From this article you will learn:
- features of the development of childhood caries,
- reasons for appearance, photos,
- how caries is treated in children under 3 years of age and after.
Bottle caries is one of the terms used in dentistry to refer to carious lesions in primary teeth (in young children). This term seems to emphasize the importance of poor nutrition in the development of dental caries in a child. And the main factors here are: firstly, the consumption of large amounts of sugar-containing foods and drinks, and secondly, a violation of the diet (for example, feeding on demand).
The most adverse effect on the development of bottle caries in children is caused by frequent night feedings of sweet and sour foods. This can be sweet porridge, sweet tea, juice, dairy products, etc. The fact is that at night salivation is very reduced, and therefore the possibility of self-cleaning of teeth is reduced (due to washing off with saliva and swallowing food particles), and also the remineralization of dental tissue is reduced. enamel with calcium contained in saliva.
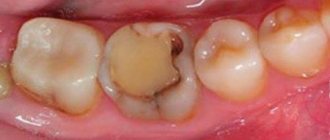
Bottle caries: photo
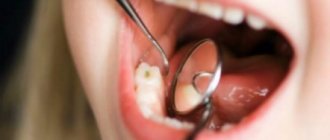
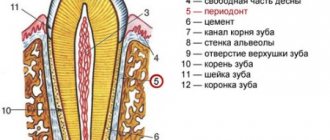
Caries of baby teeth in children can occur not only after their eruption has finished, but also when the crown of the baby tooth is only partially visible above the mucous membrane. The upper incisors and first molars are usually affected first, often all the teeth as they erupt. In young children, the development of caries is aggressive in nature, which is associated with weak mineralization of the enamel of primary teeth (its saturation with calcium, phosphates, fluoride). If we add to this poor nutrition and irregular care of the baby’s oral cavity on the part of the parents, we get a “circular form of caries” (Fig. 1.9).
Childhood caries in children under 3 years of age is usually asymptomatic. This is due not only to the characteristics of the nervous system of children, but also to the immaturity of the nerve endings in the pulp of temporary teeth. When caries occurs, children usually do not show any concern, and only a few of them refuse to eat sour fruits and vegetables and solid foods. All this leads to parents bringing their child to the dentist too late. But there is one more feature...
Important: children under 3 years of age have a very small thickness of hard tooth tissue, and therefore the appearance of even a shallow carious cavity immediately leads to the development of pulpitis (inflammation of the nerve in the tooth). At first, pulpitis can be asymptomatic, or with the appearance of paroxysmal pain in response to taking hot or cold. Pulpitis quickly turns into periodontitis, which leads to the formation of a purulent abscess in the area of the roots of a baby tooth, which can be manifested by swelling of the gums and the formation of a fistula.
Interesting point -
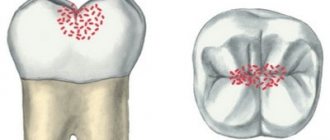
Often, a dark pigment plaque forms on a child’s teeth in the form of black spots, which can be mistaken for caries. The integrity of the enamel is not compromised, and such pigmentation is a deposition of iron salts on the surface of the enamel - due to the activity of anaerobic bacteria (actinomycetes). This type of staining is called chromogenic (Fig. 4).
This dark plaque is formed as a result of the interaction of hydrogen sulfite (a waste product of actinomycetes) with iron contained in saliva or with iron in red blood cells that can enter the oral cavity, for example, when gums bleed due to inflammation.
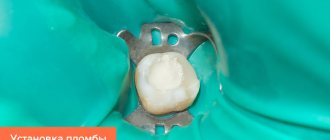
Treatment of caries of children's primary teeth
Caries of primary chewing and front teeth has long been treated without the slightest pain.
New modern techniques have reduced the use of drills and drilling to a minimum, and timely scheduled examinations make it possible to detect the disease at a very early stage. The doctors at Aza&Buka Pediatric Dentistry who work with young patients are distinguished by an amazing sense of tact and constant positivity. Knowledge of the child’s psychology allows doctors to build communication and dialogue in such a way that children sit in the dental chair without the slightest fear. If the child already has some dental phobia, then adaptation techniques can solve the problem.
