This is a fairly common disease that can occur in both children and adults, but the former are more often affected by it. In any case, it is important to know how to quickly cure a sore throat in order to quickly alleviate the patient’s condition and to prevent the development of complications. Despite the prevalence of the disease and, it would seem, a lot of known methods of treating it, you should not neglect medical help. To understand the insidiousness of the disease, you should learn more about it - what it is, what types there are and what methods of elimination are used.
This is what you will learn about sore throat and its treatment by reading this article
- What is a sore throat?
- Types of sore throat, symptoms, treatment
- Catarrhal sore throat
- Symptoms
- Treatment
- Follicular tonsillitis
- Symptoms
- Treatment
- Lacunar tonsillitis
- Symptoms
- Treatment
- Fibrinous tonsillitis
- Symptoms
- Treatment
- Quinsy
- Symptoms
- Treatment
- Herpangina
- Symptoms
- Treatment
- Ulcerative membranous tonsillitis
- Symptoms
- Treatment
- Traditional medicine in the treatment of sore throat
- Treatment of sore throat with antibiotics
- Complications of sore throat
- When should you call an ambulance?
- Nutrition for sore throat
- Mistakes in the treatment of sore throat
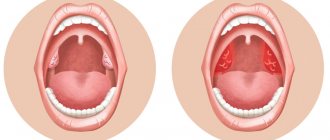
What is a sore throat?
This is a disease of infectious origin, occurring in an acute form. Its causative agent is usually bacteria (most often the disease is caused by beta-hemolytic streptococcus, staphylococcus). But viruses and fungi can provoke the disease. How to quickly cure a sore throat depends on what kind of microorganisms it is caused by, because only those drugs that can act directly on them will be effective.
The infection affects the palatine tonsils, causing them to become inflamed, which is accompanied by the accumulation of pus, swelling, and difficulty breathing. In medicine, the disease is also known as acute tonsillitis. Considering that it is infectious, tonsillitis is contagious and is transmitted by airborne droplets, through household items, and food.
how to treat a sore throat
For reference. The tonsils are lymphatic tissue that is part of the pharyngeal ring. Thanks to them, peripheral immunity is formed, they protect the body from infections.
Back to Contents
Types of sore throat, symptoms, treatment
Depending on the course of the disease, its symptoms, its varieties are as follows:
- Catarrhal;
- Follicular;
- Lacunarnaya;
- Fibrinous;
- Phlegmonous;
- Herpetic;
- Ulcerative-membranous.
General signs of the disease are:
- Pain in the throat, which is sharp and intensifies during conversation, when swallowing;
- Fever (depending on the type of illness and the severity of its course, it can reach 40 degrees);
- General weakness of the body, severe muscle weakness;
- Headache;
- Redness of the tonsils and mucous membranes of the throat;
- The appearance of white plaque on the tonsils, their enlargement.
In the first stages of the disease, it can be confused with the flu or a cold, although it is more severe. The main symptom that can be used to suspect a sore throat is severe pain in the throat, which makes it difficult to speak, eat, and breathe.
The most important thing in how to get rid of a sore throat quickly and effectively is an integrated approach. What must be included in the process?
- Bed rest. Without it, therapy may be ineffective, and this is fraught with complications;
- It is important to follow a certain diet;
- The patient needs to drink plenty of fluids, which will help fight the infection faster;
- Be sure to gargle using special preparations;
- Medicines with antihistamine and anti-inflammatory effects can be used. If the disease is of bacterial origin, then the use of antibiotics will be required. The choice of group of drugs depends on the causative agent of the disease.
In some cases, if there is a risk that the patient may suffocate and/or the infection spreads to neighboring organs, surgical intervention may be required.
Back to Contents
Catarrhal sore throat
This is a type of acute tonsillitis, which is one of the mildest forms of the disease. It is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the throat and often develops against the background of reduced immunity of the patient. Considering that the body’s defenses usually decrease in the autumn-winter period, this disease also often attacks precisely during this season.
The catarrhal type of the disease is characterized by a high percentage of transmission, but patients tolerate it much faster and easier than other types of tonsillitis.
Symptoms
Signs of catarrhal tonsillitis usually appear quickly - the incubation period ranges from several hours to 2-3 days. Its symptoms are:
- Enlargement of the tonsils and their acquisition of a bright red color, severe swelling;
- The presence of a translucent film-like coating on the tonsils;
- Difficulty swallowing;
- Sore, dry throat;
- Increased body temperature. It is not always significant - the temperature can rise to 37.2, but it is possible that it will rise to 39 degrees. Often this symptom is accompanied by body aches and weakness.
