Lips are the most vulnerable part of the human body. Due to the absence of the stratum corneum, the lips are too susceptible to the influence of the external environment, so pathogens appear and multiply most often in this area.
Candidiasis on the lips is quite difficult to diagnose in the early stages of development, since there are no symptoms for a long time, and the disease becomes latent. This is the danger of thrush: the fungus develops in the body without any clinical manifestations, and in the end it can cause oncology.
General information about candidiasis
The fungus is an infectious disease and actively develops in winter and autumn. This is due to a strong decrease in immunity and hypothermia of the body at these times of the year.
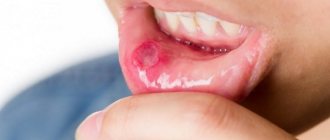
Externally, the fungus manifests itself in the form of wounds similar to seizures, which are provoked by the active reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms. Among the clinical manifestations are: loss of appetite, pain and burning in the damaged area.
The disease can manifest itself in both adults and children. Sometimes it becomes chronic. For treatment, complex therapy is used, based on the use of antifungal drugs.
Classification of the disease
Based on the depth of damage, candidiasis is divided into superficial and systemic forms. The first appear on visible parts of the body: mucous membranes, skin and its appendages. The second, systemic, are combined forms of the disease affecting internal organs. Without proper treatment, systemic (visceral) candidiasis can lead to the development of candidal sepsis. Most often, the fungus affects:
- gastrointestinal tract (esophagus, stomach, intestines);
- urinary organs (bladder, urinary tract, kidneys);
- lower respiratory tract (trachea, bronchi, lungs).
The disease is also classified based on the rate of spread of infection and the presence of relapses. Candidiasis of the liver and spleen often takes a chronic form. The acute, generalized form is asymptomatic candidemia, candida septicemia, candida thrombophlebitis, myositis, arthritis, cerebral candidiasis and other forms.
Classification of candida lesions according to ICD-10
- Candidiasis.
- Candidal stomatitis.
- Pulmonary candidiasis.
- Candidiasis of the skin and nails.
- Candidiasis of the vulva and vagina.
- Candidiasis of other urogenital locations.
- Candidal meningitis.
- Candidal endocarditis.
- Candidal septicemia.
- Candidiasis of other locations.
- Candidiasis, unspecified.
Officially, the diagnosis is made in accordance with ICD-10. In practical healthcare, such a classification is not entirely convenient, so they use the classification of deep candidiasis, which is a deeper list. When making a diagnosis, first indicate the name and form of the infection with a description of all localization points.
Skin treatment is carried out by a pediatrician in children and by a dermatologist in adults. Therapy is also carried out by doctors of other specializations, depending on the affected organ. For example, this could be a dentist, neurologist, gynecologist, pulmonologist.
Main clinical manifestations of candidiasis
Symptoms of the disease appear quite late and, at first, resemble ARVI. But candidiasis can be recognized by the following clinical manifestations: local redness and peeling, the appearance of ulcers near the corners of the mouth, rash, a feeling of tightness in the lips, emotional instability, redness of the lip border, increased sensitivity, plaque, swelling.
Such symptoms are most often observed in advanced stages of the disease, so it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor so as not to infect internal organs with the fungus.
Causes of fungus
The provocateurs of fungal infection are: emotional stress, hypothermia, sudden climate change, too hot weather, disruption of the hormonal system, diseases of the endocrine system, long-term treatment with antibiotics, failure to comply with hygiene rules, and abuse of sweet foods.
Also, candidiasis can develop if you do not wipe your lips after eating. Pathogenic organisms accumulate in the corners of the mouth and affect soft tissues and mucous membranes.
Another “risk factor” is bad habits and poor diet, as they weaken the immune system. As soon as the immune system begins to weaken, fungal bacteria immediately begin to penetrate into the deep layers of soft tissue and actively develop there.
After taking immunostimulating drugs, ulcers on the lips immediately disappear, and the disease goes into a latent state, but at the first opportunity it will reappear and cause a lot of discomfort.
Types of fungus
For effective treatment, it is necessary to determine the nature of the fungal pathology. Candidiasis happens:
- Pseudomembranous. Accompanied by a white coating on the mucous membrane, itching and burning. Then pimples appear. There is discomfort and pain when talking and eating.
