Young people often don’t think about whether stomatitis is transmitted through kissing, and carefreely kiss their other halves. At the same time, they do not take any measures for treatment, considering this disease to be trivial. Is stomatitis so dangerous that you can’t contact other people?
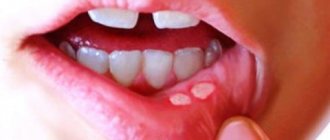
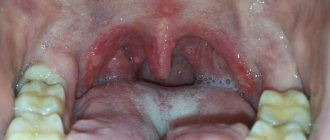
Stomatitis is an inflammation of the oral mucosa, which in most cases is accompanied by the formation of ulcers. Along with this, swelling of the mucous membrane is observed, and a white or yellow-white coating forms. When communicating, a person feels discomfort, and pain occurs while eating. Increased salivation, gums often bleed, and bad breath appears.
What is stomatitis
Stomatitis (mucositis) is a disease that is accompanied by damage to soft tissues in the oral cavity.
It can be either an independent disease or a complication of various pathological processes, for example, measles, influenza, scarlet fever, etc. Until recently, stomatitis was considered a childhood disease. Today it is becoming more common in adults too. This trend raises questions about whether stomatitis is transmitted and, if so, how to protect yourself and your child. It all depends on the form of manifestation of the disease
Hepatitis A
This is an infectious disease that affects the liver. Hepatitis A in most cases ends in complete recovery. The disease does not become chronic. But the danger is that the disease is extremely contagious and a sick person can infect a huge number of people without even knowing that he is a carrier of the virus. The infection is most contagious in the last days of the incubation period, while there are no symptoms. In this case, infection can occur not only through a kiss, but even through objects touched by the patient.
Symptoms of stomatitis
Stomatitis can be recognized by the following signs:
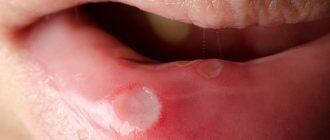
- ulcers, wounds, erosions and rashes on tissues;
- red color of the mucous membrane;
- plaque on the tongue, inner surface of the cheeks, palate;
- unpleasant taste;
- swelling of tissues;
- heavy salivation;
- bad breath;
- itching and burning – in some cases;
- discomfort and pain;
- bleeding gums – occasionally;
- increased body temperature;
- lymphadenitis.
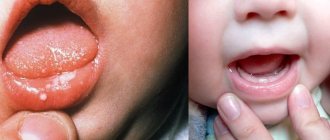
Symptoms in children are always more pronounced. The child often feels severe pain. Adults tolerate the disease easily. Its symptoms usually do not cause severe discomfort.
When the first symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor to protect yourself and, possibly, others.
How is stomatitis transmitted, is it contagious or not?
Changes in the mucous membrane of the oral cavity in a person, whether ulcers or scratches, cause discomfort and interfere with normal life. When such changes are detected, many immediately believe that it is stomatitis. How to distinguish characteristic rashes from other diseases of an inflammatory nature and what it is, whether it poses a threat to others and the victim’s body as a whole are questions that plague those who are faced with this problem.
What is stomatitis: causes and symptoms
Stomatitis is an inflammatory disease that affects the oral mucosa, which is caused by various infectious and non-infectious factors.
Over time, the usual form of the sore can become complicated, when ulcers and hemorrhages appear at the site of inflammation, causing even greater discomfort for the patient at the time of eating. Against this background, body temperature rises, malaise and drowsiness appear.
Based on the etiological factor, you can understand whether stomatitis is contagious or not for surrounding people.
For non-infectious stomatitis, the trigger is often a weakened immune system. Young children often face this problem, since their immunity is still defective.
The most common causes of the disease are:
- oral care;
- cleaning your mouth with someone else's personal hygiene devices;
- reduced immune system due to concomitant diseases;
- infectious nature;
- allergic reactions to the active components of toothpastes or rinses;
- mechanical damage from a toothbrush with rough bristles or dental sticks.
Types of stomatitis and routes of infection
In order to figure out whether the patient is contagious to others or not, it is important to distinguish between the types of stomatitis.