Caries on baby teeth in children is treated using the following technologies:
Prices
| Baby teeth | Price |
| Treatment of milk caries with placement of a filling made of glass ionomer cement | 2 350 ₽ |
| Treatment of caries with light polymerization fillings | 3 500 ₽ |
| Treatment of initial and superficial caries with Icon | 3 500 ₽ |
| Baby teeth | Price |
| Treatment of caries with filling made of glass ionomer cement | 2 350 ₽ |
| Treatment of caries with light polymerization fillings | 3 500 ₽ |
| Treatment of initial and superficial caries with Icon | 3 500 ₽ |
| Permanent teeth | Price |
| Temporary filling | 300 ₽ |
| Medical pad | 550 ₽ |
| Treatment of caries with placement of a light polymerization filling (anesthesia, cavity formation, antiseptic treatment, filling) | 2500 – 4 500₽ |
| Tooth restoration | 5 500 ₽ |
| Permanent teeth | Price |
| Temporary filling | 300 ₽ |
| Medical pad | 550 ₽ |
| Treatment of caries with placement of a light polymerization filling (anesthesia, cavity formation, antiseptic treatment, filling) | 2500 – 4 500 ₽ |
| Tooth restoration | 5 500 ₽ |
You can make an appointment with a pediatric therapist by multi-line phone or online on the website.
In our center, pediatric dentistry operates in the following clinics:
- Bratislavskaya, VDNKh, Verkhniye Likhobory, Krasnogorsk, Oktyabrskoye Pole, Petrovsko-Razumovskaya, Skhodnenskaya
Classic filling
requires a special approach when treating young patients, since the doctor has to use dental equipment, which often causes fear in children.
Aza&Buka dentistry uses both traditional and modern methods of treating caries of primary teeth, selecting a method taking into account the age of the child and the degree of neglect of the process.
Plaksina Margarita
“Modern parents are great! They themselves are not afraid of dentists, and children are taught the same thing: to come on time for preventive appointments and examinations. In such cases, doctors can intercept the very beginning of a cavity infection and prevent tooth decay without drilling.”
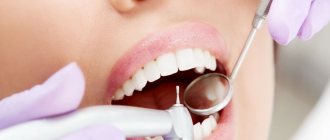
Diagnosis of caries in children
How to recognize caries in a child? A parent cannot always do this, since caries in children becomes noticeable only when there is already a hole in the tooth. Often a child is brought to the dentist “just to check his teeth,” and the doctor finds several caries after examining him with instruments.
The usual methods for diagnosing caries are inspection and probing. As a rule, this is enough to determine the presence of caries. The depth of the lesion can be assessed based on the child’s complaints and by x-ray examination.
Deep caries in a child is visible to the naked eye. At the same time, deep carious lesions on a tooth will almost always require x-rays so that the doctor can understand how far the carious process has gone, whether it is possible to save the tooth or whether removal is necessary.
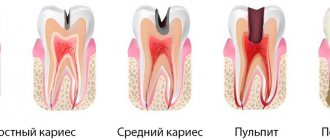
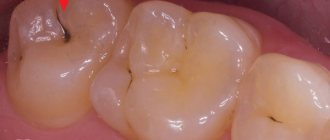
Milk caries: initial, superficial, medium, deep
Doctors distinguish 4 stages of the formation of carious areas:
- Initial caries - tooth enamel becomes covered with small spots of white or yellowish tint.
- Superficial caries - the enamel begins to deteriorate, small and light cavities are observed.
- Medium – the layer of tooth enamel is destroyed, the affected area extends deeper.
- Deep - the layers of dentin have already been affected, and the pulp is under threat.
It is necessary to treat milk caries at the very first stage, although it does not cause any discomfort in the child. The fact is that the enamel and crowns of temporary teeth are subject to rapid destruction, and the development of caries occurs very quickly. Deep caries often provokes irreversible changes, which leads to premature removal of the baby tooth.
Rodikova Tatyana
“Medium and deep caries most often occurs in schoolchildren, almost teenagers. Children brush their teeth poorly, and they talk about problems only when caries has already affected the pulp. In this case, the treatment turns out to be more unpleasant, since removal of the pulp cannot be avoided. That’s why I always ask parents to carefully monitor their teenagers’ hygiene and bring them to appointments on time.”
Clinical picture of caries
The first stage of the carious process
Caries occurs in the spot stage and in the superficial layers of enamel. Then we observe a stain on the surface of the tooth, which gradually becomes more dull, rough and porous.
The second stage of the carious process
If the enamel is chipped and a defect is formed, the tooth becomes more sensitive to irritants. Transient pain appears after eating cold, sweet and sour foods.
The third stage of the carious process
A carious cavity in dentin (tooth tissue located under the enamel). In this case, toothache appears depending on the situation, for example, when chewing on a diseased tooth or when there is a sudden change in the temperature of food, air, or when food gets into the cavity of a damaged tooth.
