Prevention of caries in children is an important point in maintaining the health of a still fragile body. Proper nutrition and care of temporary and permanent teeth are the main components of the correct approach to solving this problem.
Why is caries prevention needed in children if temporary teeth will soon be replaced by permanent ones? As practice shows, a set of timely preventive measures reduces the risk of infection of permanent teeth in children and adolescents by 80%!
What is caries in children?
Tooth decay in infants under one year of age is the destruction of mineralized tooth particles caused by the action of acids on the tooth surface produced by plaque bacteria.
An important element of this process is the imbalance between mineralization, which is the calcification of the tooth, and demineralization, literally the loss of tooth structure. Factors and causes involved in the formation of dental caries in young children include:
- bacteria present in dental plaque
- carbohydrates, that is, sugars present in food,
- predisposition of dental tissues to decalcification due to insufficient mineralization,
- composition of saliva, its quantity and ability to deoxidize the contents of the oral cavity
- time of exposure of the above factors to dental tissue.
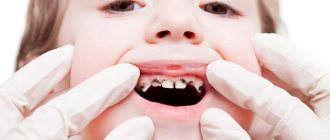
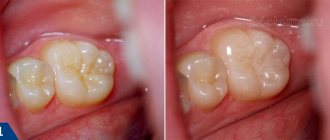
The process of tooth decay in young children begins with the erosion of tooth enamel. This is a white cavity that does not yet require dental care and may disappear with calcium and fluoride supplements. If adequate caries prevention is not applied at this stage, the deeper tissues of the tooth are affected. Caries in young children can occur on the first tooth that emerges.
Can a filling be placed on a baby tooth?
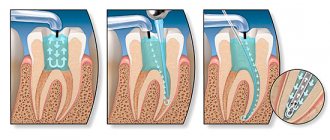
If the doctor diagnoses not the first stage of tooth decay and insists that it is necessary to put a filling, it is better to agree with him. This is the fastest and most reliable way to solve the problem of infection and protect permanent teeth.
Modern filling materials are as safe as possible for children’s teeth. Depending on the stage of caries, the doctor will select a suitable filling option. Before installing a permanent filling, the dentist may place a temporary filling for several days to fix the medication inside the diseased tooth.
If the damage is not yet serious, the doctor will limit himself to preventive measures. There are different approaches and tools for different problems.
Why is it important to prevent the development of the disease?
In 90% of cases, caries of primary teeth occurs in an acute and painful form. Children cannot tolerate toothache, which often occurs with caries and can occur at any time of the day. This is the first reason to take care of effective early prevention. There are others:
- damage to the buds of permanent teeth exposed to milk;
- malocclusions that require orthodontic treatment to correct; speech disorders;
- chronic inflammation of the gums, stomatitis;
- Otitis media, tonsillitis, sinusitis due to bacterial damage.
Endogenous prevention
This method is aimed at improving the condition of teeth from the inside. Prevention involves adjusting the nutritional system and taking additional mineral complexes (fluoride-containing preparations; vitamins A, D, C, B1, B6, etc.). Parents should exclude sweets and soda from their child’s diet or reduce their consumption as much as possible. Solid fruits and vegetables are a good substitute and are excellent for cleaning the mouth. Consumption of dairy products rich in calcium is also an excellent prevention of caries.
Prevention of caries in children
How to avoid caries in a child? There are simple steps you can take to reduce the likelihood of it occurring.
- Brush your child's teeth as soon as their first teeth appear. At first, you can use sanitary napkins with xylitol.
- Don't lick your baby's pacifiers or let your baby eat from a spoon. This can transfer bacteria from the mouth to the baby and increase the likelihood of tooth decay on newly erupted teeth.
- Avoid giving your baby juices or sugary formulas at night or at bedtime. After your last meal, you need to brush your teeth! If your baby is breastfed, after a year, reduce nighttime feedings; remember that breast milk is also sweet and can cause the development of caries.
- From 1-1.5 years old, regularly visits the pediatric dentist (once every 3-4 months).
- Don't forget about regular oral hygiene at least twice a day for 2-3 minutes.
- Brush your child's teeth yourself until he is 4-5 years old, so be sure to help him with brushing. Until the age of 8-9 years, a child still cannot brush all his teeth correctly, even if he knows how to do it correctly.
