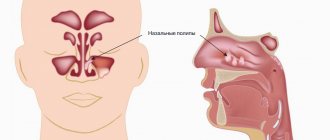
Polyps in the throat have many manifestations; the most commonly diagnosed are benign neoplasms located on the tonsils and vocal cords. The period of polyp growth can last up to several years, so when they appear, you should contact a specialist to undergo diagnostics and determine treatment tactics.
When patients come to the Yusupov Hospital with any symptoms of this disease, the oncologist conducts an examination and prescribes diagnostic procedures to identify the shape, size and location of polyps. After examination, polyps in the throat are quickly and painlessly removed by surgeons.
Causes of development of polyps in the throat
Experts have identified many factors that provoke the development of polyps in the throat, but the causes of this disease have not been fully studied. Polyps on the throat ligaments, tonsils and larynx develop as a result of the following reasons:
- allergic reactions, the source of which cannot be eliminated;
- regular overstrain of the vocal cords when singing, shouting, whispering;
- drinking alcoholic beverages and coffee that irritate the mucous membrane;
- smoking;
- inhalation of heavy metal impurities during work;
- hereditary predisposition;
- dysfunction of the thyroid gland.
An oncologist at the Yusupov Hospital, when a patient comes in with this problem, conducts an examination and determines whether it is dangerous to leave a polyp in the throat unattended, and what methods are necessary to treat it.
Benign tumors of the oral cavity
Fibroids . Oral fibroids are most common in the lower lip, tongue, and palate. They look like a smooth oval or round formation, in some cases located on a stalk. The color of these oral cavity tumors does not differ from the color of the surrounding mucosa.
Fibromatosis of the gums . Not all authors classify gingival fibromatosis as a tumor of the oral cavity; some believe that it is based on inflammatory changes. Fibromatous growths are painless, dense formations. They can be local in nature within several teeth or diffuse, involving the entire alveolar process of both the lower and upper jaw. Tumor growths in fibromatosis are localized in the gum papillae and can be so pronounced that they completely cover the crowns of the teeth. This type of oral tumor requires differentiation from hyperplastic gingivitis.
Myomas . Develop from muscle tissue. Rhabdomyomas are formed from fibers of striated muscles. Most often they are observed in the form of single nodular formations in the thickness of the tongue. Leiomyomas develop from smooth muscle fibers and are usually located on the palate. Myoblastomas (Abrikosov tumor) are the result of disembryogenesis and are diagnosed in children under one year of age. They are a round tumor of the oral cavity up to 1 cm in size, covered with epithelium and having a shiny surface.
Myxomas . These oral tumors may have a round, papillary, or bumpy surface. They are located in the area of the hard palate or alveolar process.
Pyogenic granuloma
. Develops from the mucous or connective tissue elements of the oral cavity. Often observed after injury to the mucous membrane of the cheeks, lips or tongue. Pyogenic granuloma resembles richly supplied granulation tissue. It is characterized by a rapid increase in size up to 2 cm in diameter, dark red color and bleeding when touched.
Epulis . Benign tumors of the oral cavity located on the gums. They can grow from the deep layers of the gums, periosteum, and periodontal tissues. Epulis occurs most often in the area of the front teeth. They are classified into fibrous, giant cell and angiomatous formations.
Neuromas
. They are formed as a result of the proliferation of Schwann sheath cells of nerve fibers. They reach 1 cm in diameter. They have a capsule. Neuromas are practically the only tumors of the oral cavity that may be painful on palpation.
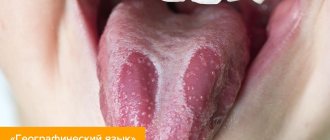
Polyps in the throat: photos and descriptions of tumors
Polyps in the throat, the symptoms of which depend on the size and location of the tumor, are formed by connective tissue, cellular elements and a small amount of fluid. Polyps are located in the throat on a thick stalk; they can have a white, pink or gray tint.
Some people who exhibit symptoms of this disease look at the laryngeal polyp in the photo and study the characteristic signs. Oncologists and otolaryngologists recommend not to carry out independent treatment of tumors, as it can cause chronic sore throat, infectious processes and irreversible changes in the voice.
The Yusupov Hospital uses modern methods for treating laryngeal polyps, which have successfully proven themselves in world medical practice. Highly qualified specialists remove the laryngeal polyp painlessly.
Complications
Nasal polyps can lead to complications because they interfere with the free passage of air and the drainage of mucous secretions from the sinuses.
Possible complications with nasal polyposis:
- Obstructive sleep apnea. In this condition, prolonged pauses in breathing occur during sleep, which increases the risk of cardiovascular disease and sudden cardiac death.
- Progression of bronchial asthma. Polyposis can aggravate the course of bronchial asthma.
- Sinus infection or infectious complications of chronic sinusitis. Nasal polyps increase the frequency of exacerbations of sinusitis and can lead to serious complications (for example, meningitis, orbital phlegmon, sepsis).
Polyps in the throat: symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of polyps in the throat can be combined with manifestations of the underlying disease. Without exacerbation under the influence of negative factors, polyps do not appear in any way, so they may not be detected by patients for a long time.
With increasing polyps and frequent trauma, tears may occur, which worsen the patient's condition. A laryngeal polyp may have the following manifestations:
- pain when the vocal cords are tense;
- hoarseness of voice;
- feeling of a foreign summer;
- increased salivation;
- cough mixed with blood;
- pain syndrome in the neck area.