The fourth stage of the carious process
With further destruction, a deep carious cavity appears in the tooth, which gradually increases in size, so that eventually the tooth is destroyed and the pain appears spontaneous and constant. At this stage, an urgent visit to the dentist is necessary, as this indicates damage to the nerve of the tooth. In this case, it is not always possible to save the tooth.
Meet our tooth fairies and find out prices
Reasons for the development of caries in temporary teeth
When visiting a dentist, parents are invariably interested in the reasons for the appearance of such an unpleasant disease. This is important because it helps prevent damage to new teeth. Sometimes it is enough to change eating habits and hygiene patterns so that the child forgets about fillings for a long time, and only comes to the dentist for examinations.
Causes of caries:
- Poor or insufficient oral hygiene. Food remains in the interdental space and on the enamel are an excellent environment for the development of carious bacteria.
- An unbalanced diet with a preponderance of sweets and carbohydrates - during the fermentation of simple carbohydrates, acids are formed that provoke the destruction of enamel.
- The lack of solid foods in the menu leads to a decrease in the frequency of chewing, reduces salivation and becomes a common cause of caries of primary teeth in young children.
- Long-term use of nipples, including on bottles and sippy cups, increases the risk of developing single or multiple bottle caries of the anterior milk teeth in children.
- Rickets is a pathology that provokes the destruction of dental tissues.
- Genetic predisposition of the child.
- Problems with bite – various anomalies in the formation of the dentition.
- Decreased natural immunity due to frequent acute respiratory viral infections, chronic diseases, and taking various medications.
- Damage to tooth germs in the prenatal period - due to maternal illness or neglect of health in the first trimester.
Types of caries
According to the place of manifestation
- Fissure caries affects the grooves and grooves on the surface of the chewing teeth - fissures. Food debris accumulates inside the fissures, which means bacteria that cause caries.
- Approximal (interdental) caries occurs between adjacent teeth, especially often when teeth are crowded. It is very difficult to clean out food debris from the interdental spaces, so plaque often accumulates there.
- Cervical caries destroys the enamel next to the gum, since it is in this place that it has lower mineralization and minimal thickness.
- Root caries characterizes the destruction of the tooth root under the gum. To diagnose root caries, additional methods are needed, since it is difficult to detect visually. In children, it occurs when there is severe destruction of baby teeth.
According to the speed of development
- Compensated caries proceeds slowly; many months can pass from the spot stage to the development of deep caries. In some cases, the process may even be reversible, but only by restoring the mineralization of the enamel in a tooth with caries in the stain stage.
- Decompensated caries develops quickly and on several teeth at the same time; sometimes from the stain stage to deep caries it can take less than 2-3 months. Numerous foci of carious lesions, increased sensitivity of teeth to irritants, deterioration of the enamel structure are signs of decompensated caries.
Comments
Is it possible to simply anoint your child’s teeth with fluoride as a preventive measure to protect against caries? Nowadays you can buy everything at the pharmacy, why go to the doctor?
Veronica (01/18/2021 at 18:00) Reply to comment
- Dear Veronica, fluoridation of children’s teeth at home is very dangerous. Firstly, it is difficult to independently identify contraindications to this procedure and carry it out as carefully as possible, and fluoride is quite toxic to the body if you overdo it or swallow it. Secondly, an excess of fluoride can lead to fluorosis. Be sure to read the article about 6 warnings for those who want to fluoride their teeth at home.
Editorial staff of the portal UltraSmile.ru (01/21/2021 at 09:15) Reply to comment
Eh, when will they invent something so that people’s teeth don’t deteriorate at all, are healthy and don’t get sick)) even baby teeth need to be treated for caries, and it doesn’t matter that they will soon fall out?
Marina (02/05/2021 at 07:31) Reply to comment
The doctor who sees my sons recommends rinsing the mouth with chlorhexedine and calendula decoctions as a preventive measure for caries in the initial stages. Is this justified or are there better means?
Stanislav (02/05/2021 at 08:51) Reply to comment
I would like to know what to do at home before going to the doctor? It’s a disaster when a child can’t even eat normally. Fluorine? How effective is it if there is already a problem?
Marina (02/05/2021 at 09:10) Reply to comment
Hello! My daughter complains from time to time of pain in her front tooth. Always points to the same tooth. She is only three years old. Could it really be caries already? In appearance, I don’t see any changes in the tooth. Maybe she's just overly sensitive? Or should I see a dentist?
