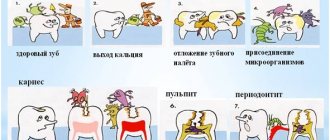
Why can caries complications occur?
Unfortunately, many people consider caries to be a harmless dental disease and seek help from a dentist only when they experience pain in their teeth. However, the appearance of pain in the tooth area indicates that the development of caries is taking its course, moving from a simple form to more and more severe conditions. According to the depth of the carious process, caries in the spot stage, superficial, medium, acute and chronic deep caries are distinguished - all this refers to uncomplicated forms. But complications arise when the lesion spreads deep into the tooth to the pulp (dental nerve) and bone tissue around it. At this stage, diseases such as acute, retrograde and chronic pulpitis and acute periodontitis, the main complications of caries, arise and progress.
Damage to the pulp or periodontium, as a rule, is a consequence of untimely contact with the dentist or poorly performed earlier filling or prosthetics, the so-called caries under the filling. From the formation of caries in the spot stage to the destruction of the pulp can take from 12 to 18 months, it all depends on the form of the course, that is, it can be acute caries or chronic caries. In any case, when demineralization has passed through the enamel and dentin, an infection enters the cavity of the crown and root canal, causing severe inflammatory and painful processes.
Causes and types of complications
The culprits in the development of caries and its complications are streptococcus bacteria – Streptococcus sanguis, mutans, viridans. These pathogenic microorganisms oxidize and destroy tooth enamel, and then penetrate deep into the hard tissue through the dentin canals.
In the absence of proper treatment, the infection affects the coronal part of the soft tissue, the pulp, and the first stage of complicated caries occurs - acute pulpitis.
Pulpitis
When the infection reaches the pulp, an inflammatory process begins in the neurovascular bundle of the tooth in the form of:
- acute focal;
- diffuse (general) pulpitis,
a characteristic symptom of which is severe, throbbing pain in the tooth and increased sensitivity to cold.
If you do not go to the dentist with pulpitis in the first 2-3 days, the acute stage of the complication becomes chronic and develops:
- fibrous;
- hypertrophic;
- concretory;
- or gangrenous chronic pulpitis.
With chronic pulpitis, the inflamed tissue of the neurovascular bundle degenerates and is gradually destroyed, dentin formation in the tooth stops, and it becomes dead.
Over time, decay processes reach the peri-apical tissues and ligamentous apparatus - periodontium.
Periodontitis
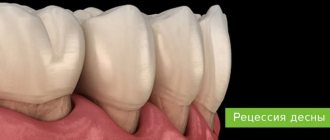
Between the root of the tooth and the alveolus there are periodontal tissues, they act as a shock absorber during chewing and hold the tooth in the socket.
With periodontal inflammation, periodontitis, the integrity of the tooth ligaments is disrupted, the jawbone becomes infected and damaged.
Symptoms of acute periodontitis:
- acute pain when biting or touching a tooth with the tongue;
- pain is transmitted along the trigeminal nerve - to the temple and jaw;
- general malaise, deterioration of health;
- increase in body temperature to 37-38 degrees.
The acute phase with severe pain lasts from 2 to 14 days, after which the disease takes on a chronic form.
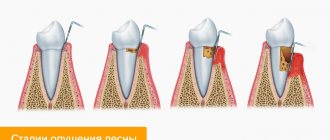
With chronic fibrous or granulating periodontitis, a fistula, that is, a through hole, can form in the gum. Patients also complain of a feeling of the diseased tooth moving out of its row and attacks of aching pain.
Granuloma
An advanced form of chronic periodontitis, granulomatous, leads to the formation of a capsule with exudate (pus) at the apex of the tooth - granulomas.
The gums of the diseased tooth become inflamed, patients complain of a feeling of bulging bone and persistent, severe pain.
A granuloma that is not eliminated in time can cause the formation of gumboil or a cyst at the root of the tooth.
Multiple caries
Another common type of complication is multiple (acute, blooming) caries, in which the infection simultaneously affects the coronal part of eight or more teeth.
In record time, caries destroys the enamel-dentin junction, penetrates the pulp and leads to tooth loss. The infection affects the cement on the roots of adjacent teeth, and the patient feels as if the entire dental arch hurts. Most often, multiple caries is detected in people with diabetes and preschool children.