- Acute atrophic. Characterized by increased dry mouth. There is also a burning sensation and pain when moving the tongue. Irritability increases and the patient becomes nervous.
- Hyperplastic. This type of candida infection is the most painful, as it is characterized by the appearance of plaques on the lips and mouth. They make it difficult to chew food. The patient feels acute pain and swelling of the oral mucosa occurs.
- Chronic atrophic. It has a recurrent nature and is manifested by the following symptoms: viscous consistency of saliva, dry mouth, redness of the skin of the lips.
Lipophilic yeast of the genus Malassezia
are representatives of the normal mycobiota of human skin and warm-blooded animals.
At the same time, Malassezia
spp.
can cause the development of pityriasis versicolor (synonyms: pityriasis versicolor, pityriasis versicolor
) or
Malassezia
folliculitis in individuals who are predisposed to these diseases, as well as in immunodeficiency states, decompensation of endocrine diseases, etc.
of Malassezia
has now been proven .
in the development of seborrheic dermatitis. It has been established that fungi of the genus Malassezia
spp. influence the course of atopic dermatitis and seborrheic psoriasis. Endogenous factors that promote colonization of these lipophilic yeast-like fungi on the skin include hyperhidrosis, vegetative-vascular disorders, endocrine diseases, metabolic syndrome, and immunodeficiency states. Exogenous factors that contribute to skin contamination and the development of Malassezia-associated diseases are climatic factors, such as high ambient temperature and high humidity. Therefore, pityriasis versicolor is most widespread in countries with subtropical and tropical climates [1].
Despite the characteristic clinical picture of pityriasis versicolor, the relative simplicity of laboratory diagnosis of the disease and the availability of a wide range of modern antifungal drugs, both systemic and local, it is not always possible to achieve 100% effectiveness in its therapy. Some of the traditional treatment methods, still often used by domestic dermatologists (Demyanovich treatment, sulfur-containing preparations), are not effective enough and are not always well tolerated by patients, since the products used have an unpleasant odor and can cause itching, burning and irritation of the skin [2] . At the same time, modern topical antimycotics (allylamines, azole derivatives), due to their fungicidal action, are highly effective drugs. Such medicinal bases as spray (aerosol) and gel, unlike cream, are highly hygroscopic and have a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect, which makes them acceptable in situations where the course of pityriasis versicolor is accompanied by a pronounced inflammatory reaction and patient complaints of itching and burning. Although the latter are not typical for pityriasis versicolor, they can occur in patients with diabetes mellitus, obesity, Itsenko-Cushing syndrome, in patients with hypothyroidism, hyperhidrosis, and with the addition of coccal biota. Use of drugs for external therapy with terbinafine
in complex therapy of dermatoses associated with
Malassezia
spp. (atopic dermatitis, seborrheic dermatitis, psoriasis), allows you to achieve stable remission of these diseases or reduce the severity of their manifestations.
At the Research Institute of Medical Mycology named after. P.N. Kashkin in the dermatological and consultative diagnostic departments, a dynamic prospective (cohort) passive clinical study was conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of terbinafine
in the treatment of dermatoses caused and associated with
Malassezia
spp.
Purpose of the study: to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of Lamisil Spray
and
Lamisil Dermgel
in the treatment of dermatoses caused and associated with
Malassezia
spp.
Material and methods
The criteria for inclusion of patients in the study were age 12 years and older; presence of one of the dermatoses caused or associated with Malassezia
spp.
(pityriasis versicolor, Malassezia folliculitis, seborrheic dermatitis, atopic dermatitis, psoriasis); detection of fungi of the genus Malassezia
by microscopy of skin scales with a KOH solution (clusters of round double-circuited budding cells up to 5-8 µm and short septate, slightly curved, sometimes branching hyphae 3-4 µm wide) and/or sowing.
Exclusion criteria were age <12 years; pregnancy; lactation; use of systemic antifungals less than a month before the start of the study, use of antifungals for local therapy less than 2 weeks before the start of the study, hypersensitivity to terbinafine
.
Malassezia were observed
spp.: 159 (60.9%) men and 102 (39.1%) women aged 11 to 78 years (median 38.5 years).
In 169 (64.8%) patients, Malassezia
spp. were detected by microscopic examination, and in 92 (35.2%) they were isolated as a result of culture.