- Let your baby's diet be rich in micronutrients. Encourage your child to chew carrots and apples to reduce plaque buildup and strengthen gums.
- Professional oral hygiene is not a luxury, but an extremely useful procedure, because only a dentist can remove hard plaque. Also, if possible, go through the procedures of enamel mineralization and fissure sealing on young permanent teeth with your child. These measures are a good prevention of dental caries in children.
Causes of caries
Caries occurs “thanks” to microorganisms living in the thickness of dental plaque. These bacteria - primarily streptococci, lactobacilli and actinomycetes - process food debris that remains on the teeth and produce acids that corrode the tooth enamel, leaching calcium from it. The tooth enamel begins to deteriorate.
The activity of bacteria varies from person to person: it is higher if a person brushes their teeth irregularly or not thoroughly enough, since soft interdental plaque is an excellent nutrient medium for them.
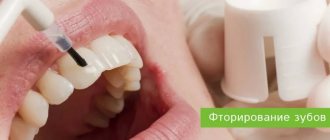
Deep fluoridation
Fluoride is known to be an important element in maintaining dental health. However, until recently, the only way to replenish this element in the enamel was toothpaste with fluoride. But its effectiveness is very low, and teeth are still susceptible to destruction. The lack of fluoride is especially felt by residents of those regions where there is a lack of it in drinking water and food.
Today, medicine offers a unique method for restoring tooth enamel and hard tooth tissues - deep fluoridation. This procedure replenishes mineral deficiencies, reduces tooth sensitivity and prevents the growth of bacteria that leads to tooth decay. For children, deep fluoridation is of particular importance, since the formation of permanent teeth occurs only in the child’s body. Insufficient intake of fluoride from food and irregular oral care can contribute to the premature destruction of tooth enamel. Using the deep fluoridation procedure, you can increase its hardness by 10 times!
What is the deep fluoridation method?
This method is based on a series of chemical reactions: they produce microcrystals of calcium fluoride that fill microcracks in the enamel. The deep fluoridation procedure itself takes place in several successive stages. First, the dentist brushes your teeth with a special paste to remove plaque and tartar. Then, using a jet of air, the teeth are dried and covered with a filling liquid, which “seals” the enamel (highly dispersed calcium fluoride and magnesium fluoride). After this, drying is carried out again and calcium and copper hydroxide are applied. A chemical reaction occurs between the first and second layers, during which microparticles of calcium fluoride are released, which very easily penetrate into the deep layers of enamel. At the same time, copper compounds formed as a result of the reaction have a strong bactericidal effect. Due to the described interaction of elements, anti-caries protection occurs.
When is deep fluoridation recommended?
This procedure is preventative and completely painless. It is aimed at long-term protection against enamel destruction and caries (the effect lasts up to two years). Therefore, it can be recommended to everyone who cares about dental health.
Deep fluoridation is especially useful in the following cases:
- to protect baby teeth in young children
- for teenagers whose bodies undergo changes associated with puberty, during which caries activity increases
- with fluoride deficiency due to poor diet or natural environment
- with increased tooth sensitivity
- with thinning enamel
- before installation and after removing braces
Due to the fact that the effect of deep fluoridation is quite long-lasting, it is enough to undergo the procedure 1-2 times a year. However, despite the obvious benefits of this preventive measure, we should not forget about other ways to take care of dental health: a balanced diet, regular brushing, regular visits to the dentist, and so on.
ORAL HYGIENE
The fundamental principle of caries prevention is keeping the oral cavity perfectly clean. Failure to comply with hygiene rules sooner or later leads to tooth damage. If you do not brush your teeth in a timely manner, then within 4–5 hours after eating, colonies of pathogenic microorganisms appear on them, which are the main cause of caries. Moreover, not only food debris, which inevitably gets stuck in the interdental spaces, but also the paraffin contained in lipstick serves as a breeding ground for pathogenic bacteria.
Along with a toothbrush (regular or electric), dentists recommend using floss - dental floss. With the help of such threads you can clean the interdental spaces in cases where you cannot use a brush. If the gaps between the teeth are large, you should use round threads; for teeth that are too close together, it is better to use flat ones. How to properly floss is shown in the pictures posted on our website.
