Description
Abscess of Bartholin's gland.
This is a circumscribed purulent process that involves the parenchyma of a large gland in the vestibule of the vagina (true abscess) or in the cavity of your duct (false abscess). The disease manifests itself as a bulky formation in the lower third of the labia majora, intense local pain, fever and general malaise. The diagnosis is made based on the results of a gynecological examination, bacteriological examination, and PCR analysis. Surgical treatment is opening of the abscess followed by drainage, removal of the purulent cyst, or removal of the gland.
Bartholin gland abscess
Additional facts
Bartholin's gland abscess (large vestibular gland abscess) is a localized purulent infection that affects one (rarely both) paired glandular organs. These glands are located in the thickness of the lips and perform the function of exogenous secretion - they produce a viscous fluid that moisturizes the external genitalia and protects them from infections. The diseases affect women of childbearing age (20-40 years), the incidence is 2%. In practical gynecology, it is often necessary to observe false abscesses of large vestibular glands. A bilateral abscess is usually due to gonorrhea. Bartholin's abscess does not develop in children; it is rarely recorded in adolescence and old age and is extremely rare in older people.
Causes
The disease is infectious and most often occurs as a complication of inflammation of the gland - bartholinitis. Gonococci, trichomonas, chlamydia were isolated from specific pathogens, and opportunistic representatives of the obligatory and facultative flora of staphylococci, streptococci, E. coli, fungi and anaerobic bacteria were isolated from nonspecific pathogens. Anaerobic microorganisms (bacterioides, peptococci, peptostreptococci, less often - clostridia) are cultured from a purulent lesion in 80-90% of cases. The cause of infection is: Inflammation of neighboring organs.
The infectious agent enters the Bartholin gland from the epithelium of the vulva, from neighboring hollow organs - the vagina, urethra and rectum, if hygienic and personal diseases are not observed (bacterial vaginosis, vulvitis, vaginitis, cervicitis, annexitis, urethritis, proctitis, enteritis, enterobiasis) .
• Contact transmission of the pathogen.
The cause of the development of pathology is non-compliance with personal hygiene rules, unprotected sex, poorly treated medical instruments, dirty hands and ordinary towels.
• Retaining cysts.
Very often, recurrent abscesses develop against the background of a retaining cyst of the Bartholin gland, which is an ideal reservoir for the growth of opportunistic flora. The inflammatory process or the presence of a cyst in no way leads to suppuration in all patients. The body's tendency to develop an abscess is mainly due to immunodeficiency. This condition is most often caused by metabolic endocrine diseases (diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism), foci of chronic infectious inflammation (tonsillitis, sinusitis, caries, bronchitis, cholecystitis), and helminth infection. An important role is played by vitamin deficiency in the diet, hypothermia, chronic excessive fatigue, prolonged stress, alcohol abuse, treatment with cytostatics and corticosteroids. Predisposing factors include wearing tight clothing, compression of the pelvic and perineal area (pants, underwear), self-medication for bartholinitis (for example, hot baths).
Pathogenesis
The gateway to exogenous infection is the excretory duct of the Bartholin gland; the infectious agent can penetrate the parenchyma hematogenously. Penetration of the pathogen causes inflammation of the mucous membrane, expressed by hyperemia, exudation and impaired microcirculation, which leads to swelling and narrowing of the lumen of the main channel. Due to the formation of scale and ulceration of the upper layer of the epithelium, obstruction of the mouth and/or adhesion of the duct walls may occur. These changes lead to stagnation of purulent exudate with further spread of the pathological process to the parenchyma of the Bartholin gland, to the soft tissues of the lips and vagina, and to tissues close to the vagina. Purulent infiltration of the gland and neighboring structures leads to the formation of an abscess: first, leukocyte enzymes melt the tissue, forming a cavity filled with pus, and then granulation tissue forms around the membrane. The cavity is a demarcation tree (purulent membrane). In a chronic abscess, the outside is covered with a layer of connective tissue. The capsule around the abscess does not prevent the body from being intoxicated by decomposition products, but it significantly impedes the entry of antibacterial drugs into the bloodstream.
Localization and code according to ICD 10
Eyelid abscess (ICD 10 code H 00.0) is what ophthalmologists call a limited inflammatory process located near the organ of vision. Inflammation leads to the formation of a cavity through purulent melting of tissue.
Based on location, abscesses of the upper and lower eyelids are distinguished. More common is the formation of a cavity with purulent contents on the upper mobile fold of skin covering the eye. The pathology can be localized at the eyelash growth line.
