General recommendations
Extirpation ends by placing a cotton swab on the operated area. If the bleeding is minor, it can be removed after a few minutes. In case of increased bleeding, it is allowed to keep the cotton wool for up to half an hour; if the process continues, the doctor uses hemostatic drugs. When the cotton wool is held for too long, the blood clot may stick to it and fall out, and the socket with the bone will lose its natural protection from the external environment.
How to stop bleeding after tooth extraction at home:
- apply a special hemostatic sponge (sold in a pharmacy);
- make a tight swab from sterile gauze, apply to the hole and bite;
- if the problem is caused by increased blood pressure, then you need to take appropriate medications;
- use ice or frozen foods pre-wrapped in a towel as a cooling compress.
Smoking after tooth extraction is unacceptable, since cigarettes contain nicotine, which constricts blood vessels. As a result of this action, the cells do not receive the required amount of oxygen and nutrients, so the regeneration processes slow down, the risk of infection increases, scarring and improper tissue fusion are possible.
On the day of surgery, you should not rinse your mouth, engage in sports or other physical activity; it is best to go home from the clinic and rest. Routine oral hygiene or rinsing is not recommended.
In nutrition, preference should be given to soft, liquid and warm foods.
What medications are needed?
Antibiotics after tooth extraction are prescribed by the surgeon who performed the extraction. You can replace medications from the list with cheaper analogues, the main thing is that they have a wide range of applications, since there are different microorganisms in the mouth. Amoxiclav is often prescribed because it is effective and has a minimum of contraindications and side effects. The drugs are taken in the course determined by the doctor.
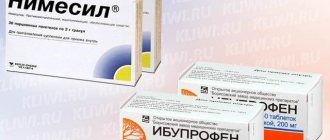
Anesthesia after tooth extraction lasts for several hours, after which pain appears, which can be eliminated with the help of analgesics. Anti-inflammatory drugs, for example Nimesil, and vitamins to strengthen the immune system can also be prescribed.
How to rinse your mouth after tooth extraction:
- chlorhexidine;
- a weak solution of potassium permanganate;
- furatsilin;
- miramistin;
- similar antiseptics.
In addition to pharmaceutical products, rinsing can be done with soda, saline solutions, decoctions of chamomile, sage, oak bark, calendula, and eucalyptus. They not only protect against infection, but also relieve swelling and accelerate tissue healing.
Temperature after tooth extraction is one of the possible symptoms, as tissues are injured and foreign elements penetrate the body. To improve your health, you need to take antipyretics.
My wisdom tooth hurts, what should I do?
According to statistics, it is wisdom teeth that most often cause problems.
Erupted “eights” are quickly affected by caries, and sometimes even remain in the bone tissue and in most cases cause discomfort. So what to do with a wisdom tooth when it hurts, haunting you day and night?
What is known about wisdom teeth?
They got their name because they begin to erupt between the ages of 18 and 30. Scientists consider them to be a vestigial organ that does not bear any functional load when chewing food for years. Therefore, at present, some people do not develop “eights” at all.
Their medical name is third molars. These teeth were originally designed for chewing rough food. This determines their specific structure (large root base, width) and strength.
But this is also the main root cause of painful processes during growth, because the larger the area of the upper edge, the more difficult it is to tear the soft tissues and pass through them. Moreover, the bone tissue has already been formed, so the “eights” need to literally break their way, which leads to the formation of edema, suppuration, tumors and other unpleasant consequences.
Typically, discomfort is caused by recumbent “eights”, which grow horizontally in the jaw. They don't have enough space to erupt and put pressure on neighboring teeth. As a result, the entire dentition shifts. Moreover, recumbent “eights” severely injure the gums, which leads to chronic inflammation.
Signs of wisdom teeth erupting
- Pain in the jaw, radiating to the ears and temples
- Inflammation, swelling and itching of the gums behind the last tooth
- Enlarged lymph nodes
- Temperature increase
- Painful swallowing
- Persistent runny nose
- Difficulty opening your mouth
- Halitosis, that is, bad breath.
The presence and nature of symptoms depends on the individual characteristics of the body. There are cases when a person does not experience discomfort or pain at all when teething: this means that the “eight” is growing correctly and does not interfere with neighboring teeth. But it is still necessary to visit the dentist, since the formation of pathology can occur in a hidden form.
What types of wisdom teeth are there? For “eights” that have difficulty erupting, there are special terms in dentistry - “dystopic” and “retained”.