Symptoms such as dizziness, nausea, vomiting (signs of intoxication) occur less frequently. If a patient has a white coating on his tongue, a doctor during a face-to-face examination can most likely assume that the causative agent of the disease is bacteria.
Treatment
Due to the high rate of disease transmission, the patient should be isolated. As for how to treat catarrhal tonsillitis, it is important to use a set of measures:
- Drink plenty of fluids;
- Due to the fact that it is painful for the patient to swallow, during treatment he should switch to pureed, liquid food;
- Bed rest is mandatory;
- To eliminate the inflammatory process and pain, sprays are prescribed (Hexoral, Orasept, Faringo-spray);
- In the absence of intoxication of the body, drugs of the sulfonamide group (Streptotsid, Septrin, Biseptol) are prescribed;
- If the temperature reaches 38 degrees or more, antipyretic medications are used (Paracetamol, Ibuprofen, Cefekon);
- The doctor may also prescribe medications with antiallergic effects (“Loratadine”, “Suprastin”, “Diazolin”);
- A good therapeutic effect is obtained by gargling, for which solutions with hydrogen peroxide, boric acid, and calendula infusion are used. The lacunae of the tonsils should be washed using an iodine solution.
how to cure a sore throat
You can cure a sore throat without antibiotics - the listed remedies are quite capable of dealing with it. Recovery can be achieved within a 6-7 day period. But if the bacterial origin of the disease is confirmed and the listed set of methods does not help, then the doctor prescribes antibiotics.
Follicular tonsillitis
This is a purulent type of the disease, characterized by a severe course. This type of inflammatory process is most often provoked by streptococci and staphylococci. Children and adolescents are most susceptible to the disease. Considering the nature and severity of the disease, how to treat purulent sore throat is a task whose solution should be entrusted to a doctor.
Back to Contents
Symptoms
The disease manifests itself acutely, rapidly, but not always with a sore throat, as is the case with many other types of tonsillitis. The first signs are similar to flu and colds - chills due to elevated temperature, muscle pain, headaches, body aches. Following these manifestations, the following symptoms of follicular tonsillitis begin to make themselves felt:
- Pain in the throat, which can radiate to the temple or ear when swallowing or talking;
- Enlarged lymph nodes, and in many patients they become so large that they feel them, and turning the head is accompanied by pain;
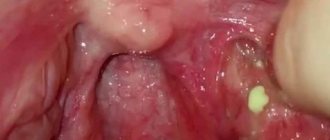
- A sign directly characteristic of follicular tonsillitis is the appearance of small purulent spots on the palatine tonsils, which are white or light yellow in color. On the affected areas they appear as bubbles;
- Due to the presence of pus, the patient develops an unpleasant taste in the mouth, as well as bad breath.
Treatment
It is necessary to exclude the patient’s physical activity and maximize the amount of fluid he consumes (tea, water). A set of measures used to quickly cure follicular tonsillitis includes:
- The insidiousness of the disease lies in the fact that it can provoke the development of a runny nose and the accumulation of purulent discharge in the nose. Therefore, in addition to antiseptic throat sprays (Iodinol, Ingalipt, Hexoral), you should also use nasopharynx cleansers (for example, Dolphin);
- Inhalation with eucalyptus helps eliminate the infection, but it is recommended to use them if the patient does not have a fever;
- It is not always possible to cure purulent (follicular) sore throat without antibiotics. The most effective in this case are representatives of the penicillin group (“Penicillin”, “Amoxicillin”);
- Furacilin solution removes purulent “sacs” well;
- If the patient is bothered by a high temperature, one cannot do without drugs that have an antipyretic effect (“Citramon”, “Paracetamol”, “Aspirin”);
- It is often necessary to use antihistamines.
Due to the fact that children often become patients with follicular tonsillitis, an important question for parents is how to treat a child’s sore throat at home. The listed methods contribute to this, and it is recommended to add to them the use of Faringosept and Doctor Mom lozenges, which help soften the tissues of the throat and eliminate purulent spots.