Anna (03/04/2021 at 10:26 am) Reply to comment
Hello. The child has caries on the central teeth, but it is white, not yellow or brown, they administered a course of Tus-Mousse gel, but the whiteness remained. What are the chances that tooth decay will continue to develop?
Alexandra (03/04/2021 at 10:36 am) Reply to comment
My son (5 years old) and I were examined by a dentist. One hole was found on the side molar. The dentist said that treatment is not necessary now. My son does not complain about pain in his teeth. So, don't touch this tooth for now? Or is it better to cure now, before the caries grows?
Anna (03/04/2021 at 11:48 am) Reply to comment
Write your comment Cancel reply
Symptoms of the disease
A child cannot always point out the source of pain and discomfort, so parents need to be especially attentive to their child’s behavior and monitor the condition of the oral cavity. The following symptoms should alert you:
- Refusal to eat, tearfulness while eating;
- Chewing food on only one side of the jaw;
- Painful sensations from hot, cold and sweet;
- Yellow or white spots, dark streaks on tooth enamel;
- Bad breath.
If you observe one or more of the signs listed above in your child, contact your dentist immediately.
Prevention, or how to avoid “bottle” caries?
After reading this, many may accuse me of advocating the abandonment of breastfeeding, or the sudden cessation of feeding during sleep! In no case! Firstly, every mother decides for herself how long to breastfeed her child. In addition, I think no one will argue that there is nothing better than natural breastfeeding, since in addition to nutrients, the child receives passive immunity from the mother due to the IgG immunoglobulins contained in milk.
Ingredients: In addition to xylitol, TeethCleaners™ contain green tea extract, which has a mild anti-inflammatory and anti-edematous effect, which helps reduce itching of the gums during teething. The composition also includes various biological natural components, such as rice and barley decoction.
- Careful oral hygiene. You should start brushing your teeth from the moment they appear as often as possible, and at least 2-3 times a day. REMEMBER: NO PLAQUE - NO CARIES! In addition, this develops in children the habit of brushing their teeth and at an older age they will be more enthusiastic about brushing on their own;
- After each meal, wipe your baby's teeth. For this purpose, there are special dental wipes Spiffies™, ZubkiChistki™, Wakodo™ Tooth Cleaner for Baby. The xylitol they contain has a bacteriostatic effect on Streptococcus mutans, which causes caries and inflammatory gum diseases. By the way, the xylitol contained in the wipes has a sweetish taste, for which children are happy to let you wipe their teeth. If you don’t have them on hand, you can use the “old-fashioned method”: ordinary gauze wrapped around your finger and soaked in water, tea or chamomile decoction. By the way, treatment with various decoctions (chamomile, oak bark, etc.) helps remove gum teeth during teething, as they have a slight anti-inflammatory and anti-edematous effect;
- Try to include solid food in your diet (apples, carrots, cucumber, etc.). Firstly, children like to chew on something, especially when they are teething. Secondly, while the child is gnawing on a carrot, the surface of the tooth is cleansed of bacterial plaque. Plus, some vegetables (carrots, cucumbers, celery stalks) and herbs (parsley) regulate the pH of saliva in the mouth (shifting it to the alkaline side), which creates additional protection against caries;
- At home, you can independently carry out remineralizing therapy to strengthen your tooth enamel. For this, there are special remineralizing gels and creams: ROCS Minerals™ and GC Tooth Mousse™;
- Do not lick the pacifier and spoon, do not give him food you have chewed. Together with your saliva, the bacterial flora of the oral cavity is transmitted, which the child’s body is not always able to cope with;
- Try not to use the pacifier unless absolutely necessary. And especially do not lubricate the pacifier with sugar or jam. Affection and love for a child are better than any pacifier. If your child is crying, contact your pediatrician, there may be a good reason for this;
- Consult a pediatric dentist as soon as your baby's first tooth emerges. The pediatric dentist will always tell you how to properly care for them.
PHOTO: Spiffies™ oral hygiene wipes for young children contain xylitol, which has a sweetish taste and a bacteriostatic effect (inhibits the growth of bacteria).
To learn how to teach a child to brush their teeth correctly and what brushing technique to use, read the article How to properly brush a child’s teeth?
If you find whitish, rough (or any other color) spots on your baby’s teeth, you should not immediately try to self-medicate and remineralize therapy, even if you are sure that this is the initial stage of caries. First, consult a pediatric dentist! A pediatric dentist will always explain and show parents how to properly care for a small child’s teeth, especially if signs of enamel destruction are already appearing, will help select individual hygiene products and, if necessary, will carry out the necessary treatment.