There are several types of malocclusion. Rare teeth are the most common. It is characterized by the presence of very wide spaces between dental units. At the same time, the chewing structures are externally similar to a comb with sparse teeth. This pathological condition cannot be ignored, as it can lead to the development of dangerous complications. Currently, there are several methods for treating rare teeth (a photo of the defect is presented below). The feasibility of using a particular method is assessed by the orthodontist.
Causes and consequences
The “culprit” of the pathology is a genetic factor. Large distances between chewing units are noticeable already at the stage of eruption of milk teeth. In extremely rare cases, pathology develops against the background of progression of dental diseases.
Rare teeth in humans are not only unsightly, but also dangerous to health. Initially, psycho-emotional instability appears. It is caused by complexes that have arisen and low self-esteem.
In addition, sparse teeth cause the following pathological conditions:
- Disorders of the gastrointestinal tract. Wide spaces between dental units do not allow for proper chewing of food. As a result, food enters the stomach in an insufficiently processed form. The natural consequence is indigestion.
- Tooth loss. Chewing units located far from each other are characterized by increased fragility. In addition, they are extremely vulnerable to any external influences.
- Inflammatory processes in the oral cavity. When there are large gaps between teeth, soft tissues also become more vulnerable to external influences. They are easily injured, and when pathogenic microorganisms penetrate the oral cavity, an inflammatory process develops.
To prevent the development of complications and make your smile perfect, you need to contact an orthodontist. Only a doctor can provide information on how to correct rare teeth in each specific case.
Anomalies of hard tissue structure
An altered shape, abnormal size or color of enamel is formed against the background of an abnormality in the structure of the hard tissues of the dental unit. Among such anomalies are:
- Hypoplasia (underdevelopment of tissue). The initial degree of the disorder is manifested by the presence of chalky spots on the enamel and areas where tissue deficiency is observed. Subsequently, all kinds of pits, grooves, and recesses appear on the surface of the enamel. The defect affects all teeth in the dentition.
- Hyperplasia (excessive tissue formation). Pathology also affects all teeth at the same time. It is characterized by areas where tissue growth is observed - tubercles, sagging enamel. The consequence of the pathology is a change in the shape and size of the teeth, a violation of the occlusion (the line of contact of the upper and lower jaws).
- Anomalies of amelogenesis (enamel formation) are expressed in the presence of brown or yellow spots on the surface of the teeth. Areas where the natural composition of the enamel is disrupted become especially sensitive. Microdentia develops against the background of pathology. The cause of the development of pathology is a deficiency of microelements that take part in the formation of dental tissue. Treatment consists of replenishing this deficiency. Additionally, local remineralizing therapy and physiotherapy are performed.
- Disturbance of dentinogenesis consists of dysfunction of the mechanism of dentin formation. The main symptoms of the disease are as follows: teeth become yellow-brown or grayish in color. The fragile dentin in these areas quickly wears off, causing tooth decay and then tooth loss. The disease occurs in genetically predisposed patients. The problem can only be solved by replacing the units destroyed by the disease with prosthetics.
Diagnostics
After the examination, the orthodontist will refer the patient for a comprehensive examination. Based on its results, the doctor will be able to make a decision on what to do with the rare teeth of the person who contacts him.
Diagnosis may include the following studies:
- Orthopantomogram. This is a three-dimensional shot of the jaws.
- X-ray examination.
- Computer diagnostics. The method is considered the most accurate and informative. It allows you to evaluate both the structure of the jaw and the location of the teeth.
Based on the diagnostic results, the orthodontist will select the most effective method of treating rare teeth. It is important to understand that it is impossible to correct the genetic factor, but doctors are able to disguise the defect so that the patient’s smile is perfect. Contrary to popular belief, if adults have sparse teeth, braces are powerless. This method of correcting the bite is not used if a person has large distances between the teeth.
Color anomalies
Healthy, young teeth look snow-white due to a thick dentin layer and high-quality enamel, which has sufficient characteristics of whiteness, shine and transparency. Lifestyle, age, genetic factors, and ecology can slightly change the color of teeth from bluish to yellow. Small deviations are not considered pathology, although they indicate a change in the quality of the enamel.
Various pathological processes occurring in the body have a more significant impact on the condition of the enamel. The cause may be carious lesions, the use of medications, or a lack of certain microelements in the body. Teeth can take on a gray, pinkish, brown, purple and even black tint.
When starting to treat a patient, the dentist excludes the development of chronic pathologies. After a course of therapy and stable remission is achieved, other causes of discoloration of the enamel are eliminated. The final stage of treatment is a course of teeth whitening.
Specialists at the Consilium Dent choose the enamel lightening technique together with the patient. The selection criteria are age, condition of the enamel, and the wishes of the patient.
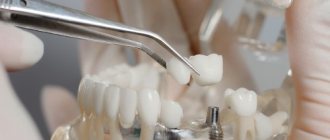
Dental implantation
The technique is the most radical. The essence of the procedure is to replace rare dental units with prostheses. The latter are screwed into the jaw using a titanium pin that imitates a tooth root.
The main advantage of implants is that they are as similar as possible to natural chewing units and fully perform the functions of the latter. As a result, food is chewed efficiently and the load between the teeth is distributed evenly. As a result, the process of forming a correct bite begins.
In addition, implanted teeth are permanent. In other words, they do not need to be removed and cared for separately.
