Bite is the way the dentition interacts when the upper and lower jaws are completely closed. An incorrect bite almost always leads to the fact that the enamel, and behind it the bone tissue of the incisors, canines, and molars, quickly wears out and is destroyed. This is why the correct bite of a person’s teeth is so important.
If you have any problems with your teeth, they can be corrected. But this will take a lot of time, because the teeth cannot just be moved, they need to be moved gradually. While studying the problem, doctors came up with many ways to combat malocclusion.
Types of human bite
There are three types of bite in people : ideal, correct and incorrect. Ideal is very rare. For a doctor to say that your jaws have no defects at all, they must meet certain characteristics. Let's list them:
- the upper dental arch has a semi-elliptical shape;
- the lower dental arch looks like a parabola;
- the arches are opposite each other (the front one is slightly in front), when closing, each upper tooth is in contact with the lower one;
- there are no obvious gaps between the teeth;
- The upper teeth overlap the lower teeth by a third.
an ideal jaw in patients, because there is still some minor flaw. Most often these are gaps between teeth or a not very smooth upper arch. But, if this does not interfere with life and chewing, the doctor will not treat or change anything. Sometimes a malocclusion is formed due to bad habits. Trainer systems will help avoid this.
Correct teeth bite
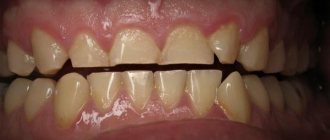
Correct bite is the closure of teeth without defects or with small defects that do not negatively affect the general condition of the oral cavity. This means that with any of the options, a person has no problems with chewing, speech, cosmetic problems are not visible, etc. Four photos of a person’s correct bites are presented below.
Fig 1. Four types of correct bite
Orthognathic
Orthognathic is the most aesthetic occlusion. With it, all the teeth are even, there are no cracks or spaces between them, the upper row of teeth overlaps the lower row by about 30% of the height. This is one of the most popular incisor placement options.
Straight
The direct type of bite in people is quite common and is easy to determine: in this case, the teeth touch the cutting edges and do not cover each other. In this case, the smile looks a little specific and turns out wide, but retains its aesthetics and healthy appearance.
Biprognathic
A biprognathic bite is characterized by an even row of teeth with no gaps, but the teeth do not grow straight down. They are slightly pushed forward, although only slightly.
Progenic
A progenic bite with normal tooth development also does not have any anomalies such as spaces between the incisors or molars. The correct jaw of this type has only one feature: in it the front lower teeth move forward slightly.
general information
In medical terminology, occlusion refers to the relationship of teeth. The dentist analyzes the state of the chewing muscles and the temporomandibular joint at the moment when the jaws are clenched.
Bite is the position of the teeth in relation to each other when the jaws are fully closed.
There are physiological and pathological or, respectively, correct and incorrect bites.
A physiological bite in humans ensures high-quality functioning of the dental system (chewing food), clear diction, free breathing and an attractive smile.
With a correct bite, the face is harmonious, the lower and upper jaws are formed proportionally, the load on all teeth is carried out evenly, the vertical axis of symmetry of the face crosses the junction between the front incisors. This allows a person to chew food thoroughly without injuring soft tissue or periodontium and without overloading the temporomandibular joint.
Malocclusion of teeth
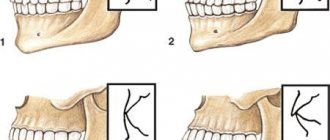
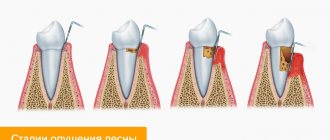
Malocclusion is a big problem that requires treatment. The most effective way to correct the position of the dentition is in children. At 30-40 years old it is possible to cope with the problem, but in adults it will take much longer. Below in the picture you can see five popular malocclusion pathologies, which often affect not only the jaws, but even the way the face looks.