Dystopic teeth are those that grow incorrectly due to lack of space in the jaw. Usually they are shifted towards the tongue, cheeks or located at an angle. Impacted teeth are unerupted teeth that remain completely in the bone. There may also be a state of semi-retention, when the tooth appears, but cannot fully erupt.
Why do wisdom teeth hurt and gums become inflamed?
Most often, pain occurs due to difficult eruption for several reasons.
- Dystopia. This is a situation where the figure eight grows incorrectly relative to the jaw due to lack of space. Trauma to the buccal mucosa, as well as the development of various bite deformities, can be the consequences of a dystopic tooth if it is not removed in time.
- Retention. This is a pathology in which the wisdom tooth erupts with a delay. In this case, the crown of the tooth can be partially cut through or completely hidden under the gum. Late eruption of the figure eight can negatively affect the patient’s general well-being.
- Pericoronitis. This is an inflammation of the gums that occurs when tooth eruption is difficult or incomplete. The reason for this is the development of infection under the hood of the wisdom tooth - this is the part of the mucous membrane that covers the tooth during eruption. The main symptoms of pericoronatitis are pain, swelling and redness of the gums.
- Caries and its complications (pulpitis, periodontitis). It is quite difficult to qualitatively remove plaque from the surface of a wisdom tooth, since the “figure eight” is located far away. As a result, caries occurs. Progressing over time, it can destroy the tooth quite severely and cause pain.
What to do if your wisdom tooth hurts?
The first and most important rule is to make an appointment with a doctor! Only a doctor can assess the severity of the situation. After the examination, you will be given an x-ray and given options for solving the problem.
If a tooth erupts and your gums hurt, what should you do?
If this pain is periodic and rather discomforting, then you can massage the gums, treat them locally with antiseptics and anesthetic gels (they will be mentioned below). As a rule, this is enough to relieve discomfort before visiting a doctor.
But sometimes a gum hood forms; the gums become swollen, inflamed, and the pain becomes more severe. What to do at home:
- sign up for an appointment with the doctor
- take an anti-inflammatory pain reliever - for example Nimesil or Nurofen.
- Take frequent baths with warm soda or saline solution
- rinse your mouth with a decoction of chamomile, calendula or sage
- treat with chlorhexidine 0.05% or miramistin
- Apply ointment "Cholisal", "Rapid" or "Asepta"
It is important, do not neglect hygiene; carefully use a brush and irrigator to thoroughly clean the surfaces of adjacent teeth. The more plaque accumulates (i.e. a breeding ground for microorganisms), the greater the inflammation.
Treatment for inflammation of a wisdom tooth
Between the chewing surface of the tooth and the hood, favorable conditions are created for the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria and the gums become inflamed. For minor inflammation, as first aid, you can rinse your mouth with an antiseptic and apply bandages with anti-inflammatory gel. These measures must be combined with taking anti-inflammatory and painkillers, but under the supervision of a doctor.
With significant inflammation, symptoms such as discharge of pus, severe swelling of the gums and cheeks, pain when swallowing, and fever are observed. In this case, you should immediately consult a doctor to avoid complications. Treatment is carried out by a dental surgeon. It consists of excision (incision) of the hood under local anesthesia and medicinal treatment of surrounding tissues. As a result, the suppuration goes away. Afterwards, antiseptic rinses and anti-inflammatory gels are also prescribed, and antibacterial therapy may be prescribed.
However, most often “wisdom” teeth are removed, because scientists have already determined that they are a rudiment that does not help us chew food, but much more often creates problems.
Wisdom tooth removal
This is a very common procedure.
Most often, the operation takes place on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia. It is possible to perform removal under oxygen sedation with nitrous oxide to reduce anxiety or under medicated sleep conditions.
Before the removal procedure, a thorough diagnosis is carried out, and, if necessary, antibacterial therapy is prescribed.
The removal itself is painless, as it is carried out using painkillers. But in the process, soft tissues are injured, so after the removal of the wisdom tooth and the cessation of anesthesia, the patient experiences pain. After a few days, the swelling finally subsides and the pain subsides.
This is also facilitated by the prescription of antimicrobial drugs. After removal, the doctor gives recommendations on nutrition, lifestyle and hygiene for several weeks. Compliance with all medical recommendations will help to avoid the development of complications and speed up the recovery process.
If your wisdom tooth hurts during pregnancy or while breastfeeding, what should you do?
You should contact your dentist at the first discomfort. At home, while waiting for a visit to the doctor, you can resort to safe local measures:
- Take frequent baths with warm soda or saline solution
- rinse your mouth with a decoction of chamomile, calendula or sage
The remaining medications will be prescribed by the doctor after consultation and examination.