How dangerous is caries in its advanced state?
So why is advanced caries so dangerous? Firstly, dental treatment in most cases will involve surgery, and any operation is always a risk: the risk of poor-quality treatment, the risk of swelling and other undesirable consequences. Secondly, serious exacerbations of caries will certainly affect your general well-being due to constant pain, which will be concentrated not only in the tooth area, but throughout the entire jaw, in the temples, ears and eyes, swelling of the gums and a sharp increase in temperature are also possible.
If caries is not treated and the pain is tolerated, the nerve of the tooth dies on its own and starts the process of decay in the carious cavity. The infection begins to penetrate deeper tissues, causing irreparable damage. The body begins to fight inflammation on its own, forming a granuloma around the tooth root, which can later increase in size and transform into a cyst. As you can see, the consequences of caries can be different, but one thing is clear - they are all serious and can have a significant impact on human health.
Features of diagnosing deep caries
Advanced caries often has the same clinical picture as pulpitis and some other dental diseases. Therefore, before starting treatment, the doctor must conduct a differential diagnosis and understand which pathology to treat.
Deep caries can be distinguished from focal pulpitis by a number of symptoms. With pulpitis, probing the cavity with a dental probe will cause pain only in one area - in the area of the pulp, while with deep caries pain occurs over the entire surface of the tooth.
The probing procedure will also help to distinguish deep caries from medium ones. On average, it is almost painless, because a fairly thick layer of dentin remains between the sensitive pulp and the bottom of the carious cavity. With a deep form, the tooth reacts to probing with severe pain. The method of electroodontodiagnostics helps to distinguish deep caries from fibrous pulpitis. In most cases, the doctor will order an x-ray to confirm the diagnosis.
What to do if complications have already occurred?
First of all, seek help from a dentist and do not put off visiting him for a day, even if you have already developed caries and are determined to have a tooth removed! Any tooth damaged by caries is a source of infection, which can spread to any area in the oral cavity, trachea or esophagus and cause a number of other diseases. In addition, the sooner you see a doctor, the greater the likelihood that the tooth can be saved.
If the clinic has modern materials and equipment important in the treatment of periodontitis and the treatment of pulpitis, you can count on a high-quality procedure. In particular, diseases such as advanced periodontitis and periostitis can also be cured, but only surgically. In general, traditional treatment consists of removing the nerve, thoroughly cleaning the canals and filling it. However, after such manipulations the tooth becomes more fragile. And do not forget that with the transition to a more complicated stage of caries, the price of its treatment also increases.
Risk factors for deep caries
Deep tooth decay with caries most often occurs in the presence of the following risk factors:
- Poor oral hygiene.
- Abuse of sweet and carbohydrate foods.
- Lack of calcium, fluorine, phosphorus, vitamin D in the body.
- Chronic pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine and immune systems.
- Genetic background.
And, of course, one of the main reasons for the development of deep caries is late diagnosis and untimely treatment.
Prevention of caries complications
Having encountered such a problem at least once, most likely, you will no longer want to exhaust your body with toothache and shell out decent sums for complex treatment. Therefore, you should not neglect preventive measures: visit the dentist once every six months and carry out hygienic cleaning. If, nevertheless, a hole has formed in the tooth and it becomes ill, you should choose a doctor with extreme caution. Remember that the result of poor treatment will be a more serious complication of caries, which may require surgery, and, worse, tooth extraction. In addition, complicated caries requires more expensive treatment than its initial formations.
Agree, you never thought that such harmless caries can cause serious consequences, including tooth extraction. Now think about what is cheaper, faster and more painless - going to the dentist for an appointment twice a year or postponing this moment for several years, then heading straight to the dentist’s office? It’s up to you to decide, of course, but life is given to enjoy joyful moments, and not to endure toothache. And dentists are ready to help us with this!
How can deep caries be cured?
A disease such as deep caries can be treated in one or two visits.
The first option is carried out according to this scheme:
- The doctor numbs the affected tooth with a local anesthetic.
- Opens the carious cavity and, using a drill, cleans it of dead and diseased tissue until dense walls and bottom remain.
- If caries is complicated by pulpitis, endodontic treatment is carried out, that is, the dental canals are filled.
