Features of superficial caries
Among the main distinctive features of superficial carious damage to teeth in children in comparison with other forms of pathologies, the following should be noted:
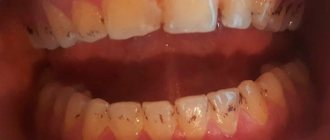
- only the enamel layer is affected by pathogenic formations. The dentin remains intact. With timely treatment, the risks of complications are minimal;
- the occurrence of an acute reaction to external stimuli, for example, sour and sweet foods, low and high temperatures;
- if superficial caries is diagnosed in children, treatment can be carried out without tissue preparation;
- Most often, the superficial form occurs in children aged 3-4 years and in adolescents.
Note! Initial caries and superficial caries are two completely different forms. The first appears as a small spot, the second occurs in the absence of treatment. It can be recognized by the presence of small-sized carious cavities.
What are the stages of dental caries in children?
Tooth decay begins gradually, and with regular examination, parents and the dentist can catch the right moment in time and begin treatment.
| Initial stage Specks appear on the enamel, which differ in color from the rest of the tooth, and over time they darken. | Superficial caries The tooth decay is still minor, but the child is already beginning to react to hot and cold. | Average caries A carious cavity appears at the site of enamel destruction; the tooth reacts very painfully to the temperature of food and drinks. | Deep caries The last stage is when not only the enamel is destroyed, but also the tooth tissue itself. If treatment measures are not taken, then inflammation of the pulp will gradually begin, and the tooth will have to be removed. |
It is better not to delay the examination, because caries in a child can develop quite quickly. The further you go, the more uncomfortable and worrying your first visit to the doctor will be.
Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of superficial foci of caries are manifested by the following signs:
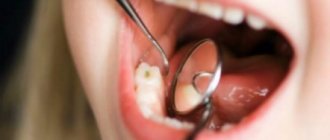
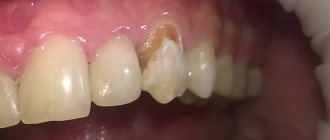
- visible defect. On the surface of the tooth there is a small cavity with uneven edges. The color of the formation is dark, the bottom is slightly rough;
- pain syndrome. When exposed to cold, hot, sweet and sour foods or drinks, sharp short-term pain occurs;
- hyperesthesia. When inhaling cold air, while brushing your teeth, increased sensitivity occurs.
These are the main symptoms and in each individual case they can manifest themselves differently.
Prevention of caries
Many pediatric dentists offer painless and fun treatment. But it is easier to prevent than to treat. Simple preventive measures will help preserve the integrity of baby teeth for as long as possible:
- Daily oral hygiene. As soon as the first tooth appears, you need to purchase children's toothpaste and a brush. Grooming should be done twice a day - morning and evening, and gradually become a healthy habit for the child.
- Proper nutrition. It is necessary to include foods high in calcium (kefir, cottage cheese, cheese, etc.), as well as vegetables and fruits, in the child’s diet. Harmful sweets and fast carbohydrates, on the contrary, should be excluded or reduced as much as possible in the daily menu.
- Preventative examinations with a doctor. A pediatric dentist should be visited 2-4 times a year. This will allow you to monitor dental health and reduce the risk of caries in your child.
It is recommended that a child’s first meeting with a dentist take place after the incisors appear – at 1-1.5 years. This will be a preventive examination, during which parents will be told the principles of caring for children’s teeth and advised on the optimal scheme for monitoring the growth of temporary units.
Watch an informational video on this topic
Factors influencing the development of superficial caries in children
The fundamental factors that result in superficial caries in children are:
- eating foods that contain large amounts of carbohydrates;
- non-compliance with hygiene rules: insufficient brushing of teeth, ignoring periodic rinsing with special means, etc.;
- drinking water with a deficiency of fluoride in its composition;
- deficiency of vitamins and mineral elements;
- severe systemic diseases;
- hormonal imbalance;
- ignoring professional hygiene, the need for which arises every 5-6 months.
Any of these factors or several at once are the primary causes of tooth enamel destruction.
Causes of caries in children
The main cause of the disease is poor hygiene. Sometimes, if a patient experiences severe stress or a sudden decrease in immunity, this affects the condition of the teeth. Parents should understand that inflammatory processes can occur even in very young children. That’s why any pediatric dentist so often talks about the importance of proper cleaning and oral care.
Accordingly, the main process for those who want to avoid caries will be home hygiene. Next, we will talk about dangers that are difficult to track right away. For example, what’s wrong when a child falls asleep with a bottle of milk, but you don’t want to wake him up.
What other causes of caries in a child can be? For example, poor nutrition leads to inflammation of the enamel. If the body does not receive enough calcium, protein and other important elements, then the teeth will be weak. As for the popular thesis that caries occurs only from sweets, we will also talk about this later. Don't rush to conclusions!