In most cases, it is possible to solve the problem using gentle therapeutic methods and avoid urgent wisdom tooth removal during pregnancy.
If possible, the surgical procedure is postponed to a later time. Its implementation is undesirable due to possible side effects (stress, fever, painful rehabilitation).
But the dentist always focuses on the condition of the teeth in a particular case. He will try to save the tooth and delay the surgical procedure if possible. However, in case of severe inflammation, for example during a purulent inflammatory process, removal will be carried out urgently, since this contributes to the spread of infection throughout the body.
The source of infection poses risks much higher than when using medications during removal. Therefore, it is very important to solve the problem in order to avoid complications for the mother and her baby.
When breastfeeding a baby, the mother must carefully monitor her own health. If there is an infection, it can be passed on to the child, since communication with him is very close.
In addition, a bad tooth causes stress and is physically exhausting, and this can have a bad effect on the quality and quantity of milk.
If your wisdom tooth hurts during breastfeeding, the first thing you should do is visit a dentist.
As with pregnancy, the need for extraction is determined only by a doctor after a thorough diagnosis. X-ray examinations can be safely performed during breastfeeding.
If it is possible to postpone the date of the operation, then extirpation is carried out closer to the end of breastfeeding, since after the procedure you may need drugs that can penetrate into mother's milk. However, if the situation is serious and requires emergency intervention, the doctor will decide to remove it.
The procedure for a woman during lactation is no different from that performed for ordinary patients.
For local anesthesia, drugs approved for pregnancy and lactation are used. They do not contain toxic components that can cause allergies and other side effects. The issue of feeding a child should be discussed with a doctor. Local anesthetics practically do not enter the blood, and components penetrate into mother's milk in minimal quantities.
If the doctor has not prescribed other medications, then you can feed the baby within a few hours. But if antibiotic therapy is necessary after a complex removal, then breastfeeding will have to be stopped for several days.
Anesthesia is used only in extreme cases, if a complex and lengthy extraction is being performed. If general anesthesia is necessary, the child is temporarily transferred to artificial nutrition. During this period, the mother must express milk regularly to ensure milk production continues.
Prevention measures
It is virtually impossible to change the atypical arrangement of 8s. But you can prevent the pain that occurs during eruption through routine removal. In this case, unexpected pain can be avoided, and, as a rule, healing in the absence of inflammation proceeds better and faster.
Particular attention should be paid to a comprehensive examination at the stage of planning a new addition to the family.
Based on x-rays, the doctor will be able to tell how the wisdom tooth will behave during pregnancy. When unfavorable factors are identified, it is easier to remove extra eights in advance.
Since teeth decay faster during pregnancy, it is necessary to carry out proper oral hygiene and undergo a preventive examination by a dentist while carrying a child.
Doctors’ recommendations for healthy teeth are very simple and known to everyone, you just need to follow them:
- brush your teeth twice a day;
- rinse your mouth after every meal
- use dental floss;
- eat well;
- limit consumption of sugary foods
- Get regular check-ups with a dentist
The most effective way to avoid trouble is to monitor the condition of your oral cavity and follow these simple and effective recommendations. Be healthy.
If your gums are inflamed
It is not always possible to avoid infection of the wound surface, especially when the patient neglects the advice of the dentist. In case of inflammation, you should consult a doctor for examination and identification of the causes of inflammatory reactions.
If the hole is not closed after tooth extraction, alveolitis develops. The natural plug can come off due to intensive rinsing, licking the wound with the tongue, resumption of bleeding and improper actions to stop it. Alveolitis is accompanied by acute pain syndrome. Not only the injured area may hurt, but also the throat, head, jaws, and neighboring teeth.
How long the gums heal after tooth extraction depends on various factors:
- complications of surgical intervention;
- the presence of inflammation or other complications;
- age criterion, the older the patient, the longer the healing and tissue restoration takes place;
- state of immunity, individual characteristics.
WHEN KETANOV IS CONTRAINDICATED
Despite its high effectiveness, ketans should not be used by people with a number of diseases.
This drug is contraindicated in:
- individual intolerance;
- bronchial and “aspirin” asthma, bronchospasms;
- impaired kidney or liver function;
- congestive decompensated heart failure;
- diseases of the hematopoietic system and bone marrow (including hemophilia);
- serious gastrointestinal problems (exacerbation of ulcerative pathology, cirrhosis, hepatitis);
- in the preoperative period (due to the real risk of bleeding);
- for polyps in the nose or paranasal sinuses;
- in conditions after a stroke.