- Infectious etiology:
- viruses;
- bacteria;
- fungal flora.
- Non-infectious nature:
- traumatic;
- aphthous.
An examination of the patient’s oral cavity and a survey will help you understand which type is present in the patient. It is important to know with whom this person communicated the day before and what complaints he had. Knowledge of the distinctive features of each listed species will be able to correctly guide the doctor as to whether there is a risk of becoming infectious or not.
Is stomatitis in adults contagious or not?
Due to the fact that there are many etiological factors, not all of them are dangerous. Infectious stomatitis is contagious in adults and children, non-infectious diseases (traumatic and aphthous) are not contagious.
Viral lesions of the mouth, regardless of the pathogen, are transmitted to others through any contact (domestic, hematogenous, etc.) with an infectious person. This species is contagious.
In children, the main cause of stomatitis is the proliferation of bacterial pathogenic flora, due to their curiosity and mania for putting everything in their mouth.
Is stomatitis transmitted through a kiss or not?
Some types of stomatitis can be transmitted through saliva (kissing). Any pimple of infectious etiology poses a certain threat to the health of the person in contact with the patient.
How can stomatitis be transmitted?
- airborne droplets (at the time of communication);
- hematogenous route (through blood);
- contact or household route (unwashed hands, use of shared utensils or other personal hygiene devices);
- from mother to child (breastfeeding);
- interaction with other biological fluids (saliva during kissing, the entry of amniotic fluid into the baby’s oral cavity, sexual intercourse).
Since stomatitis of infectious etiology is contagious for any person, you should familiarize yourself with each type in detail and learn to distinguish them from non-infectious inflammation.
Viral
The viral form is one of the most contagious among other types. This disease is characterized by the presence of a specific pathogen that causes this condition. In this regard, the following are highlighted:
- herpetic;
- enterovirus;
- influenza and parainfluenza;
- associated with the causative agent of chickenpox;
- adenoviral.
Depending on the incubation period, which lasts 5–14 days, characteristic symptomatic manifestations appear. During this period of time, the patient is contagious to others, but danger threatens when symptoms appear (presence of ulcers with blisters, soreness, elevated body temperature). More often, stomatitis is transmitted by airborne droplets.
When kissing an infected person, there is an increased risk of stomatitis (contact with infectious biological fluid).
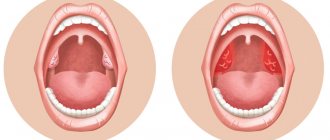
It is important not to confuse the clinical manifestations of infectious stomatitis with signs of tonsillitis (during examination, the mucous membrane of the tonsils is affected).
Bacterial
Bacterial stomatitis - manifests itself in children. This is due to a weak immune system and frequent injuries to the oral mucosa. Damaged tissue is an entry point for bacteria. In the area of implantation, local inflammation, swelling, and pain appear. There is an unpleasant odor from the mouth. When foreign microorganisms enter the blood, intoxication syndrome increases (body temperature rises, malaise, drowsiness, loss of appetite).
This species is as contagious as a viral one, and is most often transmitted through the air and through household contact.
Fungal
Fungal stomatitis in the mouth is contagious for healthy people if they use shared, poorly washed dishes, etc. The household route of transmission predominates here.
A characteristic feature of this type of stomatitis will be a white coating over the inflamed area of the mucous membrane. Intoxication syndrome is unlikely, since the fungal infection occurs only in the mucous (mucosal) layer.
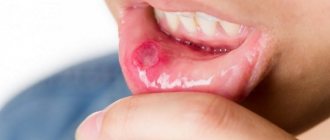
Aphthous
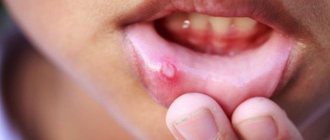
Aphthous stomatitis is an inflammation of the oral mucosa that is not associated with an infectious nature. It occurs most often against a background of stress or as a manifestation of a local allergic reaction.
Upon examination, there will be a white or yellow sore - aphtha, which brings discomfort while eating. Don't worry about your loved ones - it's not contagious!