Lacunar tonsillitis
The palatine tonsils have many depressions called lacunae. These depressions with their branches extend into the lymphoid tissue. Lacunar tonsillitis affects lacunae and has an external resemblance to follicular tonsillitis. Both types can develop simultaneously, and for an inexperienced person it is almost impossible to visually determine the type of inflammation and distinguish one from the other.
Children and adolescents are most often affected by the disease, and in people over 50 years of age it is much less common.
Symptoms
The disease develops rapidly, and within the first day all its signs appear:
- High temperature, which can be 38-41 degrees. Without this symptom, the disease rarely occurs;
- The appearance of exudate on the surface of the mouths of lacunae. It appears as a coating in the form of small yellowish islands. This is a characteristic sign of the lacunar variety of the disease, which is similar to the main symptom of follicular tonsillitis;
- Bad breath, bad taste;
- Redness of the cheeks with noticeable pallor in the area of the nasolabial triangle (another sign accompanying lacunar tonsillitis itself);
- Sore throat when swallowing or talking.
The remaining symptoms of the disease are nonspecific and include headache, muscle pain, general malaise, pain in the jaw area, and loss of appetite.
Treatment
As with other types of sore throat, bed rest and plenty of warm fluids are required. If lacunar tonsillitis strikes, how to quickly cure it will depend on what measures are taken for this. And the following are effective:
- Antibacterial rinses (Biclotymol, Miramistin, Chlorhexidine) are used as local therapy;
- Regardless of whether the task is to cure lacunar tonsillitis in an adult or cure lacunar tonsillitis in a child, it is necessary to identify its causative agent. In accordance with this, the main method of therapy is selected. If it has a viral etiology, antiviral medications are used (Kipferon, Viferon). Antibiotics of the penicillin group (Amoxiclav, Amoxicillin, Phenoxymethylpenicillin) are effective in the fight against bacterial lacunar tonsillitis. If the disease is caused by fungi, the use of Lugol's solution, Fluconazole is indicated;
- If the patient has an allergic reaction to the medications used, you need to resort to antihistamines (Cefditoren, Cefixime);
- If treatment with the listed antiviral, antifungal, and antibacterial drugs is impossible, alternative antibacterial agents (Azithromycin, Clindamycin, Josamycin) are prescribed.
Back to Contents
Tonsillitis
The tonsils act as sentinels to prevent bacteria and viruses from entering the throat. In this case, only mild irritation of the tonsils occurs. If the tonsils cannot resist bacteria, inflammation of both the laryngeal and palatine tonsils occurs, which become very swollen and painful. This is already a sore throat. Signs of the disease are the same as for a cold or flu:
- elevated temperature,
- fever,
- headache,
- difficulty swallowing,
- coating on the tongue.
Sometimes ulcers form on the tonsils, and bacteria can enter the bloodstream, causing inflammation (for example, of the heart muscle, kidneys, or internal heart septum) and damage to the joints. This can also occur with frequently recurring inflammation of the tonsils, turning into chronic inflammation.
Development of the disease
Today, there are 2 possible ways of developing the disease: external and internal. A disease caused by microorganisms that have penetrated from the environment is an external route. And internal is a sore throat caused by chronic infections of internal organs.
There can be 3 main causes of sore throat: bacteria, viruses and fungi.
- Bacteria: most often - streptococcus.
- Viruses: herpes, flu or inflammation of the adenoids developing in the human body can cause a sore throat.
- Fungus: Candida is a yeast-like fungus that causes fungal sore throat. In addition to sore throat, such fungi can cause other diseases, for example, thrush in women.
A complication of the development of sore throat, regardless of what nature it is caused by, can be caused by a decrease in immunity. This is possible due to a decrease in the level of vitamins in the body, or a lack of essential nutrients and microelements. Exacerbations of chronic diseases that are inflammatory in nature lead to a decrease in immunity. Seasonality and possible sharp drops in temperatures play an important role.
And at the moment when the immune system fails, a disease can occur in the body. All those microbes that are in the throat are activated in such conditions. Even mild hypothermia, a portion of ice cream, or wet feet can lead to this.
Fibrinous tonsillitis
Often this type of disease develops as a consequence of follicular or lacunar tonsillitis. It is difficult and the patient’s condition worsens significantly, especially if it is not treated in a timely manner.