Monotherapy with drugs containing terbinafine
—
Lamisil Spray
or
Lamisil Dermgel
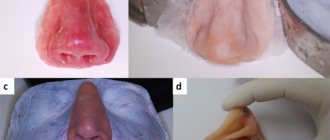
, was prescribed to 90 patients with pityriasis versicolor (Fig. 1),
Figure 1. Pityriasis versicolor in an 18-year-old girl. a - before using Lamisil Gel; b — after using Lamisil Gel for 7 days. 19 patients with external otitis and 15 patients with Malassezia-folliculitis (Fig. 2).
Figure 2. Malassezia folliculitis in a 52-year-old patient with pemphigus vulgaris, which developed while taking prednisolone 100 mg/day for 4 weeks. a — before treatment with Lamisil Cream; b — after using Lamisil Cream for 7 days. As part of combination therapy, antifungal drugs Lamisil Cream
and
Lamisil Dermgel
were prescribed to 49 patients with atopic dermatitis, 32 patients with psoriasis, and 56 patients with seborrheic dermatitis.
Lamisil Spray
and
Lamisil Dermgel
were applied to the skin 2 times a day with a 12-hour interval for 7 days.
The effectiveness of therapy in patients with pityriasis versicolor, Malassezia folliculitis, and otitis externa was assessed immediately after its completion. The criteria for clinical cure were the absence of hyperpigmented spots or folliculitis, peeling; negative iodine test. In this case, the presence of depigmented spots on hyperpigmented skin after ultraviolet irradiation (secondary leucoderma) was not taken into account. The criterion for mycological cure was the absence of both yeast and mycelial forms of Malassezia
spp., and the criterion for complete cure is the absence of clinical symptoms and
Malassezia
spp. in skin flakes obtained from the surface of the skin at the site of resolved lesions. The effectiveness of therapy in patients with psoriasis, atopic dermatitis and seborrheic dermatitis was assessed by the degree of resolution of the main symptoms of the disease (itching, hyperemia, infiltration, peeling), as well as by the results of mycological examination.
results
Pityriasis versicolor was diagnosed in 90 patients: 61 (67.8%) men and 29 (32.2%) women aged 12 to 68 years (median 39 years). The average duration of the disease was 5.7±1.2 years. 20% of patients had a relapsing course of the disease. Risk factors for the development of pityriasis versicolor were hyperhidrosis, diabetes mellitus, taking oral contraceptives, playing sports, and characteristics of work activity (working in hot shops). In most patients with pityriasis versicolor, the disease manifested itself with a classic clinical picture. The rashes were represented by single scattered or merging multiple brownish spots with pronounced pityriasis-like peeling on the surface. Most of the rashes were located on the neck, anterior chest, and interscapular area. In 15 patients, the rashes formed large lesions with finely scalloped edges and localization in large folds of the skin: under the mammary glands, in the inguinal-femoral folds, the intergluteal fold, and in the armpits. Characteristic was the presence of type 2 diabetes mellitus. In 2 patients, the rashes covered more than 50% of the skin, and all of their rashes merged, resembling a geographical map in appearance. These patients were also diagnosed with candidiasis of the mucous membranes of the mouth, tongue and candidal esophagitis. As it later turned out, the cause of the widespread mycotic process in these patients was the human immunodeficiency virus. They were not included in the study because their condition required systemic antifungal therapy.
Seborrheic dermatitis was observed in 56 people: 42 (75%) men and 14 (25%) men aged 18 to 65 years (median 41 years). The duration of the disease with seborrheic dermatitis was 3.7±0.9 years. 18% of patients had a relapsing course. Risk factors for the development of seborrheic dermatitis were disorders of the autonomic nervous system, hyperhidrosis, pathology of the digestive system, and pathology of the thyroid gland. A connection between relapses of the disease and emotional stress and exacerbation of chronic somatic diseases was identified.
Fungi of the genus Malassezia
isolated from 49 patients with atopic dermatitis: 24 (49.0%) men and 25 (51.0%) women aged 21 to 56 years (median 38 years).
Features of the course of atopic dermatitis in this group of patients were pronounced constant severe itching, the predominant localization of foci of inflammation on the scalp, face, neck, anterior chest wall, in the interscapular region, exudation and weeping. All patients had a high level of total IgE ≥1000 U/l. A connection was found between exacerbation of atopic dermatitis and an increase in the level of colonization with Malassezia
spp. A significant subsidence of atopic dermatitis was noted after the use of antifungal drugs in its complex therapy.