EXOGENIC PREVENTION
Basic exogenous procedures:
- Remineralizing therapy. In cases where dental tissues do not receive the required amount of microelements, ions of these substances can be introduced externally using iontophoresis, flossing or simply rubbing. This therapy is a course therapy. Preparations containing calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, and fluorine are used.
- Fluoridation (simple and deep). Simple fluoridation is carried out in courses of 15 procedures. A soft mouth guard filled with a fluoride-containing preparation is placed on the patient’s teeth. The duration of the procedure is 10–15 minutes. During deep fluoride prophylaxis, the patient’s teeth are coated with a special varnish with a high fluoride content. The varnish gradually dissolves. This procedure is recommended to be carried out every six months.
- Fissure sealing is the filling of grooves on the chewing surface of molars and premolars with sealant.
- Professional cleaning of the oral cavity, during which dental plaque is completely removed, tartar is destroyed using ultrasound - one of the main causes of cervical caries, which causes gingivitis.
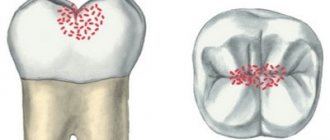
FISSURE SEALING
As a rule, in adults, tooth enamel is thinner at the bottom of fissures than in other places. In children, it generally develops over several years after tooth eruption. If the groove is deep and narrow, then food constantly gets stuck in it. Therefore, such places are the most vulnerable, and the occurrence of fissure caries is only a matter of time.
To strengthen dental tissues, the surface of the teeth is filled with a special sealant. The procedure is absolutely painless, the composition hardens very quickly. There are two types of fissure sealing:
- Non-invasive – is carried out if the surface of the molar or premolar is healthy and the fissures are not too deep and narrow;
- Invasive – used if there are small carious cavities on the chewing surface (no more than 2 mm in diameter). In this case, they are filled, and the surface of the tooth is covered with sealant. Invasive sealing is also prescribed for very deep and narrow fissures.
Fissure sealing helps prevent the formation of primary and secondary caries. The sealant effectively protects the chewing surface for five years. After this it must be replaced. This procedure is indicated for patients of any age. Sealant can be applied to both permanent and baby teeth.
Other methods for preventing childhood caries
- Remineralizing therapy - restoration of the mineral composition of the enamel, restoration of its original strength and additional strengthening. The essence of the technique is reusable treatment of the tooth surface with a special gel or paste. Remineralizing compounds are characterized by a high concentration of phosphorus, calcium and other components beneficial to dental health that improve the structure of the enamel of primary teeth. Remineralization is carried out in a dental clinic, then dental treatment is carried out at home according to prescriptions recommended by the doctor.
- Silver plating is an outdated technique, but is still popular in many Moscow clinics. Lack of treatment - darkening of teeth, loss of aesthetics. The essence of the method is to coat the enamel with a 30% solution of silver nitrate, which ensures the destruction of bacterial microflora and stops the destruction of the tooth crown.
- Ozone therapy is a non-contact treatment for young children based on the antibacterial effect of ozone. Gentle tooth disinfection at an early stage stops the formation of a carious cavity with subsequent restoration of the enamel with remineralizing compounds.
- ICON technology is a modern method of caries treatment without a drill. The idea is to treat the problem area with a special gel that penetrates deeply into the tooth tissue, destroys bacteria and seals the enamel.
- ART method: painless and gentle manual cleaning of a carious cavity with subsequent installation of a filling.
Preventive examinations
Regular visits to the dentist will help prevent tooth decay or detect its presence at an early stage. Professional teeth cleaning is recommended 2-3 times a year. These procedures can be combined with examinations, which should be carried out at the same frequency. If there are no complaints, it is enough to visit a hygienist.
Only a specialist using professional tools can detect the disease at an early stage. As a rule, it appears as a white spot. Sometimes small dark dots appear. If the putrefactive process has affected the lateral groups of the dentition, then it is impossible to notice it on your own. Blind spots also include the inner surfaces of the incisors.
Patients usually discover caries when it is in an advanced form and a small cavity has already appeared. One of the signs of a problem is also increased sensitivity. If your gums begin to bleed, there are obvious discolorations on the enamel and pain, then it is advisable not to wait for a scheduled examination, but to immediately visit a doctor.