Traumatic prosthetic stomatitis
Sores or ulcers often appear in the oral cavity due to damage from foreign bodies (solid food, dentures, toothbrush with coarse bristles, etc.). Since the dentures are not tightly fixed, their movement causes irritation and injury to the mucous membrane. At the site of unstable fixation, the tissue becomes inflamed.
Despite the safe form of the disease in this category of people, the question arises whether it is possible to become infected with traumatic stomatitis in general or not.
With ordinary prosthetic stomatitis, there is no danger to others, but if complications are detected after infection, the patient becomes infected.
Preventive measures. How to protect yourself when communicating with a sick person
In order to prevent the development of stomatitis and not become contagious, you need to learn a few points:
- oral hygiene (using your own toothbrush);
- thoroughly wash shared utensils (it is advisable to have your own cup, plate, fork, etc.);
- interrupt contact with an infectious person (wearing a medical mask, keeping a distance at the time of conversation);
- the use of vitamin complexes with reduced immunity;
- proper nutrition;
- visit the dentist once a year.
If signs of illness are detected and in order to avoid possible infection of relatives, you should immediately seek medical help from a dentist.
As a result, it should be remembered that stomatitis that has an infectious etiology is contagious. It is not difficult to distinguish this species from a non-infectious one. Knowledge of the clinical picture of the disease can preserve not only the health of the infected person, but also the health of the people around him.
Types of disease
Stomatitis has different forms, depending on which the doctor determines whether it is contagious or not, and also prescribes appropriate treatment.
Allergic stomatitis
This is a common form of the disease that is difficult to treat. From the name it is clear that the cause of its development is an allergy, but it is necessary to find out what exactly it is. These could be medications, food, materials used for prosthetics. The disease is accompanied by the appearance of ulcers, which provoke pain.
Viral stomatitis
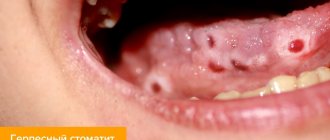
The most common type of viral stomatitis is herpetic stomatitis, the causative agent of which is the herpes virus. There are other forms that are provoked by adenovirus, enterovirus, etc. They are often found in children under 5–6 years of age, but are also common among older age groups. A feature of viral stomatitis is its erosive spread, when one ulcer appears next to another. Herpes mucositis may cause complications such as fever, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea.
This form of the disease is transmitted to others by contact and airborne droplets. If it is diagnosed, for example, in someone in kindergarten, then quarantine must be introduced. Infection occurs through dishes and toys, so the disease can quickly spread from child to child.
The virus spreads from nursing mothers to children if hygiene rules are violated. Adults become infected even through handshakes. Sneezing also causes the disease to develop.
Aphthous stomatitis
This form is common among adults. It develops against the background of a weakening of the body’s immune forces, so aphthous stomatitis is a common occurrence in spring and autumn. With this type of disease, characteristic aphthae appear - small ulcers. They can be single or group. Aphthous mucositis is not spread from person to person.
Fungal stomatitis
The disease manifests itself in children and adults, mainly in infants and women. It is provoked by fungi of the genus Candida, which are activated in the oral cavity when the immune system is weakened. The cause of fungal stomatitis can be long-term use of antibiotics. In addition to ulcers, its characteristic feature is a cheesy coating on the tongue, palate and inner surface of the cheeks.
Bacterial stomatitis
This type of disease is diagnosed when the oral cavity is affected by microorganisms, most often streptococci, staphylococci. The manifestation of bacterial stomatitis is provoked by tuberculosis, as well as sexually transmitted diseases, for example, gonorrhea, syphilis. More often, children whose immunity is not strong enough suffer from it. But everyone must be careful. The disease is transmitted from children to adults through dishes, toys, and damage to the mucous membrane.
This form is characterized by swelling in the oral cavity, redness of the mucous membrane and hardening of the palate, as well as an unpleasant odor, ulceration and cracks. Symptoms of intoxication may appear: vomiting, weakness, rapid pulse.
