The baby has a facial cleft - how to care for him and rehabilitate him after surgery
We continue a series of publications devoted to neurosurgical diseases. The project was prepared jointly with the MBOO for helping children with neurosurgical diseases “He Needs You.” We want these “terrible” diagnoses not to put pressure on parents and not to take away their hope. In our publications, the best specialists and experienced parents will talk about ways to cure and overcome, give recommendations and show that life can go on with any, even such complex, diseases.
In our first publication on facial clefts, we highlighted the types of clefts and talked about the modern surgical approach to their treatment. In the second part, we will talk about the simplest things related to nursing a baby, which present certain difficulties for babies with clefts.
Cleft lip and cleft palate are not for life!
Let’s make a reservation right away: do not confuse maxillofacial surgery (maxillofacial surgery) with plastic surgery in its pure form.
Of course, they are inextricably linked and complement each other, but the goals and objectives of maxillofacial surgeons are different. One of the main ones is early correction of congenital cleft lip and palate in its various combinations. Simply put, this anatomical defect, due to its similarity with the structure of the corresponding organs in a hare and a wolf, is rigidly referred to in everyday life as “cleft lip” and “cleft palate.” In modern world medicine it is called cleft lip and palate. According to statistics, cleft lip and cleft palate account for the lion's share of all existing congenital facial defects, namely, according to WHO, this is 1 case in 700 newborns; in Russia, up to 2,600 babies are born with cleft lip and palate every year. Children with a similar defect from birth require increased care: special nipples should be used for feeding them and more carefully protected from external infections, since due to a violation of the anatomical structure they are more susceptible to any ARVI.
It happens that the defect in a cleft lip is insignificant and consists of a small pit or groove on the upper lip. However, most often, a cleft lip in newborns looks like a 1-2 cm or longer through defect in the upper lip, the end of the nose, widely communicating with the oral cavity. A cleft palate is a pronounced anatomical defect of its anterior part (hard palate) and/or soft palate (movable velum) with impaired breathing, swallowing and speech.
The defect will definitely become a traumatic factor for the child as soon as he grows up and realizes that he is different from his peers. The child’s parents should know that timely treatment and rehabilitation will help avoid these problems. The disease does not affect the child’s mental abilities in any way!
Today, thanks to the increased modern capabilities of medicine, children with cleft lip and palate have a real chance not only to live, but to live a quality life and successfully socialize in society.
What is the optimal time for correction of cleft lip and palate in children?
Our hospital specialists can answer this question briefly: the sooner the better. With one caveat: everything is decided individually for each child. This is a principled position with fundamental scientific justification.
Our interaction with a potential patient begins before he is born. Oral and maxillofacial surgeons are approached at the stage of intrauterine diagnosis of cleft lip and palate: at 18–20 weeks of pregnancy according to ultrasound results. If the presence of this malformation is confirmed, we explain to the mother that she has the opportunity to enter the Moscow maternity hospital, give birth safely under the supervision of specialists, and then, in the absence of any other severe pathology, in the first days of life the child will be admitted to our neonatal department. Here, after the necessary preparation, he will undergo reconstructive surgery to repair a cleft lip or palate.
Early correction is aimed at ensuring that the baby can quickly switch to natural breastfeeding, begin to fully suck, swallow, breathe, and subsequently talk. In our experience, the sooner treatment and rehabilitation are carried out, the faster all these vital functions are restored, and the child will be more successfully socialized in the future.
Yuri Olegovich Volkov
maxillofacial surgeon, candidate of medical sciences, head of the department of maxillofacial surgery of the Children's City Clinical Hospital named after. G.N. Speransky in Moscow
TREATMENT
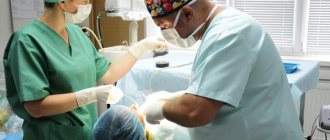
Treatment for cleft palate is only surgical. In early childhood, veloplasty (stitching of the soft palate) is indicated due to the small size of the oral cavity. Further, with the growth and development of the jaws, Limberg uranoplasty is performed. The postoperative regimen recommends careful oral care, eating exclusively pureed food, alkaline drinking, bed rest, and breathing exercises. After two weeks, a set of exercises and massage of the soft palate begin. To exclude postoperative infection, antibiotics are prescribed, and in case of severe pain, analgesics are prescribed.
Surgeries to correct cleft lip and palate in children
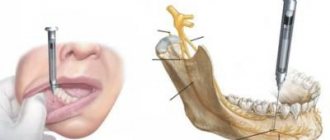
The main basic operations for the correction of congenital cleft lip are cheiloplasty and cheilorhinoplasty.* They differ in the volume and methods of surgical interventions performed, and are performed according to strict principles, but with individual characteristics.
To eliminate the cleft of the upper lip, reconstructive cheilorhinoplasty is mainly performed, which allows restoring the anatomical integrity of the organ while ensuring the functional component and creating optimal prerequisites for aesthetic well-being.
All surgical interventions are included in the basic compulsory medical insurance program and are absolutely free for parents of children from all regions of the Russian Federation.
- 1. Cheiloplasty.
An operation used for partial cleft lip without significant deformation of the nasal vestibule and its cutaneous-cartilaginous section. - 2. Rhinocheiloplasty.
The operation, used for complete cleft lips and in the presence of severe deformation of the nasal vestibule and its cutaneous-cartilaginous part, can be combined with periostoplasty for cleft lip, alveolar process and palate. - 3. Uranoplasty.
An operation used for partial and complete cleft palate, in which the hard palate and soft tissues of the velum are restored.