An abscess can be:
- External. A common type of pathology in the form of an abscess formed on the edge of the orbit. Ripening is observed from the outside. Infection of nearby tissue leads to development.
- Internal. Formation of an abscess on the side facing the eyeball. The cause is an infection of the meibomian glands located near the base of the eyelashes.
An abscess on the inside of the lower eyelid is more often diagnosed than an abscess hidden on the upper skin fold.
Classification
There are two forms of purulent pathology of the Bartholin gland: false (pseudo-abscess) and true abscess. A pseudo-abscess can exist alone for a long time, without damaging the parenchyma of the gland, or, after a short time, turn into a real abscess: the course of the pathology largely depends on the virulence of the pathogen and the immune status. • False abscess (empyema).
This is accompanied by the accumulation of pus in the lumen of the main canal of the Bartholin gland. The purulent inflammatory process does not extend to the parenchyma of the gland, limited by the mucous membrane of the excretory canal. In most cases, empyema is caused by the rapid growth of opportunistic anaerobic microflora under conditions of stagnation and often develops against the background of a long-existing retention cyst. Pseudo-abscess is recorded more often than the truth. Often occurs when infected with purulent cocci (pathogenic gonococci and staphylococci, streptococci), characterized by infiltration of the gland and adjacent soft tissues, followed by their purulent fusion and the formation of a demarcation tree around the fire. Inflammation. With endogenous infection, a true abscess can develop without previous obstruction of the excretory duct.
Causes of occurrence in adults, children and characteristic symptoms
Children and adults, regardless of gender, are susceptible to pathology. More often, an abscess is diagnosed in a child with weak immunity. Purulent inflammation of the eyelid is caused by the active proliferation of pathogenic bacteria - staphylococci, streptococci.
Factors that provoke inflammation near the eyes:
- blood-sucking insect bites;
- squeezing out acne and poor eyelid skin care;
- a foreign object caught in the eye;
- purulent inflammation affecting the sinuses or located in the oral cavity;
- improper treatment of acne, styes, boils;
- meibomite.
Routes of infection that result in eyelid abscess:
- penetration of pathogenic microorganisms through damaged skin folds in the eye area - wounds, scratches, cuts;
- spread of infection, the focus of which is in the orbital area - barley, squeezed pimple near the organ of vision;
- infection transferred through the bloodstream from its other foci - otitis, sinusitis, stomatitis, tonsillitis.
Often, the appearance of inflammation on the eyelids is caused by improper treatment of purulent formations near the eyes. Independent removal of blackheads and other formations with this localization carries the risk of consequences.
The symptoms of the pathology gradually worsen. The accumulation of purulent contents of the cavity leads to greater severity of symptoms.
The development of symptoms is not rapid, as with barley. Signs of a purulent abscess are steadily increasing, acquiring a pronounced character. The pathology causes the patient a lot of discomfort.
Abscess symptoms:
- The tissues in the orbital area thicken and become denser.
- The eye begins to swell due to swelling of the eyelid. Redness of the skin of the mobile fold. When you press your fingers on the problem area, the painful pulsation intensifies, indicating a purulent-inflammatory process. Feeling hot is evidence of a local increase in temperature.
- Vision deteriorates.
- With an abscess that has formed on the upper mobile fold of the skin, it is difficult to close the eye. The eyelid may become very swollen, making it difficult for the eyeball to close.
- With a large area of damage, symptoms of general intoxication occur in the form of fever, weakness, and elevated temperature (the indicator can reach +39.8 ⁰C).
- Feeling worse, headache.
- The appearance of a white or yellowish speck at the site of compaction is evidence of purulent contents. After a few days, the abscess will open and the pus will come out.
The release of contents from the cavity formed on the eyelid helps to alleviate the condition and eliminate unpleasant symptoms. If the pus is not completely cleared, the symptoms return and the inflammation becomes chronic. Fistula formation is observed.
Opening the tumor on your own is prohibited - there is a risk of spreading the infection.
An abscess, regardless of type, requires urgent treatment.