Other forms of stomatitis
In addition to the above types of disease, the following can also be distinguished:
- chemical stomatitis - occurs as a result of burns to the oral cavity with alkaline substances or acid;
- traumatic - ulcers are formed as a result of impact and disruption of tissue integrity;
- radiation – develops as a result of radiation.
Such forms are non-contagious and therefore do not pose a danger to other people.
Mononucleosis
This disease is also caused by the herpes virus, but not the first type, but the fourth. This virus is also called the Epstein-Barr virus. The virus enters the body through saliva and begins to multiply in the mouth and throat. For this reason, it is very easy to become infected with mononucleosis through a kiss. This disease even has a third name - “kissing disease.” Symptoms of mononucleosis are high fever, sore throat, and swollen lymph nodes. Symptoms do not begin to appear immediately, but after a couple of weeks.
Ways of transmission of stomatitis
Let's summarize. Viral, bacterial and herpetic forms of stomatitis are contagious. Knowing how the disease is transmitted, you can protect yourself and your loved ones. Ways of transmission of infection:
- airborne - sneezing, coughing;
- household items - common dishes, linen, personal items;
- toys, raw pacifiers, rattles;
- dirty hands;
- unwashed food;
- biological fluids - through saliva, blood, breast milk;
- Pets can carry the virus.
It is possible to catch the infection anywhere – from the street to your own home. You can get infected from both a child and an adult.
Cytomegalovirus
This is another member of the herpes virus family. It is very common and in most cases is in an inactive state in the body. Its activation occurs when the immune system is weakened, as well as during stressful situations. The virus is contained in all biological fluids of the infected person, and therefore can easily be transmitted through saliva during a kiss. Cytomegalovirus is especially dangerous for pregnant women, since when infected with it, the child often dies in utero. Surviving children who were infected in utero subsequently develop various abnormalities.
A kiss that tastes like “stomatitis”: is the disease contagious and how is it transmitted?
Stomatitis is a disease that is a lesion of the oral mucosa.
Often occurs as a result of an immune response to the appearance of molecules that are difficult to recognize by the body.
The appearance of such elements causes an attack on lymphocytes, forming ulcers. The body reacts in a similar way to a human organ transplant.
Stomatitis is transmitted through kissing or any other type of contact . The cause of the disease can be a simple lack of oral hygiene.
Ulcers heal within 7-14 days. People who have had stomatitis are susceptible to recurrent illness, however, with a fairly variable frequency. Sometimes the disease appears several times throughout the year, which indicates a chronic form of the disease.
Is stomatitis contagious?
The question of whether stomatitis is contagious should be considered at the level of the root cause of the outbreak of the disease.
Of course, there are contagious types - herpes and candidal stomatitis are especially dangerous. However, each disease is considered by specialists individually.
The following types of stomatitis exist:
- Viral. Generated by viruses caused by diseases such as chickenpox, herpes or influenza. Symptoms include pain in the oral cavity and fever. It manifests itself in the form of the appearance of purulent blisters, which, bursting, form wounds. This type of disease is contagious;
- Bacterial. It affects not only the mucous membrane, but also the gums, palate or sublingual area with the appearance of cracks and bad breath, as well as nausea, dizziness, increased heart rate and general weakness. In most cases, it poses a danger to newborns who do not have a sufficiently developed immune system due to their age. For adults, viral stomatitis is dangerous only through airborne droplets or in the case of sharing cutlery with a patient;
- It is known that about 20% of the population suffers from this disease, of which pregnant women predominate.
Transmission routes
As mentioned earlier, the routes of transmission of stomatitis can be completely different - from airborne droplets to traumatic.
Children often suffer from stomatitis due to poorly developed immunity, which is not yet able to fully cope with surrounding viruses.
Is stomatitis transmitted through kissing?
Prolonged contact with a sick person can also lead to infection with stomatitis.Constant exposure of the oral mucosa to foreign pathogenic microorganisms causes a decrease in the immune system and a reduction in the protective mechanisms of the oral cavity itself.
That is why the transmission of stomatitis through kissing is quite common.
How to protect yourself?
In order to protect yourself from stomatitis, first of all, you must adhere to the rules of hygiene of the gums and teeth.One of the main protective measures is strengthening the immune system through a healthy diet.
