Inflammation of the gastric mucosa caused by poor diet, negative effects of bacteria, and alcohol abuse is called gastritis. Types of gastritis are manifested by various symptoms, one of which is plaque on the tongue. This symptom may belong not only to gastritis, but also to other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and other organs.
These can be liver pathologies, dehydration, side effects of medications, as well as intoxication and dyes from food products. In order to correctly diagnose the plaque that appears on the tongue during gastritis, you need to become familiar with the features of this symptom.
What does a healthy tongue look like?
The tongue is pale pink - absolutely healthy.
Diagnosis by the appearance of the tongue was mastered by ancient healers, who believed that a disease could not be considered cured until the patient’s tongue regained its previous appearance. The tongue of an absolutely healthy person has the following signs:
- Pale pink color;
- Small taste buds without pronounced features;
- No bad breath;
- Be moderately moist;
- The presence of a small amount of translucent bright pink coating is allowed;
- There is no unpleasant odor.
If you deviate from these signs, you should consult a general practitioner or gastroenterologist and undergo the examination prescribed by him.
Features of diagnosis and treatment of pain under the tongue
Treatment of pain in the sublingual area should be carried out after a high-quality diagnosis to determine the root cause of the problem. Sometimes, pain in the frenulum under the tongue or in the surrounding tissues is treated by therapists or allergists, but in most cases this is done by dentists, because about 90% of all cases of treatment are associated with a dental problem.
Diagnosis of pain under the tongue is carried out in several stages:
- Initial appointment - the doctor collects anamnesis, finds out information about the nature and location of pain, and also examines the patient’s oral cavity;
- A complete diagnostic examination is carried out in the absence of characteristic symptoms of common dental diseases. It is possible to use hardware techniques (X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.);
- Differential diagnosis – a specialist differentiates the underlying pathology from similar diseases;
- Making a diagnosis and prescribing treatment - based on the data of the initial examination and diagnosis, the doctor establishes an accurate diagnosis and prescribes an adequate treatment regimen.
Note! The method of treatment and the choice of drugs to eliminate pain in the sublingual area directly depend on the root cause of the symptoms. For example, if your frenulum hurts due to a mechanical injury, antiseptic and anti-inflammatory solutions for mouth rinsing will be prescribed, including: chlorophyllipt, hexoral, stomatophyte, alcohol tincture of calamus, stomatidine or others. If the pain is associated with the development of bacteria or fungi, antibacterial, antifungal and anti-inflammatory therapy is prescribed.
Signs of deviations from the normal state of the tongue
It is quite possible that, once you look at your tongue, you will see a rather unsightly picture. Symptoms of deviation from the norm:
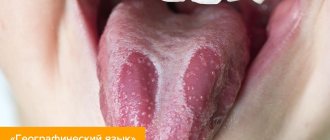
- A coating of various colors, thicknesses, and with different locations of spots appears on the back of the tongue;
- The sides of the tongue are bright red;
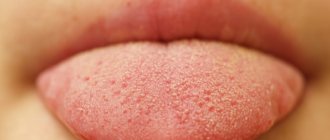
- The taste buds look uneven, some of them increase in size and begin to disturb with unpleasant sensations, taste sensations change, their intensity weakens;
- The oral cavity becomes unusually dry;
- In some cases, the appearance of pain and burning is diagnosed;
- There is an unpleasant odor from the mouth;
- After cleaning the tongue, the plaque appears again after a short time.
In the plaque that appears on the tongue, laboratory testing can reveal leukocytes, pathogenic microflora, and exfoliated epithelial cells.
This video will tell you about plaque on the tongue due to gastritis:
Burning mouth - treatment
The main goal is to eliminate the root cause found at the diagnostic stage. If it is not associated with dental pathology, the oral cavity is sanitized, worn fillings are removed and new fillings are placed, and dentures are corrected. Stomatitis and glossitis often require antibiotics. Candidiasis is treated with antifungal drugs.
General diseases are treated by a doctor of appropriate specialization, prescribing complex treatment depending on the type of pathology. Measures are being taken to improve immunity, normalize stomach function, stabilize blood glucose levels, and treat neuroses.
At home, you can alleviate the condition by rinsing your mouth with warm infusions of oak bark, sage, and chamomile. 1 tbsp is enough. per standard glass of water. Brew like tea, let cool and rinse your mouth 2-3 times a day. To prevent a burning sensation in the mouth, avoid or at least minimize spicy foods and caustic ingredients in your diet; it is better to avoid alcohol altogether.