All operations are performed using multicomponent combined intubation anesthesia and last on average from 1.5 to 3 hours. The child's stay in the hospital is usually 8 - 10 days. Within 3–5 days after the operation, the swelling of the soft tissues subsides, the child’s condition improves, and he gradually adapts to new living conditions.
Our patients
Milan
| BEFORE AFTER | Diagnosis: rhinocheiloplasty Attending doctor: Bessonov Sergey Nikolaevich |
Vasilina
| BEFORE AFTER | Diagnosis: rhinocheiloplasty, uranoplasty Attending doctor: Bessonov Sergey Nikolaevich |
What diseases do oral and maxillofacial surgeons treat?
It would be a mistake to assume that maxillofacial surgery today is limited only to the correction of congenital malformations of the face. The range of problems solved within the framework of maxillofacial surgery is quite wide.
- Firstly,
inflammatory diseases of the maxillofacial area: abscesses, phlegmon, osteomyelitis of the jaws. - Secondly,
odontogenic and non-odontogenic benign neoplasms of the bones of the facial skeleton and soft tissues of the face (papillomas, fibromas, lipomas, etc.). - Thirdly,
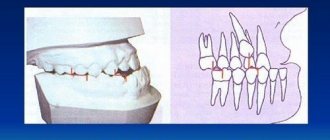
all kinds of defects and disorders of the formation of the dental system and bite.
A special problem in pediatric maxillofacial surgery is the elimination of the consequences of childhood injuries, the sad statistics of which are only growing over the years in all regions of Russia.
What are the most common maxillofacial injuries in children?
Injuries to children in the maxillofacial area can be roughly divided by periods of their lives.
At first, the baby is completely dependent on the parents and can only be injured due to their oversight (for example, falling out of the cradle). Then the child expands his living space: he begins to walk. Therefore, closer to the age of one year, the most common injuries to the soft tissues of the face are due to a fall from one’s own height. By the age of one and a half years, children begin to run, they are actively teething, and as a result of falls or other injuries, damage to soft tissues can already be accompanied by dental injuries of varying severity.
Then a child of 3–4 years old begins to ride a scooter and bicycle, which is fraught with fractures of the bones of the axial and facial skeleton.
Schoolchildren not only often get injured at home, but also become victims of careless handling of pets: cats and dogs, unfortunately, often bite in the nose and mouth. This leads to quite pronounced and extensive defects, and subsequently to deformations of soft tissues, the elimination of which sometimes requires multi-stage plastic surgeries with transplantation of soft and integumentary tissues.
And finally, teenagers between 15 and 18 years of age are more likely to get into road accidents, man-made disasters, come into contact with firearms and explosives, and we have to observe the tragic consequences of severe combined and combined injuries.
Yuri Olegovich Volkov
maxillofacial surgeon, candidate of medical sciences, head of the department of maxillofacial surgery of the Children's City Clinical Hospital named after. G.N. Speransky in Moscow
Complications
Surgeries performed on newborns with cleft lip are not characterized by complications. However, possible postoperative consequences include:
- hemorrhage on the skin - lasts 3-4 weeks and goes away on its own;
- swelling in the operation area – increases by the fourth day and goes away on its own after 3–4 months;
- bleeding from the wound - in this case it is necessary to open the wound and cauterize the blood vessels;
- hematoma is a very rare complication, the prevention of which is to stop the bleeding;
- necrosis of the wound edges.
What is special about pediatric maxillofacial surgery?
The main feature of oral and maxillofacial surgery is that it is closely related to other areas of medicine. Thus, parents of a child with a cleft lip and palate should clearly understand: the operation performed is not the final stage of treatment for the disease. Everything is individual, but as a rule, after primary reconstructive surgery, corrective surgery is required, as well as treatment and rehabilitation in several stages. Repeated operations are aimed at eliminating residual defects and deformations and improving the aesthetic appearance. Most children will have to undergo long-term rehabilitation with a professional speech pathologist-speech pathologist to eliminate organic rhinolalia - a violation of the timbre of the voice towards nasality, which is a specific sign of speech in children with a cleft. All of our patients will need multi-stage, long-term care from an orthodontist to correct their dentition and bite with various orthodontic devices, and in adolescents, with braces. Ideal conditions are to receive the necessary treatment and consultations from all specialists in one place. Therefore, it is no coincidence that the parents of young patients who need the help of a maxillofacial surgeon strive to get to Moscow: there are ample opportunities to receive qualified medical care on the basis of multidisciplinary hospitals.
Material and methods
The patients were examined jointly by a neurologist and an orthodontist. The study was carried out in 2 stages: the task of the first stage was to describe specific neurological disorders in patients with RHN; The task of the second stage was a comparative analysis of the frequency of identified neurological disorders in patients with RHN and in the control group.
The main group consisted of 21 patients with RHN (13 females and 8 males, aged from 6 to 24 years; average age 12.0±4.7 years). The control group included 11 young people, 9 females and 2 males, who did not have RGN.
Based on the results of the examination, neurological symptoms were reflected in a specially designed questionnaire.
When examining patients, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain was also used. It was carried out on MRI systems Signa HD (General Electric, USA) and Magnetom Espree (Siemens, Germany) with obtaining T1- and T2-weighted images (T1WI and T2WI, respectively) in orthogonal projections using standard pulse sequences of fast spin echo (Turbo or Fast Spin Echo - TSE or FSE, respectively) and T2VI based on a pulse sequence of fast inversion-recovery with signal suppression from free fluid (Fluid Attenuated inversion Recovery - FLAIR).
Statistical analysis of the data was carried out according to generally accepted rules; Fisher's exact test was used to assess intergroup differences. p were accepted as significant
<0,05.