Often stomatitis can be caused by a deficiency of B vitamins, zinc or iron in the body.
A preventive examination by a dentist and timely dental treatment are mandatory.
If the infection with stomatitis is permanent, then it is necessary that all family members living with the patient be examined by a doctor.
The cause of frequent stomatitis may unexpectedly be someone from your close circle, without even knowing it.
Bacterial stomatitis
The bacterial form often occurs against the background of an underlying disease. Risk factors:
- Pharyngitis.
- Laryngitis.
- Rhinitis.
- Chronic tonsillitis.
- Angina.
When the immune system is significantly weakened, bacteria begin to multiply rapidly. Staphylococcus and streptococcus are common. Bacteria lead to the appearance of a purulent rash. The bubbles open, erosions and ulcers form.
Children transmit the disease to each other through household and contact routes. Toys and personal items become a breeding ground for pathogenic bacteria. One bath towel in a family for several members contributes to the fact that stomatitis will be detected immediately in a brother and sister or in a grandson and grandmother.
Transmission of bacterial stomatitis is not uncommon in children's groups. Adults become infected less frequently. For bacteria to get inside and begin their destructive activity, there must be damage to the skin or mucous membrane.
The slightest scratch may be enough if the body's defenses are reduced. But if an adult has a strong immune system, there is little chance of contracting bacterial stomatitis. The exception is representatives of the older age group. They experience an age-related decline in their defenses.
Is it possible to get stomatitis through a kiss?
Young people often don’t think about whether stomatitis is transmitted through kissing, and carefreely kiss their other halves. At the same time, they do not take any measures for treatment, considering this disease to be trivial. Is stomatitis so dangerous that you can’t contact other people?
Stomatitis is an inflammation of the oral mucosa, which in most cases is accompanied by the formation of ulcers. Along with this, swelling of the mucous membrane is observed, and a white or yellow-white coating forms. When communicating, a person feels discomfort, and pain occurs while eating. Increased salivation, gums often bleed, and bad breath appears.
Infection with stomatitis through kissing
The symptoms of the disease are quite different, as are the pathogens. Despite the seemingly complete study of stomatitis, scientists to this day do not know the exact method of its appearance; one version is inclined to believe that stomatitis is a reaction of the immune system to irritating substances unfamiliar to the body that have entered the oral cavity. As a result, the body sends lymphocytes to fight them, and so ulcers are obtained, which clearly indicate the presence of the disease.
In addition, a fungal infection in the mouth can also play the role of a pathogen. In such a situation, kissing is also best avoided.
If we are talking about herpes, it is very easy to catch it by using the patient’s dishes, so during the period of illness it is strongly recommended to maintain personal hygiene and scald the dishes with boiling water. Upon completion of treatment, you should change your toothbrush.
There is an excellent remedy against the herpes (aphthous) form of the disease. The use of acyclovir for stomatitis helps get rid of inflammation and pain.
What if stomatitis cannot infect a partner?
There are situations when kissing does not transmit stomatitis to a partner - for example, if the cause of stomatitis is a gastrointestinal disease, poor personal hygiene, or poor-quality fitting of dentures. But even in this case, it is better to refrain from kissing. After all, the altered microflora of the mouth during stomatitis creates a bad odor from the oral cavity, which is unlikely to please your partner . To eliminate the bad odor, you can use Metrogyl Denta. Plus, Metrogyl Denta helps with stomatitis.
You should first undergo a course of treatment, and then you can move on to kissing. As a rule, the illness does not last longer than 10 days if patients adhere to good personal hygiene and take medications responsibly for topical or internal use.
What can cause stomatitis?
Many factors can lead to inflammation of the mucous membrane: from banal mechanical damage to disruptions in the body that are not related to the dentist’s field of work.