Diagnosis of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract by language
The tongue will tell you about gastrointestinal diseases.
Modern gastroenterology does not specialize in diagnosis based on the appearance of the tongue. However, an attentive person suffering from such pathologies can distinguish the symptoms of gastrointestinal diseases:
- Acute gastritis - a viscous, dense coating of white-gray color is visible on the entire surface of the tongue, with the exception of the tip and side parts. The mouth feels dry and has an unpleasant acidic taste. Perhaps, instead of dryness, increased salivation will appear. In acute gastritis, similar symptoms include heartburn and sour belching, cutting pain in the epigastric region 1-2 hours after eating, weakness, headaches, diarrhea, heaviness in the stomach. With inadequate treatment, acute gastritis becomes chronic.
- Chronic gastritis - light deposits on the tongue are replaced by occasional dark gray deposits. To the previous symptoms are added such characteristic signs of chronic gastritis as astheno-neurotic syndrome, constant irritation, aching pain that intensifies some time after eating. About 40% of all cases of acute gastritis become chronic. This condition is fraught with the spread of the process to the duodenum and the development of gastroduodenitis.
- A stomach ulcer in combination with gastritis affects the condition and appearance of the tongue - its surface becomes bright red, with gray spots of dense plaque that are difficult to clean. This picture is complemented by signs of stomatitis and cyanosis. The patient feels a burning sensation and the production of saliva increases.
- Oncological damage to the gastrointestinal tract, as well as the presence of internal circulation, is reflected in the condition of the tongue by the appearance of evenly spaced white plaque of increased viscosity, excessive saliva production, and a burning sensation in the oral cavity.
Diagnostics
How to find out what exactly caused the burning sensation in the mouth and tongue? Only a specialist can determine the reasons. First you need to visit the dentist. If there are no visible local causes that could cause this problem, you need to go to a therapist. The patient will be prescribed tests (urine, blood - general analysis and sugar, biochemical studies). It is necessary to exclude sexually transmitted diseases and AIDS. It would be useful to consult an endocrinologist - perhaps it is due to hormonal fluctuations. Based on complete information, a preliminary diagnosis can already be made. Get ready for the fact that at the same time you will have to visit a gynecologist, nutritionist, infectious disease specialist, oncologist and doctors of other specialties.
Differentiation of plaque in gastritis from other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
A thick, grayish coating is characteristic of dysentery.
It is important to suspect the onset of a dangerous disease in time. To take action and prevent complications from occurring. Differential diagnosis by tongue of gastritis from other diseases and conditions:
- A thick, grayish coating is characteristic of dysentery. In this case, the tongue looks cracked, and less saliva is produced than usual.
- Desquamative glossitis - this type of inflammation of the tongue is characterized by such symptoms as red spots of complete absence of epithelium or several altered taste buds on the tongue, covered with a white coating.
- Galvanic stomatitis is a form of inflammation of the tongue that arises as a result of a reaction to metal prostheses, manifested by spots in the form of pimples, and subsequently by the appearance of erosions against a background of white plaque.
- Infectious diseases - sore throat, scarlet fever, diphtheria, HIV infection can cause the appearance of a white coating on the tongue, but almost all of these infections are accompanied by high fever and skin rashes.
- Diseases of the heart and blood vessels - plaque is located on the anterior third of the tongue.
- Kidney disease - plaque on the tongue is localized at the back along the edges.
- Endocrine disorders - under the plaques of white plaque there are ulcers and erosions.
- Anemia is not a coating on the tongue, but blanching of the entire surface of the organ. Diseases of the respiratory system are often indicated by the localization of white plaque on the front and along the edges of the tongue.
- Diseases of the salivary glands - the appearance of a white coating is accompanied by the appearance of an unpleasant odor.
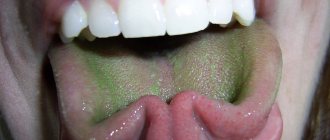
- Diseases of the liver and gall bladder - the color of the plaque is not white, but has a yellowish or brown tint. A white coating on the tongue can be caused by the consumption of dairy products, as well as the proliferation of bacteria and fungi in those who abuse sweets. Unlike plaque during gastritis, such layers are easily removed and do not form further.