The use of this medicine is limited to:
- in case of blood clotting disorders, it is necessary to control the level of platelets in the blood (especially after operations);
- use requires caution in case of hypertension, diabetes mellitus, lupus erythematosus, sepsis;
- careful use for people in professions or occupations that require special attention or speed of reactions (including drivers, representatives of dangerous professions, tourists when traveling difficult routes, etc.);
- restriction of use to patients of the older age group (over 65 years).
APPLICATION OF KETANOV IN CHILDREN'S PRACTICE, PREGNANT AND NURSING WOMEN
During pregnancy or lactation, as well as during childbirth, the drug is contraindicated for use. Ketanov should not be given to children for toothache. It is used only for adults (patients over 16 years of age). In exceptional cases, the medicine can be used to relieve severe pain in children from 2 years of age.
INTERACTION WITH OTHER SUBSTANCES
With the simultaneous use of ketanov and certain drugs, toxic effects on the body and increased side effects are possible.
Such drugs include anticoagulants (aspirin, heparin, etc.), lithium drugs, and other drugs with a similar effect.
The combination of Ketanov with other drugs requires consultation with a doctor. It is prohibited to use Ketanov with any type of alcohol. “Ketanov + alcohol” will deal a severe blow to your liver.
What and when to eat
During the rehabilitation period, food should be soft, mostly liquid, and have a comfortable temperature. How much you can’t eat after tooth extraction depends on whether there is heavy bleeding or not. If blood clotting is normal, then a protective clot is formed and securely attached within 2 to 3 hours. After this, the restriction is lifted. With complex extraction, the time can increase to 4.6 hours.
It is advisable to exclude spicy, sweet foods, carbonated drinks, alcohol, raw vegetables, fruits with a high acid content. Chewing is carried out on the opposite side of the jaw. It is better not to eat rough, hard food, as you may accidentally touch the wound.
THERAPEUTIC ACTION
Ketanov is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug with systemic effects with a particularly powerful analgesic (pain-relieving) effect.
When administered, it has a triple effect on the body:
- relieves heat and inflammation;
- has an analgesic effect.
However, it is the super-powerful analgesic effect that allows this medicine to be used for unbearable toothache.
DOES KETANOV HELP FOR TOOTH PAIN?
The drug has a very powerful peripheral effect. It is this effect of the medicine that “eclipses” all its other qualities. Ketanov is a non-narcotic analgesic substance with an excellent analgesic effect.
Ketanov helps with toothache much more strongly than other drugs from the same group.
For example:
- butadione – 453 times;
- analgin – 350 times;
- nalgesin – 50 times;
- indomethacin – 5 times.
Obviously, the most powerful peripheral effect of Ketanov compared to other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. That is why this medicine is a powerful means of relieving various pains, including those caused by traumatic or postoperative conditions.
KETANOV'S WORK IN THE BODY
The medicine inhibits the activity of special enzymes, as a result of which the production of modulators of inflammation, pain and thermoregulation is suspended. The analgesic power of the drug is equal to that of morphine-like substances. On average, the onset of action of the drug is half an hour after intramuscular administration and an hour after using the tablets.
Ketanov does not cause:
- disorders in breathing or nervous system;
- the appearance of vomiting or nausea;
- urinary retention and bowel function;
- increased pressure;
- increased heart rate;
- drug addiction.
Ketanov is able to accumulate in the liver tissue and penetrate into breast milk.
It is excreted through the urine and partially through the intestines.
Oral hygiene
It is not carried out on the first day to exclude infection and accidental injury. Chlorhexidine can be used almost immediately after tooth extraction, as it does not cause side effects; the main thing is to rinse carefully and according to the instructions. Further hygienic cleaning can be performed once a day with a soft brush, carefully avoiding the surgical area.
Floss is also used to remove food debris from between teeth and a warm saline solution is used to rinse the mouth after each meal. Do not forget about cleansing your tongue, as plaque also accumulates on it, in which bacteria actively multiply.
Removal of sutures after tooth extraction occurs on the 7th - 10th day. By this time, the wounds have already healed and restrictions on hygiene procedures are lifted. Cleaning is carried out twice: in the morning and in the evening.