Dental implantation is contraindicated if the patient has type II diabetes mellitus, HIV, hepatitis and severe heart pathologies.
Installation of a bridge
The use of fixed orthodontic structures is a modern way to fill wide gaps in the dentition.
In order for the prosthesis to be securely fixed, it is necessary to have supporting dental units. It is on them that the entire structure is attached.
The best option is to make a bridge from metal ceramics. The service life of this design is 7 years or more. At the same time, the bridge retains its original shade and does not differ from adjacent natural teeth.
Contraindications to installing a prosthesis on rare teeth:
- Acute periodontitis.
- Parafunctions of the masticatory muscles.
- Insufficient height of supporting teeth.
If there are absolute contraindications, the doctor makes a decision regarding the advisability of using a different treatment method.
Why is it important to correct malocclusion?
Correction of dental malocclusion can be carried out for both adults and children - there are no age restrictions. The problem cannot be left unattended.
Why do you need to correct dental anomalies:
- aesthetics improves;
- diction improves;
- facial muscles relax;
- the functioning of the temporomandibular joint improves;
- headaches associated with malocclusion disappear;
- the risk of developing diseases of the gums and teeth is reduced, as the pressure on the teeth is reduced, and the problem of enamel abrasion is solved.
Correcting the bite also helps to cope with psychological problems that were caused by pathology - isolation, secrecy, reluctance to communicate with other people.
Sealing
Currently, it is one of the most affordable ways to treat rare teeth. Its wide distribution is due to its low cost and ease of implementation.
The essence of the method is as follows: fillings of the same color as the natural chewing units are applied to the teeth. The procedure is considered a jewelry procedure, since the doctor must literally mold new bone structures. As a result, the teeth become wider and the gaps between them disappear. Only a specialist can visually distinguish fillings from natural dental units.
During the procedure, orthodontists use only high-quality materials. These are ceramics and porcelain.
After filling rare teeth, the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract is normalized and a correct bite begins to form.
Installation of veneers
This is a highly effective correction method. Veneers are thin plates made of ceramic or porcelain. They are placed on top of natural teeth.
The main advantage of the method is that the plates cover and protect the enamel coating of the dental units. In other words, there is no need to grind or file down adjacent teeth.
Contraindications for installing veneers:
- Severe destruction of dental units from the tongue.
- The presence of large fillings.
- Grinding of teeth.
- Having a bad habit of opening bottles with your teeth, cracking nuts with them, etc.
In addition, veneers cannot be installed if six or more chewing units are missing from the mouth.
Installation of crowns
These are non-removable structures that can be used to eliminate dental defects. The installation of crowns is also indicated in case of severe destruction of dental units. The essence of the method is to insert an artificial tooth into the gum using a pin made of metal.
Installing crowns requires some preparation. The patient's natural teeth are prepared and, if necessary, pulp removal is performed. Crowns take several days to make. During this period, the patient is provided with temporary structures. The finished crowns are completely identical to the patient’s teeth. They differ only in width, which makes it possible to hide large gaps between chewing units.
The following conditions are contraindications: loose teeth, allergic reaction to the components used, periodontal pathologies. In addition, crowns are not placed on anyone under 16 years of age.
Rare teeth in a child
Radical treatment methods are not used for children. In addition, a child under 5 years old just needs to be monitored. This is due to the fact that after teething, the jaw continues to grow, so there must be gaps between the dental units. This is a normal physiological process. It is necessary to consult a doctor only if the space between the teeth remains very wide after the eruption of all milk teeth.
Children may have braces. In most cases, after such an adjustment, the teeth will take the required position, and the distance between them will decrease.
If the cosmetic defect remains pronounced even after removing the braces, the doctor may recommend filling or installation of veneers. The advantage of these methods is that there is no need to prepare natural teeth. It is recommended to give preference to the installation of veneers. Thin plates can not only hide empty areas, but also protect the enamel from the harmful effects of external factors.
Types of bite
The bite can be correct or incorrect. If it is correct, then it does not affect the condition of the teeth and health in general. The jaws close correctly, articulation is painless, and the temporomandibular joint moves smoothly. A person can chew food normally, which has a positive effect on digestion, the state of the gastrointestinal tract and well-being.
There are 4 types of physiological occlusion:
- straight,
- orthognathic,
- physiological prognathia,
- opisthognathia.
Types of malocclusion:
- Distal. It is characterized by a large sagittal fissure - up to 9 millimeters. The teeth of the upper jaw protrude forward. More often, the appearance of the anomaly is influenced by genetic predisposition. But it can also be triggered by bad habits or untimely removal of baby teeth.
- Open. The jaws cannot be closed tightly because the side and front teeth do not touch. The pathology is often acquired.
- Deep. The upper jaw overlaps the lower jaw, so the teeth do not touch.
- Mesial. The lower jaw protrudes forward.
- Cross. The jaws do not close tightly, and the teeth grow incorrectly and are of different sizes.
- Edentia. With such a pathological bite, some of the teeth in the row are missing.
- Tremas and diastemas. The peculiarity is that the teeth are too sparsely spaced, causing large gaps to appear between them.
- Crowding. Teeth grow incorrectly and can “crawl” onto each other.
Each type of malocclusion requires specific treatment. An orthodontist will help you choose the right option after diagnosis.