Symptoms
Symptoms of the disease can be purely individual in each specific case, since we have already determined that the main cause of its occurrence is disorders of brain activity. Most often, after seeing the patient, examining and conducting a series of tests, doctors make a diagnosis of “mixed type glossalgia,” which implies a lot of possible causes for the formation of the disease.
And yet there is a small list of symptoms common to most patients diagnosed with this disease:
- the mucous membrane and shape of the tongue remain externally unchanged, while the patient feels an unpleasant burning sensation, tingling and even numbness of part or all of the tongue;
- occasionally the same symptoms appear in the area of the hard palate, cheeks and lips;
- the sensations described above can be either temporary or permanent, turning, in fact, into a chronic disease;
- many patients complain of difficulties when communicating, since the tongue gets tired very quickly during a conversation;
- approximately thirty percent of patients experience constant dry mouth, which is not eliminated even by drinking plenty of fluids;
- very often symptoms worsen before important events in the patient’s life;
- the localization of painful sensations is not permanent. The location of the lesion may change with each new attack;
- in most cases, patients with this disease experience depressive and apathetic states, sleep disturbances, or, conversely, signs of aggression and sociopathy.
If glossalgia is not treated, there is an equal probability of both its complete elimination and transition to a chronic stage.
Is plaque on the tongue dangerous - how to treat it
An ultrasound of the stomach will help clarify the diagnosis.
Plaque itself does not pose any threat to health. As soon as the underlying disease is cured, the condition of the tongue will return to normal.
As for gastritis, long-term treatment with careful adherence to the recommendations of a gastroenterologist will help relieve its symptoms.
Perhaps the doctor will conduct research aimed at clarifying the diagnosis: FGDS, ultrasound of the stomach, laboratory tests of blood and gastric juice. The following drugs will be prescribed as treatment:
- Antibiotics of 2-4 types, taken in combination:
- Pro- and prebiotics;
- Vitamins;
- Antacids;
- Proton pump blockers.
Patients with gastritis must follow a strict diet aimed at sparing the gastric mucosa and not provoking the release of excessive amounts of hydrochloric acid. With this treatment, not only the gastric mucosa, but also the condition of the tongue will definitely return to normal.
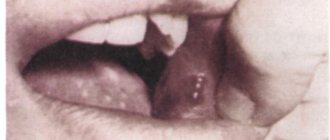
Causes of pain under the tongue
Modern medicine knows dozens of different reasons that can cause unpleasant and painful sensations under the tongue in an adult, teenager and child: from a banal mechanical injury to the frenulum, leading to tissue damage, to allergic reactions causing swelling. At the same time, there is a list of the most common causes observed in most patients.
The main causes of pain under the tongue:
- Mechanical injuries to the frenulum and muscle tissue are the most common cause of sublingual pain. As a rule, it is observed in people with a short frenulum. It is injured due to stretching, as well as in the event of mechanical trauma to tissues, for example, during eating, hygienic brushing of teeth, etc.;
- Dental pathologies of the oral cavity – stomatitis, dental problems (caries, periodontitis, periodontitis), gumboil, etc.;
- Infectious inflammation of the oral cavity - pain often manifests itself with sore throat. During this period, it is painful for a person to eat, swallow water and saliva, stick out his tongue or simply chew;
- Cellulitis or abscess of the floor of the mouth is a significant accumulation of pus in a small area of the floor of the mouth. Causes “bursting” of internal tissues, putting pressure on peripheral nerves - this provokes pain and tactile discomfort;
- An allergic reaction can be the body’s response to various irritants. Causes swelling of the soft tissues of the oral cavity, accompanied by discomfort or pain in the sublingual area;
- Asymmetry of the hyoid bone - an anatomical disorder in the growth of the hyoid bone, can provoke excessive or nonspecific pressure on the peripheral nerves, causing pain;
- Neuralgia is a general disease of the nervous system that manifests itself in its various parts. It is often a consequence of nervous shock and is accompanied by a feeling of painful numbness in the oral cavity;
- Diseases of internal organs and body systems - some areas of the tongue may reflect (irradiate) pathologies of internal organs, which is accompanied by painful sensations in the sublingual area;
Note! Most of the above problems that provoke the development of pain in the sublingual area can be caused by bacterial infections (streptococci), fungi (candidiasis), and herpes.