The Yusupov Hospital employs experienced oncologists who, when examining patients who complain, identify tumors in the throat. When visiting an oncology clinic, a patient can quickly and comfortably undergo an examination without queues at a convenient time by appointment.
Localization
The location of polyps in the mouth area may vary. The tumor can be located on the inner surface of the cheeks and lips, in the sublingual area, or on the tongue.
Location on cheeks
Polyps on the cheeks can reach impressive sizes, interfere with the chewing process, and are constantly injured by teeth when grinding food. Such neoplasms often bleed, are prone to generalized spread, and are distinguished by a variety of forms and morphological structure.
Localization on the palate
When large polyps are located on the surface of the upper or lower palate, the swallowing process is disrupted and it becomes difficult to grind food when chewing. Often the pathological process tends to spread.
Any localization of polyps in the mouth is accompanied by serious risks:
- traumatization,
- bleeding,
- infections,
- association with various diseases of the mucous membranes.
Polyp in the throat: treatment
Modern specialists offer various ways to treat polyps in the throat. Drug therapy can improve the general condition of the patient, but it does not ensure the resorption of polyps. If a patient is found to have polyps in the throat, the symptoms and treatment of which depend on the size of the tumor, the oncologist at the Yusupov Hospital selects the most gentle and effective methods for eliminating them.
Polyps localized on the mucous membrane of the tonsils, vocal cords and larynx require surgical removal. For small polyps in the throat, minimally invasive techniques are used, allowing the patient to return to active life on the day of surgery.
If treated incorrectly, there is a high risk of relapse. To eliminate tumors in the throat, you should contact highly qualified specialists at the Oncology Clinic of the Yusupov Hospital, who will perform high-quality surgical removal of the polyp.
Treatment of nasal polyposis
Treatment of chronic inflammation of the sinuses (with or without polyps) is a difficult task that requires complex treatment.
A team of doctors (therapist, allergist-immunologist, otolaryngologist) must participate in the treatment of the disease in order to determine an effective treatment regimen.
The goal of treatment for nasal polyposis is to reduce the size of the polyps or eliminate them. The first step begins with drug therapy. If the effectiveness of drug therapy is low, surgical treatment is resorted to. It does not provide complete recovery, but significantly improves the course of the disease. Therefore, it is necessary to continue conservative treatment in the postoperative period.
Use of medications for nasal polyposis
Treatment begins with drug therapy, which helps to reduce or disappear even large polyps.
Drug treatment usually includes:
- Nasal corticosteroids
Nasal corticosteroids have a predominantly local anti-inflammatory effect. They are used in the form of nasal sprays (with mometasone, beclomethasone) and help reduce nasal polyps.
- Systemic corticosteroids
If the administration of nasal medications is not effective, then systemic corticosteroids (dexamethasone, prednisolone, etc.) are prescribed orally or by injection. Because corticosteroids taken by mouth or by injection carry a risk of serious side effects, these drugs are not prescribed for long periods.
- Other medicines
The doctor may also prescribe other medications that affect inflammation of the mucous membrane. They may include various drugs for the treatment of allergic pathology (leukotriene receptor blockers, antihistamines, cromoglycates), antibacterial drugs for the treatment of prolonged or recurring infections.
Polyp surgery
If drug treatment does not shrink or eliminate polyps, endoscopic surgery may be required to remove them and correct sinus problems.
In the endoscopic technique, the surgeon uses a special optical tube that magnifies and displays an image of the operated area on a screen. Under visual control, the surgeon, using specialized micro-instruments, removes polyps and other obstructions from the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses that interfere with the outflow of fluid from the sinuses.
The surgeon may also enlarge the openings connecting the sinuses to the nasal cavity.
After surgery, it is recommended to use a corticosteroid nasal spray, as well as regular rinsing with prepared saline solutions, to help prevent recurrence of nasal polyposis.
Removal of a polyp in the throat: price
The cost of surgical treatment of a polyp in the throat depends on the method of intervention, stage and other factors. The price of this service is determined after a comprehensive diagnosis in accordance with the current price list at the Yusupov Hospital. Each patient has the opportunity to receive complete information about the scope of treatment measures and their cost.
For patients diagnosed with throat polyps, oncologists develop an individual treatment plan. The key to high quality medical services provided to patients at the Yusupov Hospital is an integrated approach to solving this problem.
Diagnostic measures
If you experience discomfort in the mouth area, you should conduct a self-examination. To do this, you will need to open your mouth wide, provide good lighting and examine the condition of the pharynx in the mirror. If necessary, you can use a small mirror to reflect hard-to-reach places (for example, the inner surface of the cheeks).
A professional examination is considered to be a dental examination using special instruments. The doctor will assess the condition of the oral cavity, exclude abscesses and cysts, especially if polypous lesions are localized in the gingiva.
In the absence of obvious dental problems, the patient is referred for consultation to a therapist and oncologist.
On examination:
- palpate regional lymph nodes,
- an ultrasound examination is prescribed,
- x-ray,
- MRI or CT diagnostics.
These methods make it possible to assess the degree of proliferation of the mucous membranes and determine the malignancy of the tumor at the earliest stages. An important examination is a biopsy of polypous lesions in the mouth and histological examination.
Among additional tests, it is necessary to collect urine, blood, and feces to exclude various diseases that could serve as a trigger for the formation of polyps. Often, eliminating the cause of the formation of polypous lesions promotes their independent “resorption.”
An important aspect in diagnosis is the study of the patient’s clinical and life history. If close relatives have oral cancer, a mandatory histological examination for cell atypia is required.