Malassezia fungi were isolated from 32 patients with psoriasis
spp.: in 17 (53.1%) men and 15 (46.95) women aged 16 to 72 years (median 49 years). The average duration of the disease was 19.4±1.8 years. The course of psoriasis in this group of patients differed from the usual. The appearance of the rash was accompanied by severe itching and burning; the lesions were most often located in seborrheic areas and in skin folds. Psoriatic rashes were covered with scales soaked in exudate. After complex therapy of psoriasis with the use of antifungal drugs, all patients, as a rule, noted a subsidence of the psoriatic process.
Otitis externa due to Malassezia
spp., were observed in 19 patients. It developed acutely, on average within 3.6±0.3 days. The onset of the disease was characterized by the appearance of severe itching, burning, and sometimes pain in the external auditory canal. The appearance of hyperemia, peeling, exudate on the surface of the skin of the external auditory canal and weeping was noted. We identified risk factors for the development of external otitis: seborrheic dermatitis, psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, chronic trauma to the skin of the external auditory canal, and water sports.
Malassezia folliculitis was diagnosed in 15 patients. It was characterized by an acute onset, the appearance of a large number of small folliculitis with a thin rim of hyperemia on the anterior wall of the chest, back, and less often on the face and scalp. The appearance of rashes was preceded by taking high doses or long-term use of medium and low doses of glucocorticosteroids, massive antibacterial therapy, and the development of immunodeficiency states.
As a result of treatment in a group of 76 patients who received monotherapy with Lamisil
(
terbinafine
), clinical recovery was observed in 74 (97.4%), mycological recovery in 73 (96.1%), complete recovery in 71 (93.4%).
Among those who received Lamisil
(
terbinafine
) as part of complex therapy, improvement was noted in 19 patients with atopic dermatitis, in 15 patients with psoriasis and in 15 patients with seborrheic dermatitis.
Positive dynamics were not noted only in 2 patients with atopic dermatitis and in one patient with seborrheic dermatitis. There was no deterioration during the process in any of the patients who received treatment with terbinafine
.
When using drugs Lamisil
(
terbinafine
), no adverse events were observed in any of the patients.
All patients receiving Lamisil
(
terbinafine
), when applied to the skin, they noted good absorption of the product, the absence of an oily sheen of the skin and a feeling of greasiness.
The use of Lamisil
, due to its pronounced anti-inflammatory and cooling effect, made it possible in a short time (24-48 hours) to reduce itching and burning when lesions were localized in the folds.
Discussion
The role of fungi of the genus Malassezia
in the development of pityriasis versicolor and
Malassezia
-associated skin diseases has been known for a long time.
However, these micromycetes began to attract special attention from mycologists due to the fact that with long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs in oncological, hematological patients and patients who underwent bone marrow and solid organ transplantation, septic conditions caused by Malassezia
spp began to develop. [3].
For the diagnosis of diseases caused by Malassezia
spp., most mycological laboratories use direct microscopy of pathological material after its treatment with KOH.
Determining the genus of the pathogen is not difficult if the tissue forms of the fungus have a characteristic appearance. However, it has recently been established that the morphology of the tissue form of the fungus is variable. Since culture diagnostics for Malassezia
spp.
is a long and labor-intensive process, there are problems in determining the species of this micromycete [3]. Therefore, this diagnostic method is rarely used. However, in recent years the situation has changed. New culture media and methods for determining the susceptibility of Malassezia
spp have been developed.
to antimycotics. This made it possible to establish the existence of 13 species of fungi of the genus Malassezia
-
M. globosa, M. sympodialis, M. furfur, M. obtusa, M. dermatis, M. restricta, M. slooffiae, M. pachydermatis, M. japonica, M. yamatoonsin, M. pana, M. coprae, M. eguina
[1, 4, 5].
In addition, it was found that different species of Malassezia
spp. have variable sensitivity to antimycotics.
Research is currently ongoing to study the influence of different Malassezia
on the development and course of Malassezia-associated diseases [6].
Thus, it has been established that M. globosa, M. sympodialis
cause the development of pityriasis versicolor in patients living in temperate climates (Western and Eastern Europe), while
M. furfur, M. obtusa
- in patients living in hot and humid climates (Thailand, Malaysia, Iran, etc.).