If a child has constant caries, then there are one or more reasons that you simply do not notice. You shouldn’t think that caries is an exclusively age-related problem and that by the end of school everything will be fine with your teeth. This is a big misconception. It is necessary to treat every case of caries and always find the cause of the problem.
Principles of treatment of superficial caries
When superficial caries is detected in children, treatment should be aimed not only at eliminating formations on the tooth enamel, but also at preventing the re-development of the pathology. To prevent complications, comprehensive and immediate therapy is necessary.
When talking about treatment, it should be understood that it is just beginning in the dentist’s office, and it will also need to be continued at home using special means and traditional medicine recipes.
Features of treatment in the pediatric dentist's office
If baby teeth are damaged by caries, then it is quite possible to treat them conservatively without the use of drills, which almost every child is afraid of. Modern dentistry offers more gentle and comfortable methods:
- Children under 3 years of age undergo silvering or deep fluoridation of their teeth. If the enamel has already been damaged by caries, it is cleaned of plaque and treated with a laser. If necessary, cracks in the chewing and frontal teeth are sealed;
- at the age of 3 to 5 years, ozone therapy can be performed to eliminate the first stage of superficial caries, and in case of major complications, treatment is carried out using the method of depophoresis. Its essence lies in the introduction directly into the root canals of a special composition with calcium and copper;
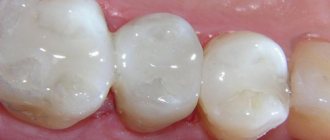
- Children from 5 to 9 years old undergo filling. Glass ionopolymers or colored compomers are used for fillings;
- Children aged 9 to 12 years already have molars and adult technologies can be used to treat them with minimal trauma. But in most cases, therapy of chewing teeth is carried out by sealing fissures.
When superficial caries in children requires complex dental procedures, local anesthesia is mandatory before such procedures are performed. If removal is necessary, such an intervention can be performed under intravenous anesthesia.
Treatment at home
Along with professional treatment of caries by a pediatric dentist, proper oral care at home will also be required to obtain an effective result. For this purpose, special rinsing compositions and toothpastes with anti-caries effects are used.
For children under 4 years of age, dental and oral care products should not contain fluoride. The therapeutic effect is provided by antibacterial active components and calcium ions.
Children over 4 years old are allowed hygiene products containing fluoride, only the concentration of the element must be minimal.
LACALUT kids, PresiDENT Baby, SILPA Putzi, Splat junior are considered good toothpastes for children. You need to brush your teeth with them twice every day. Among the rinses, Drakosha for children, Active Kids, and LACALUT Teens have proven themselves well. When treating caries with such solutions, it is necessary to rinse your mouth after every meal and always before going to bed.
In addition to professional medications, you can also use remedies prepared according to alternative medicine recipes:
- An infusion of chamomile is perfect as a rinse. To do this, pour a glass of boiling water into 1 tbsp. l. dried flowers, leave and cool to room temperature;
- a weakly concentrated solution of sea salt has a positive effect on the condition of teeth. Dissolve 0.5 teaspoons of salt in a glass of water and use for rinsing.
Important! Rinse aids can only be used after the child reaches 1.5-2 years of age, when he can already rinse and spit out liquid on his own, rather than swallow it.
Why do children under 14 years of age have an increased risk of caries and pulpitis?
During the period of formation of a permanent dentition, when the child’s permanent teeth begin to erupt, there are 2 factors that increase the likelihood of developing dental diseases and parents need to take them into account.
- The anatomical features of “freshly erupted” permanent teeth contribute to the development of caries and its complications. The incompletely formed, delicate enamel of young permanent teeth, especially in the area of numerous fissures (grooves) on the chewing teeth, is very vulnerable.
- A psychological feature of the “difficult” transitional age, when it is not easy to persuade a child to brush his teeth correctly and thoroughly, and, even more so, to go to the doctor and cure caries in a timely manner, especially if the child is afraid of the dentist.
Possible complications
Some parents are in no hurry to visit a pediatric dentist because they consider it useless to treat baby teeth. This approach is explained by the fact that permanent ones will grow instead of them anyway.
Although the carious process itself does not transfer from baby teeth to permanent ones, untreated caries lesions have a detrimental effect on the condition of the latter. If you ignore superficial caries in children , complications may very soon manifest themselves:
- caries progresses rapidly in the absence of adequate therapy. This leads to the development of periodontitis and damage to the molar tooth germ. The inflammatory process significantly slows down the eruption of permanent teeth and complicates their growth;
- premature loss of baby teeth leads to the formation of malocclusion and disrupts the structure of the maxillofacial system;
- If at least one tooth is missing in the dentition, this complicates the process of chewing food. As a result, problems arise with the functioning of the digestive system.
Remember! Even the smallest stain can lead to complete tooth decay. There is no need to risk your child's health. It is much easier to visit the dentist and, if necessary, treat caries.