Symptoms
Most of the signs of the disease are typical for sore throat - sore throat, muscle pain, inflammation of the lymph nodes, fever, fatigue. Characteristic symptoms for fibrinous tonsillitis are:
- The appearance of a gray film-like coating on the throat and tonsils. This kind of plaque occurs with diphtheria. In the absence of complications, it is easily separated without bleeding;
- If candidiasis or mononucleosis joins the disease (which often happens), it acquires a yellowish tint. In this case, there may be problems with removing plaque;
- Severe course of the disease, the appearance of complications may be accompanied by symptoms such as suffocation, severe swelling of the nasopharynx, disturbances in heart rhythms, and pain in the eyes.
Treatment
It will be difficult to get rid of the disease without the intervention of a doctor, and there is no need to take risks. How to quickly cure a sore throat in an adult and a child if it has acquired a fibrinous form?
- Be sure to maintain drinking and bed rest - there should be plenty of rest and fluids;
- In addition to traditional antiseptic rinsing solutions (iodine-containing medications, Furacilin, Chlorhexidine), you can use herbal decoctions based on sage and chamomile;
- To get rid of the disease, it is important to normalize blood circulation in the throat area, which is done with the help of compresses. A towel, previously soaked in cool water and wrung out, should be wrapped around the throat, carefully insulating it on top with a scarf or blanket. It is recommended to keep the compress for about an hour, and carry out the procedure three times a day;
- Severe disease will require the use of sulfonamides and penicillins;
- During treatment, it is advisable to consume as many foods and drinks as possible containing vitamin C - it helps destroy pathogenic microorganisms.
Quinsy
In medicine, the disease is also known as paratonsilitis or paratonsillar abscess. It usually develops as a consequence of other types of tonsillitis - a couple of days after the end of the disease. The disease affects the peri-almond tissue and is characterized by a severe course.
Symptoms
The disease begins with the same manifestations as other forms of tonsillitis. But the pain in the throat is acute and pronounced. Other characteristic symptoms of the disease:
- Severe redness of the ocomandal tissues, their swelling;
- The tonsil may be displaced, protruding above the level of the niche;
- Enlarged lymph nodes in the neck;
- Increased salivation;
- A pronounced nasal tone may appear;
- It is often impossible or very difficult to open your mouth completely.
Treatment
When the disease occurs, pus accumulates, often on one side, above the upper part of the tonsil. Antibiotics can be used for therapeutic purposes, and analgesics, antihistamines, and antipyretics can be used to alleviate the patient’s condition. But the main method of treatment, if phlegmon (accumulation of purulent discharge) develops, is the surgical method.
Definition of disease
Sore throat or acute tonsillitis is an inflammatory disease of the tonsils. In rare cases, the focus of inflammation is localized on other lymphoid formations.
Sore throat can be either unilateral or bilateral.
Other causes of acute tonsillitis are other sites of chronic infections, such as caries or chronic diseases of the nasal cavity. This disease most often affects children aged five to fifteen years, and it is of bacterial origin. Depending on the stage of inflammation and the appearance of the tonsils, the following main types of tonsillitis are distinguished:
- Catarrhal sore throat. The tonsils are red and enlarged. There is no plaque.
- Follicular tonsillitis. There are spots of purulent plaque on the tonsils.
- Lacunar tonsillitis. There are accumulations of pus in the lacunae of the tonsils. The most severe form of the disease.
Without proper treatment, serious complications of tonsillitis can develop, for example, sepsis, pyelonephritis, abscess, bleeding from the tonsils, and so on.
In some cases, sore throat is confused with ARVI. To accurately diagnose the disease, an examination by a doctor is necessary. To do this, the doctor palpates the lymph nodes located under the lower jaw. In the case of a sore throat, they are swollen and painful. A urine test will also show the presence of blood and protein.
Herpangina
The causative agents of this disease are usually enteroviruses. It can also be a complication of the flu. The external similarity of the ulcers covering the tonsils was the reason for this name of the disease. Children aged 3-10 years are most susceptible to the disease.
Symptoms
The first manifestation of herpetic tonsillitis is general weakness and fever. The following signs make themselves felt:
- Pain in the throat;
- Upon examination, the patient reveals a rash on the tonsils in the form of blisters with grayish contents. The tissues of the pharynx themselves become red;
- Difficulty swallowing;
- Pain in the area of the cervical lymph nodes;
- Children under 4 years of age do not always experience a sore throat, but the child may lose appetite due to colic and nausea.