Symptoms
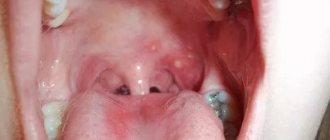
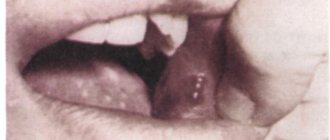
A characteristic symptom of an abscess of the large vestibular glands is a voluminous (reaching the size of a chicken egg), usually one-sided layer in the area of the middle and lower third of the labia. The purulent process is accompanied by enlargement and soreness of the inguinal lymph nodes. With empyema, against the background of pronounced edema and accumulation of the vestibular mucosa, labia majora and labia majora, a rounded edema of elastic texture is observed, which is not associated with adjacent structures, partially or completely blocking the entrance to the vagina. With a real abscess, there is also significant swelling on the affected side, the formation is inactive, there are no clear boundaries, it is attached to severely hyperemic skin. Severe pain is characteristic of Bartholin's abscess. Acute pain in the labia, radiating to the thigh, disturbs sleep, increases with walking, sitting, coughing, defecation and decreases slightly only in a forced horizontal position on the back with legs apart. The actual clinical course is characterized by an acute abscess: in addition to pain, debilitating fever (often with chills), decreased appetite, tachycardia, decreased blood pressure and weakness are noted. The general somatic symptoms of a pseudo-abscess are not as pronounced, often the temperature rises only to 38 ° C and there is slight general discomfort. With both true and false abscess, a sharp relief of the condition occurs after the opening of the abscess (or outbreak). Chronic (recurrent) purulent bartholinitis manifests itself in the periodic maturation and opening of pseudo-abscesses. The remission period is characterized by the presence of a dense, inactive and practically painless formation in the thickness of the labia and discomfort during sexual arousal, during and after sexual intercourse. During an exacerbation, all the signs of an acute abscess appear. Vaginal discharge (leucorrhoea). Purulent vaginal discharge. Malaise. Neutrophilia. Chills. Lack of appetite. Enlarged inguinal lymph nodes.
Abscess treatment
The success of abscess treatment largely depends on the time of treatment. With timely medical care, you can count on a quick recovery, otherwise the disease may lead to the development of sepsis.
Self-administration of antibiotics before surgery is ineffective
, since the supply of active substances to the site of inflammation is difficult due to the accumulation of pus in the tissues. In case of an abscess, self-medication is not allowed - this risks widespread inflammation and further spread of infection.
Preparing for surgery
Diagnosis of a purulent abscess is carried out by visual examination, as a result of which the surgeon determines the treatment tactics. Blood tests are ordered and an anesthetic is selected. The presence of fluctuation requires urgent opening of the infected area to ensure adequate outflow of exudate.
Progress of the procedure
The deep location of the abscess allows the use of a closed method of treatment, in which the recovery time is significantly reduced. Treatment measures are carried out in stages:
- treating the skin with an antiseptic;
- administering local anesthesia;
- making a small incision (up to 25 mm), which needs to be expanded with a Hartmann syringe to rupture the bridges in the cavity;
- cleansing the cavity and walls of the inflamed area, aspiration of purulent masses;
- installation of drainage for fluid outflow with parallel antiseptic treatment.
The surgery is performed on an outpatient basis and takes no more than half an hour. The recovery period and complete healing takes several weeks.
Drug therapy
After determining the severity of the inflammation, a course of antibiotics and drugs is usually prescribed to relieve inflammation and stimulate the immune system. For therapy to be effective, it is necessary to conduct tests to study pathogenic microflora and its susceptibility to antibiotics. Treatment is carried out according to three schemes:
- local application;
- oral administration;
- injection of the drug into the inflamed area.
In the absence of allergies, penicillin antibiotics are prescribed. In other cases, macrolides (erythromycin and clarithromycin) are indicated. The treatment course in both cases lasts 10 days. For external use, ointments are used (for example, Levomekol).
Recovery
During the recovery period, you must strictly follow the doctor's instructions: regularly change the dressing and observe the rules of personal hygiene. A couple of days after the operation, you must visit the surgeon at the appointed time to remove the drainage.
Timely treatment of an abscess minimizes the risks of complications. Prevention of abscess formation consists of timely and correct treatment of wounds, competent administration of injections, strengthening the immune system and immediately contacting a surgeon at the first signs of soft tissue suppuration.
Possible complications
Spontaneous opening of a Bartholin's abscess can lead to the formation of a fistula with its scars and deformation of the lips, as well as the walls of the vagina and rectum - if abscesses burst into their cavity. Sometimes non-healing rectovaginal fistulas can form when excrement drops into the vaginal lumen with large defects. Another unfavorable result of an abscess is a breakthrough into the surrounding fibers with the development of a diffuse purulent process - perineal phlegmon or, when the infectious agent enters the bloodstream, a generalized purulent process - sepsis, which causes a series of biochemical reactions that fatally disrupt the most important homeostatic functions of the body.
Diagnostics
A gynecologist and a laboratory doctor diagnose a Bartholin gland abscess. The diagnosis, as a rule, does not cause any difficulties and is based on the results of the following studies: • Gynecological examination.