The development of external otitis is promoted by M. sympodialis
, seborrheic dermatitis -
M. globosa, M. restricta
.
The course of atopic dermatitis is influenced by M. dermatis
.
It was found that Malassezia
have different sensitivity to antimycotics [6–8].
This must be taken into account when choosing an antifungal drug for the treatment of diseases caused by fungi of the genus Malassezia
, and prescribe them in accordance with the nosological form of the disease.
Most of the Russian Federation is characterized by a temperate climate. It can be assumed that the main causative agents of pityriasis versicolor in this area are M. sympodialis, M. globosa
that are highly sensitive to
terbinafine
.
The results of our study showed the high effectiveness of terbinafine
(
Lamisil
- 93.4% and 93.8%) in the treatment of pityriasis versicolor, Malassezia folliculitis and otitis externa, as well as in the complex therapy of seborrheic dermatitis, psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, the course of which was complicated by the addition of
Malassezia
spp.
However, for a small number of patients, standard treatment regimens were not sufficient. One of the factors for the ineffectiveness of therapy in these patients may be the low sensitivity of
Malassezia
species and strains terbinafine . Therefore, we can conclude that in cases of persistent, recurrent course of pityriasis versicolor, it is necessary to carry out additional diagnostic measures aimed at determining the type of pathogen and its sensitivity to antifungal drugs.
conclusions
1. Drugs Lamisil
are highly effective and safe in the treatment of dermatoses caused and associated with
Malassezia
spp.
Malassezia that are torpid to antifungal therapy
spp., it is necessary to determine the sensitivity of micromycetes
Malassezia
spp. to antimycotics.
Danger of disease
Cracks on the lips indicate a fungal infection, which can soon affect other organs. If left untreated, candida invades the blood vessels, resulting in bleeding.
Candidiasis spreads very quickly, so there is a high probability of fungus from the lip area entering the oral mucosa and developing into a tumor, and then into cancer.
People who smoke are most at risk as they expose their lips to the negative effects of smoke every day. As a result, the shape of the lips may change and cancerous tumors may appear.
Fungus under fingernails. Treatment
Diagnosis of candidiasis
The study is based on the isolation and identification of a species of fungus of the genus Candida. Currently, there are about 150 species, differing in morphological and biochemical properties. The most common fungus is C. albicans, accounting for up to 80% of cases of candidiasis of the digestive tract and up to 70% of genital infections. Before prescribing treatment, it is also necessary to determine the sensitivity of the isolated strain to antimycotics (antifungal medications): amphotericin B, voriconazole, itraconazole, fluconazole, flucytosine.
Microscopic diagnostics
1. Microscopy of a smear is taken from the area of the affected mucosa. Allows for comparative characterization of blastospores and pseudomycelia. During the study, fixed and native preparations that stain microorganisms are used. To increase the information content, pseudomycelia of cells are treated with dyes. The contrast in staining of microorganisms makes it easy to distinguish candida from other forms, including bacteria, under a microscope.
2. Bacterial culture allows you to identify the causative agent of infection and determine its concentration. The analysis is used to monitor the effectiveness of treatment, as well as to identify the sensitivity of candida fungi to various antimycotics.
Diagnostics by ELISA and PCP
1. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is based on the determination of antibodies that are produced by the immune system in response to foreign substances in the blood. This technique allows you to identify the pathogen and the degree of its development, establishing whether the disease occurs in an acute or chronic stage.
2. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a highly sensitive test that allows you to directly detect the infectious agent. Thanks to it, it is possible to differentiate Candida fungi with pseudomycelium from those that do not have it. These data are important for subsequent interpretation of results and deeper diagnosis.
Diagnosis of fungus on the lips
Diagnosing a fungal infection with its clinical manifestations is not difficult. But, to accurately determine the type of mycosis, it is necessary to undergo the following tests:
- Fungal infection culture.
- Skin scraping from the corners of the mouth for further microscopic examination.
- A biochemical blood test that helps to recognize the causes of candidal infection.
In some cases, additional tests may be prescribed (throat smear, examination of the mucous membranes of the pharynx using a video camera, x-ray). Such cases are rare, but if there is a threat of fungus getting into the esophagus area, a specialist will immediately give you a referral.
Such procedures are carried out to exclude diseases such as lichen planus, stomatitis, syphilitic papules.