Treatment
The course of the disease is usually not severe, but this does not mean that it can not be treated. Treatment of sore throat at home can be carried out using the following measures:
- Drink plenty of fluids, bed rest;
- The use of antipyretic medications (for example, Ibuprofen, Nimesulide);
- The use of antihistamines (Claritin, Loratadine, Zyrtec);
- Gargling with antiseptic agents (“Cameton”, “Yox”, “Inhalipt”);
- The use of antiviral drugs (Viferon, Tsitovir, Cycloferon).
Back to Contents
conclusions
- Sore throat (tonsillitis of any type: streptococcal, bacterial, lacunar) may not manifest itself immediately, which increases the risk of complications.
- It can be treated at home, but only not in severe forms and under the supervision of an otolaryngologist.
- A high temperature with inflamed tonsils (the throat may begin to hurt, become swollen, painful to swallow, a lump or plug in the throat) is always present with tonsillitis.
- In order to prevent the disease from developing, it is worth resorting to first aid measures, even if there are only suspicions.
- Treatment in pregnant women differs only in less severe antibiotics.
- If you do not start treatment on time, you can get complications, the throat will not go away for a long time and nothing will help.
- The best way to prevent disease is prevention.
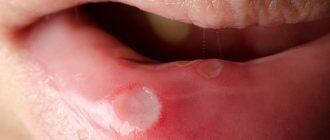
Ulcerative membranous tonsillitis
Inflammation occurs due to the interaction of an oral spirochete and a spindle-shaped rod. The risk group is people with reduced immunity.
Symptoms
Typically, the disease causes a slight increase in temperature, a sore throat, and swollen lymph nodes. There are also characteristic signs of ulcerative-membranous tonsillitis - the appearance of ulcers, a dirty greenish coating, and the presence of a putrid odor. As a rule, damage to the tonsil tissue is unilateral.
Treatment
Fighting the disease often requires hospitalization of the patient in the infectious diseases department. How to quickly cure a sore throat for an adult in this case?
- An effective method is to treat ulcers with solutions such as boric acid, manganese, rivanol, and methylene blue. Procedures should be carried out 2-3 times/day;
- If the disease does not subside for a long time and is severe, antibiotics are included in the therapy (Novarsenol, Benzylpenicillin, Miarsenol);
- Vitamin therapy is used as an additional measure (it is important to saturate the body with vitamins C, P, B).
Traditional medicine in the treatment of sore throat
How to treat a sore throat at home to achieve quick results and preferably without antibiotics, many people are interested in, and especially parents of children who are afraid to treat them with chemicals.
Treatment of sore throat at home: the most popular remedies
- Inhalations with boiled potatoes. The vegetable must be boiled, left in the pan, and allowed to cool slightly so that the patient does not get burned. Then he needs to wrap himself in a towel, bend over the pan, and breathe for 10-15 minutes. The procedure should be repeated daily;
- Beetroot broth. The vegetable needs to be boiled until it becomes soft, and then cool the broth; it should be warm, but not hot. You need to gargle with the product several times a day;
- Herbal infusions. Such healing plants as chamomile, sage, oak bark could not be ignored, because they can even help in how to cure a purulent sore throat quickly at home. This is due to their antiseptic properties and ability to relieve pain. Brew 1 tbsp. l. any of the plants in 1 glass of water, let it brew until it cools, strain. You need to gargle with the product several times a day;
- Marigold. Brew 10 flowers in 1 tbsp. boiling water, let the infusion cool under the lid. Gargle with warm, expressed liquid once a day;
- Cognac and cumin. Are you looking for how to quickly cure a sore throat in 1 day? They say this is the very means by which this can be done. You need to grind 80 g of cumin into flour, pour a glass of water into it, and boil for a quarter of an hour. Strain the resulting mass, add a quarter glass of water to it. Let the mixture boil and immediately remove from heat. Add 1 tsp to the product. cognac, take 1 tsp. at intervals of half an hour for 4 hours;
- Onion peel. This folk recipe, used at home, helps against many diseases, including tonsillitis. 3 tsp. The husks need to be boiled for several minutes in ½ liter of water. Let the broth brew for 2-3 hours, then decant. Gargle with the resulting liquid at least 5 times a day.
When it comes to how to quickly cure a sore throat, folk remedies show high effectiveness, but if the disease is severe, they may not be enough.