Fig 2. Five types of malocclusion
Distal (prognathic)
from the normal bite by its highly developed upper jaw. As a result, it bulges forward, which also changes facial features. Severe manifestations of this type of dental development disorder may require surgical intervention.
Mesial (medial)
With mesial pathology, the lower jaw is more developed, which can move forward strongly or not very much. from the progenic correct arrangement of teeth in that the lower teeth are not only slightly protruded, they almost completely cover the upper row. This type of bite is dangerous because the outer enamel of the upper incisors and canines quickly wears down, leading to caries.
Cross
A crossbite is characterized by the following characteristics: there is free space between the teeth, with some of the upper jaw incisors located in front of the lower teeth, and some behind them. This arrangement is also described as a “scissor-like intersection.” It looks very unaesthetic, and almost always with a crossbite the teeth grow in different directions.
Deep
A deep bite differs from a regular jaw in that the upper row of teeth almost completely overlaps the lower one. It is also considered an anomaly if the incisors cover the dentition by more than 30%, although sometimes the abnormalities are not visible. For example, the average person is unlikely to distinguish between a tooth overlap of 30% and 40%, since the difference between them is small.
Open
With an open bite, the upper and lower dentition are in contact with only part of the chewing teeth, and pronounced gaps appear between the incisors of the jaws (most often). Sometimes it even feels like the mouth is not closed.
Any dental pathology must be treated, because a correct bite is the key to the health of the entire oral cavity and even your gastrointestinal tract. After all, the better the food is processed by the teeth upon receipt, the easier it is to digest.
Bite in the absence of teeth
It’s interesting, but even if you have no teeth at all, there is no guarantee that with prosthetics you will be able to create the right jaw . It all depends on how damaged the dental system was before removing all its elements. If the jaws are within normal limits relative to each other, the doctor will be able to make adjustments to the prosthesis. If there are also problems with the bones, more complex methods of restoring the dentition will be necessary.
In the absence of teeth, the bite in people is determined using special wax rollers that are placed in the mouth and allow measurements to be taken. The instruments used are a ruler arc and an intraoral plate. Next, a plaster and then a regular prosthesis is created.
Bite after wisdom tooth removal
In modern man, wisdom teeth are an atavism, that is, an element that seems to be there, but is not required in life. They do not affect the correct closure of the teeth and do not harm the dentition in any way if they erupted correctly. This is why dentists recommend not touching wisdom teeth and not removing them unless necessary.
But if you decide to form the correct bite of your teeth as an adult, useless “eights” can serve you well. The fact is that after their removal, the dense dentition becomes freer, so that the remaining teeth can be positioned correctly.
How to independently determine whether it is good or not. Who can check
Usually, an incorrect bite is immediately visible because it can negatively affect a person’s face. If you have at least one friend or acquaintance with incorrectly positioned teeth, you know that such people often have difficulty speaking or biting food, and they develop a variety of speech defects. But, alas, only obvious violations are obvious to the average person.
It is important to understand that a correct bite is a complex of characteristics of your dentition. Even if you have a nice smile and your front teeth are nice and neat, there is no guarantee that everything is actually perfect. Meanwhile, this is fraught: miss one problem, and it will lead to large expenses for the treatment of damaged teeth.
You can imagine what a correct bite should be like in an adult or child, but only an experienced doctor can make a diagnosis.
VII PERIOD - from 12 to 15 years (period of formation of permanent dentition)
Prevention and treatment of dental anomalies:
- identification of dental anomalies and their orthodontic treatment
- planned sanitation of the oral cavity, mandatory consultation with a periodontist to identify periodontal diseases and their treatment
- oral hygiene training, individual selection of hygiene and prevention products
- identification of postural disorders, flat feet, torticollis, therapeutic exercises and consultation with an orthopedist. Swimming, fitness classes
- identification of gastrointestinal dysfunctions, introduction to food hygiene, consultation with a therapist
- identification and elimination of calcium deficiency
- determination of skeletal ossification disorders and consultation with an endocrinologist
- introduction to risk factors
The importance of proper bite for a person
Correct bite, timely dental treatment and careful hygiene are of great importance in a person’s life. Already in the 19th century, they understood the importance of the correct arrangement of the dentition and began to study its features. The main advantages of a correct bite:
- a beautiful and aesthetic smile that attracts people and helps them move forward in life easier;
- correct articulation, clear and understandable speech;
- ease of chewing, biting vegetables, fruits and much more.