Is it necessary to treat caries of baby teeth?
Despite the “temporary nature” of children’s teeth, treatment and care for them must be thorough and complete. Chronic inflammation in the oral cavity leads to serious problems.
- A baby tooth affected by caries can decay so deeply that it affects the germ of a permanent tooth. The infection will spread to it, and it will grow up with enamel defects or simply die.
- When a baby tooth is removed, the adjacent tooth moves into its place, causing the permanent tooth to erupt in a different place than intended. As a result, the bite is formed incorrectly, and in the future it has to be corrected with braces.
- Advanced caries reduces immunity and causes ENT diseases and even allergies.
- Painful sensations prevent the baby from biting and chewing food correctly, which causes digestive problems.
- The child will be embarrassed about his bad teeth, which will prevent him from communicating with his peers.
It is necessary to treat caries at any age at the initial stage, and it is better to accustom your child to this in advance.
Diagnostic methods
To accurately determine the nature of dental damage, doctors use many methods. The main types of diagnostics include:
| Inspection of the tooth surface with staining to identify carious spots. |
| Probing. Allows you to determine the depth of the carious cavity, assess the condition of the pulp chamber, the density of the affected tissue, and the degree of pain. |
| Electroodontometry. A test to determine the degree of excitability of the pulp. Normally, in an inflamed or necrotic state, it reacts differently to irritation. |
| Percussion (tapping). In case of caries, the procedure is painful for the patient; a healthy person will not pay attention to it. |
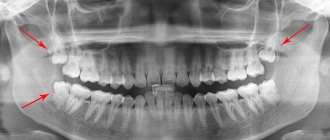
| X-ray. Using interproximal radiography, it is possible to identify hidden caries and determine the depth and extent of tooth damage. The method is used only in combination with other diagnostic methods. |
These methods are applied only to carious teeth; healthy teeth are not subject to unnecessary diagnostics. Only a doctor with special education can determine what the research should be like. The patient can assist by providing the results of previously performed diagnostics. Using them, dentists determine how long ago the problems arose, how quickly dental caries and its complications develop.
Complications of caries
The destroyer of tooth enamel and dentin, caries, can lead to tooth loss and also cause severe inflammation of the pulp, peri-apical tissues and jaw.
Cariogenic bacteria streptococci, which form hollow cavities in untreated teeth, tend to infect the connective tissues that make up most of our organs. And this is fraught with the development of diseases such as endocarditis, chronic tonsillitis, lymphadenitis and abscess.
How quickly advanced forms of caries develop
Typically, from the moment a carious spot appears on the enamel to the formation of deep caries, it takes from 1 to 4 years; the infection affects root canals 2 times faster.
But there are cases when complete tooth destruction and the formation of complications occur in just 3-4 months; this is acute caries. The reason for this is individual resistance, that is, the susceptibility of teeth to caries.
Signs that caries has reached the deep layers of dentin:
- the appearance of short-term pain;
- increased sensitivity to cold and hot;
- bad breath.
And not always, when the form is neglected, the tongue rests on a deep relief cavity in the tooth - sometimes it is just a small hole in the enamel, behind which lies an almost completely destroyed tooth.
Features of multiple caries
This disease has a rather rapid course, unlike other types of caries: in a short period of time, the lesion covers almost the entire dentition. It is the speed of spread that is one of the main features of “blooming” caries. This course of the disease is due to the rather thin enamel of children's teeth and the special structure of dentin, which has low-mineralized zones that reach the pulp. Thus, the carious process penetrates through hard tissues (enamel, dentin) and quickly spreads to the pulp.
You can lose a tooth with multiple complicated caries in just a couple of months! In general, the disease affects from 6 to 20 teeth, and each of them may have several carious lesions. In this case, the transition from the initial stage to the deep stage occurs many times faster than in the chronic course of the process. Sometimes only “stumps” remain from the chewing units. By the age of 3-4 years, a child may be left with almost no teeth at all.
Treatment of multiple dental caries
First of all, treatment should be comprehensive, especially if caries is caused by general diseases. After all, if you do not eliminate the reason why your teeth are decaying, then the treatment will be in vain: the carious process will begin all over again. Experienced pediatric dentists in such cases refer the little patient to the appropriate specialists.
Modern dentistry is aimed at maximum preservation of teeth, and even milk teeth. After all, if you remove them ahead of time, problems with the eruption of the radical units may subsequently arise. In order to prevent the destruction of hard dental tissues, the specialist prescribes the following measures:
- at the chalk stain stage, dentin and enamel strengthening minerals (F, Ca) are used;
- at the middle stage, carious cavities are cleaned and closed with a filling;
- in case of deep damage, the tooth pulp is partially or completely removed, the canals are cleaned, filled with composite, and a filling is installed.
A small patient who has undergone treatment for multiple caries must then be observed by a doctor once every three months. If prevention requirements are not followed, the process may begin to develop again.