Interpretation of results
If there are clear signs of candidiasis (thrush), and during a laboratory test blastospores and pseudomycelia of the fungus were identified, the study ends here. A diagnosis is made and treatment begins.
If a microscopic examination gives a negative result, this does not indicate the absence of infection. The disease can occur in a latent chronic form. It is necessary to carry out a number of other tests, for example, microscopic examination of scrapings, determination of Candida DNA in scrapings, urine, and prostate secretions. Also prescribed:
- Clinical blood test.
- Test for HIV infection.
- Determination of trace element reserves in the body.
- Test for glucose and carbohydrate metabolism metabolites.
These laboratory tests can help identify conditions that may be causing the fungus to grow.
Treatment of candidiasis
Treatment of fungal infection involves taking antifungal and antiseptic agents. For the initial stage of the disease, local preparations are used: various ointments, sprays and creams. In advanced stages, systemic treatment is recommended.
Medication
To effectively treat fungus, experts prescribe local antiseptics (Orasept, Fukortsin, Chlorhexidine), multivitamin complexes (Pikovit, Vitrum, brewer's yeast), and antifungal drugs (Fluconazole, Itraconazole).
Systemic therapy
Also, for effective treatment, medications are prescribed that have a systemic effect on the entire body. Such drugs are:
- Ketoconazole. Contraindicated in cases of liver and kidney dysfunction. It is forbidden to take more than 1 tablet per day.
- Diflucan. It has a strong antifungal effect and is excellent at fighting fungus. It has a number of side effects and contraindications, so you should consult your doctor.
Local therapy (ointment for lip fungus)
Includes ointments and gels that can accelerate tissue regeneration. With fairly high efficiency, topical drugs have almost no contraindications or side effects. Most often, experts prescribe the following remedies:
- Amphotericin. Antifungal ointment, which should be used to lubricate the corners of the mouth in the morning and evening.
- Kanesten. The drug has the same effect, but can also be used to lubricate ulcers on the lips.
List of drugs
When choosing drugs for fungus, it is necessary to focus on effectiveness, the presence of side effects, symptoms and course of the disease. It is important to take into account individual intolerance to the components.
Antifungal antibiotics
If the fungal infection is systemic in nature, an integrated approach is required. Deep tissue damage, separation of the nail plates and severe itching of the skin against the background of deteriorating general health suggest the use of not only local remedies, but also tablets.
Among external remedies, it is worth highlighting medications that contain naftifine. This component has an antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effect. When taken regularly and in combination with other therapeutic agents, recovery occurs quickly.
Preparations with naftifine:
| Exostat solution 1% 15ml |
| Mycoderil cream 1% 15g |
| Exoderil cream 1% 15g |
External preparations for dermatomycosis and keratomycosis
Yeast, mold and dimorphic fungi can be cured with Terbinafine-based products. Popular drugs with this active ingredient:
| Lamicide drops for nails 15ml |
| Lamicide spray for legs 15ml |
| Lamisil cream 1% 15g |
| Fungoterbin 1% 15g |
| Exifin gel 1% 15g |
| Terbizil cream 15g |
| Terbix cream 1% 10g |
| Exiter cream 1% 15g |
Medicines containing ketoconazole effectively fight fungal infections of the head and groin area. List of drugs:
| Shampoo Sulsen forte 250ml ketoconazole |
| Shampoo Sulsen mite for dandruff 1% 250ml |
| Sulsen forte paste 2% 75g ketoconazole |
| Sulsen mite paste 1% 75g |
| Shampoo Sulsen mite for dandruff 1% 150ml |
| Shampoo Sulsen forte from perch 150ml |
| Nizoral cream 2% 15g |
| Mycozoral ointment 2% 15g |
| Sebozol shampoo 100ml |
Products based on miconazole, a synthetic substance with an antifungal effect, are effective against dermatomycetes and yeast, as well as the causative agent of lichen versicolor. Preparations containing miconazole:
| Mykozon cream 2% 15g |
| Ginocaps vag caps x 10 |
Antifungal agents for systemic candidiasis
The Candida fungus spreads inside the body: on the respiratory system, in the digestive system, on the genitals. Sometimes it infects the nervous and cardiovascular systems.
Often, with systemic candidiasis, the fungus also affects external tissues - nail plates, skin on the legs and arms. To get rid of the disease, it is important to start therapy in a timely manner. To treat candidiasis, drugs containing clotrimazole are used.