Both in childhood and in adulthood, it will take time to form the correct bite. But it’s worth spending, because your health largely depends on the correct position of your teeth. And in business or in life, a beautiful smile often helps to establish strong personal or business relationships. Therefore, healthy teeth are very important.
Problems caused by malocclusion
Malocclusion in people almost always leads to quite serious problems, and not only with the oral cavity. Among the consequences of incorrect closure of the dentition are:
- Increased stress on teeth, which leads to premature tooth loss. It is possible to develop periodontal disease, which accelerates the process. As a result, by the age of 40-50 a person is left without teeth.
- Unpleasant gum sensitivity. The gums begin to react to hot and cold foods, and often unsightly and painful ulcers form on them.
- Disease of the temporomandibular joints. It is also caused by excessive stress, since it is this organ that compensates for the absence of some teeth. It all starts with discomfort, pain, clicking sounds and tingling in the masticatory muscles. Next, your head will begin to hurt systematically, and changes in appearance may also appear.
- Problems with the gastrointestinal tract. There are many types of gastrointestinal diseases that appear due to poorly chewed food. The lack of necessary processing of food entering the stomach leads to excessive stress on the organ, and its strength limit is not infinite.
- Psychological consequences. A person sees a flaw in himself and this creates uncertainty, an inferiority complex, low self-esteem, modesty, timidity and other psychological problems.
Remember that the formation of a correct bite is a matter of health, and not just a solution to aesthetic problems. This is why it is so important to see a dentist on time.
Important! If a child has a malocclusion on his baby teeth, it must also be treated! Although the teeth will be replaced over time, they will grow in the same places where their milk predecessors were. In addition, in childhood the body adapts faster and recovers more easily, so treatment will be faster.
Causes of pathological bite
There are many reasons for malocclusion. In most cases they are the same for children and adults. A harmful myofunctional habit such as a love of chewing a pencil and many other factors can serve as an impetus for the appearance of disorders.
There is an opinion that dental malocclusion occurs only in children, but it is erroneous. Birth defects usually appear in childhood. In adults, changes are often associated with injuries, unhealthy lifestyles, and advanced diseases of teeth and gums.
In children
The causes of incorrect jaw position and abnormal development of teeth in a child can be called:
- injuries that the baby received during childbirth, if there were complications;
- poor heredity and genetic tendency to an irregular jaw shape;
- malnutrition of the fetus during pregnancy, which may be associated with a woman’s illness;
- the formation of mouth breathing, which not only moves the teeth, but also prevents the nasal sinuses from fully developing;
- Incorrect positioning of the baby during breastfeeding or bottle feeding;
- love for prolonged sucking of collars, fingers, toys, abuse of pacifiers;
- rickets or disruptions in the body’s metabolic processes, as well as poor nutrition, lack of food with fluoride and calcium;
- incorrect position during sleep, thumb sucking during sleep;
- delayed replacement of temporary teeth with molars and too early start of teeth change.
In adults
The appearance of malocclusion in an adult is almost always associated with one or more reasons from the following list:
- chronic diseases of the nasopharynx, especially affected by constant nasal congestion;
- multiple carious lesions of teeth, in which a person incorrectly distributes the load on the jaws;
- improper and poor nutrition due to which the teeth do not receive the necessary vitamins and minerals to restore the protective layer of enamel, as well as metabolic failures in which the body cannot extract the necessary microelements from food. The lack of fluoride and calcium has a particularly negative effect;
- injuries of the dental system, etc.