By palpation and examination of the labia, it is possible to determine the asymmetry of the vulva and the formation of a painful volume with signs of inflammation: swelling, hyperemia, local increase in temperature and zones of fluctuations.
Enlargement and sensitivity of the inguinal lymph nodes also indicate the inflammatory nature of the formation. • Laboratory identification of the pathogen.
Culture analysis of the discharge from the canal is performed to prescribe optimal antibiotic therapy. As a result of the study, opportunistic pathogens and their sensitivity to antibiotics were identified. PCR testing is performed to identify hidden infections and treat them appropriately. With the help of research you can detect trichomonas, chlamydia and gonococci. In addition, a clinical blood test and bacteriological analysis of a vaginal smear are prescribed. Bartholin's abscess is differentiated with the help of a furuncle (carbuncle) of the lips, painful tuberculous abscess, purulent cyst of Gartner's stroke, malignant tumors - cancer and sarcoma of the vulva, cancer of the Bartholin's gland. To exclude malignant neoplasms in case of abscess recurrence in women over 40 years of age, a histological examination of a biopsy of the pathological formation is performed. A gynecological oncologist, a physiophysiologist, and a pathologist may be involved in the differential diagnosis.
Treatment methods for abscess
Diagnosis of an abscess and prescription of eyelid therapy is carried out by an ophthalmologist after examining the patient, collecting anamnesis and complaints.
Need advice from an experienced doctor?
Get a doctor's consultation online. Ask your question right now.
Ask a free question
Additional diagnostic methods - x-rays, laboratory tests - will be required to identify the causative agent of the disease. The diagnosis for more severe symptoms is called cellulitis.
In addition to drug treatment, surgical intervention for an abscess is often required.
Surgical
The need for surgical treatment of the eyelid is caused by the localization of the focus of purulent-inflammatory lesions. Urgent prevention of the spread of infection through surgical intervention is necessary due to the proximity of the abscess to the eyes and frontal sinuses. Their infection can have more serious consequences.
The ophthalmologist determines the degree of neglect of the pathology. If it is superficial, it can be opened on an outpatient basis. The consequences are minimal. If the disease is advanced and severe, the patient will be sent to hospital treatment with surgical intervention.
In case of subperiosteal abscess, they resort to subperiosteal orbitotomy, in case of retrobulbar abscess, they resort to opening the periosteum.
For eyelid surgery, local anesthesia is used.
Medication
Treatment of an abscess on the eyelid with medication involves the inclusion of a procedure for sanitation of a purulent-inflammatory focus formed in the area of a mobile skin fold.
The doctor prescribes drugs related to sulfonamides and other antibiotics for systemic use.
Treatment for an abscess on the eyelid includes:
- antibacterial drugs of the penicillin series intravenously or intramuscularly, injections are given four times a day;
- Tetracycline tablets, the dosage is prescribed by a specialist, should be taken orally three times a day;
- Sulfadimezine tablets up to 8 times during the day;
- analgesics, antihistamines.
The patient will require maintenance therapy, treatment of the nasal mucous membrane with drugs with a vasoconstrictor effect. You will need to lubricate or irrigate the nasal passages with a solution of adrenaline hydrochloride at a concentration of 0.1% to relieve swelling of the eyelid and inflammation.
For an abscess on the eye, it is recommended to take vitamin complexes and undergo autohemotherapy.
The duration of the course of conservative treatment is determined by the doctor.
When the abscess is opened, you need to visit a specialist for antiseptic treatment of the damaged area of skin on the eyelid. An ointment may be prescribed to help heal a wound after an abscess.
Folk remedies
An abscess on the eyelid cannot be treated independently using folk recipes. Improper home therapy can provoke a premature breakthrough of the abscess, leading to infection penetration into the deep layers of tissue.
Alternative treatment can cause irreparable harm to health and lead to serious complications. Compresses can be applied to the pathological area only with the permission of the doctor, following the rules of manipulation. This may reduce symptoms.
Treating an abscess with herbs alone is ineffective. It can be used as an auxiliary method, including in complex eyelid therapy.
Treatment
Bartholin's abscesses are treated quickly. The choice of surgical method depends on the form of suppuration (empyema or abscess), the type of process (primary or recurrent), the skills of the operating gynecologist and the wishes of the patient. In case of abscess of large vestibular glands, the following is carried out: A 5-6 cm long incision is made from the mucous membrane, through which the contents of the abscess are emptied, the cavity is disinfected and a drainage tube is installed in the incision. The cavity is washed daily for a week. Abscess opening can be performed on a true or false abscess. After wide opening, the pseudo abscess may occur again. • Incision with installation of the word catheter.