Popular remedies for the treatment of mycotic diseases caused by the Candida fungus:
| Flucorem 0.5% gel 15g |
| Kanizon plus cream 15g |
| Kanizon cream 1% 20g |
| Candide cream 15g |
| Clotrimazole-Akrikhin ointment 1% 20g |
| Clotrimazole-Akos ointment 1% 20g |
| Candide B cream 15g |
| Candiderm cream 15g |
Recommendations from experts
To speed up the healing process, you must follow the recommendations. Also, these tips are perfect for preventing fungus that has a recurring nature:
Nutrition
The diet should be enriched with protein and fiber, and eating sweets, sour and highly salty foods is out of the question, because they are a favorable environment for the growth of bacteria. Eat more fermented milk products, they destroy pathogenic bacteria.
Consultation
You cannot prescribe medications for yourself, as they have many contraindications and will not be effective for everyone. Also, you should forget about treatment with folk methods from Baba Nyura. Need specialist advice.
The most effective treatment is in combination with medications and ointments.
Smoking
For a speedy recovery, it will be necessary to eradicate this habit, since the harmful effects of nicotine smoke on the surface of the lips will only worsen the course of the disease.
Hygiene products
It is strictly forbidden to use toothpastes with an aggressive composition (antiseptic, whitening agents). They irritate the oral mucosa and provoke fungus.
In addition to these recommendations, you need to take care of yourself and not lick your lips in the cold, try to smear them with Vaseline or a special moisturizer. Do not kiss people who have a pronounced fungal infection on the lips, and also visit the dental clinic regularly.
Thrush on the lips and in the mouth - treatment with folk remedies
Traditional medicine can be quite effective and increase the effect of medications. The following recipes are used to treat fungus:
- St. John's wort oil. Soak a cotton swab in the oil and apply to the ulcers for 15 minutes. Wash off with chamomile infusion and apply moisturizer. The procedure must be repeated 3-4 times a day.
- Soda. The fungus cannot exist in an alkaline environment. Therefore, to eliminate it, you need to make a soda solution (a teaspoon of soda in a glass of water) and rinse your mouth with it. It is also recommended to blot the corners of your lips and lips with it.
- Nystatin. Grind one tablet into powder and add freshly squeezed aloe juice. Apply the mixture to your lips for 20 minutes and rinse with warm water.
- Essential oils. Buy tea tree oil, an oil solution of vitamin A and E, bergamot and lavender oil at the pharmacy. Mix the ingredients in equal proportions and apply it to your lips.
- Herbs. It is necessary to make a decoction of herbs. Mix dry herbs of chamomile, sage and calendula in a ratio of 2:1:1. Pour boiling water over the herbs and leave for 3 hours. Apply lotions 3-4 times a day.
- Lemon . Squeeze lemon juice and mix with a teaspoon of honey and a few drops of aloe juice. Apply to lips for 10 minutes. You can also use freshly cut lemon peels. They perfectly disinfect the skin of the lips.
- Decoction. To prepare the decoction you will need: dill seeds, oak bark and St. John's wort. Mix the ingredients in equal proportions and pour boiling water. Leave for 2 hours. After this time, the decoction can be used either orally (a tablespoon on an empty stomach) or topically (wipe ulcers and rinse your mouth after eating).
- Juice. To make medicinal juice that will kill pathogenic microorganisms, you need to take cranberries, viburnum and carrots. Grind everything in a blender and add a spoonful of honey. Consume before meals. Excellent for removing plaque and pain.
- Calendula. This plant is rich in natural antibiotics, which perfectly relieve inflammation and accelerate tissue regeneration. Recipe: brew calendula flowers and currant leaves, wait until the tincture cools and drink. You can add a little honey for taste.
- Lotions with onions. Squeeze onion juice and mix with the same amount of chopped garlic. Soak gauze with this mixture and apply to lips for an hour. Do the procedure three times a day.
- Aloe. Cut two aloe leaves and scald them with boiling water. Carefully cut off the peel and squeeze the juice into a container. Add half a teaspoon of honey to aloe juice and wipe your lips with the mixture. You can also take aloe juice with honey orally. This will anesthetize and disinfect ulcers located in the oral cavity.
White plaque in a child's mouth
General practitioner, rehabilitation specialist Volkova A.V.