literally “torn out” from the jaw. |
| Deep extraction | Typically, it is subjected to rear molars, or simply teeth that have not fully erupted (impacted) for various reasons. After this procedure, severe postoperative swelling is inevitable. |
| Presence of chronic diseases not related to dentistry | Swelling may be increased if there are health conditions such as diabetes or hypertension, blood and vascular diseases, or low immunity. In this case, the extraction is always more difficult and is accompanied by painful swelling of the tissue. |