Inhalations
For sore throat, inhalation is an effective method of treating a sore throat - during inhalation, tissues are heated, medicinal extracts go directly to the site of the disease. Home inhalations are often carried out on the basis of herbal decoctions; below are several sample recipes.
- Prepare a decoction of dry St. John's wort and chamomile - pour 3 tablespoons of herbs into a liter of water, bring to a boil, cool - you can get a burn from the steam. To enhance the effect, add a few drops of any coniferous essential oils. Inhalation is carried out as in the previous recipe - for 20 minutes.
- Take 2 tablespoons of crushed dry chamomile, mint, sage, pour in a liter of warm boiled water. Bring the mixture to a boil over low heat, then remove from heat and allow to cool slightly. The patient bends over a vessel with a decoction, his head is covered with a towel. You need to breathe through your mouth - this is how steam with healing extracts reaches the affected areas.
It is important to know that inhalations are contraindicated at elevated temperatures; they are usually carried out at the last stage of treatment, as an additional procedure to restore the mucous membrane of the throat.
Complications of sore throat
Primary types of the disease are usually not severe, but if they are not treated, complications are possible in the form of their transition to more severe forms (for example, follicular, phlegmonous tonsillitis). If these diseases are not treated, infection may spread and pus may enter other organs. Private local complications of tonsillitis include:
- Otitis;
- Edema of the larynx;
- Inflammation in the lymph nodes;
- Bronchitis, tracheitis, pneumonia.
Systemic complications are also possible:
- Heart diseases;
- Kidney diseases;
- Joint ailments.
Back to Contents
Mistakes in the treatment of sore throat
Most often they are:
- Gargling for children under 4 years of age. They do not know how to retain liquid in the throat, so this method of treatment should be avoided, replacing it, for example, with rubbing, taking syrups;
- How to quickly cure a sore throat without antibiotics is an interesting question, and it is possible, but not always. You can do without them if the disease is not severe, but in some cases, avoiding them until the last minute can lead to serious complications;
- If antibiotics cannot be avoided, be sure to complete their course to the end, even if the patient begins to feel better. Otherwise, the therapy will be ineffective and complications may occur;
- How to cure a sore throat in one day? Unfortunately, this is not always possible. Most often, this takes at least several days.
Relief of sore throat due to sore throat
And the most important mistake is self-medication. Yes, if you have a sore throat, how to quickly cure your throat, doing it at home, becomes a pressing topic. But you need to remember that no matter what, in your opinion, proven remedies you use, without a doctor’s recommendations you can go down the wrong path, provoking complications of the disease. In addition, no medications, and especially antibiotics, can be prescribed independently, just as their doses and duration of treatment cannot be determined.
Prevention
The following will help reduce the risk of disease:
- compliance with personal hygiene rules, in particular regular hand washing2;
- hardening: air baths, rubdowns and showers with gradually decreasing water temperature, gargling with cold water2;
- morning exercises and physical education classes2;
- sanitation of the oral cavity: carious teeth, sore gums, chronic rhinitis, sinusitis, adenoids;
- sanitation of ENT foci of infection - therapy of rhinitis, sinusitis, solution to the problem of nasal congestion, which forces you to breathe through the mouth and reduces the protective functions of the mucous membrane of the oropharynx2.
The information in this article is for reference only and does not replace professional advice from a doctor. To make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment, consult a qualified specialist.
Literature
- N.L. Kunelskaya, A.B. Turovsky. Sore throats: diagnosis and treatment // “Breast cancer”. - 2010. - No. 7, p. 438.
- V.S. Dergachev. Angina. Clinic, diagnosis and treatment algorithm. Choice of local antibacterial therapy // “Breast Cancer”. – 2007. – No. 18, p. 1350.
- G. Z. Piskunov, I. B. Angotoeva. Acute tonsillopharyngitis // Attending physician. – 2007. – No. 2.
- P.A. Kochetkov, V.M. Svistushkin. Acute streptococcal tonsillitis - modern principles of therapy // “Breast Cancer”. – 2014. – No. 26, p. 1891.
- Polyakova T.S., Polyakova E.P. Chronic tonsillitis: diagnosis, treatment, prevention // “Breast cancer”. – 2004. – No. 2, p. 65.
- Instructions for use of the drugs HEXORAL® SOLUTION and HEXORAL® AEROSOL.
- Instructions for use of HEXORAL® TABS and TABS CLASSIC.
- Instructions for use of HEXORAL® TABS EXTRA.