- To treat inflammation, isolate the sensitive pulp from the effects of filling material, and build up dentin, a therapeutic or insulating pad is placed at the bottom of the cavity.
- After all the above manipulations, the tooth is closed with a filling.
Treatment in two visits is carried out according to this scheme.
During the first visit, pain relief is performed, the cavity is opened and the affected tissue is removed. A medical pad is placed in the cavity and closed with a temporary filling. On the second visit after a few days or weeks, if the patient has no complaints, the temporary filling is replaced with a permanent one.
Treatment in two visits is considered preferable because it is possible to observe the condition of the tooth before installing a permanent filling. If pain, discomfort and other symptoms occur, additional therapeutic procedures can be performed to ensure that the affected tissue is completely removed. When treating a tooth in two visits, complications and relapses of caries occur much less frequently.
Classification of caries by localization
Scientist Black (USA) developed a classification of carious cavities by location:
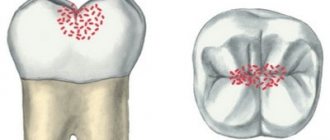
- Class I: damage to cavities in the area of fissures and natural recesses of the teeth;
- Class II: damage to cavities located on the contact surfaces of small and large molars;
- Class III: damage to cavities located on the contact surfaces of the incisors and canines without involving the cutting edge;
- Class IV: damage to cavities located on the contact surfaces of the incisors and canines, involving the cutting edge and corners;
- Class V: damage to cavities located in the neck area of all groups of teeth;
- Class VI: damage to cavities of atypical localization - the cutting edges of the frontal teeth and the cusps of the chewing teeth.
Treatment of caries, is it painful to treat?
Caries is a slow-moving pathological process occurring in the hard tissues of teeth, which develops due to the influence of certain external and internal factors.
At the initial stage of development, caries is characterized by focal demineralization of the inorganic part of the tooth enamel and its gradual destruction, affecting the organic matrix, as a result of which this leads to a violation of the integrity of the hard tissues of the tooth with the formation of cavities in the dentin, and in the absence of timely treatment - to the occurrence of inflammatory complications with side of the pulp, leading to periodontitis.
Treatment of caries is completely painless, since all dental procedures are performed under complete anesthesia.
Types of caries in front teeth
Oral microorganisms metabolize small carbohydrate particles. The organic acids formed in this process (lactic, acetic, propionic) significantly influence the occurrence of caries. First, a sticky and sticky plaque (plaque) appears, which consists of bacterial cells and an intercellular substance called the matrix. There are two types of dental plaque:
- Supragingival (siipragingi-valis). Causes caries and gum inflammation (gingivitis);
- Subgingival (subgingivalis). Causes the occurrence of periodontal diseases.
Supragingival dental plaque settles in hard-to-clean places that contribute to the occurrence of caries (retention zones). A film appears on clean enamel in which colonies of bacteria form. The plaque becomes mature and cannot be removed without special cleaning. Over time, under the influence of saliva, plaque turns into tartar, and underneath it, the enamel is destroyed and bacteria penetrate. First of all, the grooves and pits on the surfaces of the teeth, the approximal and cervical surfaces of the teeth are subject to caries.
A large accumulation of plaque above the gums leads to tooth decay
Caries between front teeth
Caries on the proximal surface is most common. Improper and untimely cleaning of the oral cavity leads to the rapid growth of plaque, which grows up and down, under the gum. Therefore, the carious cavity can be quite large, the tooth decay is so great that prosthetics are recommended.
Radical caries
The thickness of the enamel becomes thinner closer to the neck. Due to the anatomical structure of the dental crown, it is easier for colonies of bacteria to gain a foothold from below. Therefore, tartar forms here more often, and the carious cavity penetrates into the dentin much faster.
Contact
When there is not enough space in the plaque for an overgrown colony, it spreads to the neighboring tooth, “infecting it.” Usually, the adjacent tooth also has weakened areas of enamel, so caries begins there too.
Other types
There is still no single and universal classification of caries. Based on the analysis of clinical manifestations, as well as various forms of progression of caries of the anterior teeth, in addition to topographic (takes into account the anatomical localization, root, contact), we can also distinguish:
- dynamic caries (the degree of damage to the dental crown and root, as well as the speed of development of the disease are taken into account);
- chronological (takes into account the prevalence of caries depending on the age of the patient).