Diet for the prevention of caries in children
Caries bacteria feed on sugar: glucose, fructose or sucrose. Sweets are the main ally of this disease. Although children love them, they should not overuse them. Sugar in desserts not only contributes to the development of tooth decay. It also includes refined carbohydrates such as white sugar, flour and processed foods. The following methods should be followed: dental caries in children
- Eliminate sugar from your diet.
- Replacing colored drinks with water.
- Avoid processed foods.
- Refusal of products containing preservatives.
It often happens that the child drinks colored and carbonated drinks, eats cookies, chips, lollipops or candies as a snack, and drinks milk or cocoa before bed. All of these everyday activities can lead to tooth decay in young children. To prevent serious illness, which is unfortunately not getting enough attention, you need to choose healthier alternatives to popular snacks, sweets and drinks.
The correct level of minerals and nutrients, the dose of vitamins, the rational dosage of sugars and the solid consistency of food are factors that can effectively prevent the formation and development of dental caries in young children. Doctors are confident that every child will be grateful to their parents for developing good habits, proper oral hygiene and diet, which affects the life and health of children not only now, but also in the future.
To prevent caries treatment in young children, it is worth conducting a preventive dental examination every 6 months and removing tartar. Children should be constantly encouraged to prevent tooth decay because it is easier to prevent than to cure, especially when it hurts, and visits to the dentist are frequent and unpleasant for the child.
Nutrition rules
Doctors recommend limiting the consumption of sweets, replacing carbonated drinks with compote, and confectionery with dried fruits. After each meal you should rinse your mouth thoroughly.
A balanced diet must include:
- fermented milk products;
- nuts;
- fresh herbs;
- cheese;
- dietary fish varieties with low fat content;
- meat.
It is better to refrain from eating too cold or hot foods or drinks. Alternating temperatures negatively affects enamel. As a result, cracks appear, which promotes the growth of bacteria.
How to choose toothpaste for a child
Since young children often swallow toothpaste, and sometimes even eat it secretly from their parents, the composition of the toothpaste must be extremely safe for health. Unlike adults, infants do not need large amounts of fluoride, so a child's first toothpaste should not contain fluoride. You should be aware that excessive consumption of fluoride, especially if it is constantly ingested, can lead to damage to tooth enamel and the development of fluorosis.
For preschool children, you can purchase toothpastes with a minimal fluoride content, but in fact, toothpastes with fluoride are recommended only for adults whose teeth have already been fully formed.
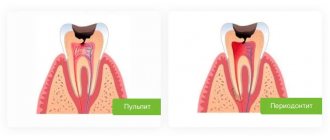
Causes of the disease
The leading cause of caries is the activity of oral bacteria. The normal microflora of the mouth consists of many microorganisms. Among them there is a group of cariogenic bacteria that negatively affect the enamel. In the absence of factors that weaken the body’s defense response, the number of opportunistic microorganisms does not exceed the norm and the disease does not develop. But if there are too many bacteria, the organic acid they produce begins to gradually dissolve areas of the enamel layer. Primary prevention of caries is aimed at eliminating the causes and conditions that contribute to its occurrence.
The following factors contribute to the development of the carious process:
- disorders of mineral metabolism in the body;
- changes in the composition of saliva (increased viscosity);
- abnormal bite;
- crowded teeth;
- poor oral hygiene;
- addiction to sweet, sticky, viscous foods;
- cracks, chips of enamel;
- heredity;
- deficiency of fluorine, calcium, phosphorus in drinking water and food;
- reduced immunity.
The causes of caries are different, but the main mechanism of development is the same - lack or lack of oral hygiene. Primary prevention of dental diseases begins with regular removal of bacterial plaque, which creates a favorable environment for the proliferation of cariogenic microorganisms. This differs from secondary prevention, which consists of treating the disease and its complications.
School dentist
In this case, the work of a pediatric school dentist is very important. It is the school pediatric dentist who must competently convey to parents and children how important preventive dental examinations and timely treatment of caries are. In principle, schools currently provide entire treatment and preventive programs. Participation in them is not strictly obligatory and the decision to participate in these programs, of course, is made by parents. If you decide to refuse the services of a school dentist, we advise you to definitely find a good pediatric dentist, since in any case, healthy teeth are the result of the right approach to treatment and preventive monitoring of their health.