WHAT ARE THE ADVANTAGES OF THE DRUG
The main advantages of Ketanov are its following features:
- the ability to relieve severe pain of various origins, when other medications are helpless;
- minimum “side effects” when taken (compared to other painkillers);
- long-term analgesic effect (at least 6-8 hours);
- the possibility of abrupt drug withdrawal and the absence of addiction syndrome (withdrawal) even after a long course of administration (up to 6 months).
BY-EFFECT
Unfortunately, in some people this drug can cause a lot of unpleasant phenomena in the body. The most common of them include:
- dyspeptic symptoms (dry mouth, nausea or vomiting, inflammation of the stomach or exacerbation of ulcers, constipation or diarrhea, stomach pain);
- neurological changes (headache or dizziness, nervousness or excessive drowsiness, hyperesthesia of some parts of the body);
- from the ENT organs (sometimes it reduces hearing or provokes ringing in the ears, and can impair vision);
- therapeutic disorders (high blood pressure, slow heartbeat);
- from the urinary organs - swelling is sometimes possible.
Pathology and norm
With any invasive procedure, swelling occurs in the soft tissues. It goes away on its own within a few days. The same can be said about pain. Cheekbones, adjacent teeth, head, and neck may hurt. If after 3 or 4 days the symptoms do not disappear, but increase, then this indicates pathology.
What are the complications after tooth extraction:
- alveolitis, osteomyelitis, most often occurring with dry socket;
- inflammation near the seams;
- damage to the adjacent dental unit;
- perforation of the bottom of the maxillary sinus, if extraction is performed on the upper jaw;
- fracture of the alveolar process, sharp edges of the alveolus that injure soft tissues;
- neuritis of the inferior alveolar nerve;
- postoperative cyst;
- paresthesia, which is characterized by numbness, loss of sensitivity of the cheeks, tongue, jaw and other adjacent areas;
- ondogenic phlegmon, periostitis;
- a hematoma in the neck can occur in people suffering from arterial hypertension (blood leaks out of the vessels into the tissue);
- soft tissue abscesses.
Pus and flux after tooth extraction characterize an acute inflammatory process that requires urgent treatment. Purulent inflammation can occur with insufficient antiseptics during surgery or poor postoperative care, with a dry socket, when food particles get into the hole. A new surgical operation is required to remove necrotic masses.
When to see a doctor:
- on the second and third days the swelling does not subside, but the cheek continues to swell;
- the pain becomes more intense and is difficult to eliminate with medications;
- the high temperature lasts for several days, normally it should decrease within 24 hours;
- no appetite, nausea, weakness;
- when pressing on the gum, pus is released, and its edges turn red;
- when palpating the hole with the tongue, no blood clot is detected.
If inflammatory processes are started, this can lead to the melting of bone tissue, an abscess and the spread of infection.
How long does it take for a tooth to heal after extraction?
If the extirpation is successful and there is no bleeding, then on the second or third day the hole becomes covered with a grayish coating, and by the end of the week it becomes bright pink. When pressing on the gum, the exudate does not come out. The swelling completely subsides and the pain goes away. The processes of restoration of soft and bone tissues begin.
What not to do on the first day so as not to damage the formed clot:
- rinse your mouth intensively;
- lick the hole;
- blow your nose;
- spit;
- brush your teeth.
After two weeks, the mucous membrane acquires a healthy color, the hole is not visualized as a separate part, since by this time the epithelial layer is completely restored.
How long a wound heals after tooth extraction depends on the presence or absence of complications. If everything is in order, then after about a month the replacement of the void in the socket with bone and connective tissue is almost complete. We can talk about complete healing after 3 or 4 months. By this time, a smooth surface has formed in place of the removed dental unit, which does not in any way remind of the operation performed.
6. Medications after removal.
After the procedure, the doctor prescribes a number of medications to take. Under no circumstances should you take any medications on your own, without consulting a doctor.
Painkillers should be taken in case of pain, at intervals and in the amount recommended by the doctor. Each case is individual; it happens that the patient does without taking painkillers.
Antibiotics. In some cases, after removal, antibiotics are prescribed for 5-7 days. As a rule, these are situations when the doctor removes a tooth in the stage of inflammation, complex extraction or removal of several units of teeth. Only a specialist surgeon decides whether to take antibiotics or not.
Antihistamines. Reduces the likelihood of swelling.
Antiseptics. Used as a rinse. BUT, remembering that rinsing movements are prohibited in the first days. A small amount of solution is taken into the mouth and simply held in the mouth, then calmly spit out. Such baths must be done if the tooth was removed during the inflammation phase, if the flux was exposed, if there are teeth affected by caries in the oral cavity.