A relatively new method in domestic gynecology.
The purulent contents are removed through a 3-5 mm incision and sanitation is carried out, after which a word-catheter is inserted into the hole - a silicone tube with an inflatable balloon, which provides fixation and helps to form a channel for the outflow of secretions. The catheter is left in place for 1.5-2 months. Surgery is prescribed for single-chamber false abscess; the probability of relapse is about 10%. Through an incision in the mucous membrane of the vulva and the capsule of the cyst, the abscess cavity is cleaned and washed, after which the walls of the capsule are sutured to the mucous membrane of the labia to form a complete duct. Marsupialization is used to treat multilocular or small false abscesses when placement of a catheter is not possible. Relapse occurs in 10% of cases. • Destruction of the Bartholin gland.
Through an incision in the vaginal mucosa, the gland along with the duct is completely removed, then its bed is sutured. Due to the risk of massive bleeding, a blood transfusion may be required. The operation is indicated for recurrent pseudo-abscesses, when other methods have not given satisfactory results: the absence of an organ completely eliminates relapse. To prevent local and generalized purulent complications, systemic empirical antibacterial therapy with broad-spectrum drugs (penicillins protected by an inhibitor, macrolides, nitroimidazoles) is prescribed; after determining the type of infectious agent, specific treatment is carried out. If necessary, detoxification therapy is prescribed (intravenous administration of saline solutions).
Bartholin gland abscess - symptoms and treatment
Treatment for a Bartholin gland abscess is always surgical . Sometimes surgery is combined with drug therapy (broad-spectrum antibiotics, antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory drugs) and physiotherapeutic treatments that prevent relapses and improve immunity.
It is believed that if the patient does not have signs of a systemic inflammatory reaction (sepsis), cellulitis, multiple abscesses, or immunosuppression, then there is no need for antibiotics. In the presence of the above pathologies, while waiting for the results of bacteriological culture, therapy with a broad-spectrum antibiotic active against several pathogens is prescribed.
Treatment of false abscess is carried out on an outpatient basis or in a hospital with a day stay. Therapy for a true abscess requires only hospital treatment [7][12].
Types of surgical treatment of Bartholin gland abscess.
Excision and drainage of the abscess. An incision is made into the abscess capsule with a surgical scalpel, and the contents of the abscess are removed with a syringe. Then the abscess cavity is washed with antiseptics and a rubber drainage is installed. Subsequently, the gland cavity is treated daily with antiseptics, the drainage is changed, and sterile dressings with antibacterial ointment or antimicrobial gel are used.
Opening the abscess and forming a new opening of the Bartholin gland duct. To prevent the abscess from reoccurring, a new opening of the Bartholin gland duct is formed. To do this, perform one of the following operations:
- Laser treatment (vaporization) for false abscesses. The abscess is removed without traumatizing healthy tissue using a laser beam. The method is non-contact, does not cause bleeding or scars, and promotes rapid restoration of tissue and functions of the gland. The operation is performed on an outpatient basis [15].
- Installation of a Word catheter - a small inflatable balloon with saline solution. The catheter is in the cavity of the Bartholin gland for 4-6 weeks, by which time the Bartholin gland duct should have formed. The method is used after inflammation has resolved [11].
- Marsupialization - the edges of the wall of the cavity of the Bartholin gland are sutured to the border of the surgical wound to form an artificial opening of the duct and left open until healing.
Opening an abscess using the radio wave method is painless , does not leave a burn, and after treatment, no scars. A small incision is made, there is no bleeding during the operation, and the tissue is quickly restored [15].
Puncture aspiration is the removal of the contents of an abscess using a puncture . It is carried out when a disease is detected in pregnant women.
Removal of the Bartholin gland is indicated for suspected malignant process (lumpy surface of the abscess capsule), for swelling that does not go away after surgical treatment for more than a month, for relapses of the disease more than twice. In case of true or recurrent abscesses of the Bartholin gland, the formation is removed along with the gland. The procedure can cause complications such as the formation of fistulas between the rectum and vagina, sepsis and bleeding. When the Bartholin gland is removed, the paraurethral glands take over the function of moisturizing the labia [7].
Small abscesses can regress without treatment, maturing and opening on their own. Elevation of the lower extremities, local procedures using ozonated saline and ultrasonic cavitation with antiseptic solutions will help speed up the resolution of inflammation.
After surgery, physiotherapeutic treatment - magnetic therapy, irradiation of blood with infrared laser (ILBI) or ultraviolet light (UFO), treatment and restoration of the acidic environment of the vagina with antiseptic solutions using ultrasonic cavitation [7][12][14].