The following causes lead to stomatitis :
- neglect of oral hygiene recommendations;
- injury to the mucous membrane from sharp edges of teeth or fillings, dentures or other objects;
- dental diseases - caries, tartar, etc.;
- allergies - not only to food, but also to hygiene products and even dental materials;
- various diseases - from viral to endocrine, such as diabetes;
- poorly made prostheses;
- expired prostheses;
- metabolic or immune disorders;
- problems with microflora in the body;
- direct contact with the mucous membrane of pathogenic microorganisms;
- bad habits - smoking, drinking strong alcohol;
- reaction to certain medications.
The mucous membrane is much easier to damage than the skin. Especially in the mouth, where it is always exposed to temperature changes, touched by teeth, dentures, braces and solid food particles.
The cause of dental disease is mainly pathogenic bacteria (for example, caries is caused by streptococcus), which also harm the gums. And tartar is a hardened plaque that contains not only microbes, but also other unfavorable components. In addition, if the stone is subgingival, then the mucous membrane suffers first.
In many cases, allergies are discovered suddenly. The patient may not be aware of its presence, since he calmly eats any food. However, chemicals in toothpaste or mouthwash can cause a reaction. Studies have shown a negative effect on the mucous membranes of sodium lauryl sulfate, contained in some toothpastes. If the problem began soon after the restoration or treatment of the tooth, then you should consider the possibility of the body's response to the filling or crown material.
Decreased immunity can also cause deterioration of gums. And metabolic disorders affect not only the supply of microelements to the body’s tissues (including the mucous membrane), but also the composition of saliva, a decrease in the protective properties of which makes the oral cavity vulnerable to bacteria. Approximately the same can be said about the beneficial microflora: if it is in order, it helps to suppress the work of harmful microorganisms; if it is disrupted, the microbes attack vulnerable areas.
The cause of stomatitis in adults and children can be obvious - direct entry into the mouth of a large number of pathogenic bacteria. They can get from contaminated surfaces. Simply put, if a child constantly puts various objects into his mouth, stomatitis may occur. If an adult has carried through the years the bad habit of biting nails or pens, this can also contribute to the appearance of inflammation.
Medicines can have different effects on the body, in particular, they can affect the immune system, microflora and saliva production. Dry mouth is promoted by antihistamines and antihypertensive drugs, anticoagulants, antipsychotics, antispasmodics, etc. And a low level of saliva production provokes the growth of bacteria. Antibiotics and anti-asthma medications can lead to Candida infections in the mouth. There can be many options, including the influence of the sugar contained in the medicine. stomatitis often appears in adults as a result of treatment for a completely different pathology.
Treatment
Despite the fact that when stomatitis develops in adults, its symptoms and subsequent treatment are interrelated , that is, based on the manifestation of the disease one can roughly get an idea of the cause, in no case should you self-medicate!
Stomatitis can have several causes, and when treating one, a completely different disease can develop.
It may not be stomatitis at all, but, for example, a simple allergy or herpes.
Active substances contained in both medications and medicinal plants may cause allergies or be contraindicated for some people.
The likelihood of contracting aphthous stomatitis
People with serious chronic diseases are susceptible to aphthous stomatitis. Most often these are diseases:
- Oral cavity.
- Throat.
- Upper respiratory tract.
The presence of a focus of infection weakens local immunity. The consequence is the appearance of blisters, ulcers, and plaque. A yellow-white coating is characteristic. Erosive changes become pronounced if left untreated.
The disease may not cause concern for a long time. In any disease, with exacerbation of chronic diseases, the eroded surfaces become painful.
The risk of developing aphthous stomatitis increases:
- Poor nutrition .
- The presence of long-term non-healing wounds in the mouth.
- Presence of untreated teeth.
- Gum diseases .
- Incorrectly fitted dentures .
- Oral injuries
Diet for stomatitis
Stomatitis often worries children, becoming a consequence of insufficient immune forces of the body, weakened by some disease.
Aphthous stomatitis is typical for those suffering from diabetes.
Aphthous stomatitis itself is not contagious. Communication with a person who has signs of the disease is not dangerous. The risk of infection arises when a patient with aphthous stomatitis “adds” a viral infection to the underlying disease.
Redness of the throat may indicate pharyngitis, purulent discharge from the tonsils may indicate tonsillitis. In these cases, the pathogen is transmitted to a healthy person through contact with a sick person.