How to effectively correct an overbite. Treatment methods for abnormalities
Treatment of dental malocclusion begins with assessing the condition of the oral cavity and carefully studying the problem. Next, the dentist can recommend one of the popular ways to restore the correctness of the dentition:
- Braces. They can solve almost any bite problem. They are divided into metal, plastic and ceramic, sapphire, self-ligating, lingual. Each type has its own advantages, for example, metal ones are the cheapest, but also the most noticeable, but lingual ones are very expensive, but are placed on the inside of the teeth, so they are not visible.
- Kapu. A mouthguard is a removable polymer structure that is harmless to enamel and can be easily removed while eating or brushing your teeth.
- Surgical intervention. Allows you to correct almost any bite problem. It is required only in very complex cases, usually with congenital pathologies.
- Laser treatment. This is not an independent way to correct a bite. Auxiliary procedures using lasers accelerate regeneration and help reduce the risk of complications.
Modern methods are almost always safe and cause only minor discomfort. But after the course of treatment you will not recognize yourself: you will become more confident, braver, healthier. And sometimes the correct bite changes the appearance in the photo and in reality, forming healthier and more pleasant facial features.
Fig. 3. Braces and mouth guard for malocclusion treatment
Types of bite correction
Orthodontic and surgical types of bite correction depend on the nature of the pathology. In case of skeletal abnormalities, surgical intervention is necessary to correct the bite. In other cases, with dental anomalies, only orthodontic treatment is sufficient. In our clinic, we use aligners for this - invisible mouth guards that allow you to correct all types of dental bites in a person of any age. The technology allows you to achieve a guaranteed result within a predetermined period, and even before the start of treatment you will see what your smile will look like after the bite is corrected.
Conclusions. Expert advice
There are many different types of overbite. Correct is an arrangement of teeth that does not interfere with chewing or speech. If the teeth are not closed properly, excessive stress is placed on the teeth and they are destroyed faster. The bite is preserved even in the absence of teeth. Removing a wisdom tooth does not disrupt the bite and is not mandatory, but may be recommended in case of correction of damaged dentition.
Even if you know what a correct bite looks like , you will not be able to make a correct diagnosis. But you can appreciate the importance of correct bite and the global nature of the problems that its violation causes. This is a good motivation to visit the dentist. The doctor will make a diagnosis and offer modern methods of correcting the bite: installing braces, wearing a mouth guard or other methods. On average, treatment takes from one to 3 years, depending on the complexity of your case.
V PERIOD - from 6 to 9 years (initial period of mixed dentition)
Prevention and treatment of dental anomalies:
- detection of malocclusions and their orthodontic treatment
- planned sanitation of the oral cavity and regular hygiene using special-purpose products
- observation of the sequence of eruption of the first permanent molars, incisors and massage of the alveolar process
- selective grinding of unworn cusps of temporary teeth (usually canines)
- plastic surgery of a shortened or improperly attached frenulum of the tongue
- plastic surgery of a shortened or improperly attached frenulum of the upper or lower lip (if there is a diastema, three)
- removal of retained primary incisors and erupted supernumerary teeth
- identification of postural disorders, flat feet, therapeutic exercises and orthopedic consultation
- fighting bad habits of sucking and biting fingers, lips, cheeks, tongue, various objects, with habitual incorrect posture
- detection of nasal breathing disorders. Consultation with an ENT doctor. Sanitation of ENT organs. Removal of adenoids and velopharyngeal tonsils for orthodontic indications in cases of severe malocclusion
- the use of therapeutic exercises to normalize nasal breathing, swallowing, and posture
- training from a speech therapist in the correct pronunciation of individual sound phonemes
- early removal of the buds of 3 molars (wisdom teeth) at the age of 7 years